Memory
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Encoding
Process by which a stimulus is translated into a mental representation that may be stored in memory
Storage
changes in the neural system that allows retention of information. involves moving encoded information to a memory store
Retrieval
a process of recovering information from a memory store
Atkinson and Shiffrin’s Multi-Store Model of Memory
attention filters information from sensory memory to STM, rehearsal maintains information in STM and transfers it to LTM, and retrieval brings information back from the LTM when needed
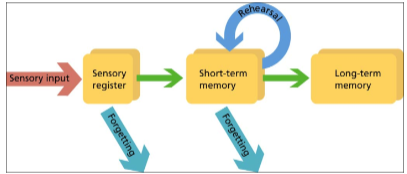
Sensory Memory
receives input form the environment and holds information in an unprocessed form. if information is attended to, it goes into STM
Short Term (Working) Memory
limited to 5-9 chunks of information, holds information for 30-60 seconds
long term memory
relatively permanent, assumed to be unlimited. we store different types of memories in different parts of the brain-borne out by research into neurological impairment
Semantic (LTM)
memory for meaning
Episodic (LTM)
our own individual memories
Procedural (LTM)
memories of how to do something
Central Executive
the boss of working memory, allocates data to the subsystems: phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad. decides which information is attended to and where it is sent
Phonological Loop
component of working memory model that deals with spoken and written material. spoken words are held for 1-2 seconds. written words must be converted into a spoken code and then enter memory store
phonological store
holds information in a speech-based form
articulatory process
allows us to repeat verbal information in a loop
visuospatial sketchpad (inner eye)
stores processes information in a visual or spatial form. helps us keep trach of where we are in relation to other objects. displays and manipulates visual and spatial information held in long-term memory
episodic buffer
acts as a backup store which communicates with both long-term memory and the components of working memory
levels of processing model
focuses on the depth of processing involved in memory, and predicts the deeper information is processed, the longer a memory trace will last
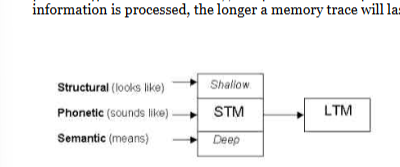
shallow processing
only involves maintenance rehearsal (repetition) and leads to fairly short-term retention of information
structural processing (appearance)
when we encode only the physical qualities of something
Phonemic Processing
when we encode its sound
semantic processing (deep processing)
when we encode the meaning of a word and relate it to similar words with similar meaning
elaboration rehearsal (deep processing)
involves a more meaningful analysis of information and leads to a better recall
divided attention
the ability to process two or more responses or react to two or more different demands simultaneously
Explicit memory
info you consciously work to remember
implicit memory
info remembered unconsciously and effortlessly
effortful processing
active processing of information that requires sustained effort
automatic processing
the unconscious processing of incidental or well-learned information
flashbulb memory
immediate and permanent memory as the result to emotionally charged, surprising, and or consequential events
Serial Position Effect
probability of recalling any word depended on it position in the list. words presented at the beginning or end are better remembered than words in the middle
Spacing Effect
learning is more effective when repeated in spaced-out sessions
Chunking (Mnemonic Device)
separating disparate individual elements into larger blocks makes them easier to recall
Methods of Loci (Mnemonic Device)
people remember information by visualizing familiar spaces
Retroactive interference
when more recent information gets in the way of trying to recall older information
proactive interference
difficulties in learning and retention caused by the interference of previously learned material
Recall
ability to remember something without being prompted
Recognition
ability to recognize something you have seen before
Context-Dependent Memory (Environment)
when recall is stronger when a subject is present in the same environment in which the original memory was formed
Mood-Congruent Memory
individuals are more likely to recall memories that are congruent with their current emotional state
State-Dependent Memory
ability to recall something may be based on the state the person was in when the information was encoded and retrieved
Source Amnesia
inability to remember where, when, or how previously learned information has been acquired, while retaining the factual knowledge
Anxiety and Stress (Eyewitness Testimony)
Clifford and Scott (1978) found that people who saw a film of a violent attack remembered fewer of the 40 items of information about the event than the group that did not see a violent attack
Reconstructive Memory
recall is subject to personal interpretation dependent on our cultural norms and values
Weapon Focus
not unusual for a witness to be able to describe the weapon in a crime in better detail compared to the person
Leading Question
a question that suggests what answer is desired or leads to the desired answer
Misinformation Effect
the impairment in memory for the past that arises after exposure to misleading information
Anterograde Amnesia
can recall past but not make new memories
Retrograde
cannot recall past memories
Encoding Failure
failure to encode information
Retrieval Failure
failure to retrieve information
Storage Decay
gradual fading of the physical memory trace
Forgetting Curve
the course of forgetting is initially rapid, then levels off with time
Tip of the Tongue Phenomenon
a state in which one cannot quite recall a familiar word but can recall words of similar form and meaning