Gases Unit Chem
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
gases ___ their containers
fill
are gases compressible?
yes! (liquids and solids are not)
What is pressure caused by?
the collisions the particles have with the container and eachother
what is 1 torr equal to?
1 mm of Hg
how many mm of Hg is equal to one ATM
760
volume must be measured in ____
Litres
Temperature equals the average ____ _____ of the particles
kinetic energy
are ideal gases collisions elastic? Why or why not?
Yes, there is no net loss of energy
Do Ideal gases have interactive forces? (attraction or repulsion)
No
temperature must be measured in ____
Kelvin
What was Boyle’s law?
pressure and volume are inversely proportional. (K = PV)
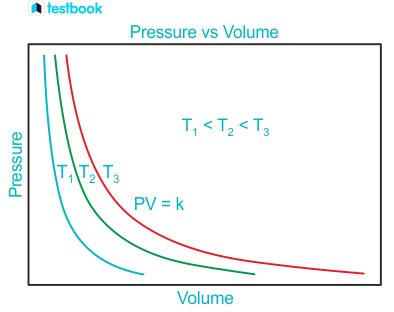
what coloured line has the highest temperature?
red
What is Charles’ law?
volume and temperature are directly proportional. (k=V/T)
what is Gay-Lussac’s law?
pressure and temperature are directly proportional. (k = P/T)
what is the combined gas law?
P1V1 / T1 = P2V2 / T2
equal volumes of gases at equal temperature and pressure contain ____ numbers of particles
equal
What is Avogadro’s law?
volume of gas is directly proportional to the number of moles (V = nVm)
Do real gases have a mass?
yes
Gases behave ____ at low pressures and high temperatures
ideally
Gases behave ___ at high pressures and low temperatures
not ideally / real
ideal gases have ____ motion
constant
do real gases obey PV = nRT?
No
What is the ideal gas law?
PV = nRT
What is Dalton’s law?
the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of all of the partial pressures. (Total pressure = P1 + P2 + P3….)
How do you find mole fractions?
n = m/MM
What’s Avogadros formula?
number of particles = number of moles X Avogadros’ constant