reaction of aqueous ions in solution
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
lewis acid and lewis base definition
lewis acid: electron pair acceptor
lewis base: electron pair donor
in the formation in complex ions what is the Lewis base and the Lewis acid
the ligand is the lewis base because its donating a pair of electrons in the coordinate bond
the metal ion is the lewis acid
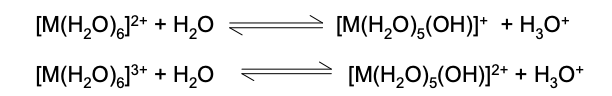
Acidity or hydrolysis reactions
reaction of hexaaquacopper with hydroxide ions w/ colour change
[Cu(H2O)6]²⁺ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) ———> Cu(H2O)₄(OH)₂ (s) + 2H₂O (l)
colour change from blue solution to blue ppt.
reaction of hexaaquacopper with limited NH3 w/ colour change
[Cu(H2O)6]²⁺ (aq) + 2NH3 (aq) ———> Cu(H2O)₄(OH)₂ (s) + 2NH4+ (aq)
colour change from blue solution to blue ppt.
reaction with of copper with excess NH3 w/ colour change
blue ppt. dissolves to form deep blue solution
Cu(OH)2(H2O)4 (s) + 4NH3 (aq) —> [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ (aq) + 2H2O (l) + 2OH- (aq)
reaction of hexaaquairon (II) with hydroxide ions w/ colour change
[Fe(H2O)6]²⁺ (aq) + 2OH- (aq) ———> Fe(H2O)₄(OH)₂ (s) + 2H₂O (l)
colour change from green solution to green ppt.
reaction of hexaaquairon (II) with limited NH3 w/ colour change
[Fe(H2O)6]²⁺ (aq) + 2NH3 (aq) ———> Fe(H2O)₄(OH)₂ (s) + 2NH4+ (aq)
colour change from green solution to green ppt.
reaction of hexaaquairon(III) with hydroxide ions w/ colour change
[Fe(H2O)6]³⁺ (aq) + 3OH- (aq) ———> Fe(H2O)₃(OH)₃ (s) + 3H₂O (l)
colour change from purple solution to brown ppt.
reaction of hexaaquairon(III) with NH3 w/ colour change
[Fe(H2O)6]3⁺ (aq) + 3NH3 (aq) ———> Fe(H2O)3(OH)3(s) + 3NH4+ (aq)
colour change from purple solution to brown ppt.
reaction of hexaaquaaluminium (III) with hydroxide ions w/ colour change
[Al(H2O)6]³⁺ (aq) + 3OH- (aq) ———> Al(H2O)₃(OH)₃ (s) + 3H₂O (l)
colour change from colourless to white ppt
reaction of hexaaquaaluminium (III) with NH3 w/ colour change
[Al(H2O)6]3⁺ (aq) + 3NH3 (aq) ———> Al(H2O)3(OH)3(s) + 3NH4+ (aq)
colour change from colourless solution to white ppt.
what type of molecule is Al(H2O)₃(OH)₃ and what does that mean
Al(H2O)₃(OH)₃ is an amphoteric molecule
reacts with both acids and bases
reaction of hexaaquaaluminium (III) with excess hydroxide ions w/ colour change
Al(H2O)₃(OH)₃(s) + OH- (aq) ———> [Al(OH)₄]- (aq) + 3H₂O (l)
colour change from white ppt. to colourless solution
reaction of Al(H2O)₃(OH)₃ with acid
Al(H2O)₃(OH)₃ + 3H+ (aq) ———> [Al(H2O)6]³⁺ (aq)
reaction of hexaaquacopper with CO₃²⁻ , including colour change
[Cu(H₂O)₆]²⁺ (aq) + 2CO₃²⁻ —→ CuCO₃ (s) + 6H₂O (l)
colour change from blue to blue/green ppt.
reaction of hexaaquairon (II) with CO₃²⁻ , including colour change
[Fe(H₂O)₆]²⁺ (aq) + 2CO₃²⁻ —→ FeCO₃ (s) + 6H₂O (l)
colour change from green sol. to green ppt.
reaction of hexaaquairon (III) with CO₃²⁻ , including colour change
2[Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺ (aq) + 3CO₃²⁻ —→ 2Fe(H₂O)₃(OH)₃(s) + 3CO₂ (g) + 3H₂O (l)
colour change from purple sol. to brown ppt.
effervescence
reaction of hexaaquaaluminium (III) with CO₃²⁻ , including colour change
2[Al(H₂O)₆]³⁺ (aq) + 3CO₃²⁻ —→ 2Al(H₂O)₃(OH)₃(s) + 3CO₂ (g) + 3H₂O (l)
colour change from colourless sol. to white ppt.
effervescence
Explain why an aqueous solution containing [Fe(H₂O)₆]³⁺ ions has a lower pH than an aqueous solution containing [Fe(H₂O)₆]2+ ions
Fe3+ is smaller than Fe2+ / has a higher charge density
so Fe3+ is more polarising - it polarises water molecules more
so there more O-H bonds are weakened/break and more H+ ions are released
An aqueous solution of iron(II) sulphate is a pale-green colour.
When aqueous sodium hydroxide is added to this solution a green precipitate is formed.
On standing in air, the green precipitate slowly turns brown.
Suggest an explanation for the change in the colour of the precipitate.
Fe2+ is oxidised to Fe3+ by the oxygen in the air
Fe(II) ions are pale green and Fe(III) ions are are brown.
Explain, with reference to electrons, why the two ions are different colours.
Fe(II) and Fe(III) ions have different number of electrons in d sub-shell
Therefore different wavelengths of light are absorbed by the different ions
So the electrons get excited and are raised to higher energy levels, causing different wavelengths of light to be transmitted