AP Psych Unit 1.2: Schools of Psychology
Seven Schools of Psychology
There are seven schools or approaches to psychology, each with different focuses. These include:
- Behavioral Perspective
- Biological Perspective
- Cognitive Perspective
- Humanist Perspective
- Psychoanalytic Perspective
- Social-Cultural Perspective
- Evolutionary Perspective
Behavioral Perspective
Focuses on observable behaviors over feelings.
Deals with how we learn, and believes we behave in ways because we have been conditioned to do so. We have to recondition in order to change.
B.F. Skinner and Ivan Pavlov are pioneers of behavioral perspective.
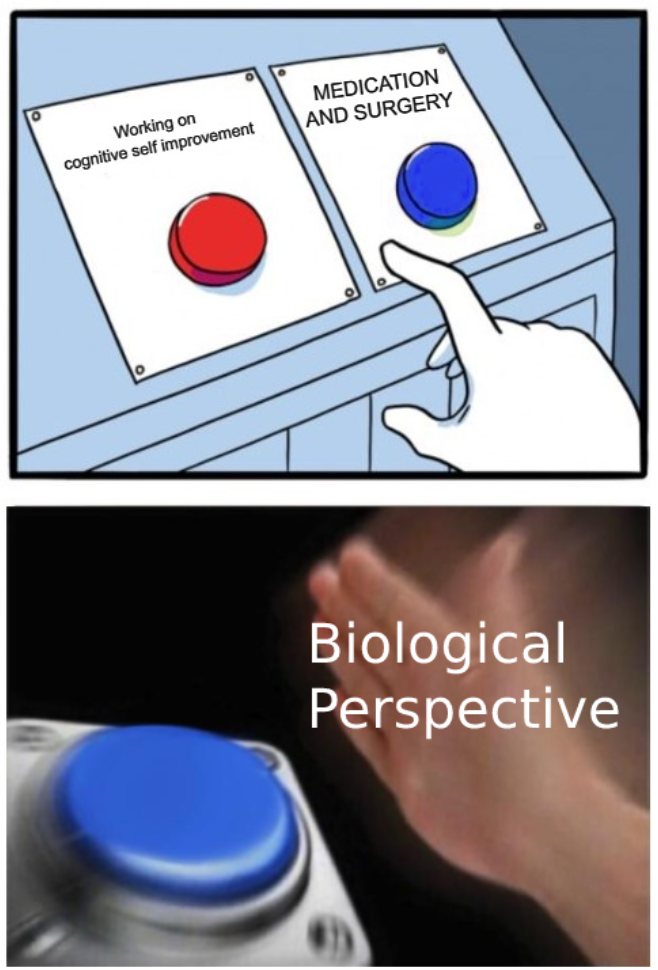
Biological Perspective
Refers to the function of brain and body chemistry.
Deals with transmission of messages through the mody and how it is linked to moves and motives.
Have to change body chemistry in order to change behavior.

Cognitive Perspective
Thought process or thinking EVERY TIME you see it
Focuses on how we think or encode information
Cognitive therapy attempts to change the way you think

Humanist Perspective
Focused on spirituality and free will.
Strive to be best with “self actualization” Happiness is defined by the distance between our “self-concept” and “ideal self”.
Abraham Maslow developed a hierarchy of needs and Carl Rogers was a promoter of love and acceptance towards others.

Psychoanalytic Perspective
The prefix “psycho” is “unconscious”.
Focuses on the unconscious mind.
We repress many real feelings and aren’t aware of them.
In order to improve, we have to address the true feelings we have.
Sigmund Freud was the largest influence in psychoanalysis, along with Carl Jung.
Typically can deal with childhood.

Social-Cultural Perspective
Much of your behavior and feelings are dictated by the culture that you are living in.

Evolutionary Perspective
Focuses on Darwinism - we behave the way we do because we inherited the behaviors.
They must have ensured our ancestor’s survival if we inherited that behavior.
