body fluids & electrolytes pt. 1
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
body fluids
composed of water (solvent) and electrolytes, carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, & minerals (solutes). intracellular in RBC, WBC, & tissues. extracellular in intravascular + extravascular (interstitial & transcellular)
functions of body fluids
dissolve & deliver substances (nutrients) to cells. account for blood volume (necessary to maintain BP & tissue perfusion): high blood volume → hypertension, low blood volume → hypotension. protect & lubricate body tissues (ex: CSF)
cerebrospinal fluid
protects brain & spinal cord
amniotic fluid
protects the fetus
synovial fluid
lubricates joints
pleural fluid
lubricates lungs’ surface
pericardial fluid
lubricates the sac in which the heart beats
electrolytes
substances that will dissociate into ions in solution & so acquire the ability to conduct electricity. essential components of all living matter
electrolyte functions
regulate osmotic pressure & fluid distribution between compartments (Na+). transmit nerve signals (Na+, K+). conduct neuromuscular impulses (Mg2+, Ca2+, K+). maintain acid-base balance (HCO3-, Cl shift). activate enzymes as cofactors (Mg2+, Ca2+)
major extracellular cations/anions
Na+, Cl-, HCO3- (2nd major)
major intracellular cations/anions
K+, P-
factors that affect fluid & electrolyte balance
ion transport (Na-K ATPase pump), hormones (aldosterone, ADH), pressure (crystalloid osmotic [Na+], hydrostatic, colloidal osmotic/oncotic [albumin]), lymphatic system
active transport
requries energy (ATP). Na-K-ATPase is an enzyme that pumps K+ into cells and Na+ out of cells.
passive transport
diffusion, requires no energy. Cl-, HCO3- move freely in & out of cells.
what happens when Na-K-ATPase loses its function?
serum K+ increases while Na+ decreases. pathologic in-vivo: occurs in energy-deficient (DM) or O2 deprived (hypoxia) cells. a problem in vitro (lab) when specimen is chilled to decrease RBC/WBC metabolism
aldosterone
plasma volume control. released from the adrenal cortex in response to apparent low BV/BP, which triggers RAS system. action in distal & collecting renal tubule. stimulates Na+ & water reabsorption in exchange for K+ or H+, a Na+ saving hormone. high serum [Na+] → high serum osmo → high BV/BP
![<p>plasma volume control. released from the adrenal cortex in response to apparent low BV/BP, which triggers RAS system. action in distal & collecting renal tubule. stimulates Na+ & water reabsorption in exchange for K<sup>+ </sup>or H<sup>+</sup>, a Na<sup>+</sup> saving hormone. high serum [Na<sup>+</sup>] → high serum osmo → high BV/BP</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/102dfeaa-ed43-4f1f-8daa-ecba56b65cf0.png)
hypo-secretion of aldosterone
low BP
hyper-secretion of aldosterone
high BP & ECF expansion. high serum Na+ (high serum osmo). low urine Na+ (low urine osmo). serum K+ & H+ low. urine K+ & H+ high
antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
plasma osmolality control. produced by hypothalamus, stored by posterior pituitary. secreted when plasma osmo rises & when BV/BP low, regardless of osmo. action in renal collecting duct. increases permeability of tubule membrane to water (reabsorption of water from urine), a water saving hormone
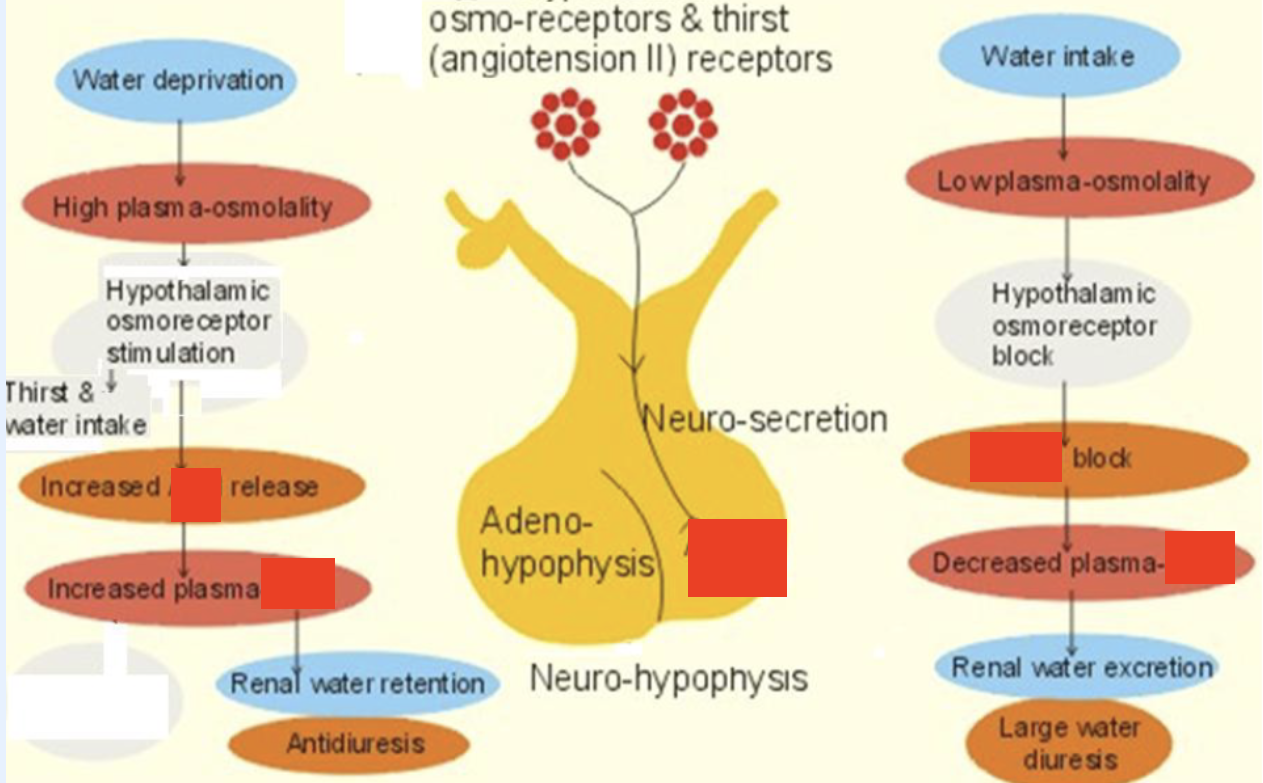
hypo-secretion of ADH
occurs in diabetes insipidus (DI). if access to water → polydipsia/-uria -. urine volume high, urine [Na+] + osmo low, serum Na+ + osmo high
hyper-secretion of ADH
occurs in syndrome of inappropriate diuretic hormone (SIADH). urine [Na+], urine osmo, & SG high. serum [Na+] + serum osmo low
crystalloid osmotic pressure
osmotic pressure that depends on dissociated ions & small molecules (crystals_ as osmo-active particles. regulates the distribution of water between intracellular & extracellular spaces: maintains cell shape. expressed as plasma osmolality
plasma osmolality (serum osmo)
concentration of plasma in terms of total # of electrolytes per kg plasma (mainly Na+). unaffected by large molecules like glucose, urea, proteins, & chylomicrons. mOs of solutes/kg of solvent (mOs/kg).
plasma osmo of Na
concentration (mmol/L): 135
osmo: 270 (with anions)
plasma osmo of glucose (90 mg/dL) & urea (14 mg/dL)
concentration (mmol/L): 5
osmo: 5
osmolality reference range
280 - 310 mOs/kg
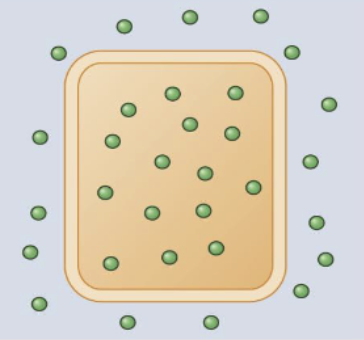
iso-osmolality
concentration of electrolytes is the same on either side of the cell membrane
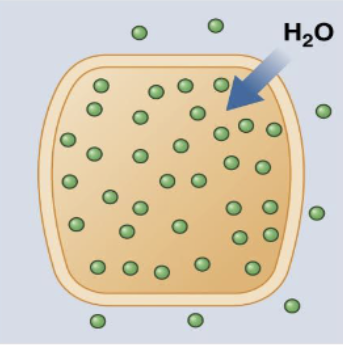
hypo-osmolality
serum osmo < 250 → cerebral edema. caused by SIADH (high ADH), hyper-hydration
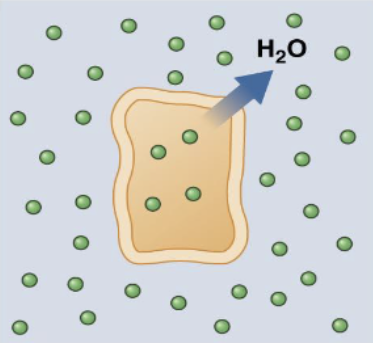
hyper-osmolality
serum osmo > 320 → brain cells shrinkage. caused by dehydration (common), DI (low ADH), DM
urine osmolality
often measured following an abnormal plasma osmo or plasma Na+ test. range is wide, depends on water intake. reflects amount of osmotically active constituents in urine (Na+, Cl-, K+, urea). assesses state of hydration, concentrating ability of kidney tubules, electrolyte balance
how does urine & serum osmo help differentiate DI from SIADH?
DI: urine osmo low, serum osmo high (excess water excretion & not responsive to water restriction).
SIADH: urine osmo > 200 mOsmol/kg, serum osmo low (excess water retention → body water high in all compartments).
how does urine & serum osmo ID failure of renal tubular urine concentrating function?
urine/serum osmo ratio → 1 (typically ~2-3) with loss of urine concentrating ability, even when urine should should be more concentrated
estimating serum osmolality
addresses issues of hydration & [Na+]. considers only common solute measurements from BMP (will be different from measured osmo). contributions from Ca, Mg, & their anions are ignored. can be more crudely approximated as 2 x Na
![<p>addresses issues of hydration & [Na<sup>+</sup>]. considers only common solute measurements from BMP (will be different from measured osmo). contributions from Ca, Mg, & their anions are ignored. can be more crudely approximated as 2 x Na</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e7d77c9c-05a4-4244-96ba-e5558b2694ee.png)
how is osmolality measured?
based on colligative properties of solns (# dissolved particles in soln): osmotic pressure, vapor pressure, boiling/freezing point. use cryo-osmometer to measure serum & urine directly. higher osmo = more its freezing point is depressed below 0C (solute reduce bonding forces b/t solvent molecules)
osmolar gap
measured plasma osmol - estimated plasma osmol. high = excess of uncounted low MW particles. endogenous: ketone bodies (DKA). exogenous: ethylene glycol (antifreeze), useful crude toxicology screen as many drugs have low MW
hydrostatic pressure
pressure exerted by a fluid within a closed system. regulates water distribution b/t intravascular & extravascular spaces
intravascular hydrostatic pressure
force of blood pressing outward against blood vessel wall (fluid-pushing pressure inside capillary). drives water out of arteriole & venule blood vessels. propels blood with heartbeat. increased with elevation
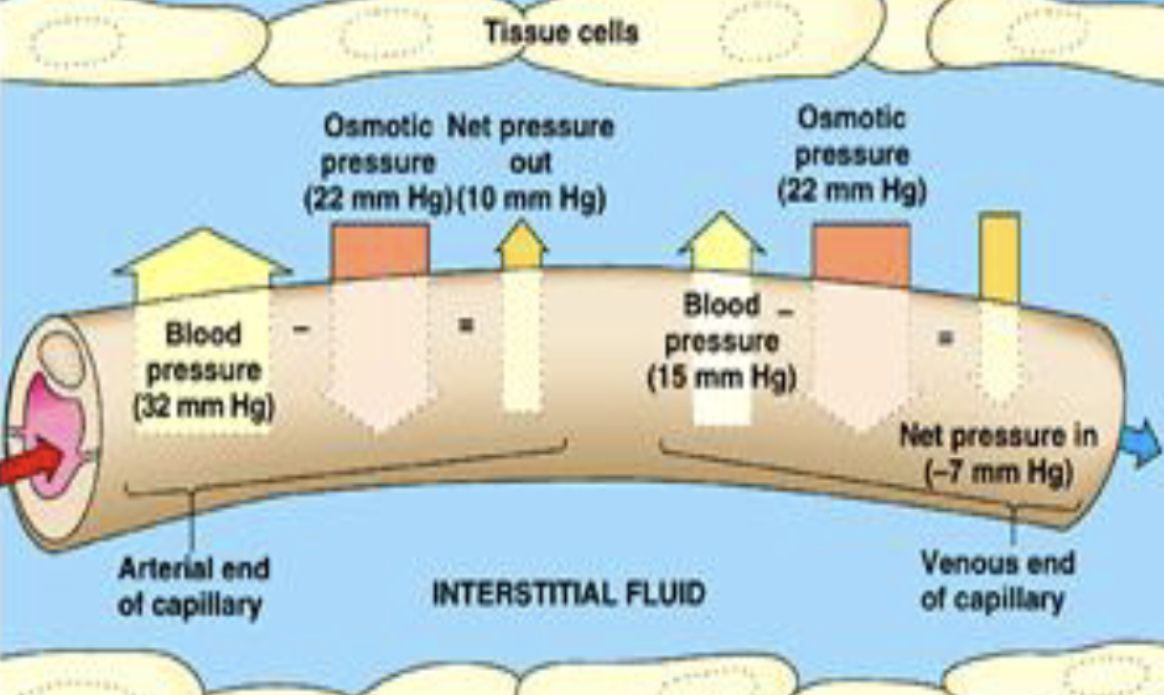
colloidal osmotic (oncotic) pressure
depends on large, colloidal particles (proteins, lipids). regulates distribution of water b/t intravascular & extravascular spaces. essential to maintain intravascular fluid volume (BV/BP). albumin is main regulator
why is albumin the main regulator of oncotic pressure?
its plasma concentration is less than its interstitial fluid concentration. its MW is less than other plasma proteins → more particles for a given weight → greater osmotic effect
edema
excessive accumulation of interstitial fluid. causes: low serum protein, heart failure, blockage of lymphatics
how does low serum protein contribute to edema?
from either inadequate protein synthesis (severe liver disease), protein loss (via renal or GI tract), or inadequate protein intake
how does heart failure contribute to edema?
high right-sided pressures cause elevated hydrostatic pressure in the capillaries, leading to more fluid movement into the interstitium
how does blockage of lymphatics contribute to edema?
typically from surgical excision of lymph nodes & associated lymph vessels: lymph system normally returns excess interstitial fluid to the general circulation
sodium (Na+)
most abundant cation in ECF, plasma Na+ determines > 90% of plasma osmolality. maintains electrolyte balance & thus water distribution b/t intracellular & extracellular spaces, a/w BP. required for nerve impulse transmission (CNS) & muscle contraction
what is Na+ regulated by?
Na-K-ATPase pump, thirst, kidney function (renin, aldosterone, ADH)
why is Na+ measured?
to assess hydration, and in conditions a/w water & electrolyte imbalance. must interpret [Na+] in context of hydration status Na+/BV
hyponatremia
serum [Na+] < 135 mmol/L. most common electrolyte D/O, w/ diverse etiologies. symptoms primarily due to hypotonicity of blood, causing cerebral edema. classified into 3 types based on measured serum osmo: equal (isotonic), low (hypotonic), high (hypertonic)
classification of hyponatremia
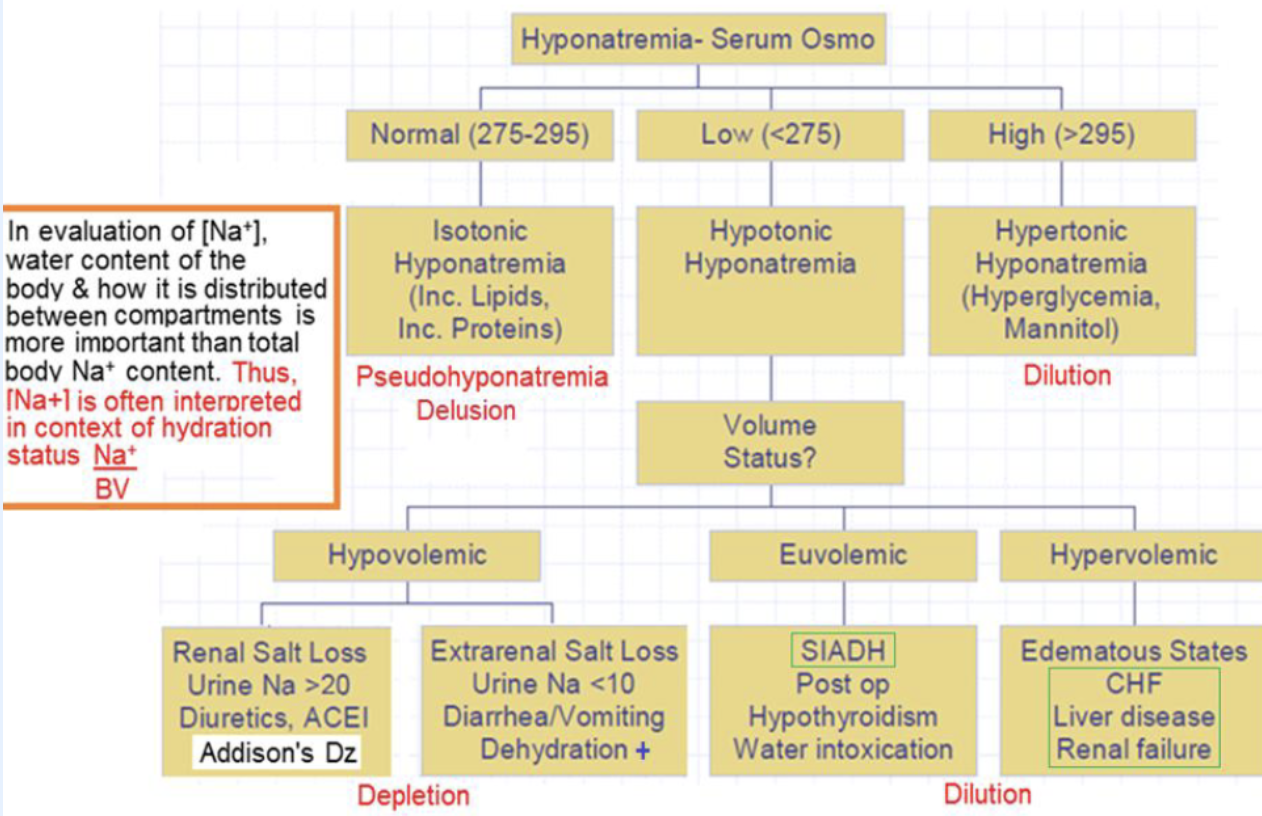
isotonic hyponatremia (pseudohyponatremia)
delusion: normal Na+ & water. only an issue when “indirect method” used to measure Na+, or specimen has hyperlipidemia or hyperproteinemia in multiple myeloma. error is due to predilution required by indirect method: assumes normal water content (93%), so underestimates [Na+]. direct method not affected
![<p>delusion: normal Na<sup>+</sup> & water. only an issue when “indirect method” used to measure Na<sup>+</sup>, or specimen has hyperlipidemia or hyperproteinemia in multiple myeloma. error is due to predilution required by indirect method: assumes normal water content (93%), so underestimates [Na<sup>+</sup>]. direct method not affected</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/19f6ce03-be43-4981-8d0e-1dccb4c9c6ee.png)