Chapter 8 - Photosynthesis
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Photosynthesis
process by which light energy is converted to chemical energy and stored in sugar or other organic molecules
series of reactions which convert light energy, carbon dioxide, and water → sugar and oxygen
involves a series of redox reactions and the passing of electrons
autotroph
organism that makes its own food to grow and does not have to feed off of other organisms
photoautotroph
uses light energy to synthesize organic molecules
excites electrons causing environment to fuel organic molecules
mixotrophic
can go through autotrophic pathways but also consumes other organisms like heterotrophs
chemotrophic
uses heat energy to generate organic molecules
what organisms are capable of photosynthesis (eukaryotes and prokaryotes)
Eukaryotes
plants
multicellular algae
unicellular eukaryptes
Prokaryotes
cyanobacteria
purple sulfur bacteria
heterotrophs
organisms which must feed off of other living things
animals consume plants and/or other animals
decomposers feed off of dead organisms or organic litter
ex. fungi and most prokaryotes
rely on the oxygen produced as a by-product of photosynthesis from autotrophs in order to breathe
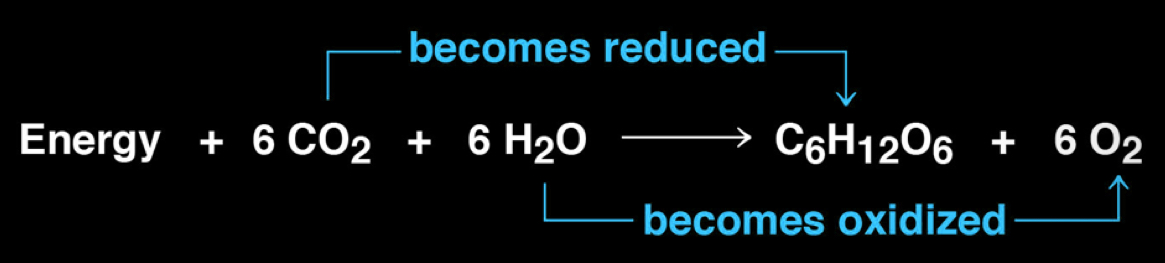
photosynthesis vs. cellular respiration
simplified equation for photosynthesis is the reverse of the equation for cellular respiration BUT they are not the direct reverse reaction
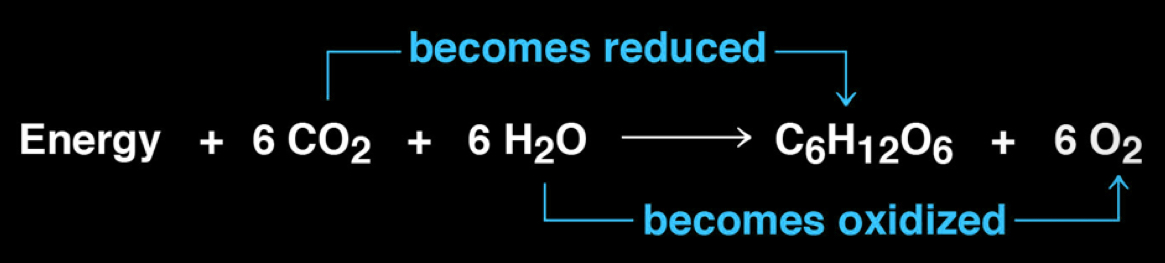
leaf structure
has chloropalsts, veins, and stomata
mesophyll
interior tissue layer of the leaf composed of photosynthetic cells
each mesophyll cell contains an average 30-40 chloroplasts
stomata
opens and closes which allows CO2 to enter and O2 to exit the leaf
chloroplasts (+ chlorophyll)
double membrane bound organelles
filled with a dense fluid called stroma
in the stroma, there are a series of membrane bound sacs called thylakoids
chlorophyll - green pigment which absorbs light energy and is found in the thylakoid membranes
overview of photosynthesis
an anabolic pathway which creates complex sugars from simple building blocks
requires the input of energy by utilizing energy
made up of two distinct parts:
Light reactions
Calvin cycle (AKA dark reactions/light-independent reactions)
steps of light reactions
Light is absorbed by chlorophyll in the thylakoid membranes
Light (electromagnetic energy) interacts with water which splits to produce electrons, protons, and oxygen (leaves the cell through stomata or goes to chloroplasts for cellular respiration)
electrons are temporarily stored in NADP+
solar energy from light is used to reduce the electron carrier (NADP+ → NADPH)
chemiosmosis results in phosphorylation by using light energy to phosphorylate ADP → ATP
products created in the light reactions (NADPH and ATP) power the calvin cycle
steps of calvin cycle
carbon fixation occurs to attach CO2 (from environment) into organic compounds
Uses NADPH and ATP to help reduce the fixed carbon into carbohydrates
simple sugars can be used as fuel in respiration or in any other synthesis reactions
NADP+ and ADP are recycled back into light reactions
The Light Reactions
AKA Hill reactions/light-dependent reactions
utilizes a series of protein systems bound to the thylakoid membrane
uses light energy to split water and create chemical energy (NADPH and ATP)
Photosynthetic Pigments
substance which absorbs visible light
different pigments absorb different wavelengths of light
Types of photosynthetic pigments and their functions
Chlorophyll a - main light capturing pigment
absorbs violet-blue and red light
reflects green light which is why it looks green
Chlorophyll b - accessory pigment
absorbs blue and yellow-orange light
reflects green which is why it looks green
Carotenoids - accessory pigments which are photoprotective
absorbs violet and blue-green light
reflects orange, yellow, red colour
pulls and absorbs light away from vulnerable tissues to protect them for UV
What’s special about carotenoids
they pull and absorb light away from vulnerable tissues to protect them from UV
Melanin
another pigment which makes up the brown colour of things
excitation of electrons
when a pigment absorbs light, one of the pigment’s electrons are excited to a higher electron shell
in an isolated state, this potential energy is transformed into heat and released as photons of light, as the electron falls back down to a lower shell
Photosystems
Complex of pigments, small organic molecules, and proteins.
Composed of a reaction-center complex (which houses chlorophyll a) surrounded by light harvesting complexes
what do light-harvesting complexes contain
Light harvesting-complexes contain variety of pigments (chlorophyll a and b, and carotenoids)
broadens area and spectrum of absorption
2 types of photosystems
Photosystem 2 (P680)
Photosystem 1 (P700)
Number represents the wavelength of light they absorb at the highest frequency
how is light moved around in photosystems
they are hot potatoed between pigment molecules
Reaction-center Complex
Allows the conversion of light energy to potential energy to chemical energy
done by transferring the electron to the primary electron acceptor
loss of energy as heat or light is prevented
steps of reaction-center complex
photon of light is absorbed by a pigment in the light-harvesting complexes
energy is eventually transferred to special pair of chlorophyll a in the reaction-center complex
The special pair of chlorophyll a molecules transfer the excited electron to the primary electron acceptor
how do the light reactions use Photosystems 1 and 2
the light reactions utilize two photosystems in order to provide the energy required for carbon fixation in the Calvin Cycle
Each photosystem is followed by an ETC allow for the production of ATP in PS 2 and NADPH in PS 1 through the use of linear electron flow
Steps of Linear electron flow
photon stimulates an electron from pigment in light-harvesting complex of photosystem 2 into a higher energy electron shell
energy continues to be passed on as it excites and passes electrons then goes back to the ground state
process is repeated until P680 pair reaches the reaction-center complex
electron is transferred from P680 to primary electron acceptor
P680 → P680+
Enzyme catalyzes splitting of water into electrons and photons
electrons are passed on to the P680 pair
protons are released into the thylakoid space
oxygen is released but leaves the cell as a by-product
Electrons are transferred from the primary electron acceptor through an ETC
electrons are transferred from ETC to PS 1
flow is always PS 2 → PS 1
Energy from the ETC is used by cytochrome complex to pump protons into the thylakoid space
generates an electrochemical gradient used by chemiosmosis and ATP production
Pigments in light-harvesting complexes energy of PS 1 are stimulated
electrons are passed around through pigments to P700 pair in reaction-center complex and then passed onto he primary acceptor
P700+ accepts electrons from ETC
electrons are passed from primary acceptor of photosystem 1 into another ETC
NADP+ reductase catalyzes the production of NADPH using electrons from the ETC
NADPH can now be used in the Calvin Cycle to power carbon fixation
Chemiosmosis and ATP production (how it is connected to this chapter)
protons are pumped into the thylakoid space from the cytochrome complex of ETC following PS2
diffusion through ATP synthase drives ATP production
Light reactions summary
Light activates PS2, H2O is split, and electrons are fed into the ETC, producing O2 and H+
ETC pumps H+ into thylakoid space and moves electrons to PS1
proton gradient allows for chemiosmosis and ATP synthesis
light stimulates PS 1 and electrons are passed from the 1st ETC to the 2nd ETC
NADP+ reductase catalyzes production of NADPH
ATP and NADPH generated in the light reactions are used to fuel the calvin cycle
Calvin Cycle
occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast or cytoplast in unicellular organisms
3 phases:
carbon fixation
reduction
regeneration
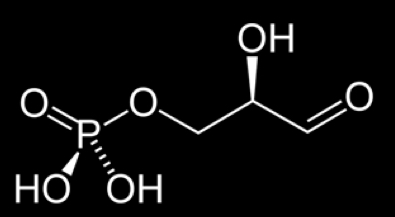
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate (G3P)
simple sugar produced is G3P, not glucose
produced in energy investment phase of glycolysis
1 G3P glucose = 3 turns of the Calvin Cycle
Steps of the calvin cycle more in depth
Carbon fixation
rubisco catalyzes the conversion of ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) to an unstable 6-carbon molecule by adding CO2
this molecule immediately splits into 2 molecules of 3-phosphoglycerate
Reduction
Phosphorylation of 3 phosphoglycerate by ATP
Reduction by NADPH and loss of a phosphate group which produces G3P
1 of the 6 G3P molecules produced exits the cycle
for every 3 turns of the cycle, there is a net output of 1 G3P
Regeneration
regeneration of ribulose biphosphate (RuBP) is necessary in order to restart the cycle
5 molecules of G3P are turned into 3 molecules of RuBP through a series of enzymatic reactions
reactions require the input of 3 molecules of ATP
How many ADP and NADP+ molecules are produced per cycle of the Calvin Cycle
1 glucose = 2 G3P = 6 turns of the calvin cycle
(3 ADP and 2 NADPH) x 2
Photorespiration
biochemical pathway which uses some elements of photosynthesis and cellular respiration
occurs when availability of CO2 is low due to hot and dry climates
instead of binding CO2, rubisco binds O2
outcomes of photorespiration
production of CO2
use of ATP
less energy efficient
alternative modes of carbon fixation
C4 Plants
CO2 is fixed into a 4-Carbon compound
physical compartmentalization for separation into steps
CAM plants
open stomata during the night and close them during the day
store intermediate organic acids in vacuoles
no physical compartmentalization
temporal separation of steps
what percent of organic materials stored created through photosynthesis is used as fuel in cellular respiration of the organism
50%
how is excess organic materials stored in plants and where
stored as starch
locations stored in:
seeds
tubers
fruits
G3P structure (draw it)
What does photosynthesis create
oxygen in our atmosphere and 150 billion metric tons of carbohydrates each year