AP Bio Unit 6
4.0(1)Studied by 31 people
Card Sorting
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 9:01 PM on 5/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
1
New cards
The primary source of hereditary material
is DNA and in some cases RNA
2
New cards
Genetic information is stored as
the sequence of bases in DNA and RNA
3
New cards
Before genetic information is passed from parent to daughter cells
DNA is packaged into chromosomes
4
New cards
Many viruses use
RNA molecules to encode genetic information
5
New cards
DNA and sometimes RNA
exhibits specific nucleotide base pairing
6
New cards
How are DNA and RNA structurally similar
* Both are polymers containing nucleotides
* Both are chain-like molecules
* Both follow base pairing rules
* Both are chain-like molecules
* Both follow base pairing rules
7
New cards
Specific nucleotide base pairing is conserved through
evolution
8
New cards
DNA and RNA both follow conserved base pairing rules in which
pyrimidines pair only with specific purines
9
New cards
Pyrimidines (def and identify the bases)
have a single ring structure (includes uracil, cytosine, thymine)
10
New cards
Purines (def and identify the bases)
have a double ring structure (includes adenine and guanine)
11
New cards
Prokaryotic organisms typically have which kind of chromosomes
circular chromosomes
12
New cards
Eukaryotic organisms have which type of chromosomes
multiple, linear chromosomes
13
New cards
Prokaryotic genomes are typically ------- then eukaryotic genomes
Prokaryotic genomes are typically smaller than eukaryotic genomes
14
New cards
Plasmids
small extra-chromosomal, double stranded, circular DNA molecules
15
New cards
Prokaryotic plasmids are found
in the cytosol
16
New cards
Eukaryotic plasmids are found
in the nucleus
17
New cards
Genetic information is transmitted from one generation to the next via
DNA or RNA
18
New cards
Most of the time genetic information is transmitted via
DNA
19
New cards
Heritable information provides for
continuity in life
20
New cards
(Historical experiment that proves DNA is the carrier of information) Griffith
* Mice injected with live cells of harmless strain R do not die. Live R cells are in their blood.
* Mice injected with live cells of killer strain S die. Live S cells are in their blood.
* Mice injected with heat-killed S cells do not die. No live S cells are in their blood.
* Mice injected with live R cells plus heat-killed S cells die. Live S cells are in their blood.
\
* Mice injected with live cells of killer strain S die. Live S cells are in their blood.
* Mice injected with heat-killed S cells do not die. No live S cells are in their blood.
* Mice injected with live R cells plus heat-killed S cells die. Live S cells are in their blood.
\
21
New cards
Plasmids are
small-extra chromosomal, DNA molecules (mainly in prokaryotes)
22
New cards
DNA replication ensures
continuity of hereditary information
23
New cards
Semiconservative replication
the process by which DNA makes copies of itself, each strand, as it separates, synthesizing a complementary strand.
24
New cards
Central Dogma (main flow of genetic information)
DNA ^^→^^ RNA %%→%% Protein
^^Transcription^^
%%Translation%%
^^Transcription^^
%%Translation%%
25
New cards
Flow of genetic information in some viruses
RNA → DNA → RNA → Protein
26
New cards
Structure of DNA
double helix made of nucleotides
27
New cards
The backbone of DNA is
covalent bonds (do not break apart easily)
28
New cards
The bonds formed in between nucleotides in DNA are
hydrogen bonds that break apart easily to use or replicate strand
29
New cards
How many hydrogen bonds are between Adenine and Thymine
two
30
New cards
How many hydrogen bonds are between Cytosine and Guanine
three
31
New cards
Nucleotides are
subunits of DNA
32
New cards
Chargaff’s Rules
* A to T 2 hydrogen bonds
* G to C 3 hydrogen bonds
* A purine binds with a pyrimidine
* G to C 3 hydrogen bonds
* A purine binds with a pyrimidine
33
New cards
DNA strands run in an
ANTIPARALLEL WAY
34
New cards
Example of antiparallel
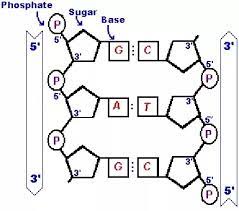
35
New cards
Structure of Eukaryotic Chromosome
* DNA wraps around histones (protein) to form spools or nucleosomes
* Spools of wrapped histones then wrap/coil to form chromatin fiber
* Chromatin fiber then bundles/coils to form chromosome
* Spools of wrapped histones then wrap/coil to form chromatin fiber
* Chromatin fiber then bundles/coils to form chromosome
36
New cards
Visual of the structure of Eukaryotic Chromosomes
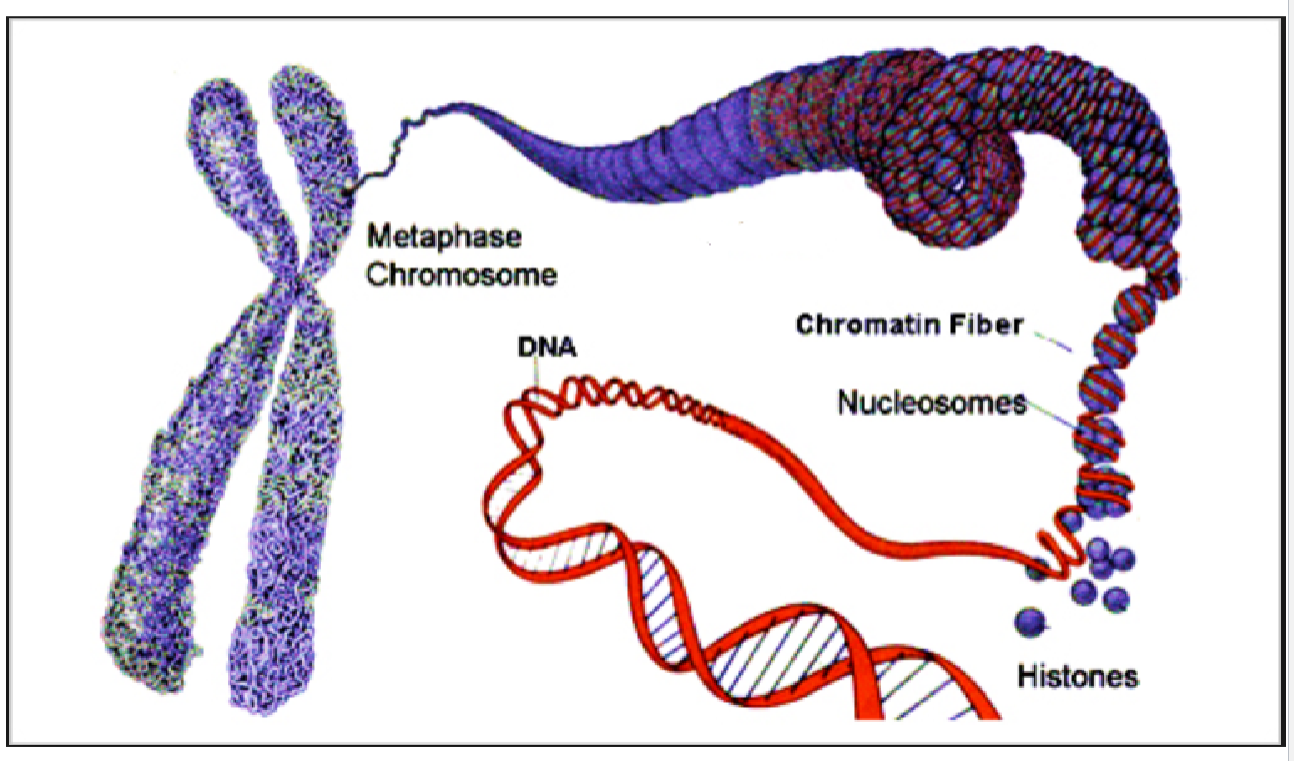
37
New cards
RNA molecules are used to
facilitate protein synthesis using DNA information
38
New cards
Ribosomes
contain RNA and assemble protein
39
New cards
Transcription is the process in which
an enzyme directs the formation of an mRNA molecule
40
New cards
DNA Replication
* Two strands of double helix unwind
* Each strand serves as template for the new strands
* DNA polymerase adds new nucleotide subunits
* Additional enzymes and other proteins required to unwind and stabilize DNA helix
* Each strand serves as template for the new strands
* DNA polymerase adds new nucleotide subunits
* Additional enzymes and other proteins required to unwind and stabilize DNA helix
41
New cards
DNA Helicases
Open the double helix by disrupting the hydrogen bonds that hold the two strands together.
42
New cards
Topoisomerases
Break one or both DNA strands, preventing excessive coiling during replication, and rejoin them.
43
New cards
DNA Polymerases
Link nucleotide subunits together.
44
New cards
DNA Primase
Synthesizes short RNA primers on the lagging strand. Begins replication of the leading strand.
45
New cards
DNA ligase
Links Okazaki fragments by joining the 3’ end of the new DNA fragment to the 5’ end of the adjoining DNA.
46
New cards
Telomerase
Lengthens telomeric DNA.
47
New cards
Bidirectional
starting at the origin of replication, strands replicate at the replication fork
48
New cards
From what direction can new nucleotides only be added to the old strand
New nucleotides can only be added to the old strand from the 3’ to 5’ direction
49
New cards
Telomeres
short, non-coding repetitive DNA sequences
50
New cards
Telomeres shorten slightly
with each cell cycle
51
New cards
Telomeres can be extended by
telomerase
52
New cards
Absence of telomerase activity may be the cause of
cell aging
53
New cards
Most cancer cells have ---------- to maintain…
Most cancer cells have telomerase to maintain telomere length and resist apoptosis
54
New cards
Humans have 46 chromosomes and thus
46 DNA molecules
55
New cards
DNA Polymerase proofreads
DNA polymerase proofreads each nucleotide that it adds against the template
56
New cards
If an error is made, DNA Polymerase
deletes the nucleotide and continues synthesizing DNA
57
New cards
DNA Repair/Excision Repair
* Nucleases cut out (incise) the incorrect nucleotide
* DNA Polymerase adds the correct nucleotide
* Ligase connects the new nucleotide to the strand
* DNA Polymerase adds the correct nucleotide
* Ligase connects the new nucleotide to the strand
58
New cards
DNA Repair mechanisms
DNA polymerases proofread DNA sequences during DNA replication and repair damaged DNA
59
New cards
When proofreading and repair mechanisms fail, an error becomes
a mutation- a permanent change in the DNA sequence
60
New cards
Structure of RNA
* Formed from nucleotide subunits
* Each nucleotide subunit contains ribose, a base, and three phosphates
* Like DNA, RNA subunits are covalently joined by a 5’--3’ linkage to form alternating sugar phosphate backbone
* Each nucleotide subunit contains ribose, a base, and three phosphates
* Like DNA, RNA subunits are covalently joined by a 5’--3’ linkage to form alternating sugar phosphate backbone
61
New cards
Function of DNA
It permanently stores a cell’s genetic information, which is passed to offspring
62
New cards
Functions of RNA
Some serve as disposable copies of DNA’s genetic message; others are catalytic
63
New cards
mRNA
Messenger RNA, contains information transcribed from DNA
64
New cards
rRNA
Ribosomal RNA, main component of ribosomes, where polypeptide chains are built
65
New cards
tRNA
Transfer RNA, delivers amino acids to ribosomes
66
New cards
Sequences of the RNA bases, together with the structure of the RNA molecule, determine
RNA function
67
New cards
The Central Dogma
Transcription Translation
DNA %%→%% RNA → Protein
%%RNA Polymerase%% Ribosomes
DNA %%→%% RNA → Protein
%%RNA Polymerase%% Ribosomes
68
New cards
The three basic steps of TRANSCRIPTION
1. %%Initiation%%
2. Elongation
3. @@Termination@@
69
New cards
The process of TRANSCRIPTION
* DNA opens at the appropriate site
* RNA Polymerase attaches to the DNA (%%Initiation%%) and adds RNA nucleotides (Elongation). The sequence is read from the 3’ to the 5’ end of the DNA strand. Either DNA strand may be used.
* When RNA Polymerase reaches the appropriate sequence, it stops adding nucleotides and detaches from the newly formed mRNA (@@Termination@@).
* RNA Polymerase attaches to the DNA (%%Initiation%%) and adds RNA nucleotides (Elongation). The sequence is read from the 3’ to the 5’ end of the DNA strand. Either DNA strand may be used.
* When RNA Polymerase reaches the appropriate sequence, it stops adding nucleotides and detaches from the newly formed mRNA (@@Termination@@).
70
New cards
DNA replication and transcription both
synthesize new molecules by base-pairing
71
New cards
In TRANSCRIPTION…
a strand of mRNA is assembled on a DNA template using RNA nucleotides
* Uracil (U) nucleotides pair with Adenine (A) nucleotides
* RNA Polymerase adds nucleotides to the transcript
* Uracil (U) nucleotides pair with Adenine (A) nucleotides
* RNA Polymerase adds nucleotides to the transcript
72
New cards
TRANSLATION occurs in
the cytoplasms
73
New cards
In TRANSLATION…
a polypeptide chain (aka protein) specified by the mRNA is synthesized
74
New cards
Three steps in TRANSLATION
* Initiation
* Repeating cycles of elongation
* Termination
* Repeating cycles of elongation
* Termination
75
New cards
Each sequence of three nucleotide bases in the mRNA constitutes
a codon
76
New cards
TRANSLATION requires
tRNA’s and cell machinery, including ribosomes
77
New cards
tRNA structure
tRNA has the anticodon on one end and the amino acid that corresponds to the codon on the mRNA
78
New cards
Universal start codon
AUG
79
New cards
Three stop codons
UAA, UAG, UGA
80
New cards
TRANSLATION in a nutshell
1. mRNA interacts with the rRNA to INITIATE translation at the start codon (AUG)
2. The sequence of nucleotides is read in triplets (codons), each codon encodes for a specific amino acid
3. tRNA brings the anticodon and amino acid to the mRNA
4. Amino acids are added until the stop codon is reached
5. The newly formed amino acid is released
81
New cards
Proteins have 4 levels of structure
Primary: the sequence of amino acids bonded by peptide bonds
Secondary: Alpha helix or Beta pleated by hydrogen bonds
Tertiary: Folding due to interactions from side chains
Quaternary: Peptide chains interact with different chains to form protein
Secondary: Alpha helix or Beta pleated by hydrogen bonds
Tertiary: Folding due to interactions from side chains
Quaternary: Peptide chains interact with different chains to form protein
82
New cards
In eukaryotic cells enzyme-regulated modifications occur to the mRNA transcript
* Addition of poly-A tail, which is made of adenine nucleotides and protects from enzymes and is added at the 3’ end
* Addition of GTP cap, which is made of modified guanine nucleotides, helps ribosomes attach to the mRNA, and stabilizes and is added at the 5’ end
* introns
* exons
* splicing
* Addition of GTP cap, which is made of modified guanine nucleotides, helps ribosomes attach to the mRNA, and stabilizes and is added at the 5’ end
* introns
* exons
* splicing
83
New cards
Introns
sequences of an mRNA transcript that do NOT code for amino acids and are excised during RNA processing
84
New cards
Exons
sequences of an mRNA transcript that DO code for amino acids and are retained during RNA processing
85
New cards
Alternative splicing
the process of splicing introns and connecting retained exons
86
New cards
Coupled transcription and translation in bacteria
Unlike eukaryotes, translation of the bacterial mRNA molecule usually begins before the 3’ end of the transcript is even finished
87
New cards
Retroviruses
flow of genetic information is reversed by reverse transcriptase, ex of retroviruses, HIV and AIDS
88
New cards
Reversetranscriptase
Enzyme that turns RNA into DNA
89
New cards
Phenotypes are determined through
protein activities
90
New cards
Example of how phenotypes are determined
Melanin Synthesis
• At least 8 different genes are involved in melanin production (main determinant of skin color) \n • These genes are co-dominant \n • Sexual reproduction allows for different proteins to be synthesized, therefore, producing many different melanin shades
• At least 8 different genes are involved in melanin production (main determinant of skin color) \n • These genes are co-dominant \n • Sexual reproduction allows for different proteins to be synthesized, therefore, producing many different melanin shades
91
New cards
Genetic Engineering techniques
can manipulate the heritable information of DNA, and in special cases RNA
92
New cards
Electrophoresis
Identifies length of DNA fragments
93
New cards
Process of Electrophoresis
1. Cut DNA with restriction enzymes
2. Place fragments on a gel and a solution and apply a current
3. The smaller pieces will travel further than the larger ones, DNA travels from negative to position
94
New cards
Bacterial Transformation
Bacteria can import bits of DNA and express genes from it
95
New cards
Bacterial Transformation can be used to make
recombinant DNA: Mix of DNA from 2 species
96
New cards
Plasmids can be used to express human genes in bacteria
1. Make DNA copy from human mRNA
2. Use restriction enzyme to paste DNA onto a plasmid
3. Introduce plasmid into bacteria
4. Bacteria now expresses new gene
This is how insulin is made!
97
New cards
Restriction Enzymes
Cuts DNA at specific locations, allows 2 pieces of DNA to join together
98
New cards
Genetically Modifies Organisms (GMO)
allows plants to produce new proteins/express different (resistant typically) genes