697 Week 11 Monday Flashcards: Gait deviations
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Inpatient Stay vs Outpatient Course
Inpatient Stay- Designed for individuals who are ready to roll. Well healed, have been mobile at
home, prosthesis fit and preliminarily adjusted
● Typically a 5-7-day rehab admission with goal to establish a wearing schedule, provide gait
training and education/instruction on donning/doffing as well as adjusting fit during the day;
opposite sessions for gait training and prosthetic/skin checks, patient should be stretching
and strengthening
Outpatient Course - Sometimes a better option for individuals predicted to take longer to achieve
tolerance for prosthetic weight bearing; more health problems, etc. OR who may need more
interventions to prepare for prosthetic ambulation (flexibility, strengthening, etc)
Things to do during every day of an inpatient stay

Liners Purpose
Interface Protection: Liners serve as a protective
barrier between the residual limb and the prosthetic
socket. They help prevent friction, pressure points,
● Cushioning: Liners often have padding to provide
cushioning, which helps distribute pressure evenly
Liners:
and skin irritation.
across the residual limb.
● Volume Management: Liners can help manage
volume fluctuations in the residual limb due to
changes in swelling, muscle atrophy, or weight loss/gain. This is especially important during the
initial fitting stages and over time as the residual
limb adapts.
● Socket Suspension: Some liners are designed with
features to aid in suspension, helping to hold the prosthetic limb inside the socket
Socks purpose
Volume Adjustment: Prosthetic socks come in different
thicknesses or ply, allowing users to adjust the fit of their
prosthetic limb by adding or removing layers. This is
Socks:
particularly useful for accommodating volume changes
throughout the day or during various activities.
● Moisture Management: Socks made from moisture-
wicking materials help keep the residual limb dry,
reducing the risk of skin breakdown and discomfort
caused by sweat.
● Comfort and Protection: Similar to liners, socks provide
additional cushioning and protection against friction
and pressure points.
● Alignment Correction: In some cases, socks may be
strategically layered to correct minor alignment issues
or to fine-tune the fit of the prosthetic limb.
Establishing a wearing schedule
Initial phase: start wearing for short periods (1-2 hours) and gradually increase time in prosthesis every day as comfort allows
After initial time, try to get them to wear it as long as possible to get used to it
Continue to gradually increase the wear time over weeks and months, but allow the residual limb adequate time to adjust
Make sure the patient has follow up appointments scheduled with the prosthetist to address concerns and make adjustments if needed
TKA Line
Trochanter: This point corresponds to the greater trochanter of the
femur. In prosthetics, the alignment of the socket and the prosthetic
knee component should be aligned with the trochanter to ensure
proper weight distribution and stability.
Knee: The knee joint of the prosthesis should be aligned with the
anatomical knee joint of the user. Proper alignment ensures natural
movement and stability during walking and other activities.
Ankle: The ankle joint of the prosthesis should also be aligned with
the anatomical ankle joint to facilitate smooth and efficient gait
mechanics. Proper alignment reduces stress on the residual limb and
other joints, improving overall comfort and function.
A/P View
The A/P view provides a frontal perspective, looking at the
prosthesis from the front and/or back of the user.
● In this view, prosthetists assess the alignment of the
prosthetic components in terms of their position
relative to the user's midline and symmetry between
the left and right sides.
● Proper alignment in the A/P view ensures that the
prosthetic components are positioned centrally and
symmetrically with respect to the user's body,
optimizing balance and stability.
Sagittal View
The sagittal view provides a side perspective,
looking at the prosthesis from the side of the user.
● In this view, prosthetists assess the alignment
of the prosthetic components in terms of their
position relative to the user's anatomical joint
axes, such as the knee and ankle.
● Proper alignment in the sagittal view ensures
that the prosthetic components are positioned
in line with the user's natural joint axes, allowing
for smooth and efficient movement during
walking and other activities.
Circumduction TFA description and potential causes
Description: The individual swings the prosthetic limb in a lateral arc during the swing phase rather than lifting it straight through.
Causes:
Anatomic: abduction contracture, poor knee control
Prosthetic: long prosthesis, excessive stiffness of knee unit, inadequate suspension, small socket, excessive plantarflexion
Circumduction TFA Implications and interventions:
Increased Energy Expenditure- Excessive lateral movement requires more effort, leading to fatigue and decreased endurance over time.
Higher Risk of Secondary Musculoskeletal Issues - Hip hiking and trunk compensation may lead to low back pain, hip pain, or joint overuse injuries on the intact side. Increased stress on the ipsilateral hip flexors and abductors due to abnormal movement patterns.
Reduced Gait Efficiency and Speed - The extra movement makes walking less fluid and slower, which can limit mobility and daily activity performance.
Increased Fall Risk - The lateral movement disrupts balance and stability, especially in crowded or uneven environments.
Toe clearance issues can result in tripping or stumbling.
Potential Prosthetic Fit and Alignment Problems - May indicate excessive prosthetic length, insufficient knee flexion, or inadequate suspension, requiring prosthetist evaluation.
Prosthetic Adjustments: Ensure proper length, knee flexion settings, and suspension fit.
Gait Training: Emphasize hip and knee flexion strategies to encourage a more natural swing phase.
Strengthening & Flexibility: Improve hip flexor and core strength while addressing tight hip abductors and weak knee flexors.
Cueing & Feedback: Use verbal, tactile, or visual feedback to reinforce proper gait mechanics.
TFA rotation of foot on heel strike Description and cause
Description: The prosthetic foot rotates when it lands on the ground, as opposed to landing and falling in the sagittal plane
Cause: Anatomic: hip rotator weakness/contracture, femoral retroversion
Prosthetic: stiff heel cushion, foot is malaligned to shank
TFA rotation of foot on heel strike implications and treatment
Implication: Excess energy expenditure, further risk of developing or reinforcing a contracture at the hip
Treatment: Anatomic: work on ROM and strengthening for the hip, especially for rotators
Prosthetic: adjust rotation of prosthetic foot, and swapping out the cushion for more compliance
TTA Contralateral early heel description and cause
Description: Contralateral or early heel rise or vaulting allows for clearance of the prosthetic with decreased hip/or knee flexion. Compensation for a prosthesis that is too long, inadequate suspension, or a learned gait pattern
Cause: Prosthetics: prosthesis that is too long, inadequate suspension, decreased weight acceptance through the prosthetic
Anatomic: learned gait pattern, decreased strength of hip flexors on prosthetic side
TTA contralateral early heel rise implications and treatments
Implications: Decreased stance time on prosthetic limb, decreased gait speed
Treatment: Prosthetic: Adjust the suspension
Anatomical: Strengthen hip flexors and trunk
TTA lateral trunk description + cause
Description: The patient would have a lean toward the side with the TransTibial Amputation
Cause: Short prosthesis, poor fit
TTA Lateral trunk implication + treatment
Implication: increased energy expenditure and fall risk
Treatment: Increase Prosthetic length
Medial/lateral knee instability description + cause
Description: The patient would have wobbling & instability in medial to lateral movements
Cause: Weakness of the hip flexors, prosthetic sizing issues, abd/add mm weakness
Medial/lateral knee instability implication + treatment
Implication: Pt will have reduced ROM, Decreased mobility, & hyper focused in order to reduce instability
Causes: Banded hip flxn, ball squeezes, hip abd,, and fixing the prosthetic sizing.
TFA Excessively forced hip flexion during terminal swing description + cause
Description: The individual increases anterior sagittal plane movement of the prosthetic limb at the hip.
Cause: Reduced knee friction
Taut extension aid (too strong of an extension moment because of it being too tight)
TFA Excessively forced hip flexion during terminal swing implication + treatment
Implications: increased energy expenditure
Treatment: fix the knee friction
TTA Excessive knee flexion during stance phase description + cause
Description: The individual uses an increased bent knee when putting weight on it
Cause: Increased ankle dorsiflexion, socket flexion, and posterior foot placement
Weak knee
TTA Excessive knee flexion during stance phase implication + treatment:
Implications: increased energy expenditure
treatment: Cane training
Tactile feedback gait training between // bars
T-band knee stability w/ perturbations (progress into different gait phases)
Eccentric knee extension
TFA Vaulting Description + causes
Description: The individual will raise the contralateral heel off of the ground.
Cause: Long prosthesis, inadequate suspension, inadequate knee friction, excessive plantarflexion, small socket (anatomical) walking speed exceeding that for which friction in sliding knee unit was adjusted
TFA Vaulting Implication + Treatment
Implication: Increased energy expenditure, imbalance/increased pressure during heel strike,
Treatment: Prosthetic adjustments to ensure proper limb length, socket fit, knee flexion, and foot alignment are essential. Gait training to promote symmetrical and efficient gait mechanics.
TTA knee hyperextension causes
Description is self explanatory
may be due to insufficient socket flexion, weak knee extensors, anterior foot placement, or inappropriate prosthetic foot
TTA knee hyperextension implication + treatment
Increased instability during gait and balance, excessive knee joint stress, and increased energy expenditure
Gait training, reassessing TTA fit, and ankle prosthesis positioning
TFA Lordosis description + causes
Description:
Lordosis: Terminal stance
Excessive B hip flexion, lumbar lordosis, anterior pelvic tilt
Causes:
Prosthetic: poor posterior brim support, inadequate socket flexion
MSK: Weak hip extension, hip flexion contracture, very short residual limb
TFA Lordosis implication + treatment
Clinical Implication:
Spinal pain, poor postural
and reactive balance, further contractures
Interventions: PPT, hip flexor stretch, hip extensor strengthening, fix prosthetic
TTA Premature Heel rise description + cause

TTA Premature Heel rise implication + treatment

TTA abnormal limb rotation description + cause
Abnormal limb rotation (excessive internal or external rotation of the prosthetic limb during swing) | Insufficient suspension, and misalignment of suspension components (improper placement or fit of suspension straps or cuffs can lead to rotation). Outshooting to evade foot drop: If the individual has weak ankle dorsiflexion (foot drop), they may excessively rotate the limb to help clear the foot during the swing phase. |

TTA abnormal limb rotation Implication + treatment

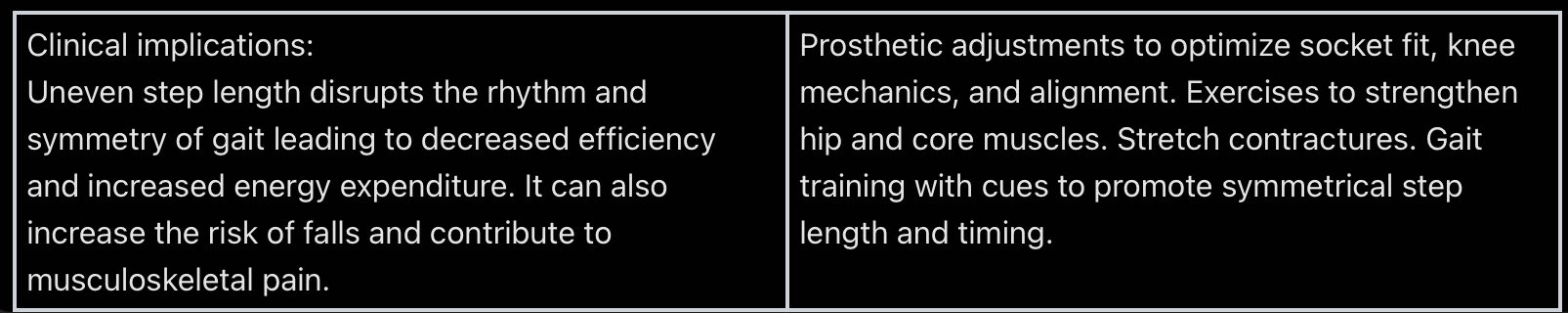
TFA Uneven step length description + cause

TFA Uneven step length implications + treatment
TTA foot slap description + cause
7A. Description:
Foot slap of the prosthetic limb occurs when the foot plantarflexes too quickly and strikes the ground with a loud slap
7A. Potential cause:
Anatomical:
- Eccentric quad weakness causing excessive knee flexion
- Flexion contracture of the knee or hamstring tightness
TTA foot slap treatment + implication
7A. Clinical implication:
- increased energy expenditure
- imbalance
- Msk implication: high risk of knee joint complications with instability, pain or weakness
- decreased aerobic capacity
7A. Interventions:
- eccentric quad strength/endurance
- Hamstring strength/endurance
- stretching into knee extension and HHS: prone with ankle weight
- gait training with adjustments to heel cushion, socket set more into extension or posteriorly
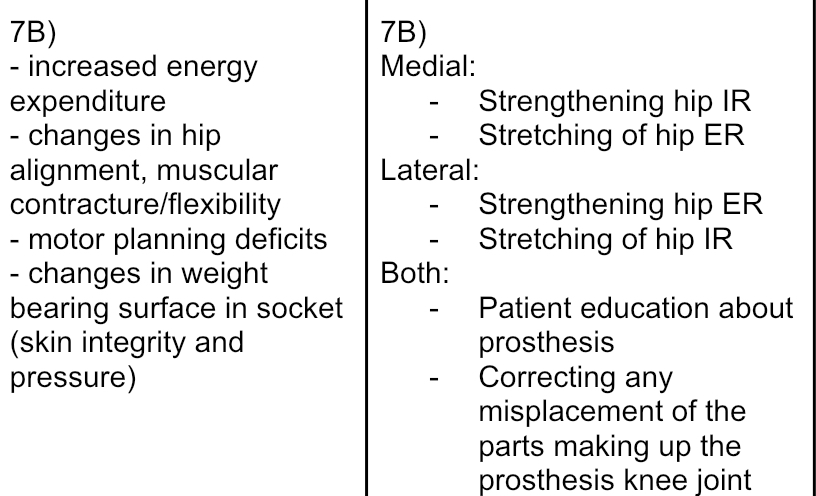
TFA medial or lateral heel whip description + cause
7B)
(Medial)
- The heel of the prosthetic limb moves towards midline after toe-off (during swing phases) and forces the knee laterally
(Lateral)
- The heel of the prosthetic limb moves laterally after toe-off (during swing phases) and forces the knee medially
TFA medial or lateral heel whip implication + treatment
TTA ER in late stage description + causes
Description: External rotation in late stage: Suble outward turning of the leg and foot as the body prepares to move forward in the late phase
Causes: Contralateral muscle imbalances proximally, tight ER rotators ipsilaterally.
TTA ER in late stage implication + treatment
Implication: Lack of stability w excessive movements (running, walking over objects or compliant surfaces)
Treatment: Strengthen IRs of hip, external cueing w/facilitatory techniques to reduce ER.
TFA Wide stance description + causes
Spread out legs, wide BOS
tight abductors, long prosthesis, abduction contracture
TFA Wide stance treatment + implication
Implication: decreased foot clearance, limited hip flexion, slow gait speed, less energy efficiency due to slow speed
Treatment: Stretching abductors, reducing prosthetic length, and socket adjustments to limit abduction.
TTA Hip ER during heel strike description + causes
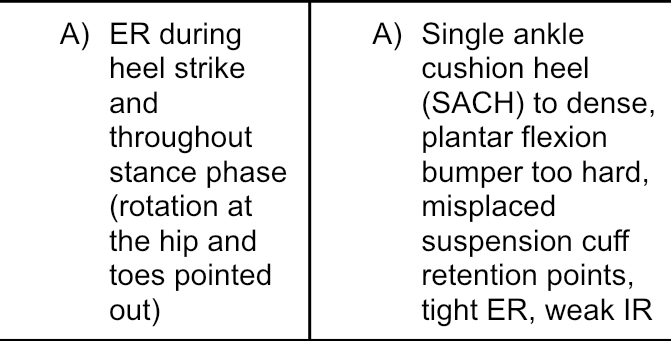
TTA Hip ER during heel strike Implication + treatment

TFA Foot slap description and causes

TFA foot slap implication + treatment

TTA toe drag description + cause
Caused by inadequate suspension of the prosthesis, a prosthesis that is too long, or lower-limb weakness in the hip abductors or ankle plantar flexors on the contralateral side.
TTA toe drag implication + treatment
Implication: tripping and falling
Strengthen contra plantar flexors and hip abd, adjust prosthetic
TFA Uneven Heel rise description + cause
Description: Heel rise during terminal stance, refers to an asymmetry in the amount or timing of heel lift during double support
Cause: too much friction, taut extension aid
TFA Uneven heel rise implication + treatment
Increase energy expenditure, circumduction. Uneven heel rise disrupts the symmetry of gait and can indicate problems with knee control and weight transfer
Decrease knee flexion, kt tape for hip extensors. Prosthetic adjustments, gait training to promote symmetrical weight transfer.