Final
1/222
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
223 Terms
Population - Definition
All people occupying an area OR all those sharing one or more characteristics
Do NOT necessarily interact with one another
Variety of ways to define → Geography or common qualities
Population - Examples
Prisoners
Senior Nursing Majors
Community - Definition
Collection of people who share important feature of their lives
Community Classifications
Geographic
Common Interest
Health Problem
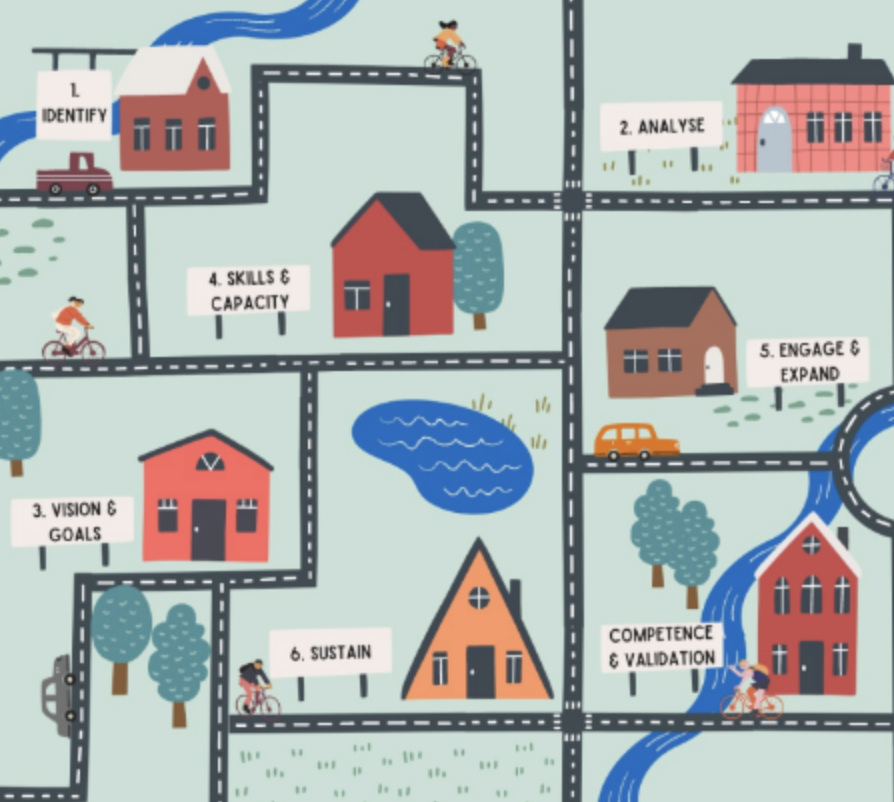
Geographic Community - Definition
Provides clear target for analysis of health needs

Common Interest Community - Definition
Collection of people with interest or goal that binds them together
Widely scattered
Large variety of possibilities
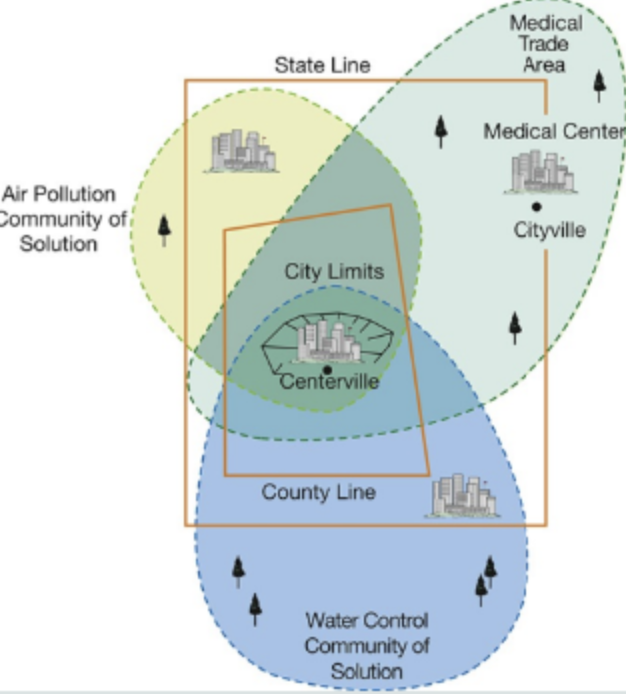
Health Problem Community - Definition
Group of people that come together to solve a problem that affects them all
May or may NOT be geographic
Important force for change
Health Problem Community - Examples
Flint Michigan lead in the water → Used the media to gain attention for help
Idaho food insecurity → Made a food pantry/grew food and brought it to those in need
Wellness
Health + Capacity to develop a person’s potential to lead to a fulfilling and productive life (QOL)
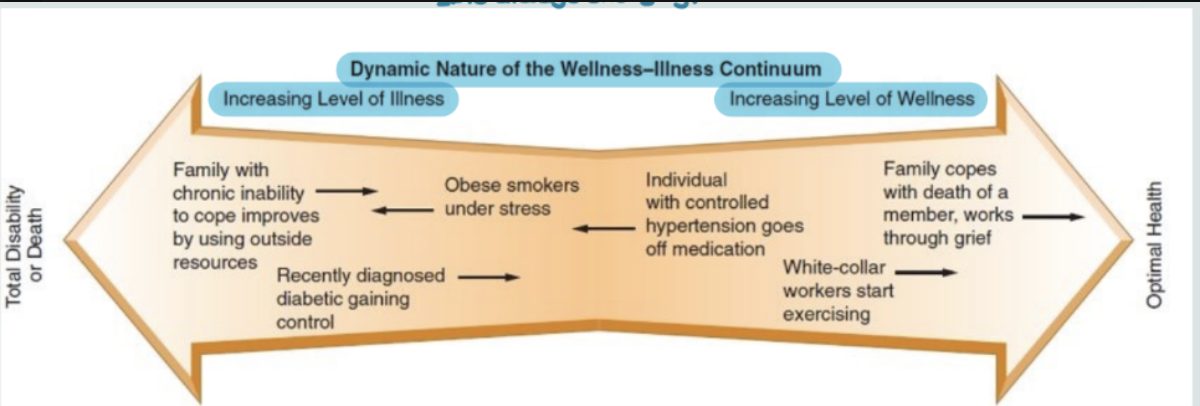
Health Continuum
Illness and wellness are a balancing scale that is always changing
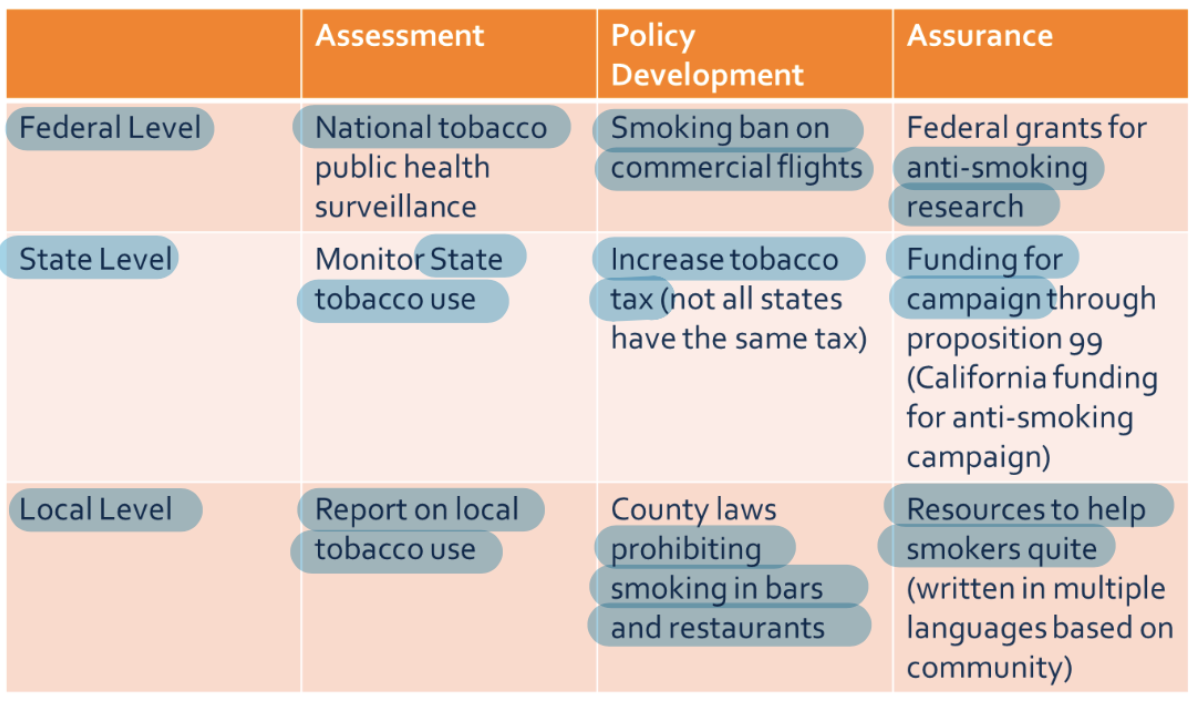
Core Functions of Public Health - Three Functions
Assessment
Policy Development
Assurance
Core Functions of Public Health - Assessment
Health needs
Risks
Environmental conditions
Political agendas
Financial and other resources
*All parts of the assessment will be gathered in a variety of ways (Interviews, surveys, etc.)
Core Functions of Public Health - Policy Development
Synthesize and analyze assessment data to create comprehensive public health policy
Provide leadership to evaluate health concerns and develop a plan
Core Functions of Public Health - Assurance
Pledge that the services necessary to achieve goals are provided
May require encouraging actions
DOING THE WORK to make the changes needed based on assessment
Core Functions of Public Health - Examples

Manager - Definition
Utilize problem-solving functions to manage health services
Manager - Actions to Function
Planning → Assess needs and define goals in order to carry out strategic/operational planning
Organizing → Framework for people/tasks to reach desired outcomes
Leading → Directs, influences, or persuades others to effect change through two way communication
Controlling → Monitors plan and makes sure it stays on course
Evaluating → Adjust or correct plan to meet desired goals
Early Home Care Nursing - Progression
Religious and charitable groups with no knowledge about diseases
Medieval Times → Development of sick institutions including hospitals
Early 1600s → St. Frances de Sales organized Friendly Visitor Volunteers
1617 → St Vincent de Paul started Sisters of Charity in Paris consisting of nuns and laywomen to serve the poor and needy

District Nursing (1800s-1900s) - Definition
Visiting nursing
Worked outside the hospital in community settings
Focused on care and health promotion including cleanliness and wholesome living
1800s → Industrial Revolution - General Info
Life Expectancy = 40 (better in rural areas)
COD = Cholera, TB, typhoid, accidents, childbirth
Food = Markets or grown
Refrigeration in late 1800s
Day = 12-16 hour work days, child labor, pollution
Florence Nightingale
1800s → Industrial Revolution - Nurses Roles
Began professionalizing → Training schools
Public health began addressing poor conditions and epidemics
Worked in hospitals, poorhouses, emerging clinics
District nurses did home visits in urban areas
1960s → Post War Modernization - General Info
Life Expectancy = 70 years
COD = Heart disease, cancer, stroke, accidents
Food = Grocery stores, refrigerators/freezers, use of canned, frozen, and processed food
Day = 9-5, women questioning their place in traditional roles
1960s → Post War Modernization - Nurses Roles
Licensed, trained professionals
Working in hospitals, schools, public health departments
Growth of community health nursing, school nursing, and occupational health
Began specialized roles → Peds, OR, Psych
NP movement emerging
Steps of EBP
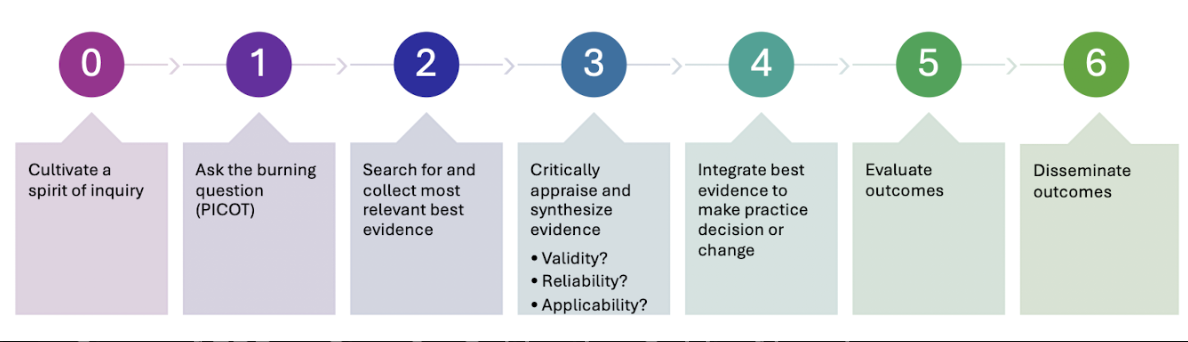
Steps of EBP → Step 0 - Cultivating Spirit of Inquiry
Must continually examine, question, and challenge current practice to make effective change → Ask the questions!

Steps of EBP → Step 1 - Ask the Question
In the form of PICOT
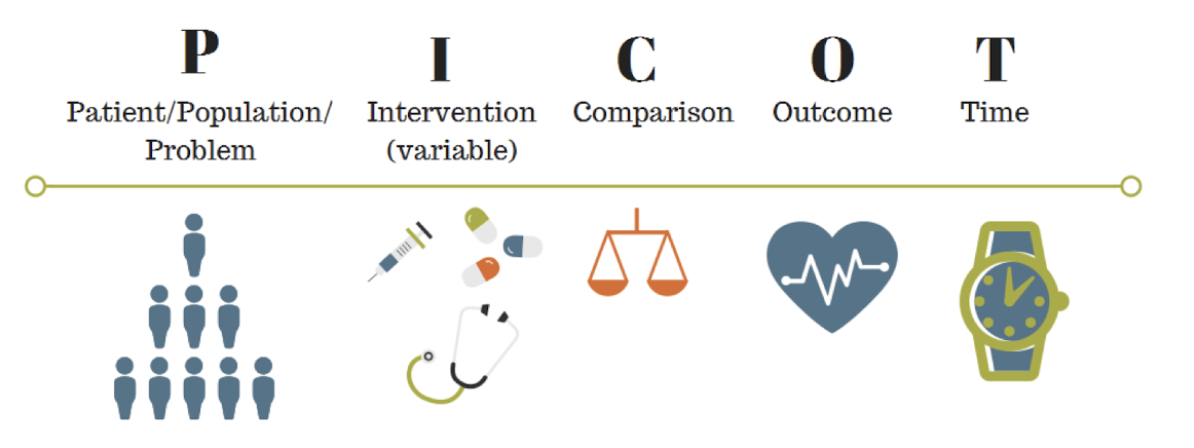
What does PICOT stand for?
P → Patient/Population/Problem
I → Intervention
C → Comparison
O → Outcome
T → Time
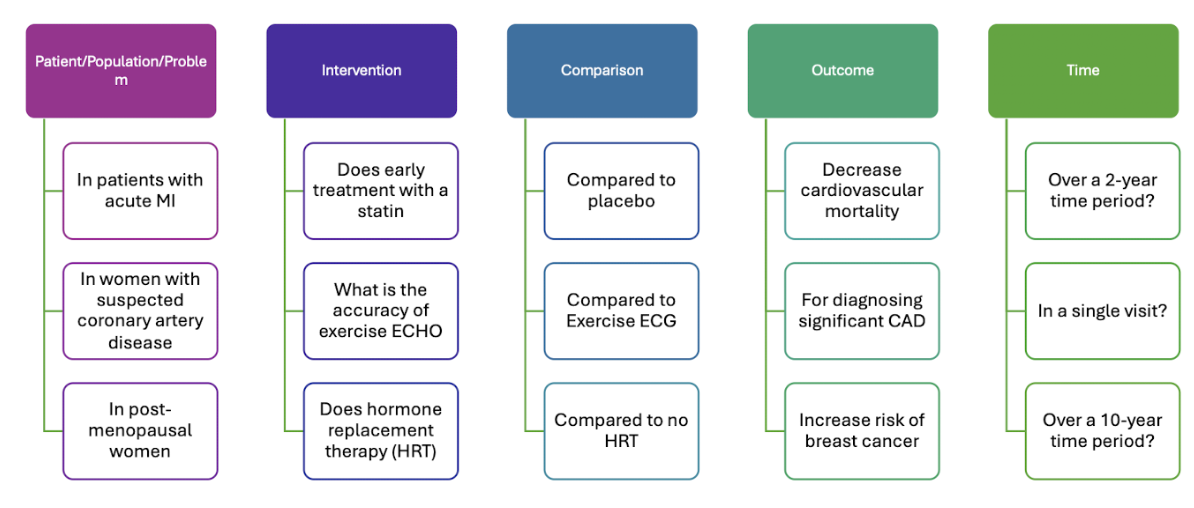
Steps of EBP → Step 1 - PICOT Examples
Steps of EBP → Step 2 - Find the Evidence
Search for all relevant research on clinical questions and critically analyze the evidence
Look at BIG data sources

Steps of EBP → Step 3 - Critically Appraise Evidence (3 Questions)
What is the evidence’s validity?
Is it true/legit?
Is the evidence reliable?
Is there bias? Large enough sample size?
Is the evidence applicable?
Does is look at your population?
Appraising Evidence - Definition
Systematically examining research to assess its trustworthiness, value, and relevance in a specific context
Steps of EBP → Step 4 - Integrating the Evidence
Decisions based on evidence, clinical expertise, and knowledge of patient’s values
ALWAYS consider if you can apply the findings to your population and if it will benefit them

Steps of EBP → Step 5 - Evaluate Outcomes of Change
Compare baseline and post-intervention data
Necessary to ensure you have achieved the best results
Collect data using a method that is efficient, cost-effective, and reliable

Steps of EBP → Step 6 - Disseminate Outcomes of EBP
Share to improve the C/PHN
Can be used in the future

Meta-Analysis Review - Definition
Statistical method used to combine results of multiple smaller research studies to increase statistical power of overall findings
Ethical Principles
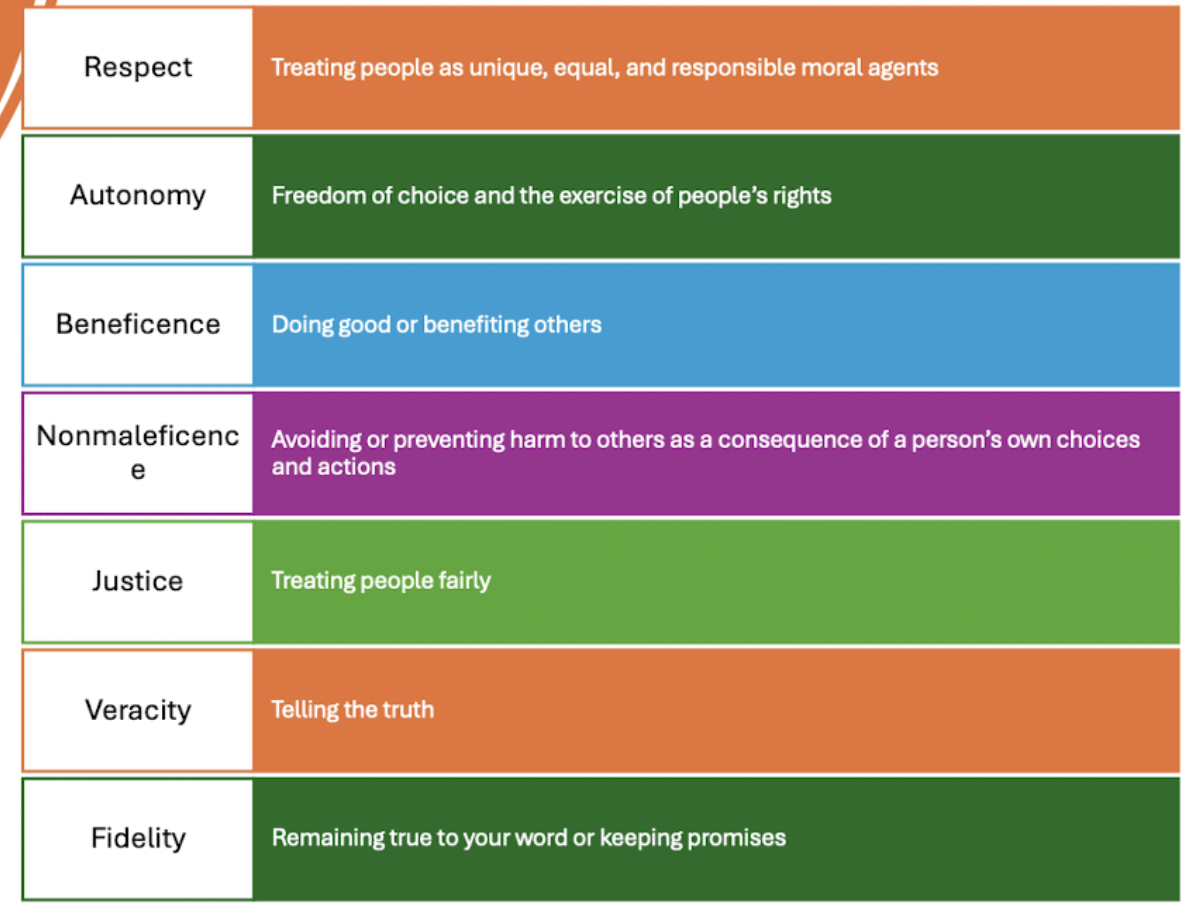
Respect - Definition
Treating people as unique, equal, and responsible moral agents
Emphasizes a person’s importance as a member of the community/healthcare team
Autonomy - Definition
Freedom of choice
Right to be involved in the decision making process
Beneficence - Definition
Doing and promoting good
Nonmaleficence - Definition
Avoiding or preventing harm
Avoiding negative consequences
Justice - Definition
Treating people fairly
Fair distribution of benefits and costs
Veracity - Definition
Tell the truth
Accurate information in timely manner and treating patients as equals
Fidelity - Definition
Remaining true to your work and keeping promises
Leads to improved decisions and better health
Ethnocentrism - Definition
Preference for one’s own culture
Biased belief that one’s culture is the best approach to life
Ethnorelativism - Definition
Ability to understand and value different cultures from their own terms, without judging them as superior or inferior to one's own culture
Five Characteristics Shared by ALL Cultures
Learned
Integrated
Shared
Tacit
Dynamic
Enculturation - Definition
Process of learning one’s culture
Patterns of cultural behavior are acquired
Culture Traits - Integrated
“Whole”
View in relation to connection to other components and to whole NOT independently

Culture Traits - Shared
Product of aggregate behavior, not individual habit
Share values within a culture
Provide standard for behavior
Expands understanding of human behavior
Culture Traits - Tacit
Unspoken and unexpressed
“Just know” how to act and what to expect from others

Medicare - Definition
Federal health insurance for adults age 65 ad older and people with disabilities
Medicare A - Definition
Hospital insurance

Medicare A covers …?
Inpatient hospitals
Limited-skilled nursing facilities
Home health and hospice services
Medicare B - Definition
Preventive insurance

Medicare B covers …?
Outpatient visits
Services to diagnose and treat health issues
Preventive services
Medicare C - Definition
Medicare advantage

Medicare C is a … plan that replaces … and …?
Private plan
Medicare A and B
Medicare C covers …?
Regional provider networks
May cover dental, vision, and prescriptions
Medicare D - Definition
Drug plan

Medicare D covers … and is a … plan?
Prescription drugs
Voluntary plan

Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) - Definition
Eliminated pre-exisiting conditions exclusions
Expansion for Medicaid
Requirement of preventative care without copay
Deductible - Definition
Amount paid by the insured person out of pocket before insurance coverage kicks in

Premium - Definition
Regular, monthly payment made to an insurance company to keep health insurance coverage active
Done regardless of whether medical services are used that month
Cost for having insurance, separate from out-of-pocket costs
Managed Care - Definition
Systems that contract to coordinate medical care for specific groups to promote provider efficiency and control costs
Managed by regulating use of services and levels of provider payment
Managed Care - Examples
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMO)
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO)
Epidemiologic Triangle - Components
Host
Agent
Environment
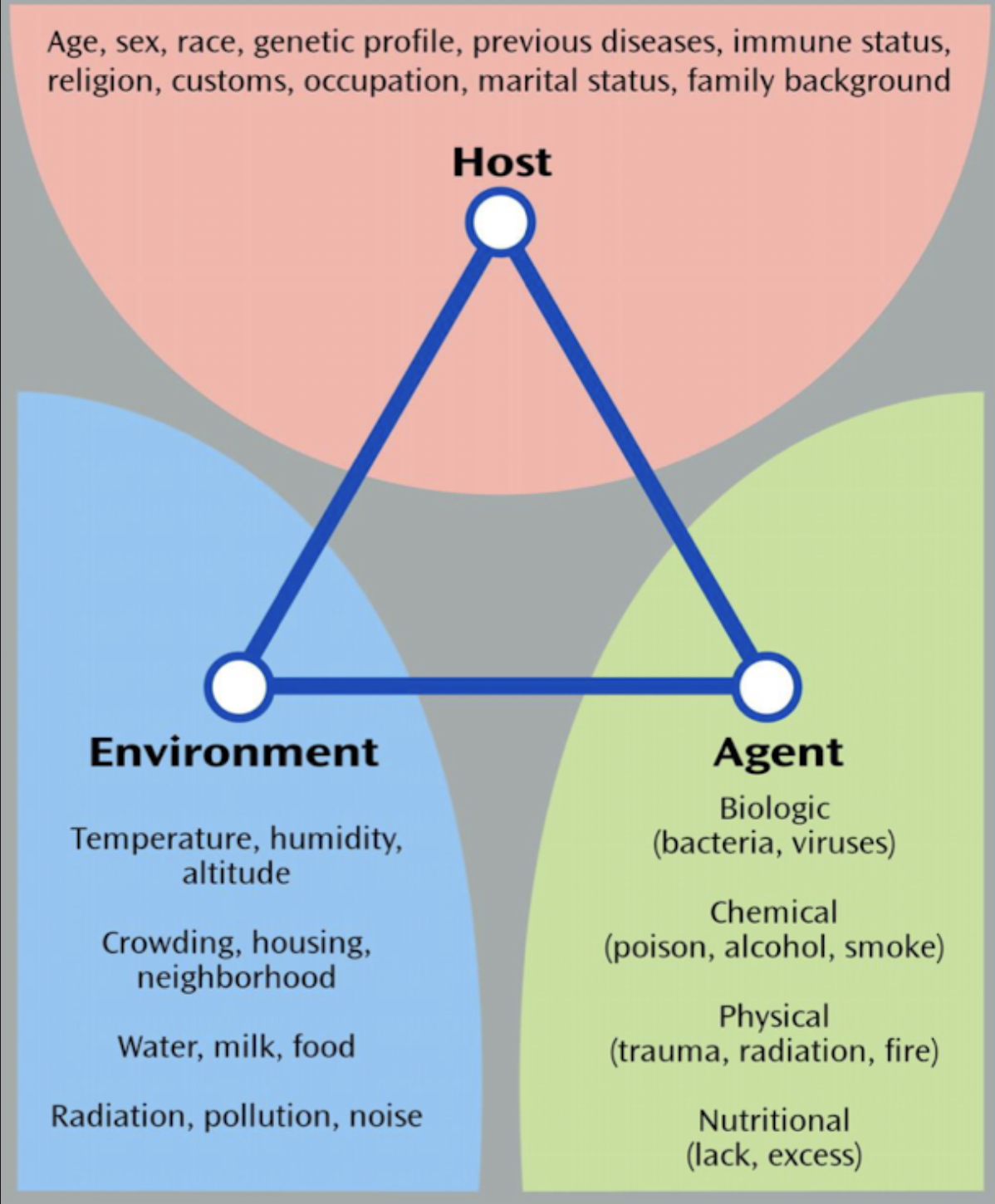
Epidemiologic Triangle - Host Definition
Susceptible human or animal who harbors and nourishes disease-causing agent
Can get the disease
Epidemiologic Triangle - Host Examples
Me and you
Epidemiologic Triangle - Agent Definition
Factor that causes or contributes to health problem or condition
Can be infectious or noninfectious
Epidemiologic Triangle - Agent Types
Biologic → Bacteria, viruses , worms, insects, fungi
Chemical → Liquid, solid, or gas forms
Nutrient
Physical → Anything mechanical that can cause trauma
Psychological → Like terrorism
Epidemiologic Triangle - Agent Examples
Flu
Covid
RSV
Epidemiologic Triangle - Environment Definition
All external factors surrounding the host that might influence vulnerability or resistance
Both physical and psychosocial
Physical → Geography, climate, weather, water, food supply, animals, plants
Psychosocial → Social, cultural, economic conditions
Incidence Rate - Definition
All new cases of a disease or health condition appearing during a given time

Incident Rate - Purpose
Describe how quickly disease occurs in a population → DISEASE RISK
Can utilize to monitor intervention effectiveness
Denominator people MUST have potential to move to the numerator

Prevalence Rate - Definition
All of the people with a particular health condition existing in a given population at a given point in time

Prevalence Rate - Purpose
Describe a specific point in time → DISEASE BURDEN
Numerator now includes both new cases and pre-existing cases
Natural History of a Disease - Definition
Any disease or health condition which follows a progression known as its natural history
Refers to events that occur before the disease development, during its course, and during its conclusion
Natural History of a Disease - Stages
Susceptibility
Subclinical Disease
Clinical Disease
Resolution/Advanced Disease
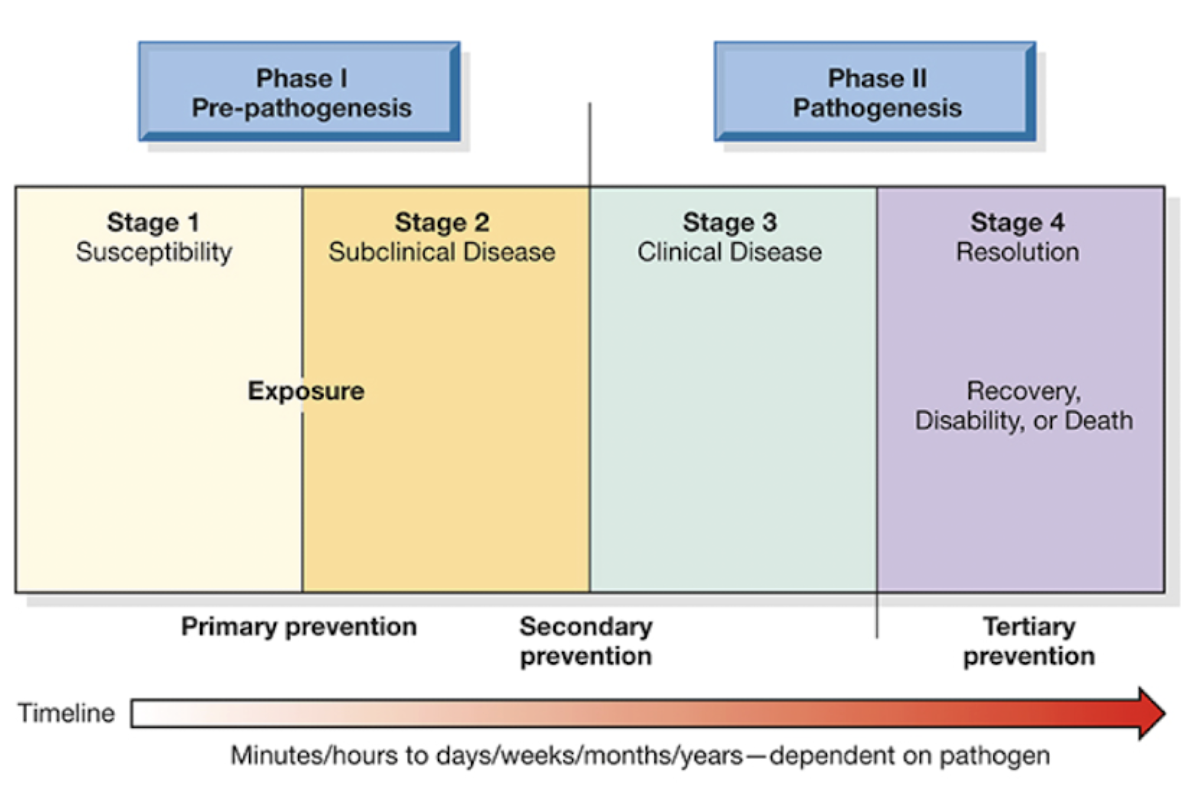
Natural History of a Disease - Susceptibility Stage
Host and environment factors influence population’s vulnerability
People have not really been exposed to the disease yet
Natural History of a Disease - Subclinical Disease Stage
Invasion by causative agent; people are asymptomatic
People are exposed to the disease, but are asymptomatic
Natural History of a Disease - Clinical Disease Stage
Disease or condition evident in population
S/S develop in people so that a diagnosis can be made
Natural History of a Disease - Resolution/Advanced Disease Stage
Disease or condition concludes in renewed health, disability, or death
People recover, adapt, or are disabled after disease
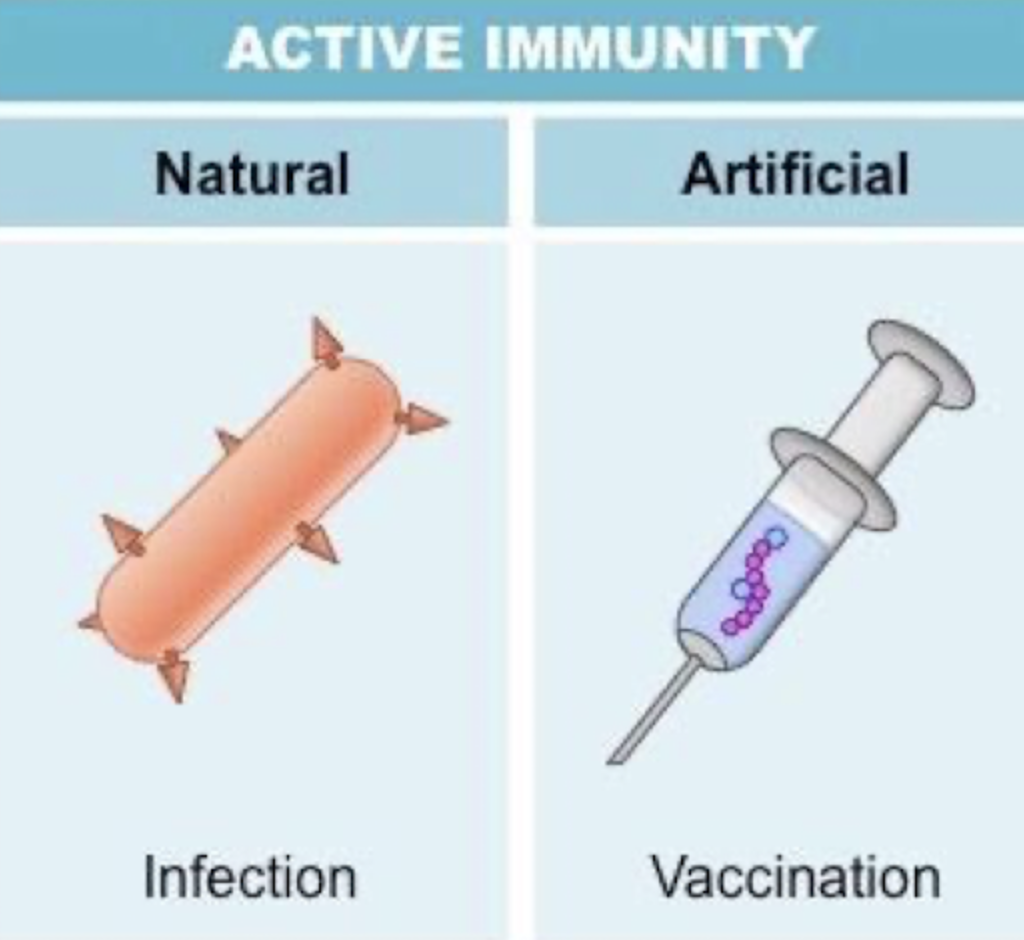
Active Immunity - Definition
Long term → Sometimes lifelong
Naturally via fighting infection and surviving
Artificially via vaccines
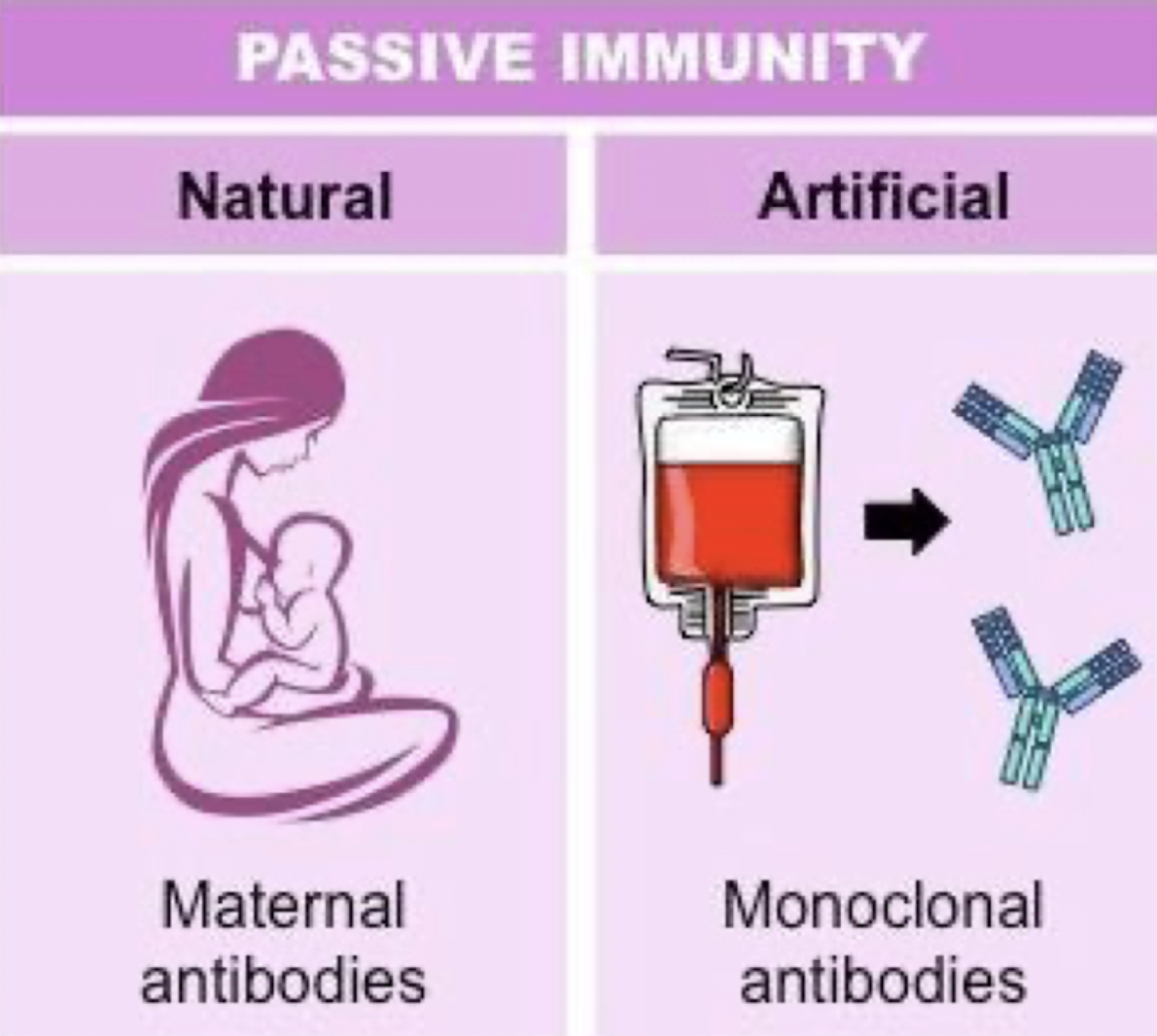
Passive Immunity - Definition
Short term
Naturally when protection is transferred from another another animal or human to help → Wanes with time (decreases in strength)
Ex: Measles → Get the vaccine at 1 year old because mother has vaccine and passes antibodies
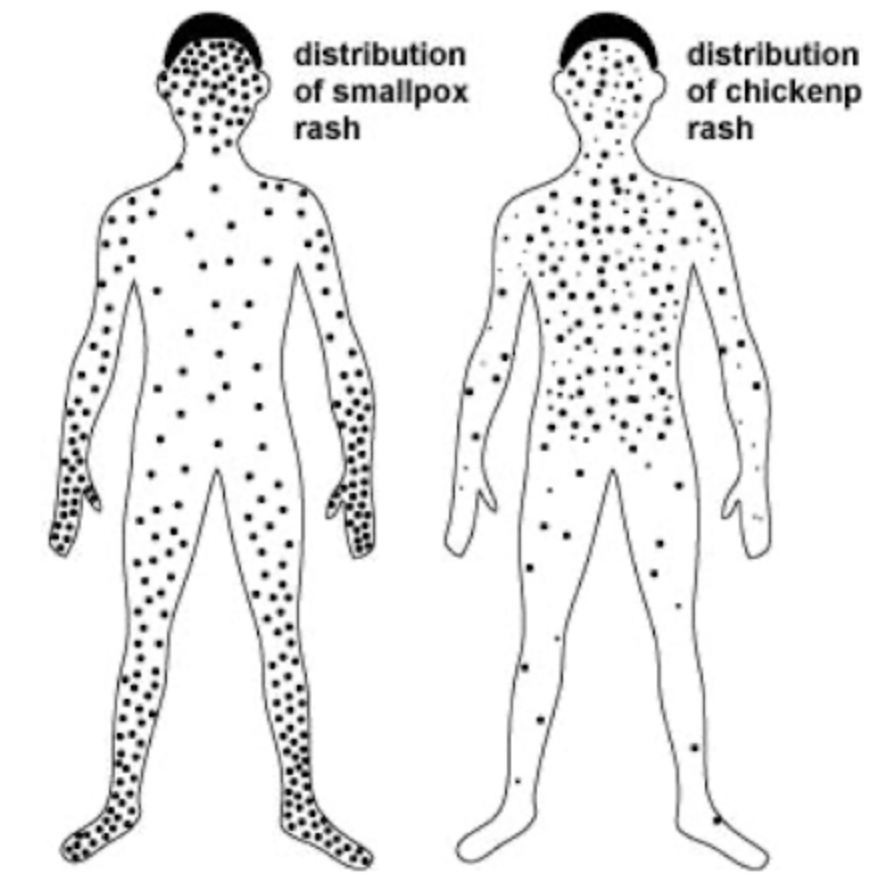
Cross Immunity - Definition
Immunity to one agent providing immunity for another related agent
Ex: Cowpox vaccine protects against smallpox
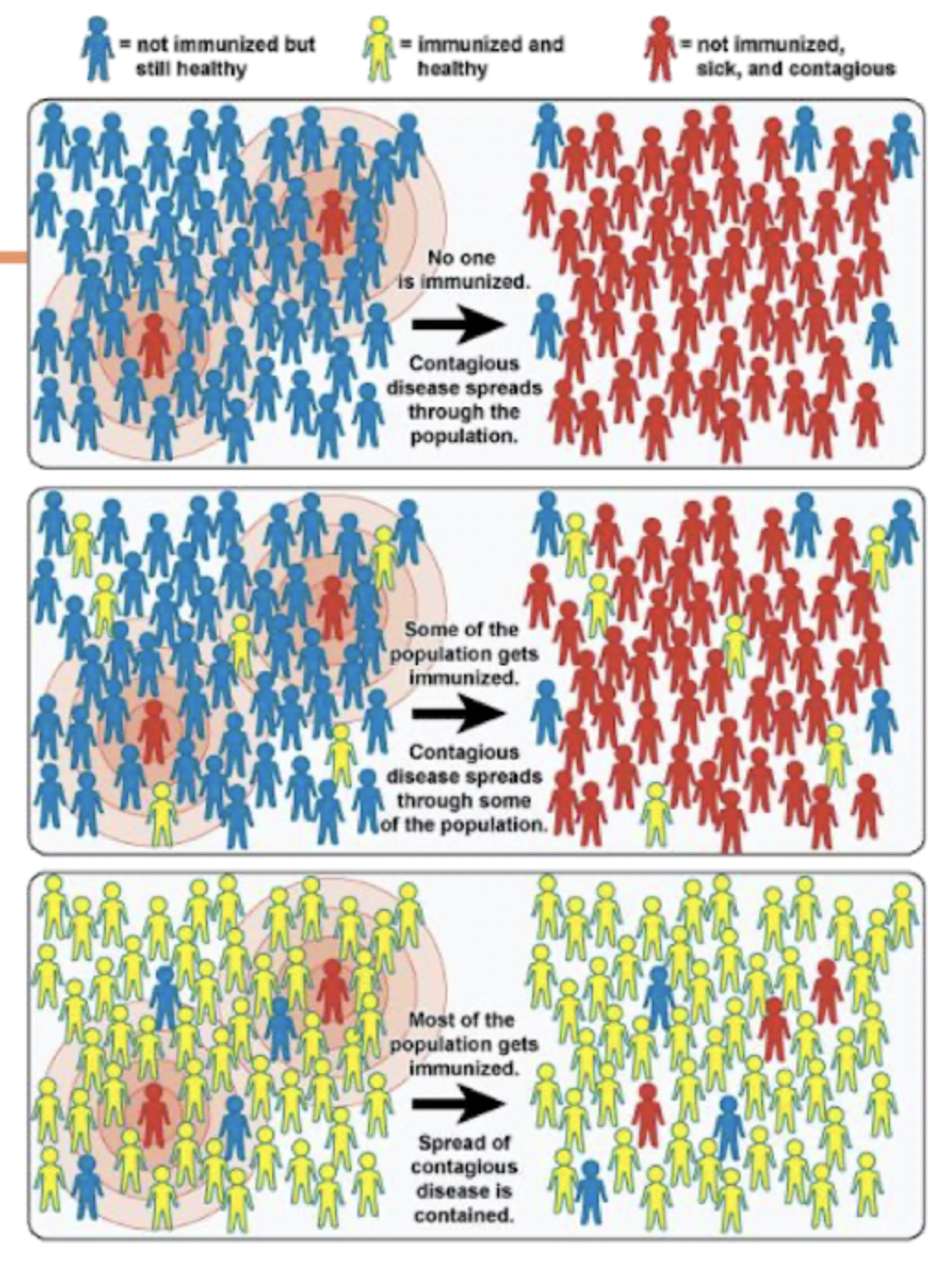
Herd Immunity - Definition
Population Immunity
Fraction of population that needs to be immune to protect the rest
Depends on how infectious the disease is
Modes of Transmission - Definition
How a disease is passed from one source to another
Person to person
Animal to person
Person/Animal indirectly via reservoir
Modes of Transmission - Direct Examples
Person to person
Animal to person
Modes of Transmission - Indirect Examples
Reservoirs → Ex: Contaminated water
Disease Transmission - Human Reservoir Definition
Person to person disease transmission without intermediaries
Ex:
STDs
Measles
Mumps
Streptococcal infection
Many respiratory pathogens
Disease Transmission - Animal Reservoir Definition
Animal to animal disease transmission with humans as incidental hosts
Disease Transmission - Environmental Reservoir Definition
Plants, soil, and water that house diseases
Ex: Fungal agents
Measles - Causes
Rubeola virus
Measles - Transmission
Airborne
Direct contact
*Can get it from just being in the same room where a person with measles has been
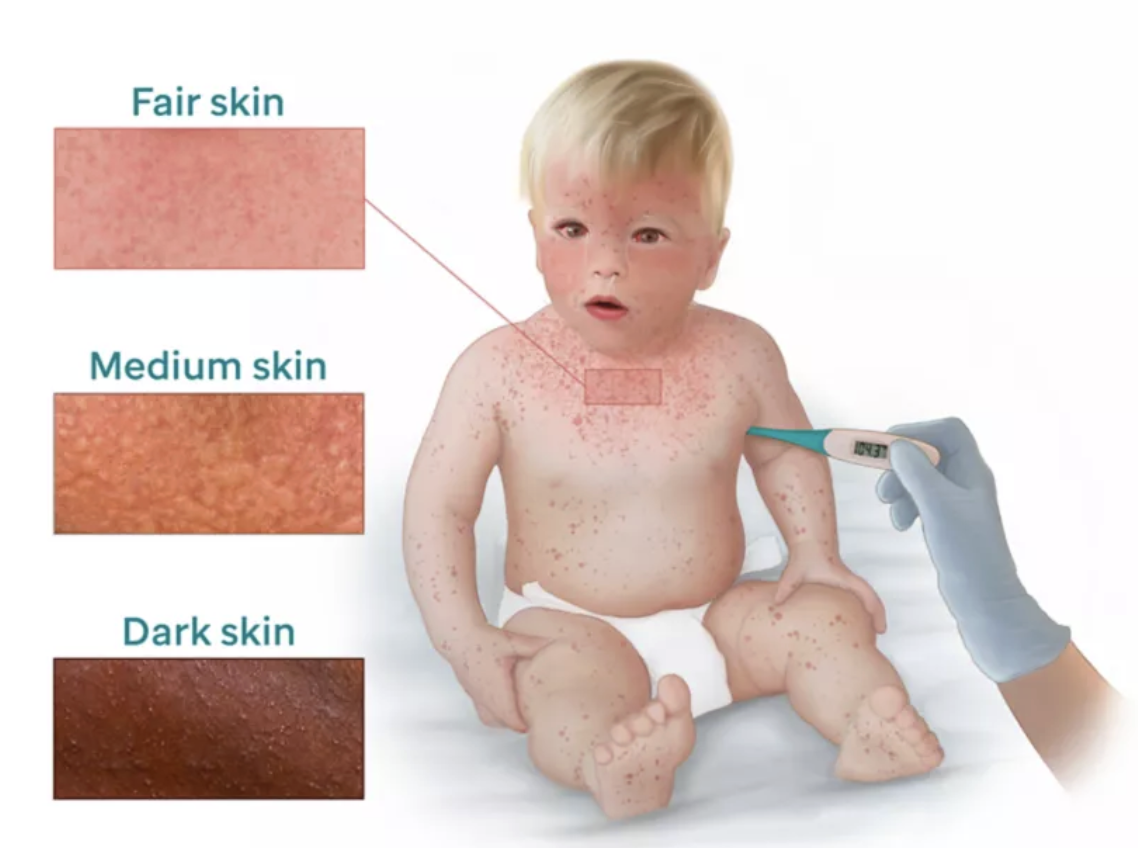
Measles - S/S
PROMINENT RASH
Early → 4-7 days after exposure
Runny nose, cough, red and watery eyes, small white spots inside the cheeks
When do Measles S/S usually start?
10-14 days after the exposure
Most people who get measles die from … related to the disease?
Complications!
Measles - Complications
Blindness
Encephalitis
Severe diarrhea and dehydration
Ear infections
Severe breathing problems → Includes pneumonia
Bioterrorism - Definition and Examples
Deliberate release of biologic agents to cause harm
Ex:
Anthrax
Smallpox
Mpox (Monkeypox)
Smallpox - Definition
Disease caused by the variola virus that was eradicated in 1980