Socio-cognitive development
4.0(1)
4.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
1
New cards
what is theory of mind?
the capacity to attribute mental states (such as desires, beliefs, knowledge) to others in order to predict or explain behaviour
2
New cards
what is theory of array?
understanding that something is still there even if something has been placed in the way
3
New cards
what did Daniel Dennett find?
children get excited when they know something that other people don’t know
4
New cards
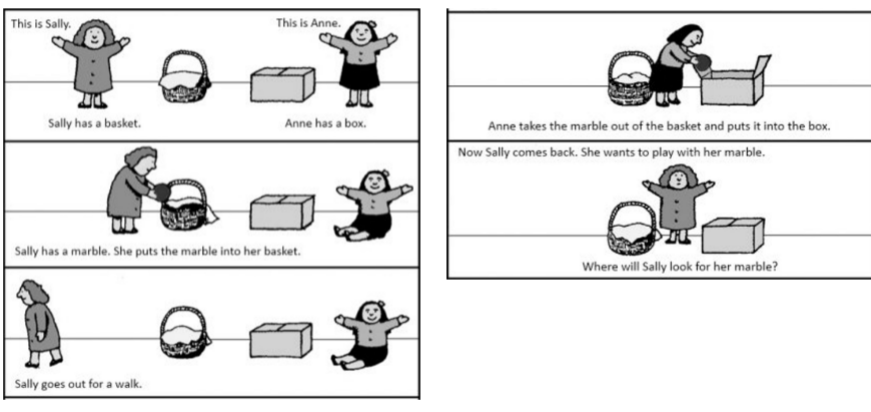
what is the unexpected transfer false-belief?
* a task used to test false-belief understanding in children
* helps children to understand that their view of the world is not the same for everyone
* they begin to understand this at 3.5-4 years old
* helps children to understand that their view of the world is not the same for everyone
* they begin to understand this at 3.5-4 years old
5
New cards
what is the unexpected contents false-belief?
when a child attributes a false-belief about the contents of a prototypical container to someone else
6
New cards
what is the appearance-reality task?
* show a box of candy ( like skittles), ask a child "what is in the box?", they think its skittles, but when we open the box its just colourful ribbons
* So now that the child knows that, we ask, what would your friend say is in the box ?
* Answers vary , the younger they are they'll answer from there perspective, that there are ribbons in the box and not from their friends perspective.
* So now that the child knows that, we ask, what would your friend say is in the box ?
* Answers vary , the younger they are they'll answer from there perspective, that there are ribbons in the box and not from their friends perspective.
7
New cards
belief-based emotion task
* Implications of having a false belief for emotions
* Molly has skittles and leaves them on the tables. Molly goes for a walk, her friend comes round and replaces them with beans, ,Molly is really excited for her skittles, how will she feel when she sees the packet
* Children who understand will say she feels happy
* Molly has skittles and leaves them on the tables. Molly goes for a walk, her friend comes round and replaces them with beans, ,Molly is really excited for her skittles, how will she feel when she sees the packet
* Children who understand will say she feels happy
8
New cards
what is a second-order false belief?
* Dad is giving Simon and Mary chocolate
* They put their chocolate in the fridge
* Simon decides he wants to eat the chocolate so he put it in his backpack
* Mary saw Simon move it, Where does Simon think that Mary will look for the chocolate?
* Children should understand this by 6-7 years old
* They put their chocolate in the fridge
* Simon decides he wants to eat the chocolate so he put it in his backpack
* Mary saw Simon move it, Where does Simon think that Mary will look for the chocolate?
* Children should understand this by 6-7 years old
9
New cards
what is faux pas understanding?
\
* Holly and Poppy were sitting at the front of the school bus. Holly said “I can’t believe that that new girl Michaela made us lose our game today. She is so bad at sports”.
* The school bus stopped to let them off and they turned around to leave the bus. Michaela was sitting in the seat right behind Holly and Poppy. Poppy, saw Michaela said “Oh hi Michaela, see you at school tomorrow.”
* children have to get all 7 questions about the scenario correct to pass
* should pass at 7-8 years old
* shows the implications of breaking social conventions on peoples feelings
* Holly and Poppy were sitting at the front of the school bus. Holly said “I can’t believe that that new girl Michaela made us lose our game today. She is so bad at sports”.
* The school bus stopped to let them off and they turned around to leave the bus. Michaela was sitting in the seat right behind Holly and Poppy. Poppy, saw Michaela said “Oh hi Michaela, see you at school tomorrow.”
* children have to get all 7 questions about the scenario correct to pass
* should pass at 7-8 years old
* shows the implications of breaking social conventions on peoples feelings
10
New cards
describe the silent films task by Devine and Hughes (2012)
* to pass you need to respond to a mental state and offer an appropriate response
* given to children aged 8-11
* examples:
* Why do the men hide? (Couldn't pay their rent)
* What does the women think? (Thought they weren't there)
* given to children aged 8-11
* examples:
* Why do the men hide? (Couldn't pay their rent)
* What does the women think? (Thought they weren't there)

11
New cards
the development of social cognition
* visuo-spatial perspective taking
* false-belief understanding
* appearance-reality
* situational determinants of emotion; belief-based emotion
* false-belief understanding
* appearance-reality
* situational determinants of emotion; belief-based emotion
12
New cards
advanced theory of mind
* second-order false-belief
* self-conscious awareness and knowledge of social ‘rules’ (faux pas)
* understanding sarcasm, irony and double entendre humour
* silent films task
* self-conscious awareness and knowledge of social ‘rules’ (faux pas)
* understanding sarcasm, irony and double entendre humour
* silent films task
13
New cards
problems with theory of mind measures
* complexity of language demands
* implicit vs explicit theory of mind
* single item at a single point in time
* appropriate reflection of how theory of mind is used in everyday situations?
* memory burden
* implicit vs explicit theory of mind
* single item at a single point in time
* appropriate reflection of how theory of mind is used in everyday situations?
* memory burden
14
New cards
what are the classic theories of theory of mind (‘the big three’)?
* theory theory
* simulation theory
* modularity theory
* simulation theory
* modularity theory
15
New cards
describe theory theory (Gopnik and Wellman, 1992)
* children are like scientists trying to figure out how minds work
* children form a ‘theory’ about minds
* limitations
* academic-centric
* doesn’t explain how ToM develops
* untestable
* children form a ‘theory’ about minds
* limitations
* academic-centric
* doesn’t explain how ToM develops
* untestable
16
New cards
describe simulation theory (Harris, 1991)
* imagination - a ‘like me’ analogy to understand others
* development hinges on getting increasingly good at imagining others’ perspectives
* limitations:
* imagination appears to be the *outcome* of development
* how do we test this theory?
* development hinges on getting increasingly good at imagining others’ perspectives
* limitations:
* imagination appears to be the *outcome* of development
* how do we test this theory?
17
New cards
describe modularity theory (Leslie, 1987)
* also called theory of mind mechanism theory
* ToM underpinned by discrete, innate circuits in the brain
* acquisition of ToM is a process of maturation
* limitations:
* how do we get to complex forms of thinking?
* influence of the environment?
* not enough genes to claim innate knowledge
* ToM underpinned by discrete, innate circuits in the brain
* acquisition of ToM is a process of maturation
* limitations:
* how do we get to complex forms of thinking?
* influence of the environment?
* not enough genes to claim innate knowledge
18
New cards
aspects of socio-cognitive neuroscience (biological basis foe theory of mind)
* mirror neurons
* localisation of function
* localisation of function
19
New cards
how do mirror neurons support a biological basis for theory of mind?
* FOR: allows us to directly understand the meaning of the actions and emotions of others by internally simulating them without reflective mediation (Gallese et al., 2004)
* AGAINST: mirror neurons play an important role in the anticipation of action but do provide an explanation of the complex problems of conceptualising human understanding (Carpendale et al., 2018)
* AGAINST: mirror neurons play an important role in the anticipation of action but do provide an explanation of the complex problems of conceptualising human understanding (Carpendale et al., 2018)
20
New cards
how does localisation of function support a biological basis for theory of mind?
* FOR: neuroimaging studies can help reveal if there is a neural correlate of forms of thinking
* AGAINST: is there a localised brain area that specialises in theory of mind understanding?
* AGAINST: is there a localised brain area that specialises in theory of mind understanding?