5- cleaning and shaping canals
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the main goal and 2 objectives of clinical endodontics?
Prevent and treat microbial contamination of pulp and root canal
To cure periradicular periodontitis
Preserve natural teeth for long term function and aesthetics
What is the success rates of orthography root canal treatment
95% in irreversible pulpitis
85% in infected, necrotic pulp
What are causes of pulpal pathosis?
Microorganisms breaching the dental hard tissue barrier, common in caries
What are the 4 objectives in cleaning and shaping?
Remove infected soft and hard tissue
Disinfecting irritants access apical canal space
Can deliver medicaments and subsequent obturation
Retain integrity of radicular structures
What is the mechanical objective of root canal treatment?
ensure that all root canal surfaces are properly cleaned and shaped
Irrigants help clean areas that mechanical instruments cannot reach
What are 3 potential challenges in mechanical preparation and what do they do?
Deviations- instruments stray from natural canal path
Zipping- over enlargement of canal near apex
Perforations- accidental creation of hole in the root
These leave parts of canal inaccessible for disinfection
Why do we preserve radicular dentin and what do we need to ensure it?
Prevents weakening of root structures and fractures
Need to keep 0.3mm of dentin thickness to avoid perforations
Need proper access cavity prep and coronal third enlargement
What is the Schiller’s tapering principle?
Advocates a uniform continuous taper to facilitate obturation- should maintain og shape and guided by curvature of root canal
The canal shape after prep also influences antimicrobial efficacy
How do you achieve effective irrigation?
Dispense fluid with syringe and needle- passive irrigation reaches 1mm beyond needle tip
Larger apical canals and flexible needles- deeper penetration and better debridement
Always irrigate between files
Intermittent agitation of canal content to prevent debris forming
Better- open ended needles
What are characteristics of k type instruments?(made of, use, type, motion)
Stainless steel
Use to penetrate and enlarge root canals
2 types- k- endo, h- reendo (re treatment)
Has reaming motion- continuous rotations- less canal transportation or filing motion- inserted and withdrawn- higher risk of transportation
Can be precurved
How is the precurving technique achieved?
Overbending k files
Be careful to avoid xs strain
Can cause permanent deformation- flutes may be too tightly wound or open so can’t be used as it may fracture
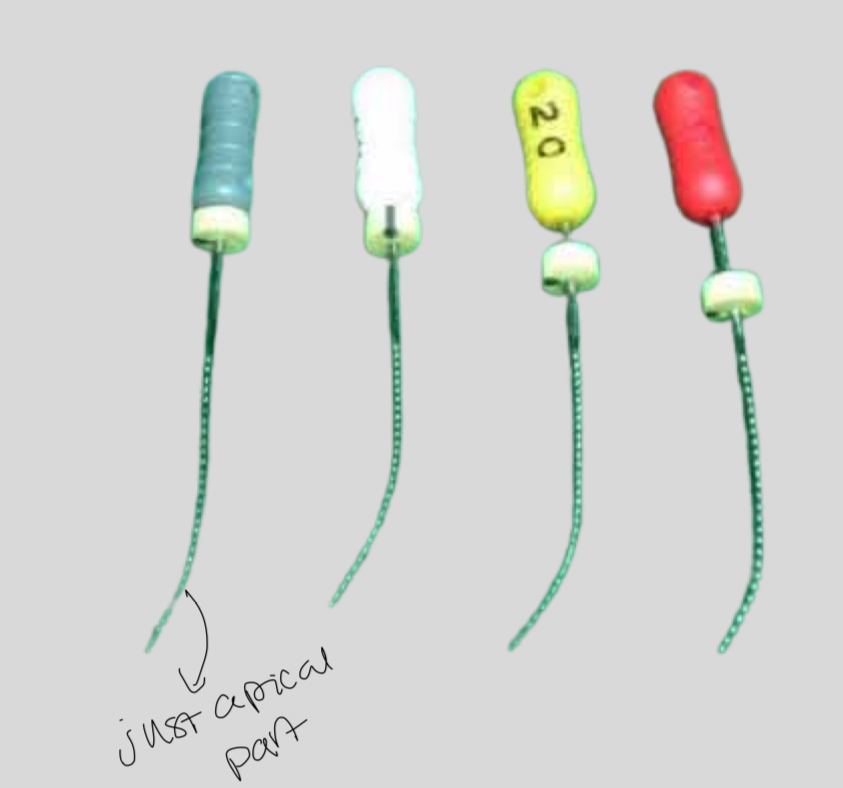
What are 4 uses of k files?
Conductometry- determining working length
Create glide path
Manual shaping techniques- step back or crown down
Patency
How is coronal third enlargement conducted?
Initially small gg drills then bigger rotary instrument so form bigger coronal canal so file can fit in easier
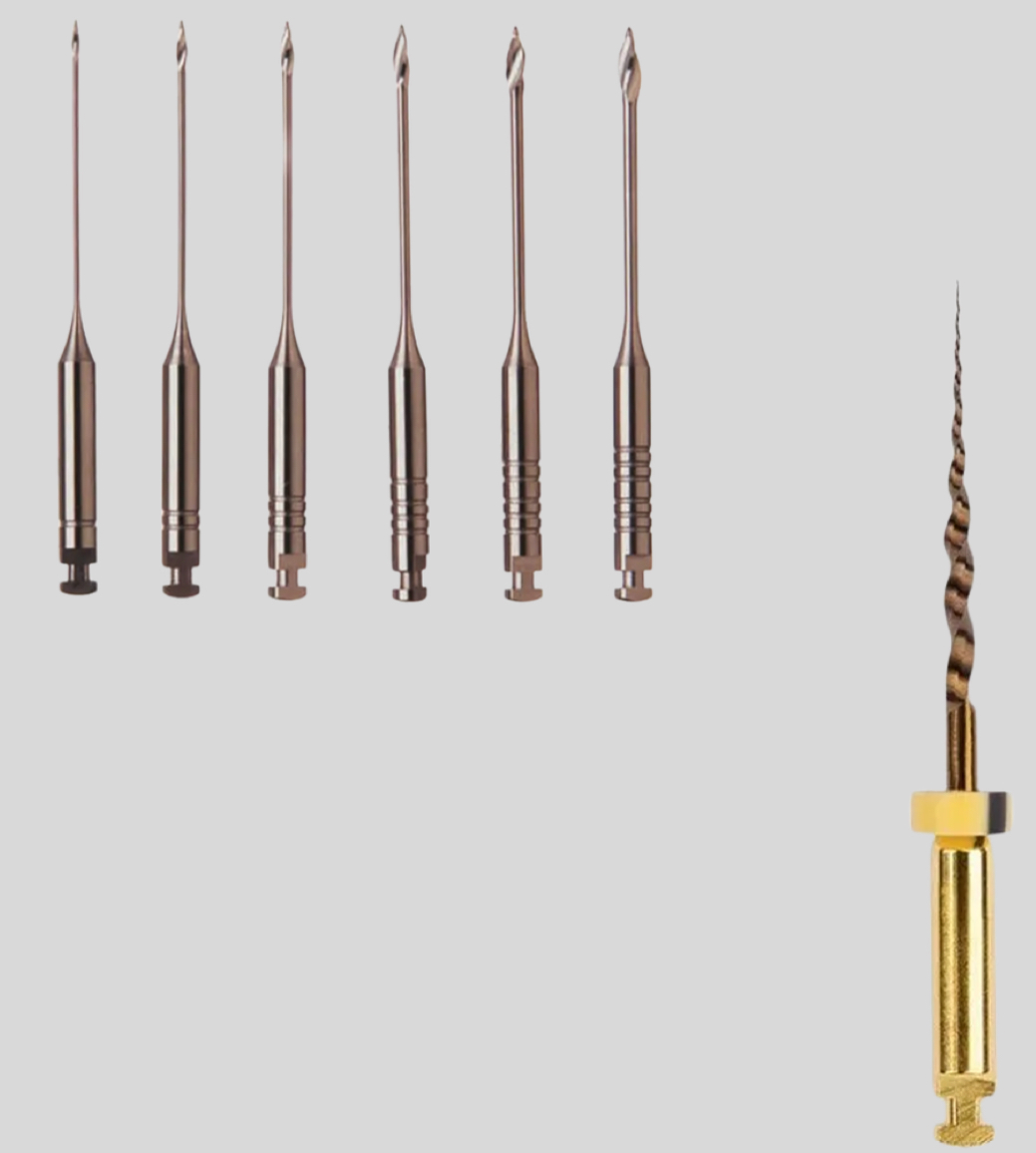

What and how is the reference point found in conductometry?
Use either 10, 15 or 20 k file
reference point- repeatable landmark on tooth from which the working length is measured
What is a glide path, achieved by and minimises?
smooth and clear route from the coronal orifice (top opening) to apex
Achieved with manual and rotary instruments
Apical pre enlargement minimises biomechanical prep failures like canal transportation and ledge formation at diff levels, reduces pecking motions for working length
What does the size of the master apical file refer to, matches and depends on?
Largest file size used at apical extent
Theoretically matches final gutta percha used to fill the canal
Depends on anatomy of root, calcification of canal, vital or necrotic
What is the importance of MAF?
Effective cleaning and shaping
Prevent perforation and fractures- large size helps with clean and shape but higher risk of fractures
Optimal filling- ensures root canal is filled with gutta percha so good seal to prevent bacteria re entering
How do we determine the size of the master apical file?
Tactile feedback- initial binding/resistance gives idea of size of canal at apex, then increase 2-3 file sizes
Root canal averages- usually 20, 30, 40, posterior and smaller anterior teeth
Use larger files for necrotic teeth- tissue causes walls to be irregular and harder to clean, increase size by 1 or 2 than vital
What is patency?
Canal prep technique where you keep apical portion clear, can pass small file (6-10 k file) through foramen to ensure canal is negotiable
Small k file passively moved through apical constriction 0.5-1mm beyond minor diameter
What is the step back technique?
Gradually widen canal from apex to crown
The smallest file reaches the working length first, and each subsequent file is stopped 1 mm shorter than the previous one
Why is the step back technique used?
Create continuously tapered tunnel and smooth walls
Maintain og canal shape and position of apical foramen
Keep apical opening as small as possible to stop infection
Why do you need a tapered shape in the step back technique?
Remove infected dentin
Irrigation
Obturation (condensation)
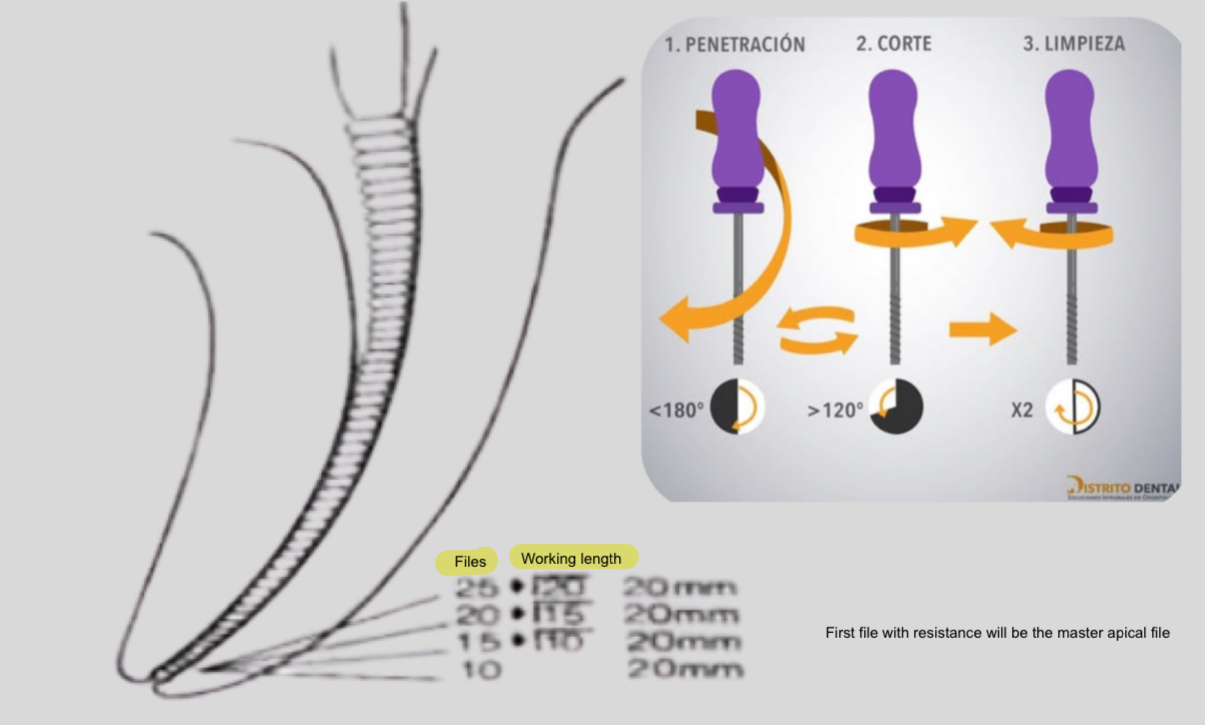
How is the step back technique conducted?
Determine working length
Prep apical portion of canal- shape and widen, use files 10, 15, 20, 25 for the glide path
Choose MAF at WL
Enlarge canal by 3 more sizes, each step you remove 1mm of dentin to get taper shape
Movements for prep- watch winding- both ways, reaming- clockwise cutting
What is recapitulation?
MAF is inserted to working length to clear out any debris collecting in apical part
What is different with the crown down technique?
From crown to apex
Don’t use MAF
Use files from largest to smallest- start with 80 till resistance then 70, 60
Don’t apply pressure
What are the 5 objectives of irrigation in endo?
Flush out debris
Lubricate canal
Dissolve tissue
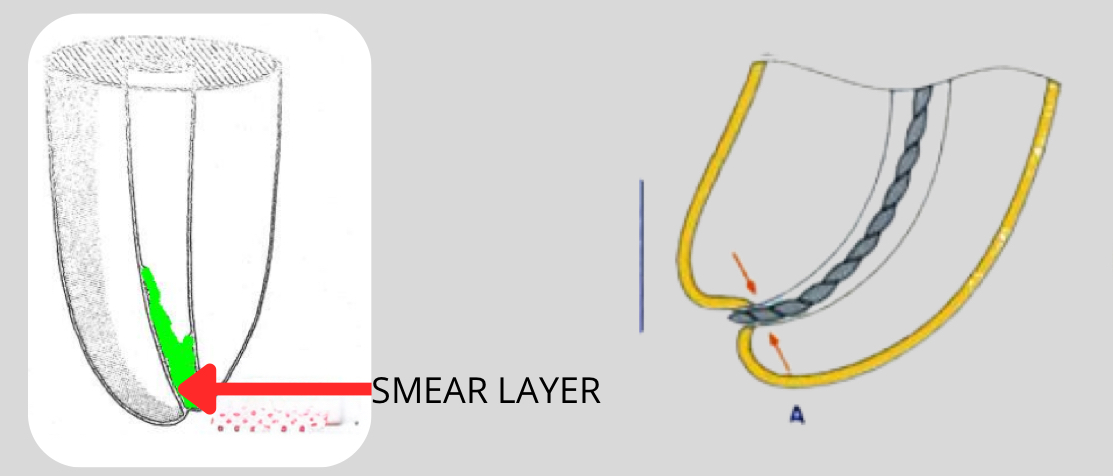
Prevent or dissolve formation of a smear layer during instrumentation
Detach biofilms
What are the criteria for irrigants?
High efficacy and broad antimicrobial activity against anaerobic and facultative microorganisms
Inactive endotoxin
Non toxic when in contact with vital tissues
No anaphylactic reaction
What does the effectiveness of irrigation rely on? (4)
Penetration depth of the needle
Diameter of the root canal
Irrigation pressure, viscosity of the irrigant
Type and orientation of the needle
Advantages vs disadvantages of Sodium Hypochlorite (NaClO)
Cheap, lubricant, whitens, broad spec, inactivates endotoxins
Bad taste and smell, corrosive, very toxic, unstable, reduce adhesion to dentin
How do you increase the effect of NaOCl?
Heat solution before
Increase conc of hypochlorite
More time in canal, more disinfection
Vibration of hypochlorite
Advantages vs disadvantages of Chlorhexidine?
No bad smell or taste, stable, high antimicrobial activity, low toxicity, increase adhesion with dentin
Can’t remove pulp tissue, doesn’t neutralise endotoxins, reacts with other irrigants
What is the advantage of EDTA?
Can remove smear layer with another component