Development of Nervous System
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
Development of Nervous system occurs starting week ____ until _____
week 4 until adulthood
the brain weighs how many grams at birth?
800g
Weight of the brain at 6 y.o
1,200g
Weight of the brain of an adult
1,400g
Manifestations of abnormalities
Malformation
Growth retardation
Functional Defect
Death
Pre-embryonic stage is AKA
Conceptus
True/False: Abnormalities can be seen as early as the Conceptus stage
False
Embryonic stage span what weeks of development
Weeks 3-8
Process by which the blastula becomes a gastrula
Gastrulation
Gastrulation marks the start of the formation of these cells
Ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
Neural tissue appears at ____ week of development
3rd week
Establishes basic body plans of vertebrates
Primitive Streak
Defines the rostral direction; notochordal process develops above and somites from beside the notochord
Primitive Node / Hensen’s Nodes
Induces epiblast cells to form neuroectoderm
Notochord
Process of cell to cell signaling; Mesoderm induces the ectoderm to become neuroectoderm & form the neural plate
Neural Induction
Neural induction starts when?
16th-17th day of intrauterine life
The Notochord defines the longitudinal axis of the embryo by production of _________
cell adhesion molecules
the notochord determines the orientation of the __________
vertebral columnT
the notochord persists as the _______ of the IVD
nucleus pulposus
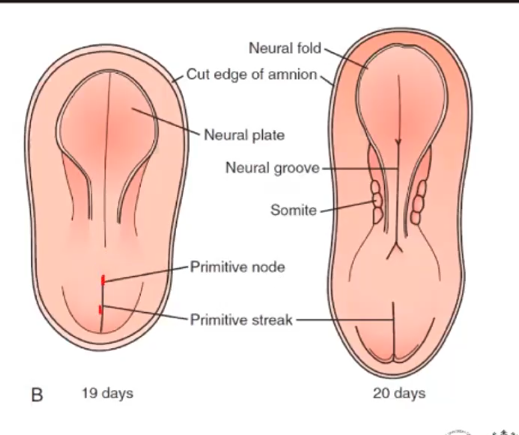
Slipper shaped plate of thickened ectoderm
Neural plate
The neural plate forms at day __
day 18
The neural plate is located in the?
mid dorsal region in front of the primitive gut
this part of the neural plate becomes the neural folds
Lateral edges
The neural folds form at day ____
day 20
At 21 days, the neural folds become the _______
neural tube
The primitive streak emerges as a groove at the ________
caudal part of the embryo
Primitive streak initiates _____
gastrulation
Closure of the neural tube proceeds in what direction
Bidirectionally
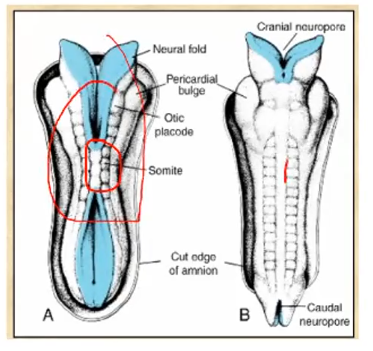
Unclosed part of the neural tubes are called _____
Anterior and Posterior Neuropores
Cranial / Anterior neuropore closes at day ___
24
Caudal / Posterior neuropore closes at day ___
day 26
A process by which the neural plate folds over on itself and fuses in a zipperlike fashion to become a neural tube
Neurulation
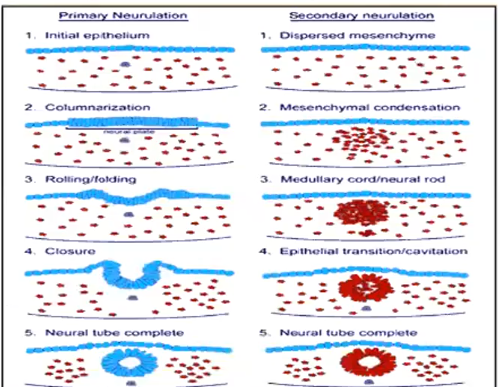
Process by which the brain and the cervical, thoracic, upper lumbar part of the spinal cord are formed
Primary neurulation
Neurulation begins and ends at what days?
Begins at day 18 and ends by Day 28
Process by which the caudal part of the spinal cord (lower lumbar, sacral, & coccygeal segments) are formed
Secondary Neurulation
Mass of cells that develop in the caudal part of the neural tube and it enlarges eventually to become continuous with the neural tube
Caudal Eminence
When does secondary neurulation occur?
Days 20-42
Primary Neurulation vs Secondary Neurulation
Primary | Secondary |
Starts at ectoderm | starts at mesenchyme |
Forms a tube | condenses and hollows; undergoes epithelial transition; Cavitation |
Neural Tube related birth defects
Anterior Neuropore | Posterior Neuropore |
Anencephaly | Spina bifida occulta |
Encephalocoele/Cranium bifidum | Spina bifida aperta |
Chiari I malformation | Spina bifida cystica |
Failure to close of the anterior neuropore causes
Anencephaly, encephalocoele, Chiari I malformation
Failure to close of the posterior neuropore causes
Spina bifida oculta, aperta, cystica
Defective Primary Neurulation
Dysraphic Defects
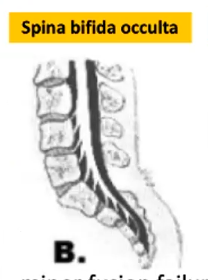
Minor fusion failure of the posterior vertebral arches unaccompanied by herniation of meninges or neural tissue
Spina bifida occulta
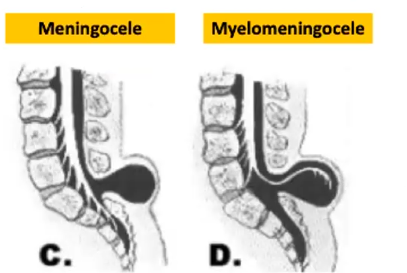
Collectively designates meningocele, myelomeningocele, and other cystic lesions
Spina bifida cystica
Anencephaly is 37 times more common in _____
females
Prevention of Anencephaly
Folic acid
The rostral end of the neural tube undergoes __________ giving rise to three primary brain vesicles
Cephalization
Cephalization begins when?
Week 4
Between the 4th and 8th weeks, the brain tube folds sharply at 3 locations:
Mesencephalic flexure
Pontine flexure
Cervical flexure
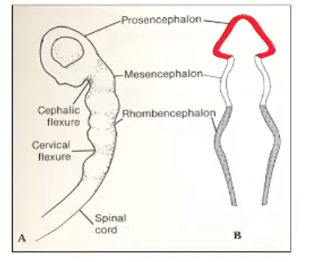
Primary brain vesicles
Prosencephalon
Mesencephalon
Rhombencephalon
Further subdivision of the brain vesicles created how many secondary vesicles?
5 secondary brain vecicles
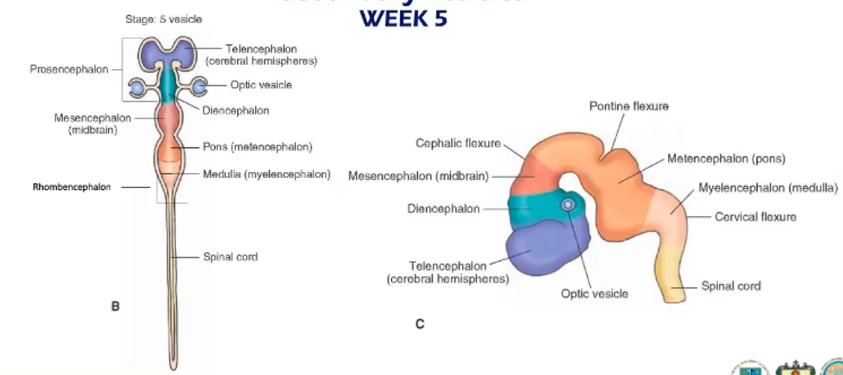
At week ___, the 3 primary vesicles becomes 5 secondary vesicles
Week 5
Lateral expansions of the telencephalon
telencephalic vesicles (become the cerebral hemispheres)
The pontine flexure is found between the _____ and ____
between mesencephalon (midbrain) and metencephalon (pons)
Process of forebrain development
ventral induction
Adult derivatives of the Telencephalon
Cerebral cortex
Subcortical white matter
Olfactory bulb
Basal ganglia
Amygdala
Hippocampus
Adult derivatives of the Diencephalon
Thalamic nuclei and associated structures
Optic nerve and retina
Congenital Dysgenesis of the Diencephalon characterized by underdevelopment (hypoplasia) of the optic nerves, abnormal formation of structures along the midline of the brain, and pituitary hypoplasia.
Septo-optic Dysplasiya
Lumen of the neural tube persists as the _____________
ventricular system of the adult brain
Cavities of the telencephalic vesicles become what ventricles
Lateral ventricles
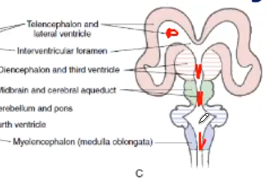
Diencephalic cavity become what ventricles
Third ventricle
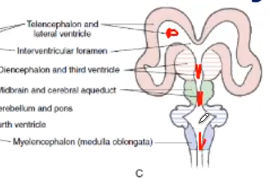
Rhombencephalus cavity become what ventricles
fourth ventricle
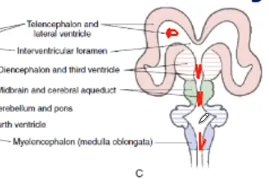
Mesencephalon cavity become what ventricles
Aqueduct of Sylvius
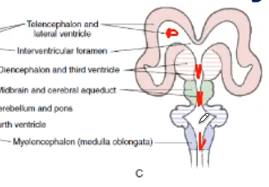
channels that connect the paired lateral ventricles with the third ventricle at the midline of the brain
Interventricular Foramen (Foramen of Monro)
an opening of the fourth ventricle at the caudal portion of the roof of the fourth ventricle
medial aperture or foramen of Magendie
Function of the foramen of magendie
allows flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) from the fourth ventricle into the cisterna magna
paired apertures located in the lateral recesses of the fourth ventricle, within the posterior cranial fossa
Foramen of Luschka
The primary site of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) production is
choroid plexi located within the lateral, third, and fourth ventricles of the brain
Choroid plexus develops where?
Where pia mater and ependyma are in direct contact
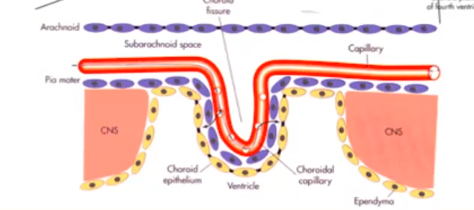
Occurs when flow of CSF is disrupted during development
Congenital Hydrocephalus
Likely site of blockage that leads to Congenital Hydrocephalus
Aqueduct of Slyvius
True/False: Congenital Hydrocephalus can be heredited
True
Peak time period of Neuronal proliferation
3-4 months
Sites of Neuronal Proliferation
Ventricular zone and subventricular zone
During neuronal proliferation, proliferative units are produced by?
Symmetrical divisions of stem cells
During neuronal Proliferation, what happens to proliferative units before migration?
Proliferative units later enlarge by asymmetrical division of the stem cells before migration
___________ multiply in the periventricular region producing neuroblasts & glioblasts
Blast cells (pluripotential)
Layers of the wall of the neural tube
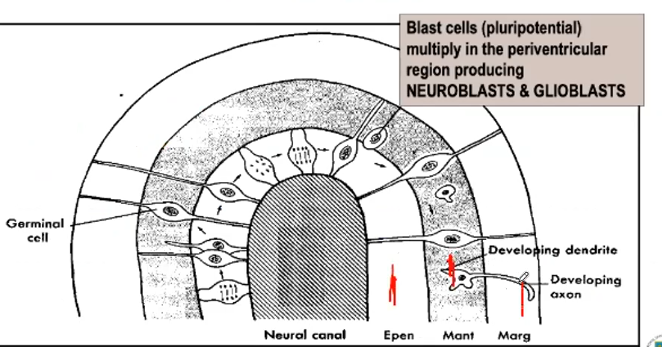
Stages of Neuron development
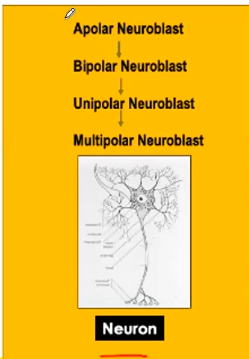
Stages of Neuroglia development
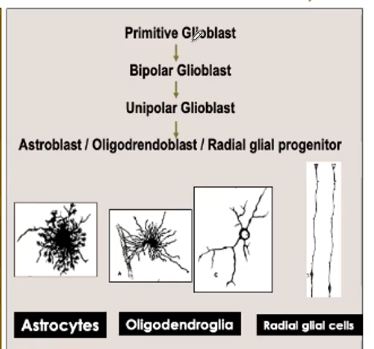
_______ guide migration of developing neurons
Radial Glia
Peak time period of Neuronal Migration
3-5 months
Major events of Neuronal Migration in the Cerebrum
radial migration of the cerebral cortex, deep nuclei
Major events of Neuronal Migration in the Cerebellum
radial migration: purkinje cells, dentate nuclei
tangential migration: external—internal granule cells
The most common form of cell transit
Radial migration
Number of neurons that go into apoptosis
40%-60%
Development of Axons is facilitated by ________
neuronal growth cones
Development of dendrites is driven by ________
genes controlling calcium regulated transcription process
Point of contact between two brain cells
Synapse
First synapses are generally observed when?
23rd week / second trimester of pregnancy
Peak of production of synapses
1st year of life
True/False: Massive production of synapses if followed by sudden reduction
False; Gradual reduction
Process of removal of redundant or otherwise unnecessary synaptic connections
Synapse pruning
Until synaptogenesis, stages of brain development is largely driven by?
gene driven
Once brain reaches point where synapses are reduced, process of pruning becomes driven by?
Experience
process in which axons are wrapped with fatty cells
Myelination
Regions involved in _______ myelinate later than other regions
regions involved in higher cognitive ability