anatomy exam 1
1/178
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
179 Terms
4 subsystems of speech
respiration, laryngeal, velopharyngeal, pharyngo-oral
Lungs, Rib cage, Diaphragm and other muscles that open up the lungs to allow air to flow in
contains VF (voice box)
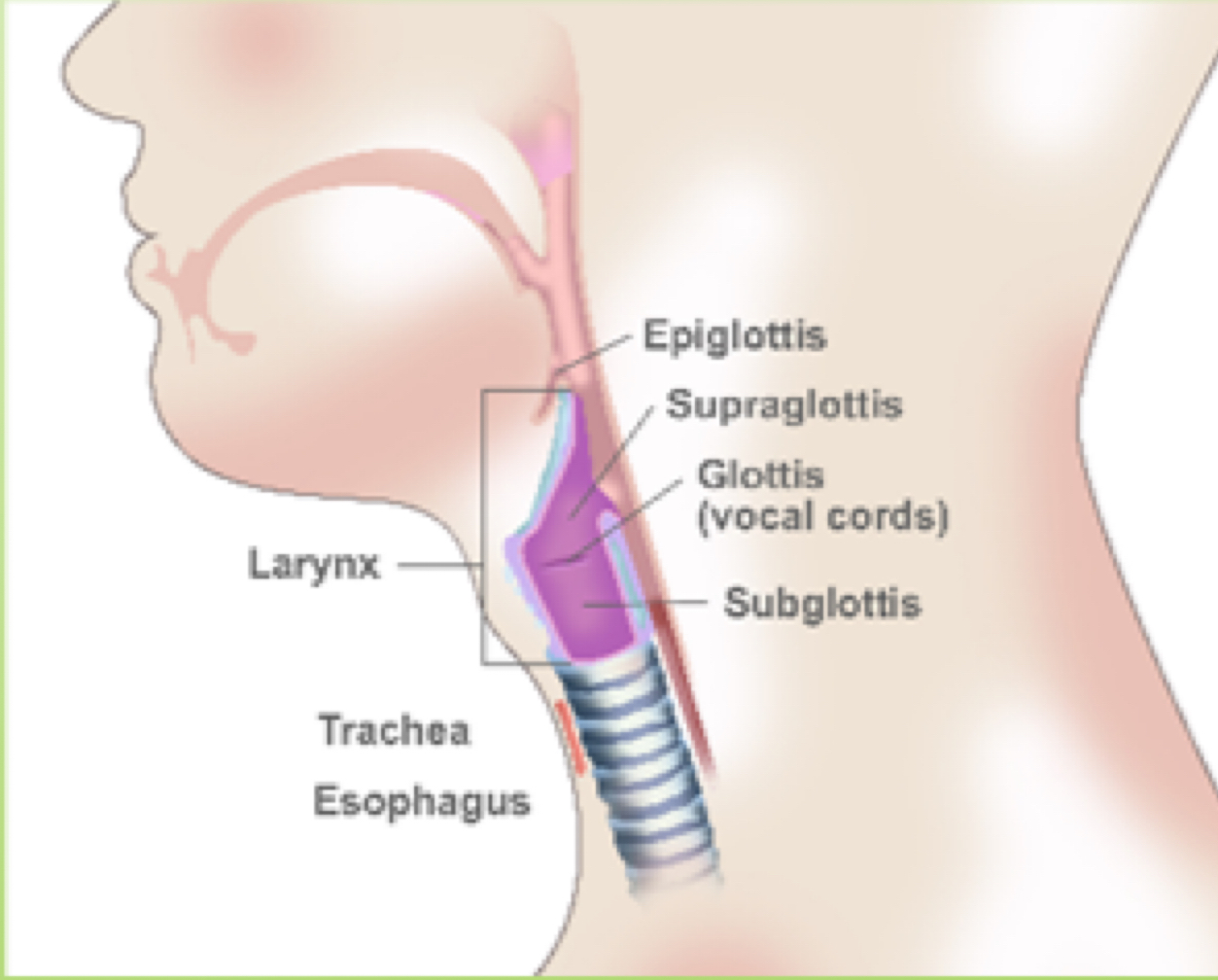
allows air to flow into the lungs and out again
voiceless
Voice: air lungs is pushed up through the closed VF, which causes them to vibrate. Voicing
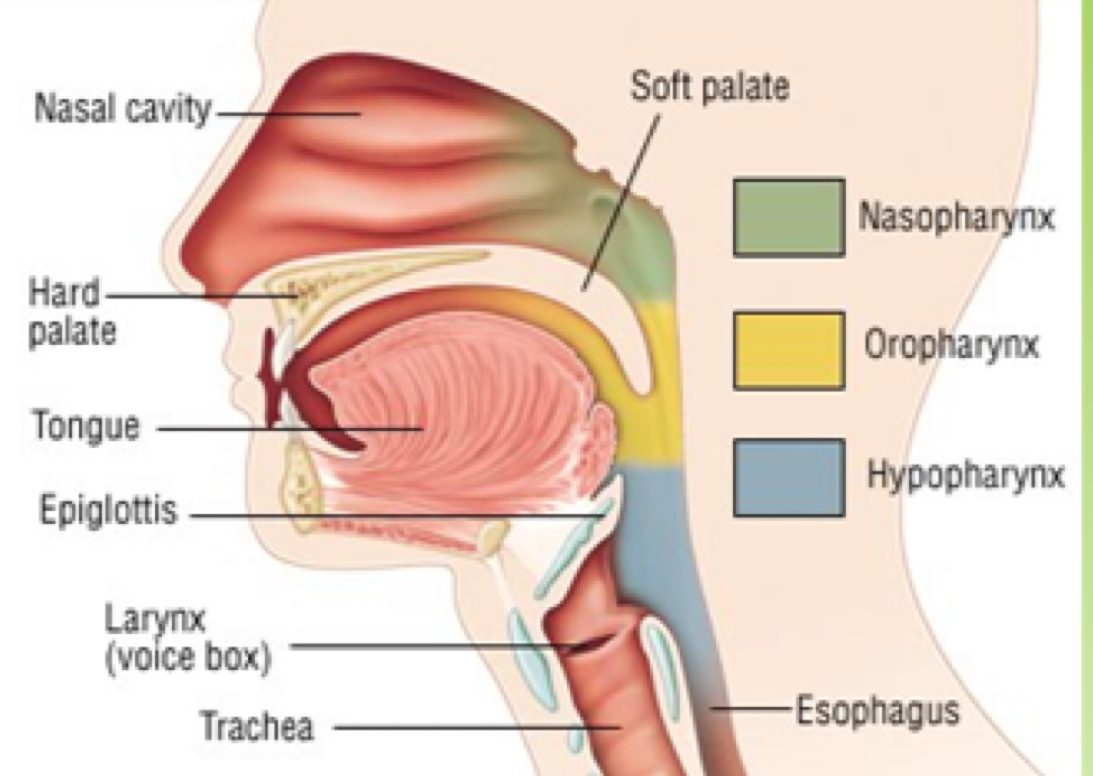
Velopharygeal Nasal
open: nasalance
closed: non nasalance
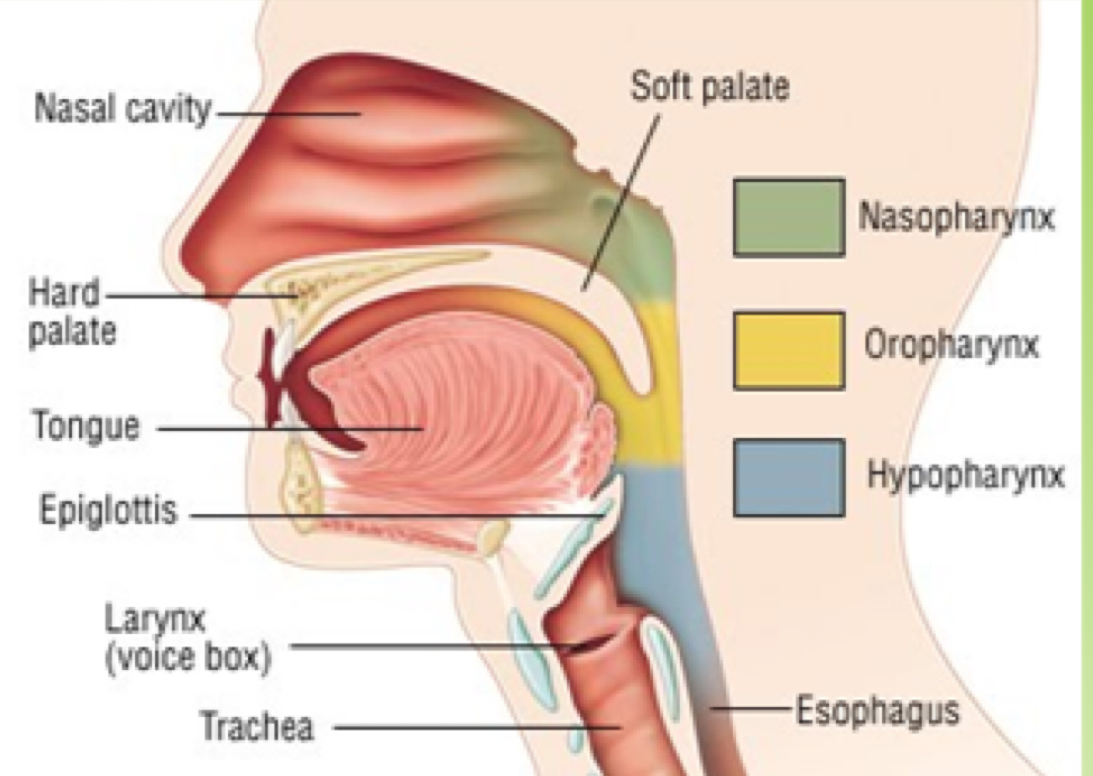
articulation
prepares and transports food: swallowing
sound has intensity frequency and duration
4 subsystems for hearing
outer ear
middle ear
inner ear and auditory nerve
central auditory pathway
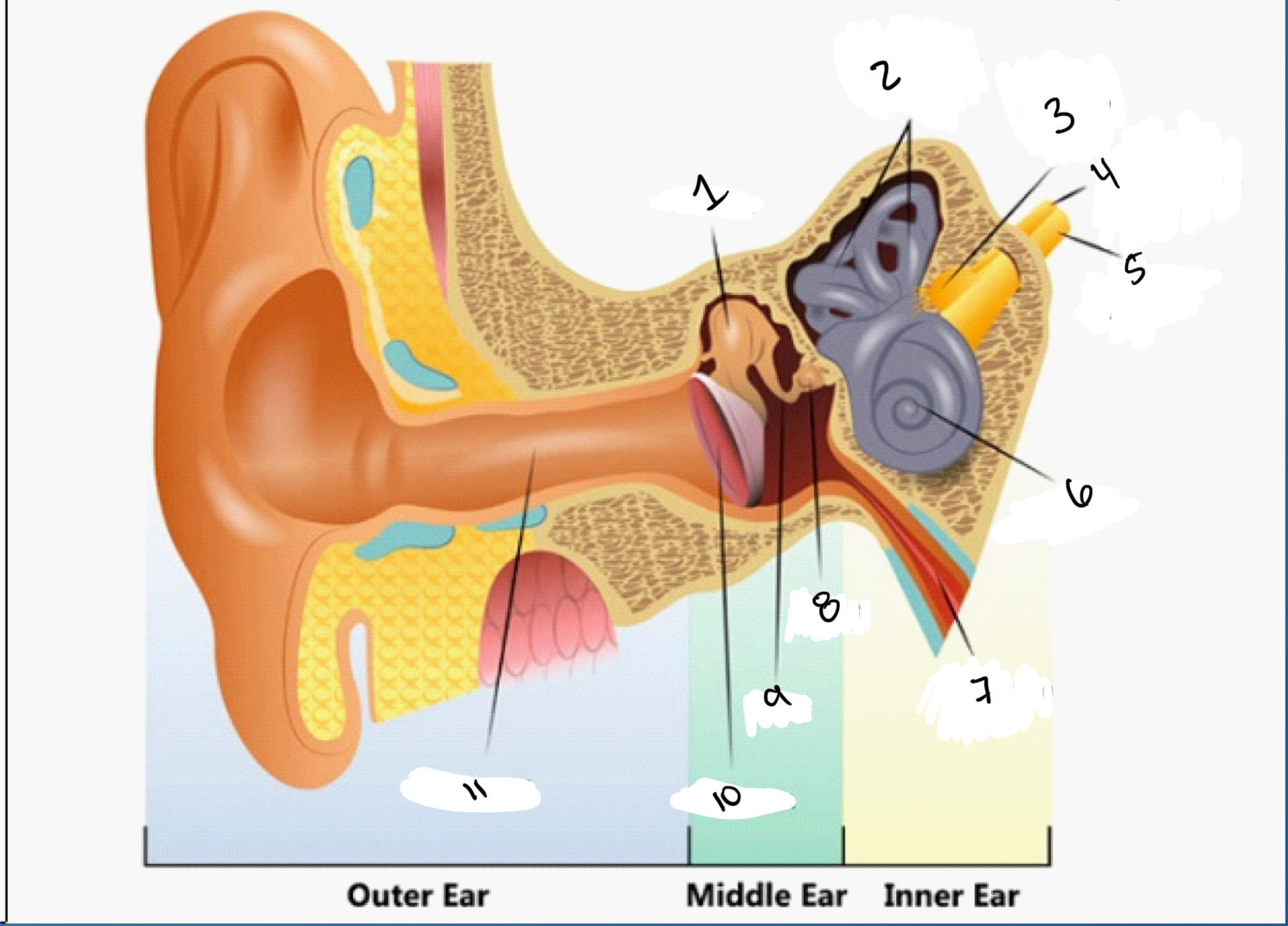
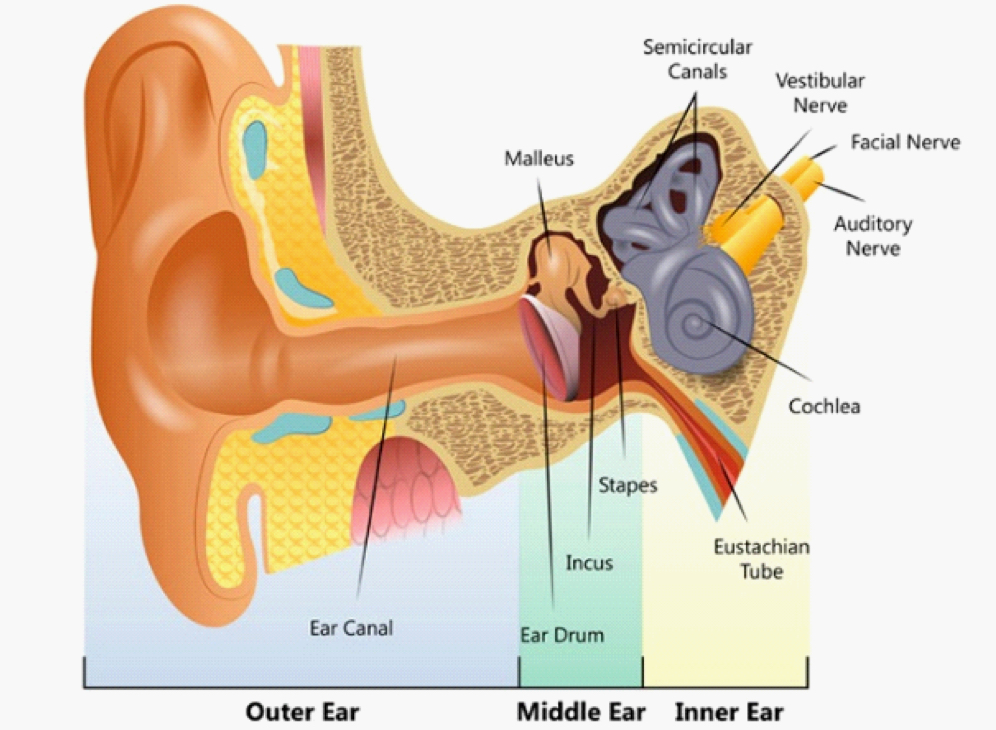
Name the outer middle and inner ear
Malleus
Semicircular canals
Vestibular nerve (detecting balance)
Facial nerve (facial expression)
Auditory nerve
Cochlea
Eustachian tube
Stapes
Incus
Ear drum
Ear Canal
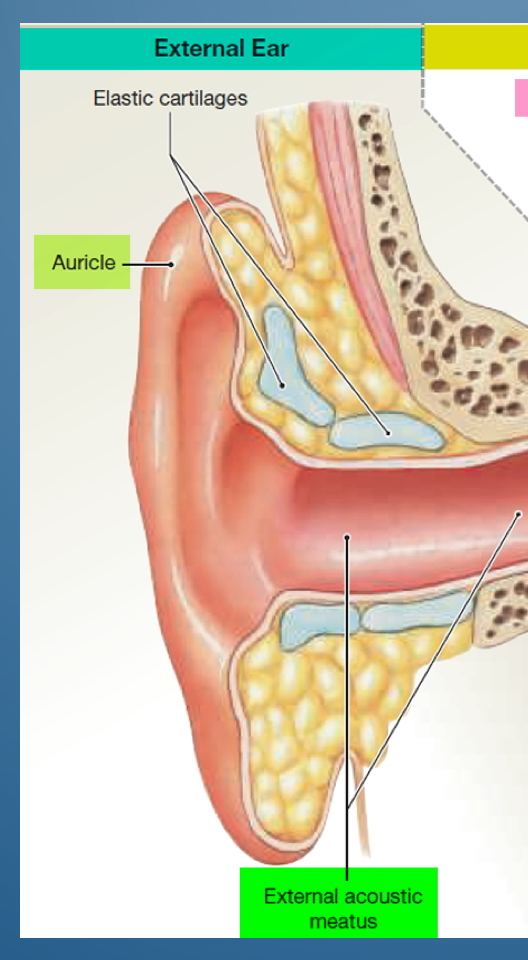
1. Elastic cartilages
2. Auricle
3. External acoustic meatus
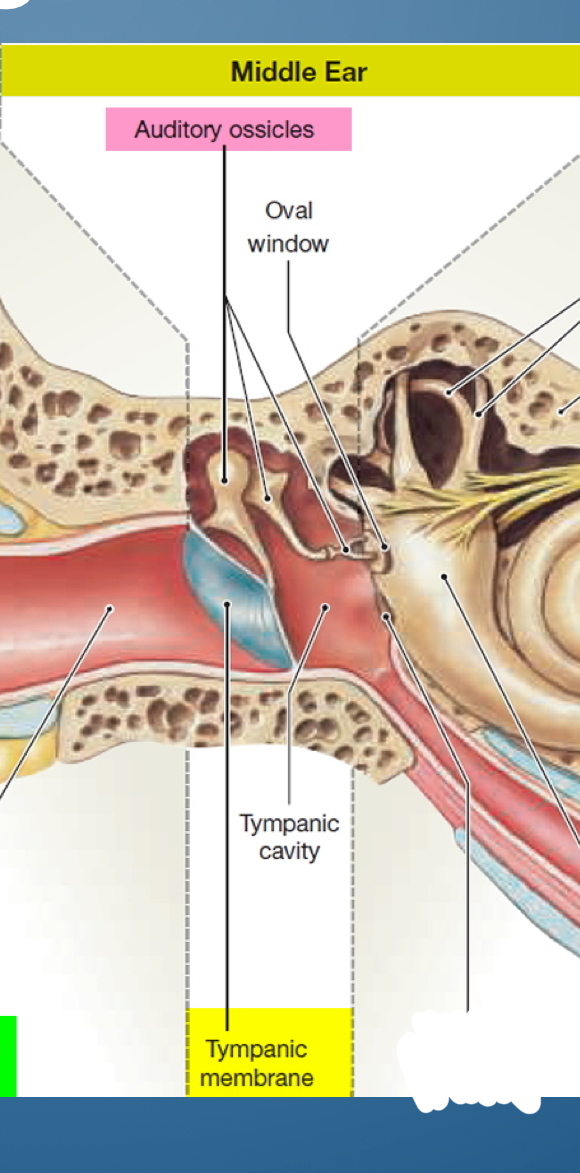
1. Auditory ossicles
2. Oval window
3. Tympanic cavity
4. Tympanic membrane
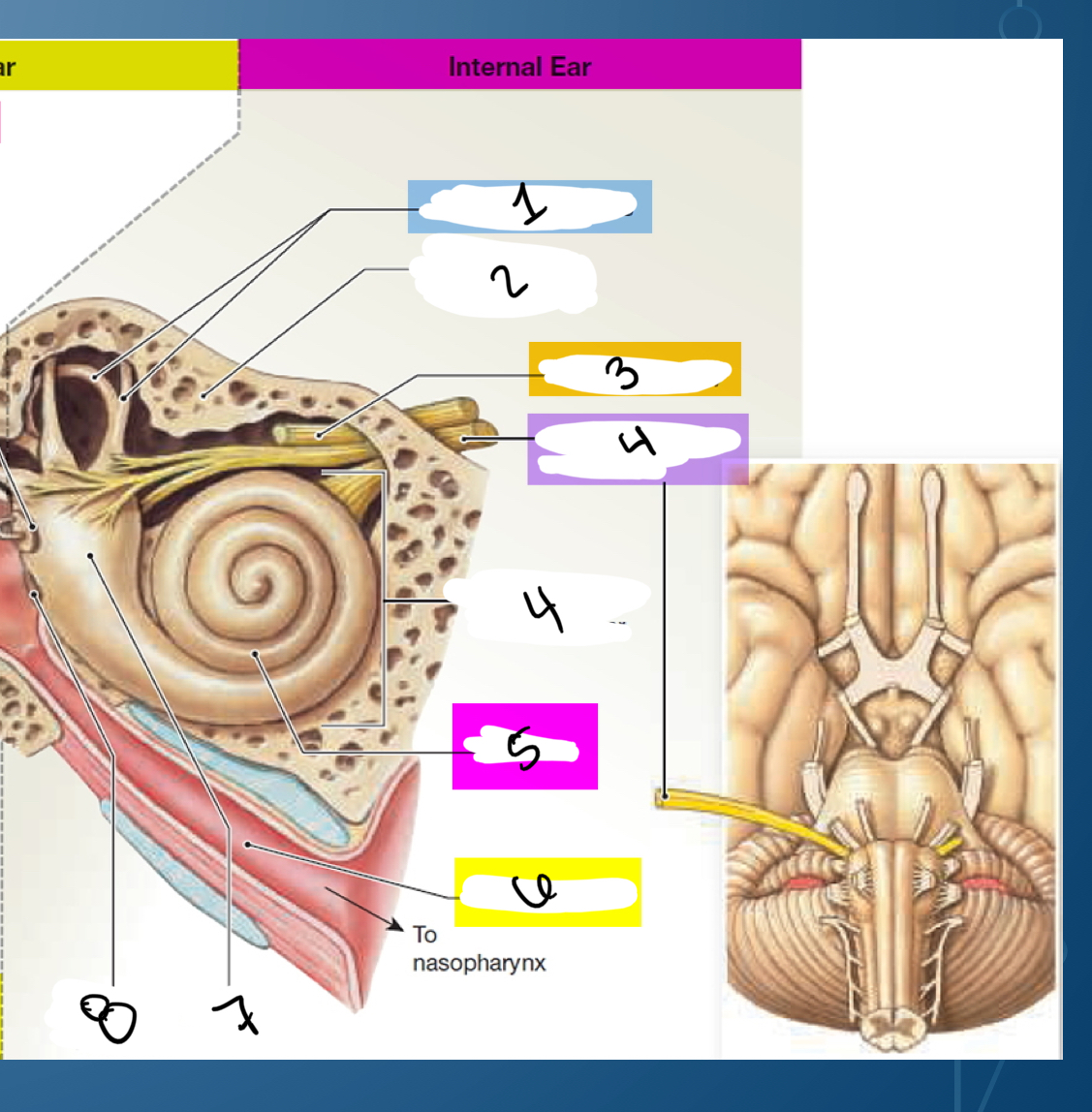
Name internal ear
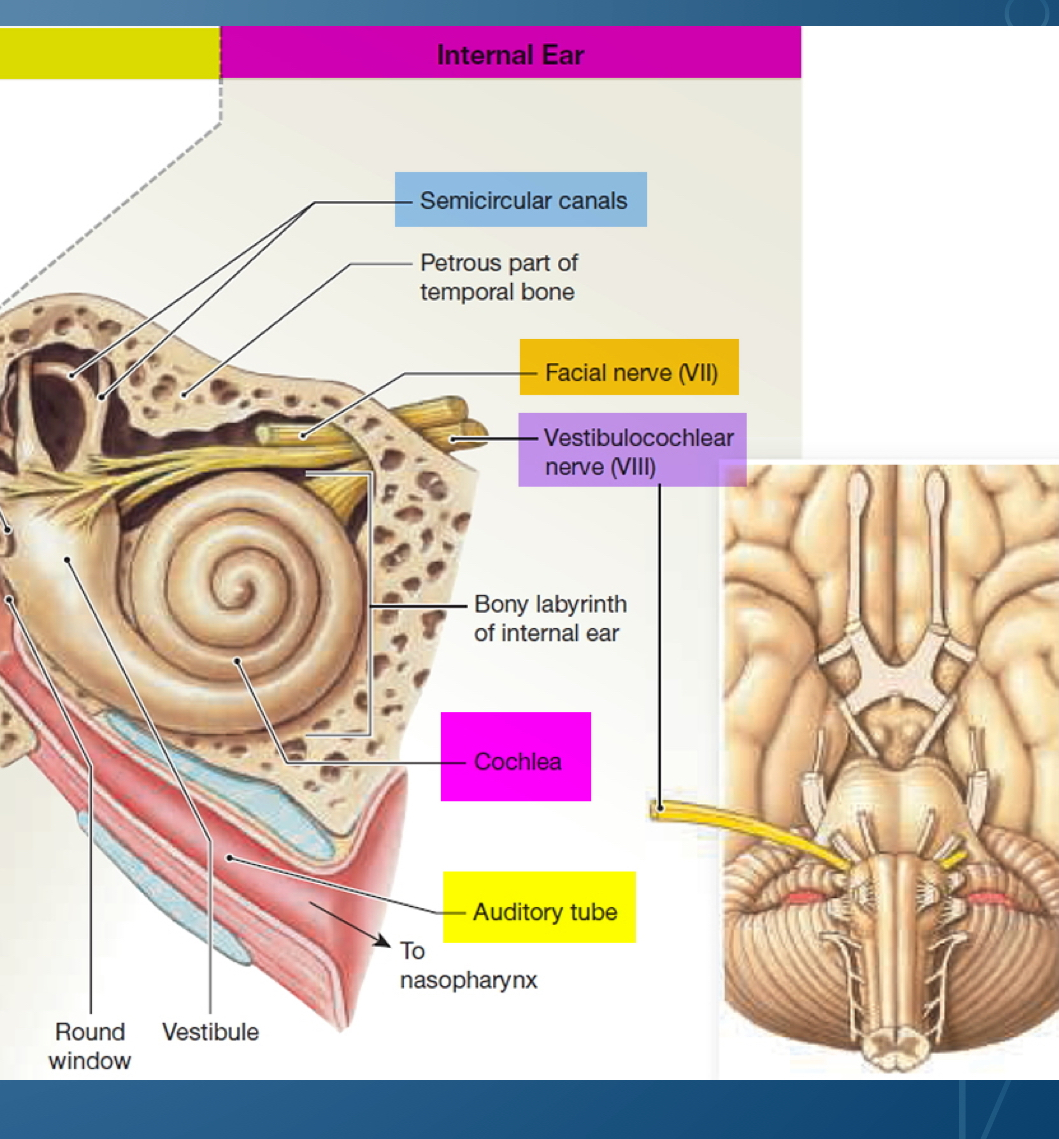
Semicircular canals
Patro is part of temporal bone
Facial nerve VII (7) (facial nerve)
Vestibulochoclear nerves VIII (8) (special sensation of hearing, and its vestibular portions are involved in balance, spatial sensation, and posture)
Bony labyrinth of external ear
Cochlea
Auditory tube
Vestibule
Round window
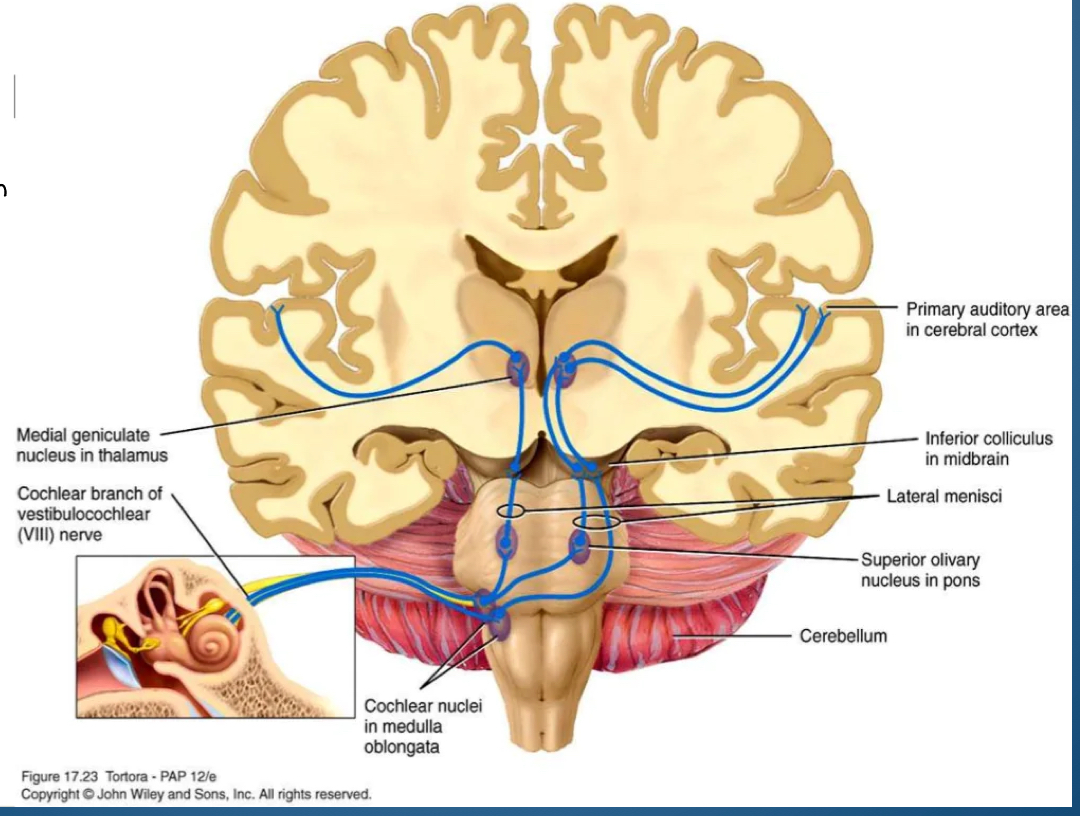
Cochlear nuclei is one __________________
one side
(is the first central auditory structure to receive input from the cochlea via the auditory nerve.)
central auditory pathway
Cochlea to
Brain stem (central) to
Cochlear nuclei on one side to
Bilateral pathway: lateral Lemniscus to
Thalamus to
Primary auditory cortex
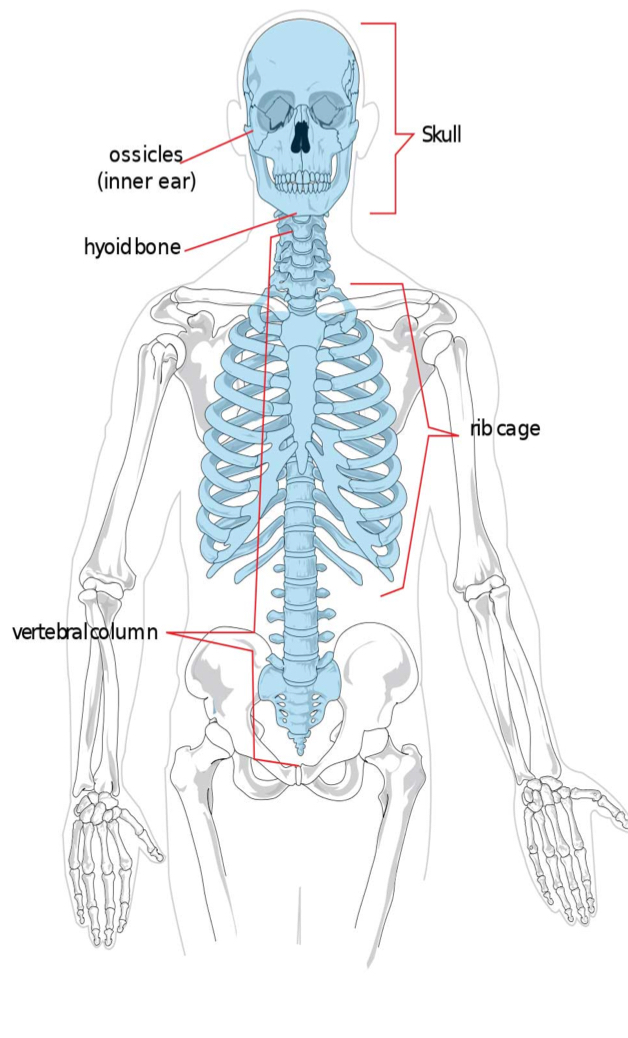
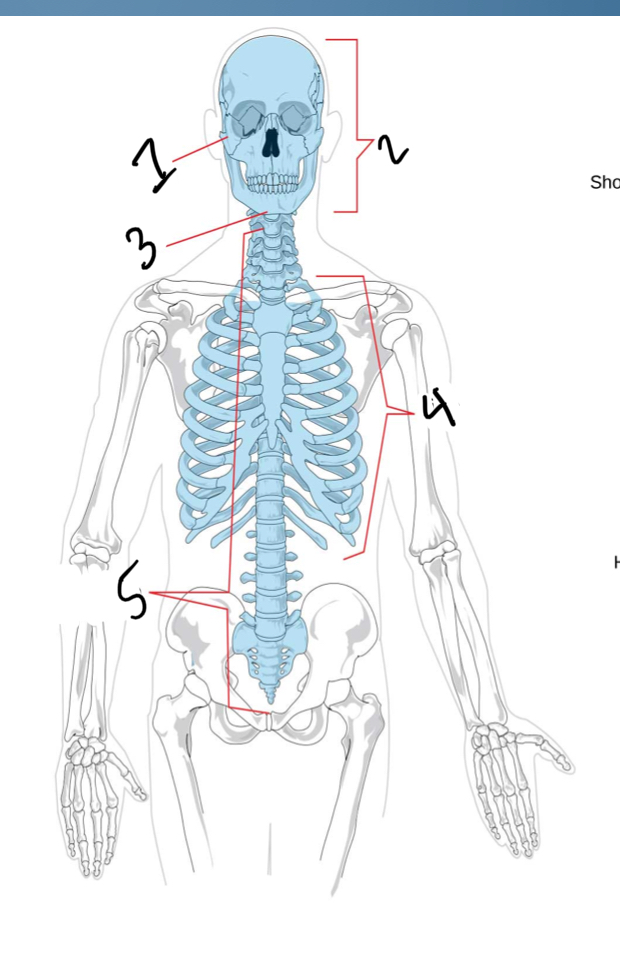
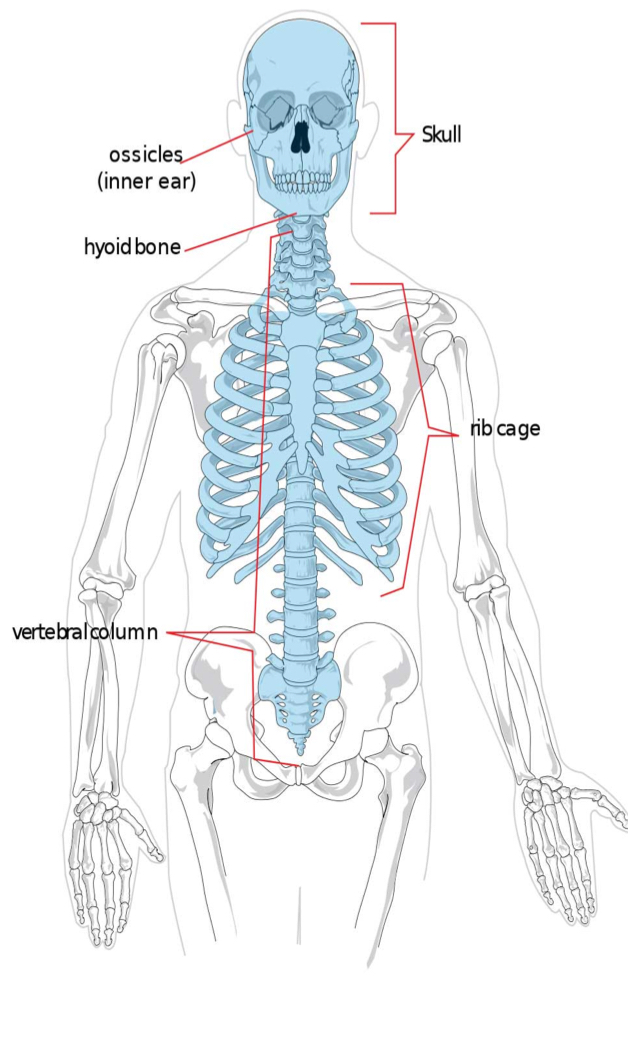
Name the axial skeleton
Ossicles (inner ear)
Skull
Hyoid bone
Rib cage
Vertebral column
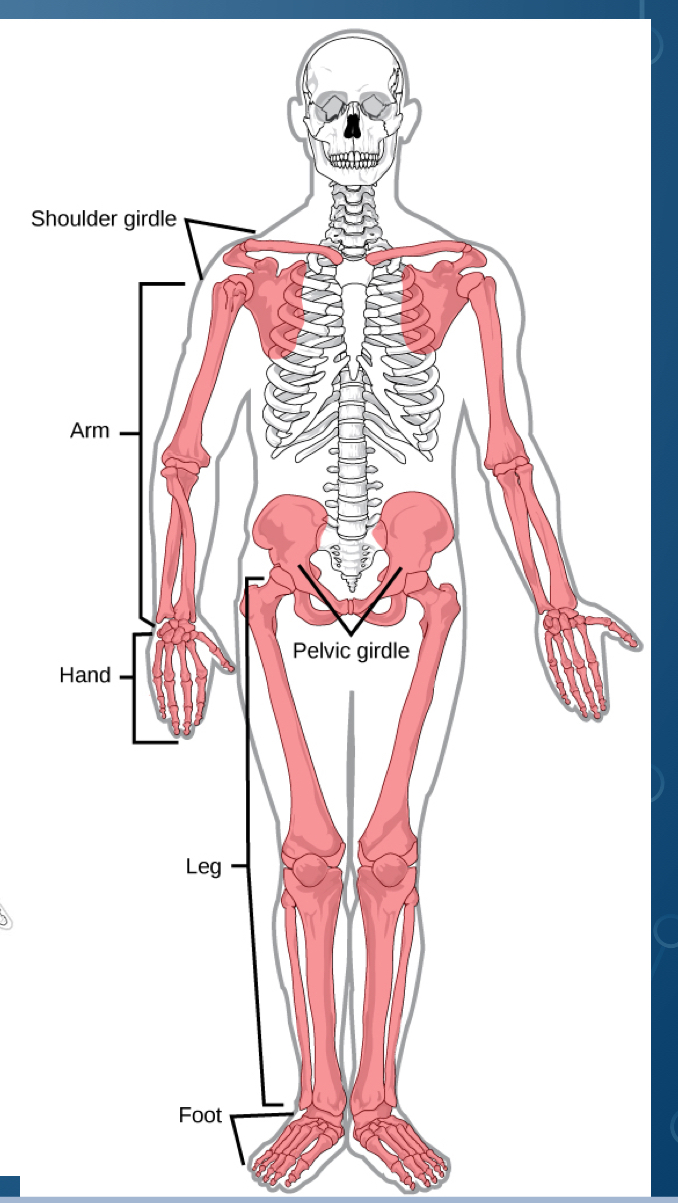
Part of the axial skeleton
appendicular skeleton supports
limps supporting gesticulation (gestures) grasping and walking
Viscera cranium (facial bones)
has \__________, and \___________
cranial base
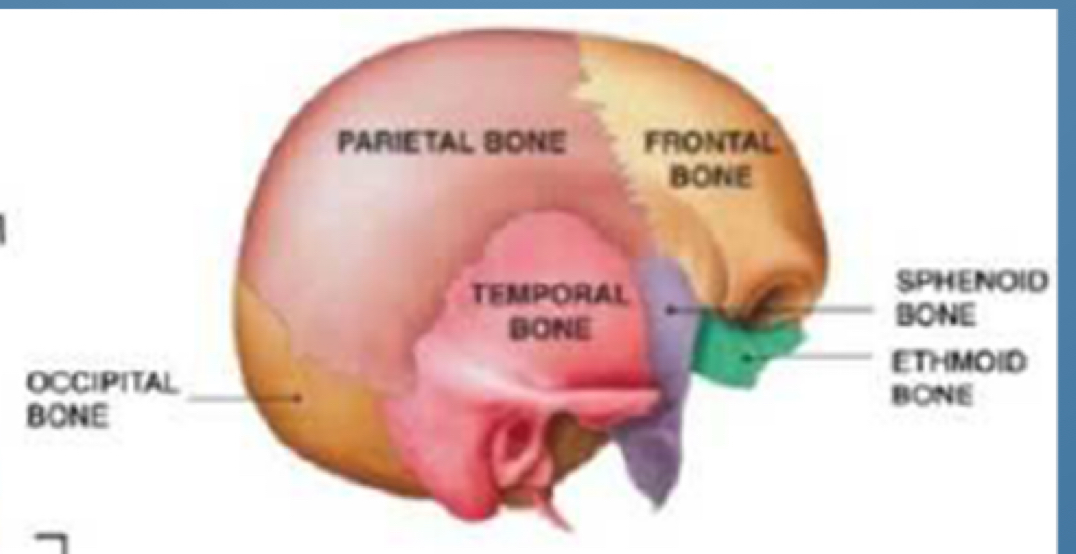
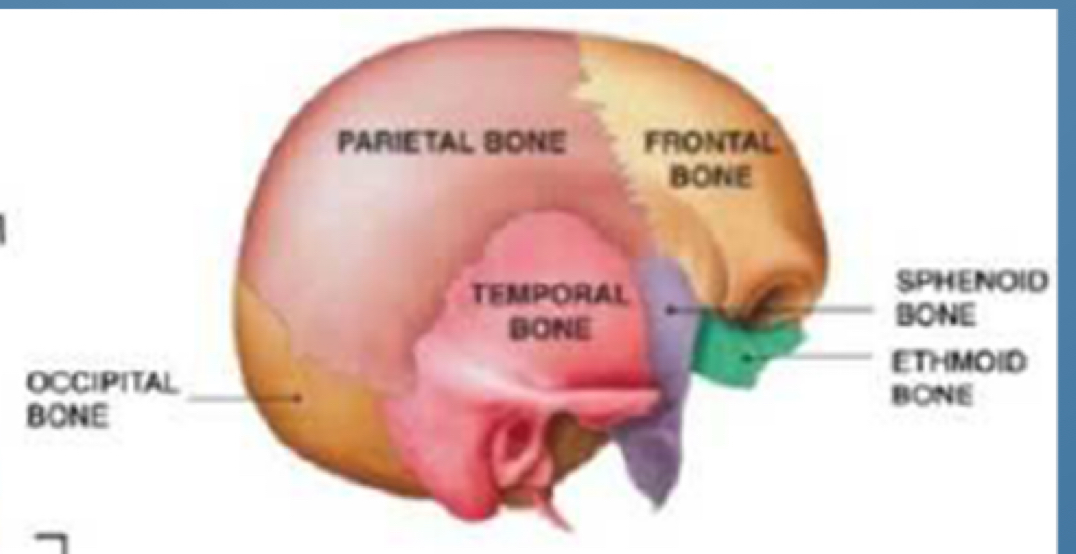
Cranial base front to back
FESTO
FRONTAL (FRONT)
ETHMOID
SPHENOID
TEMPORAL
OCCIPITAL (BACK)
Vicero cranium (facial bones)
Nasal bone,
Zygomatic,
Maxilla,
Mandible
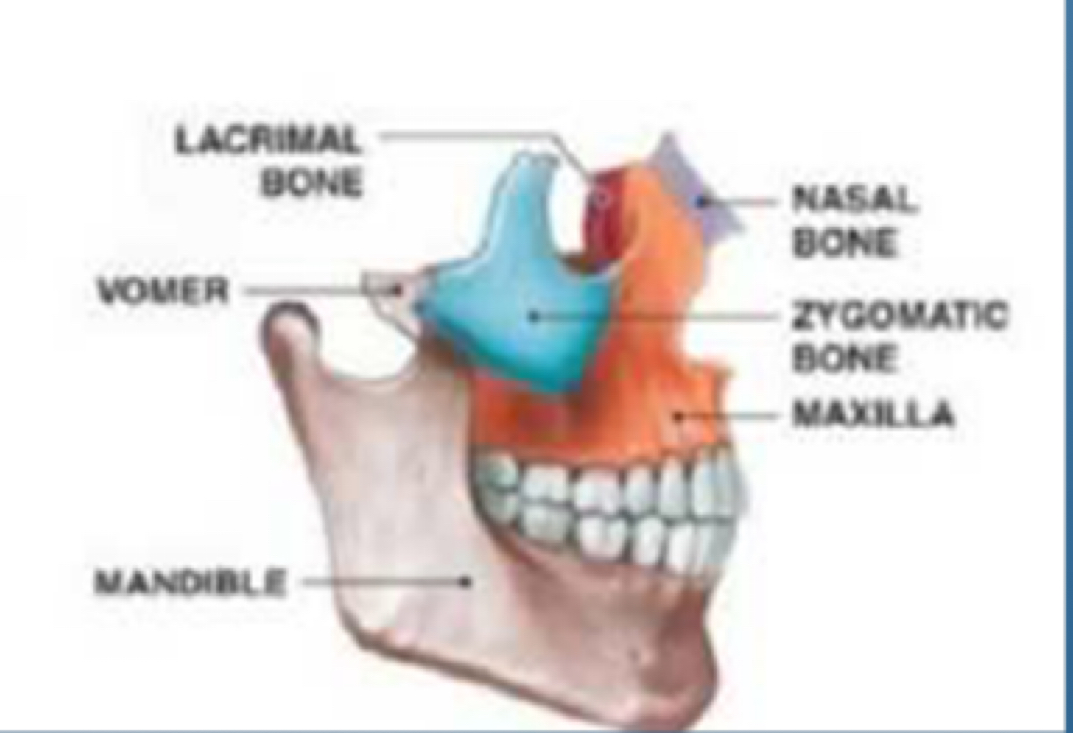
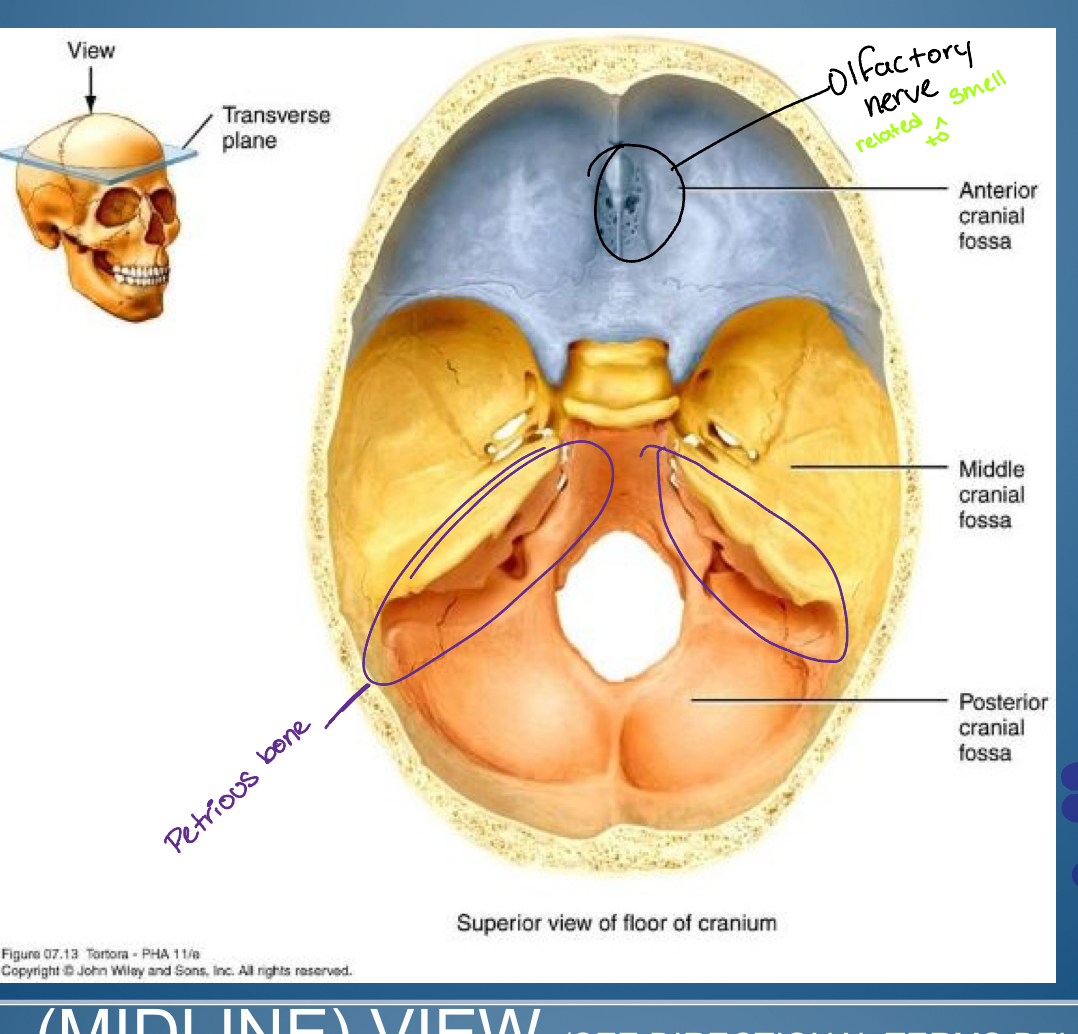
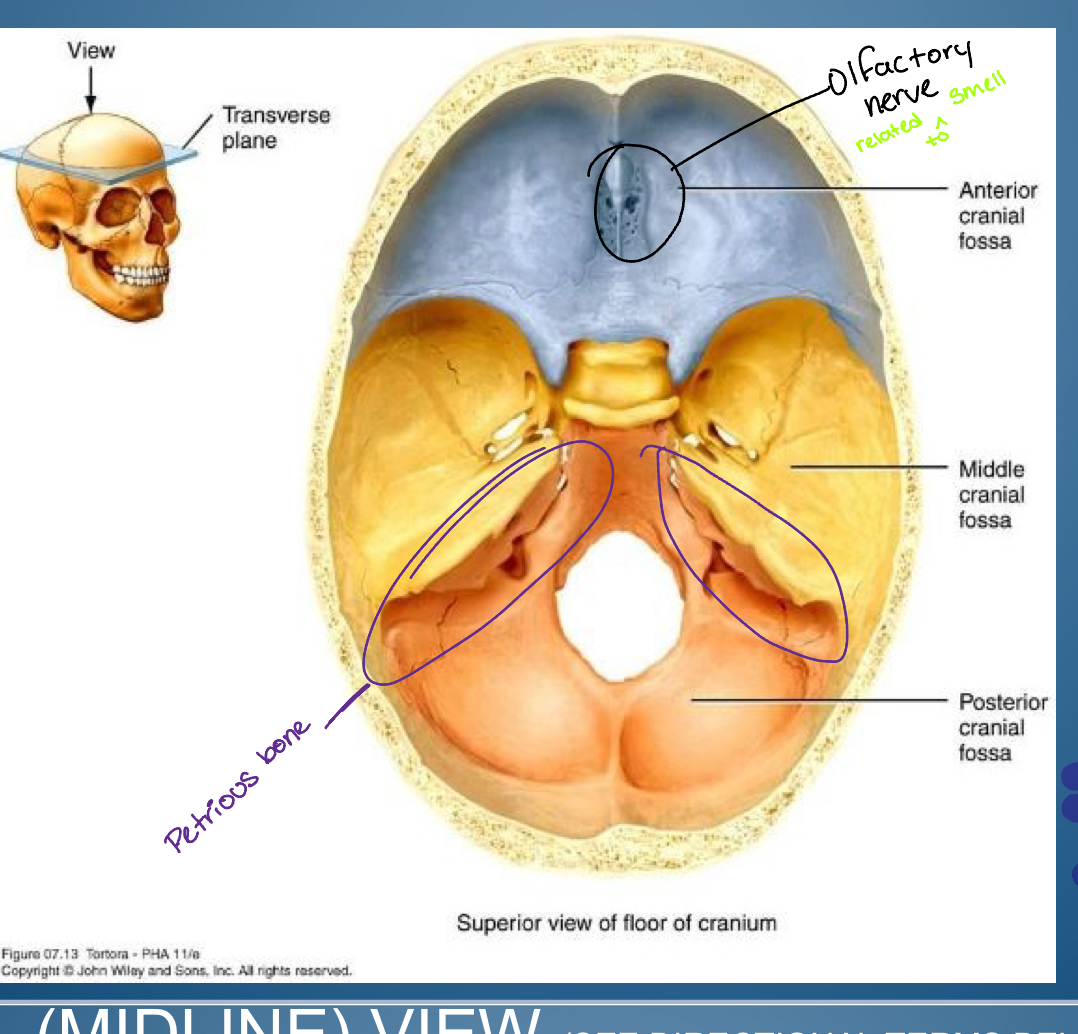
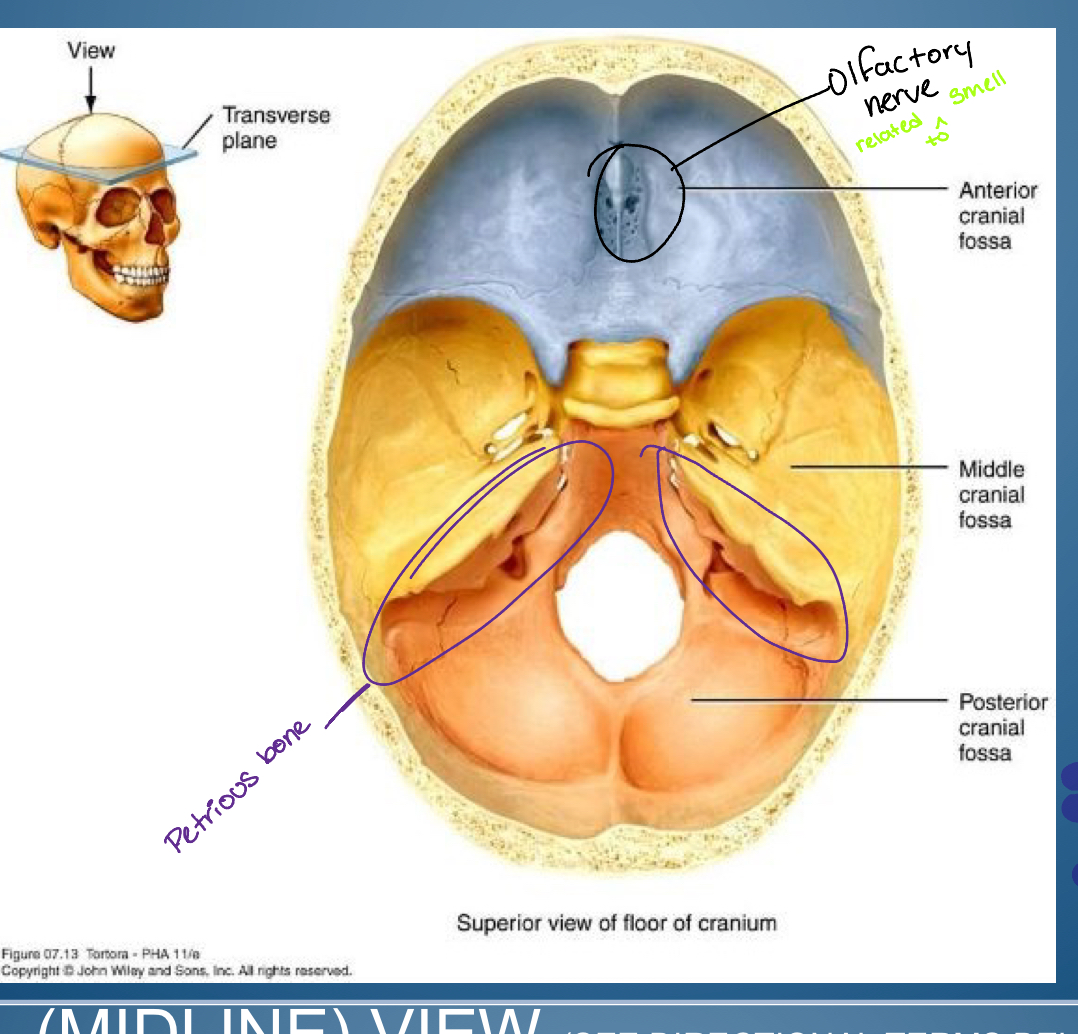
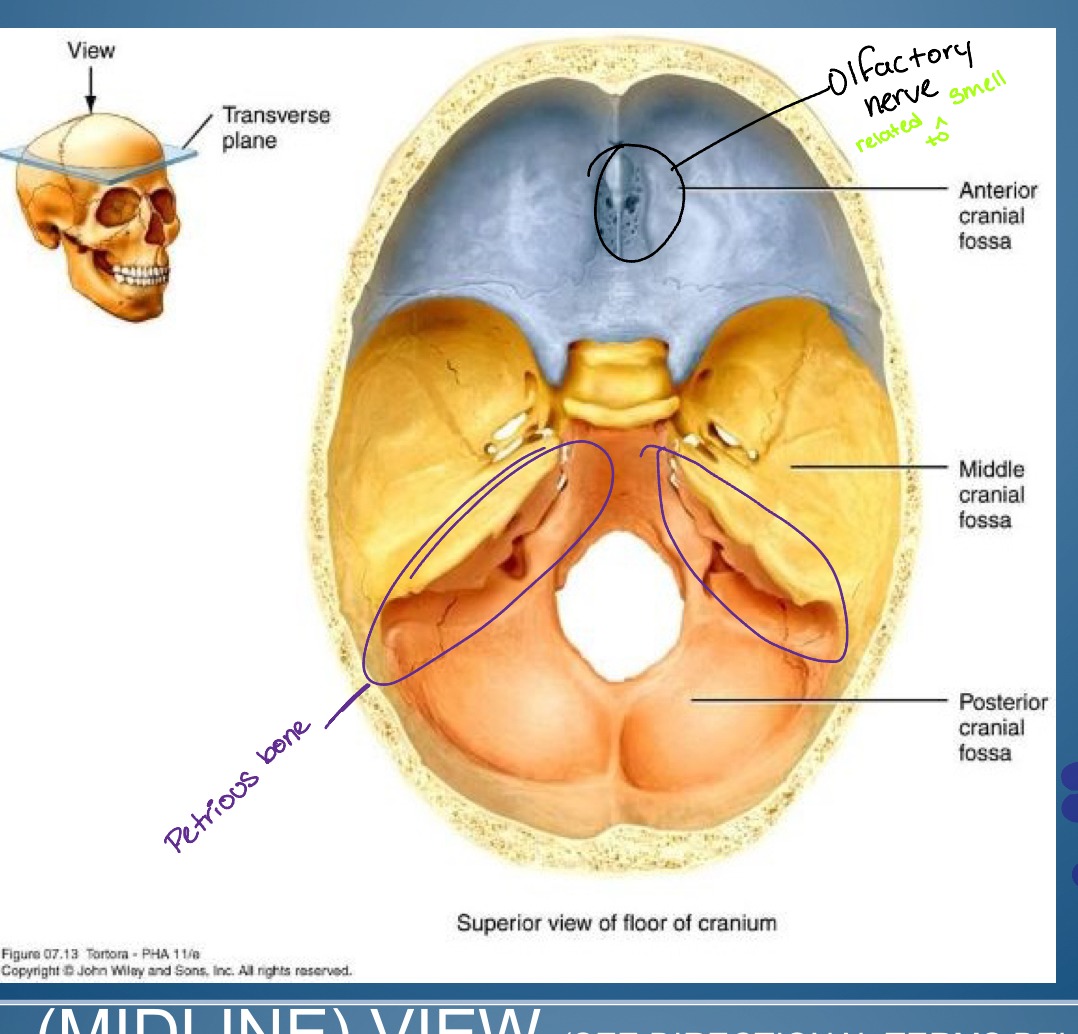
Base of (hint cranial)
-Anterior cranial fossa
-Middle cranial fossa
-Posterior cranial fossa
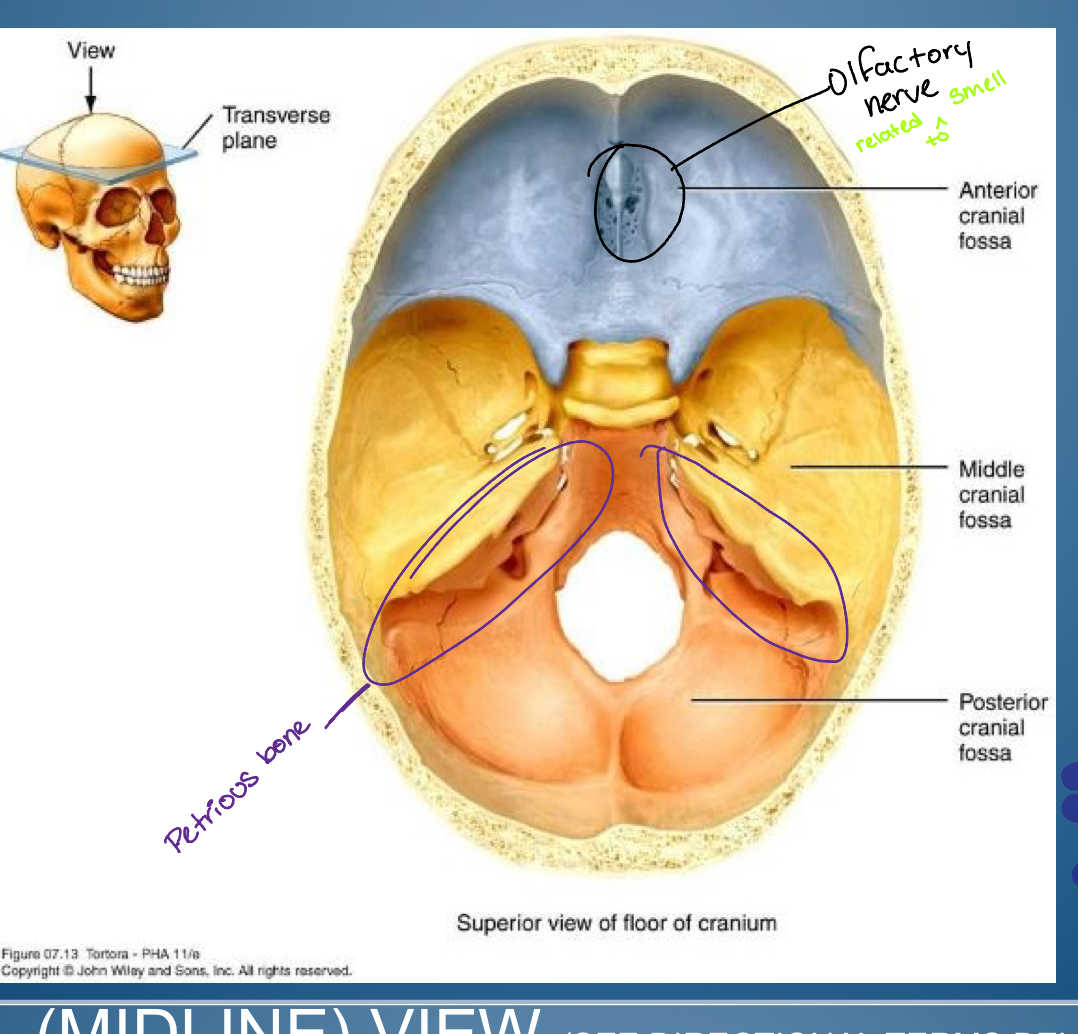
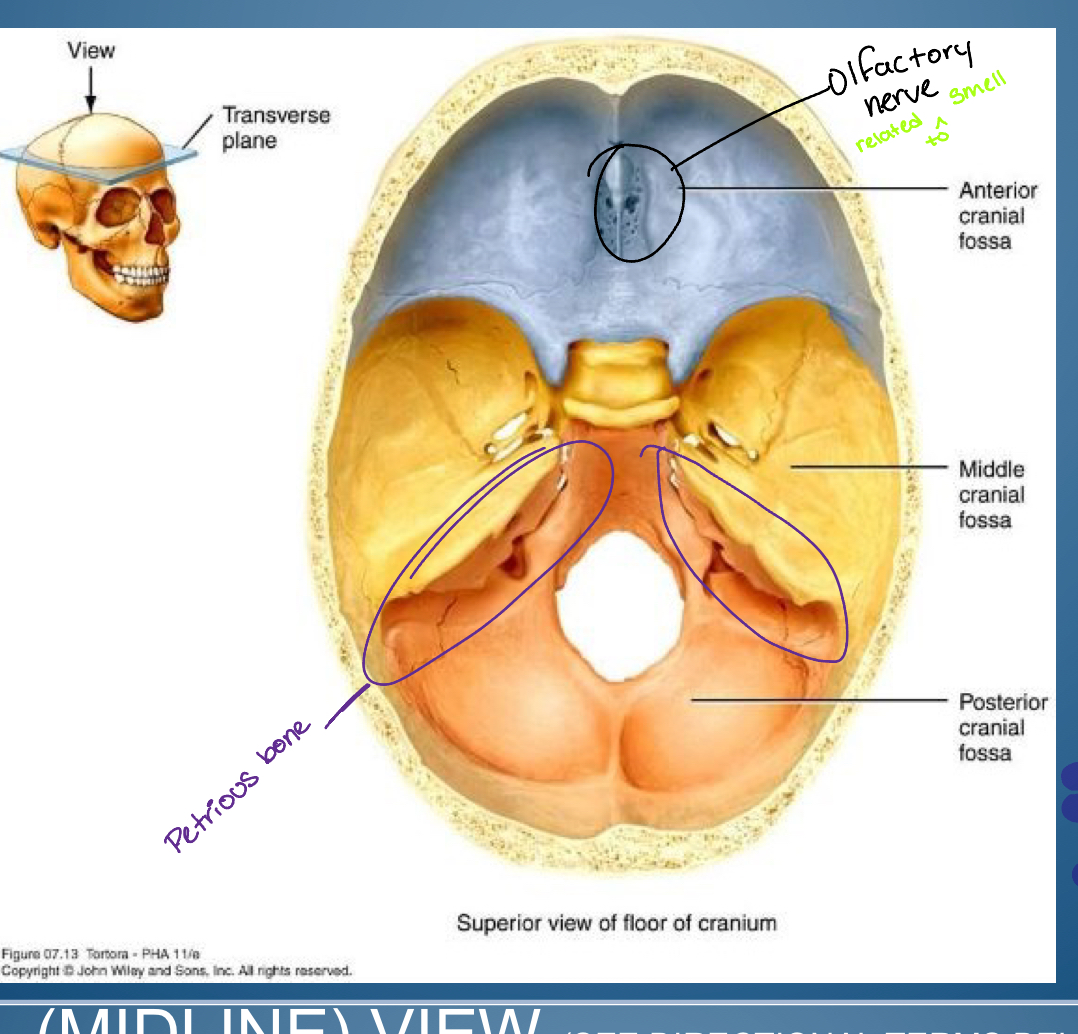
1. Crifrom plate ( entry of olfactory nerve: smell )
2. Frontal bone plus lesser wing sphenoid
\
\
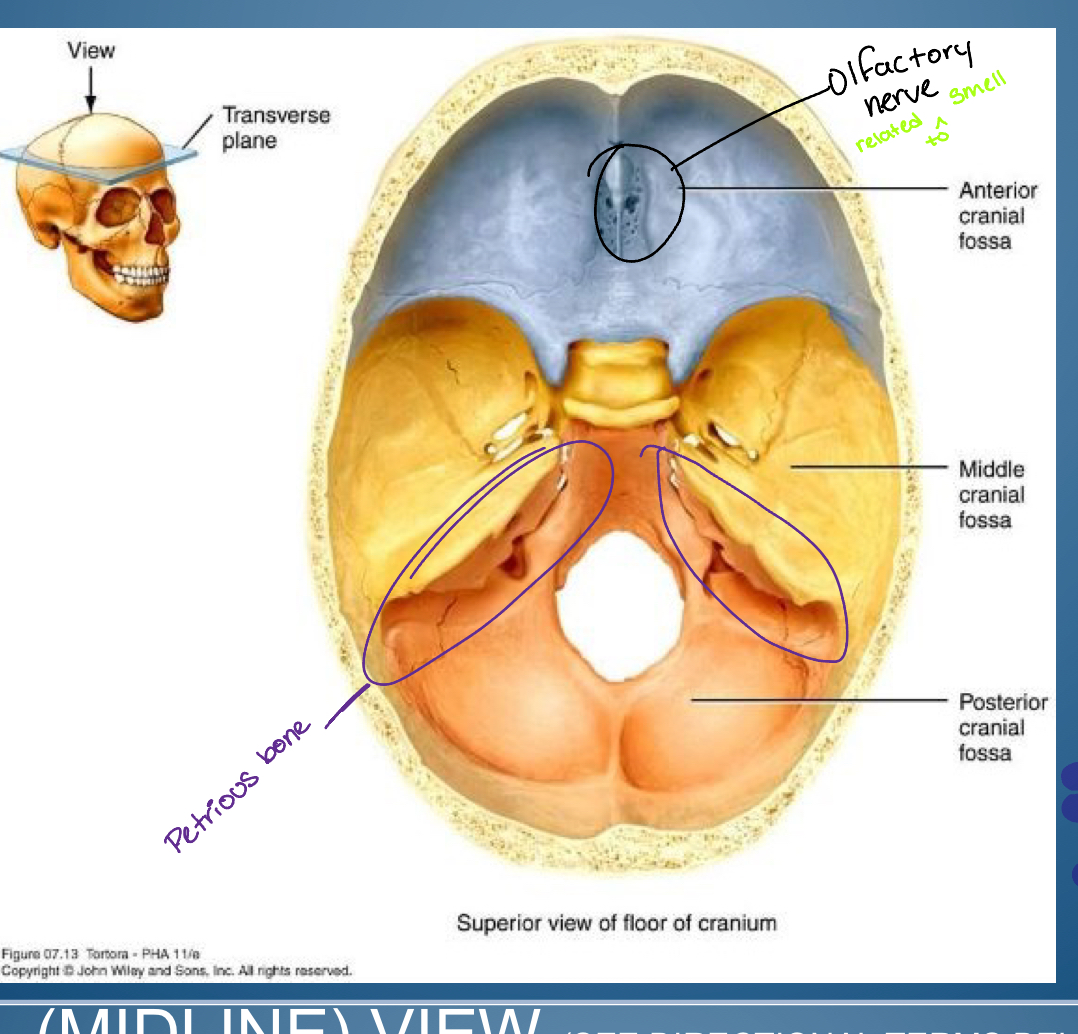
temporal bone
medial flack petrous portion of temporal bone
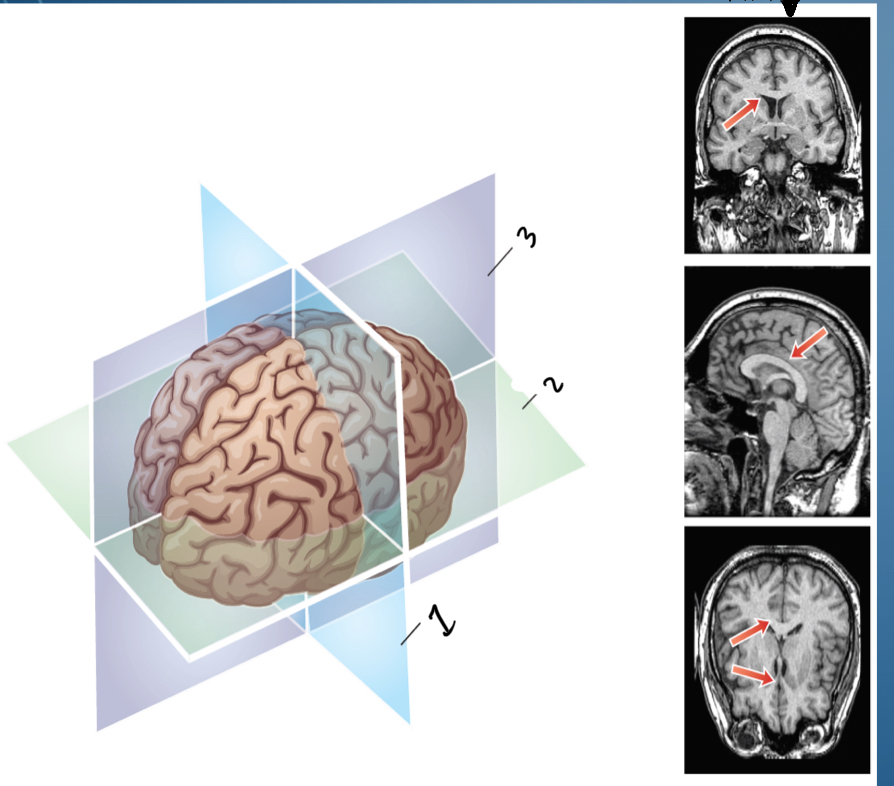
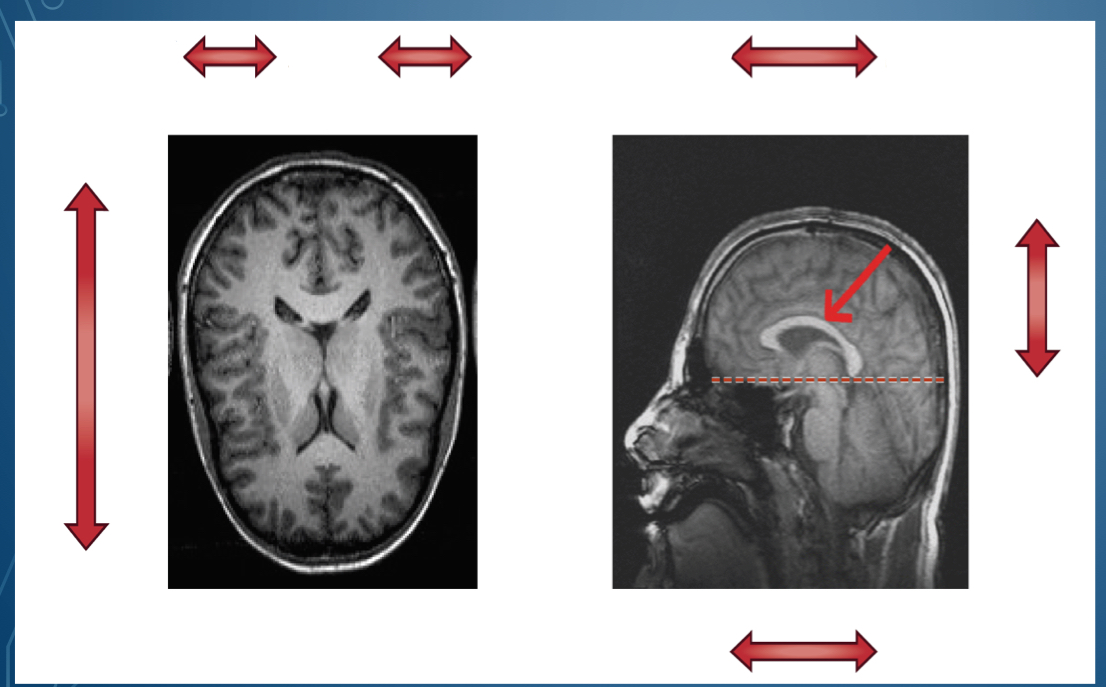
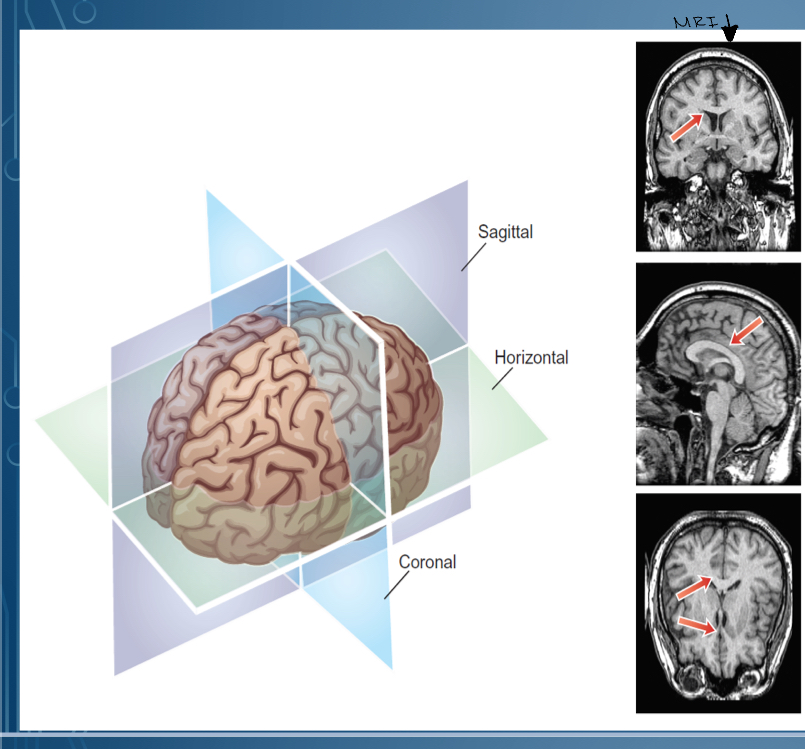
2. Transverse/Horizontal (horizontal cut into upper and lower) crown
3. sagittal (vertical cut into left and right halves) middle/ midline
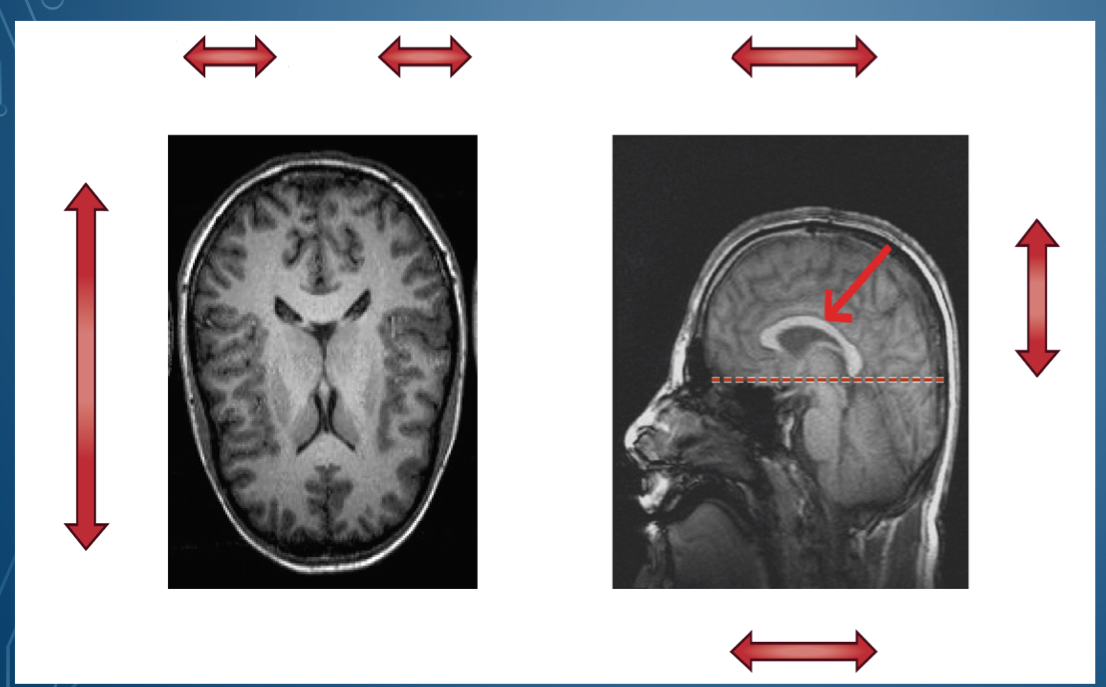
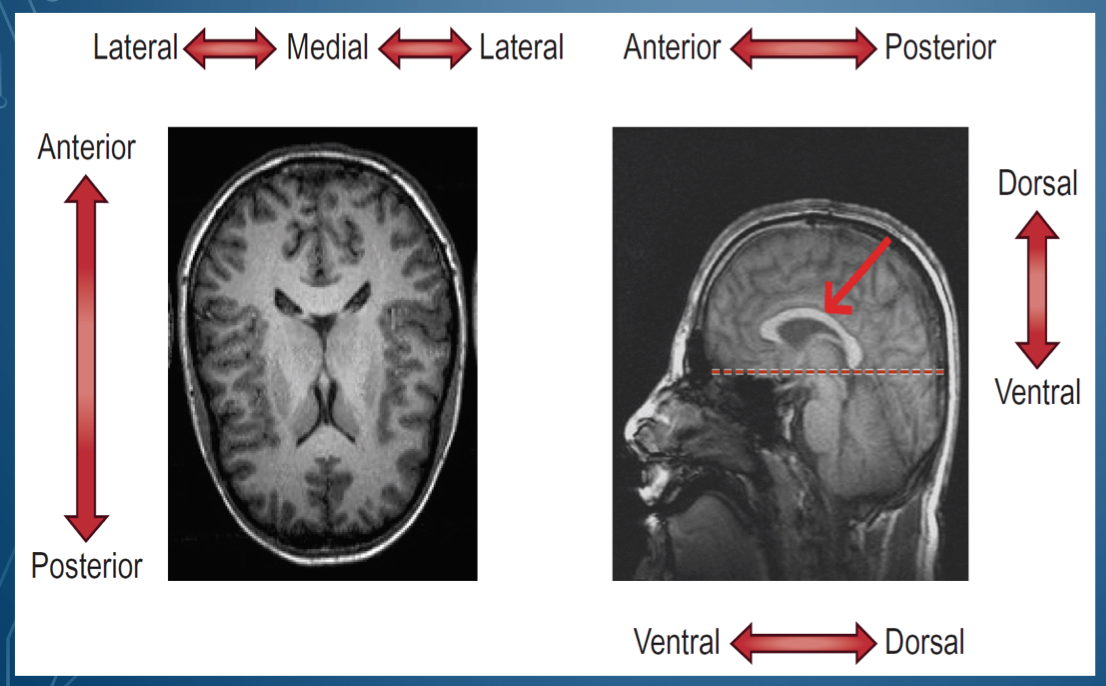
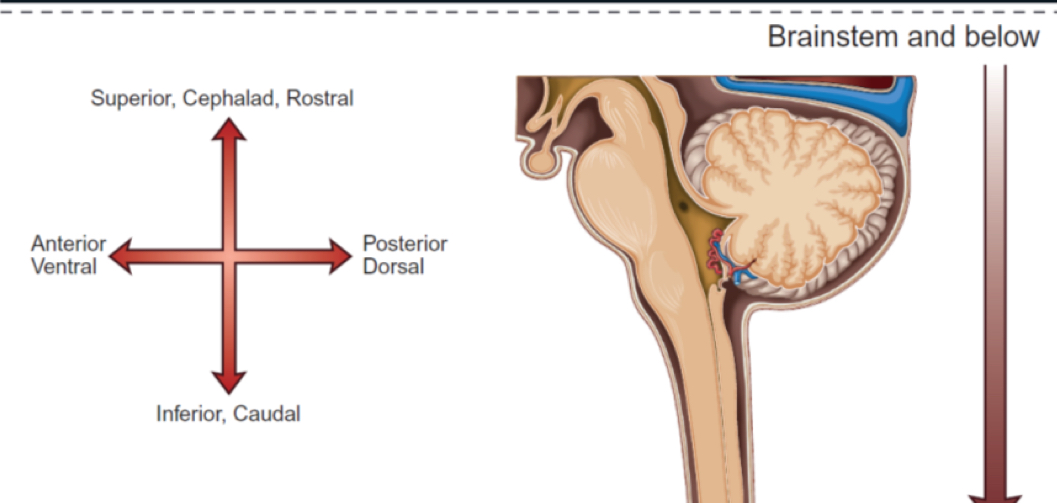
where is dorsal located?
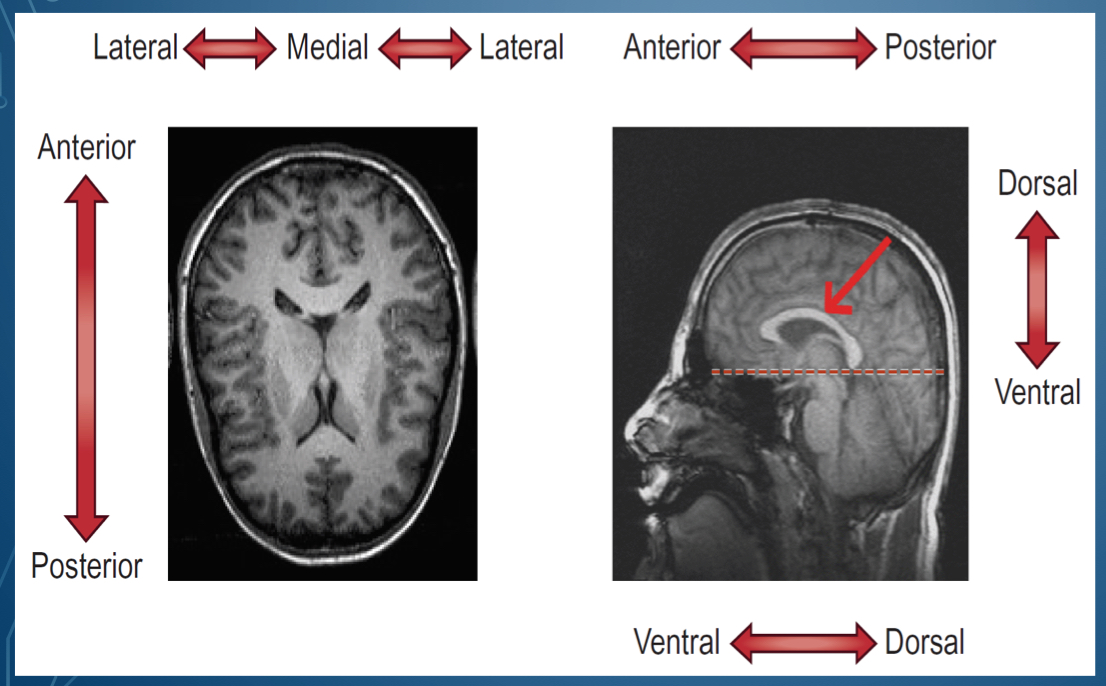
Where is ventral located
bottom of brain
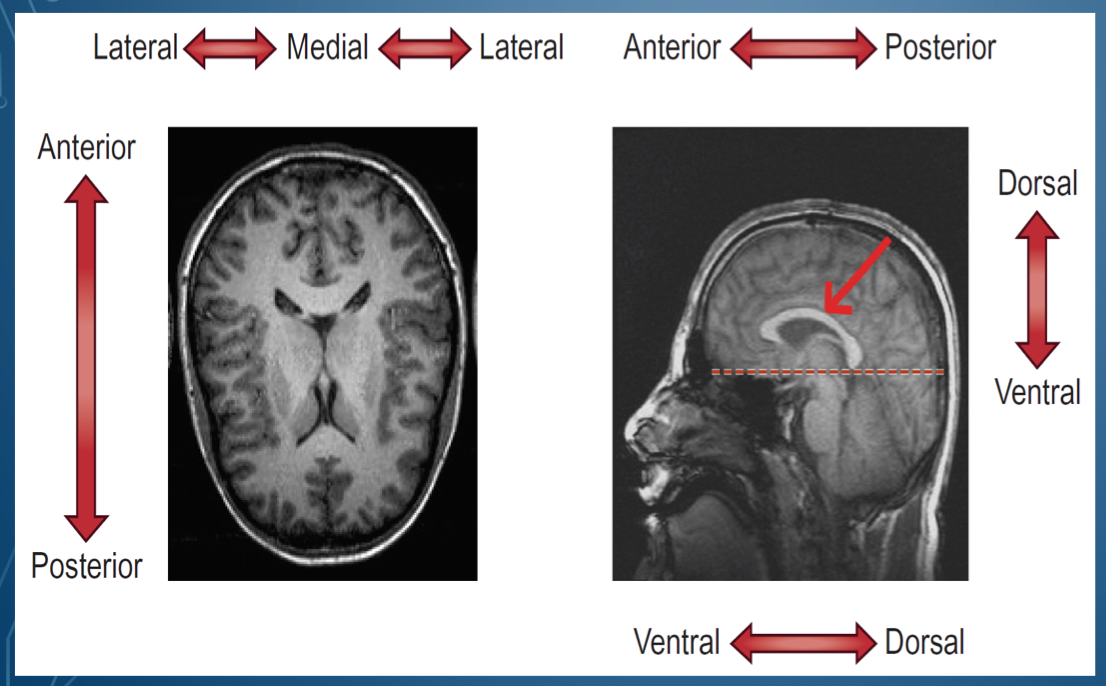
What is the top of the head called
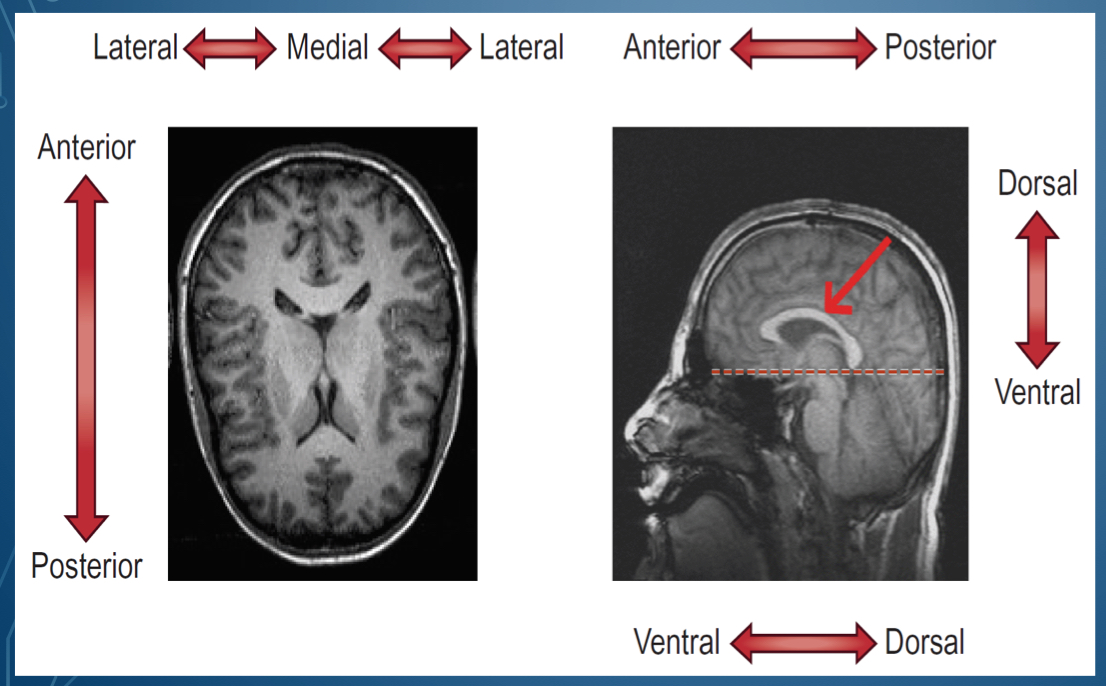
Side of the head is called
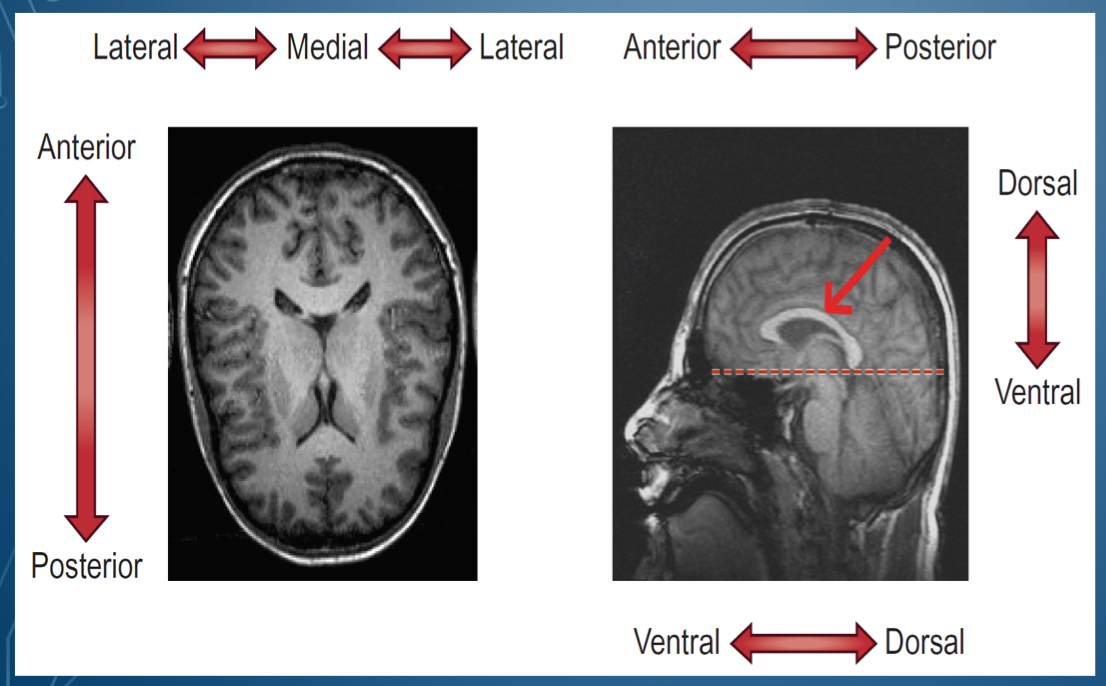
in front of the head is \__________
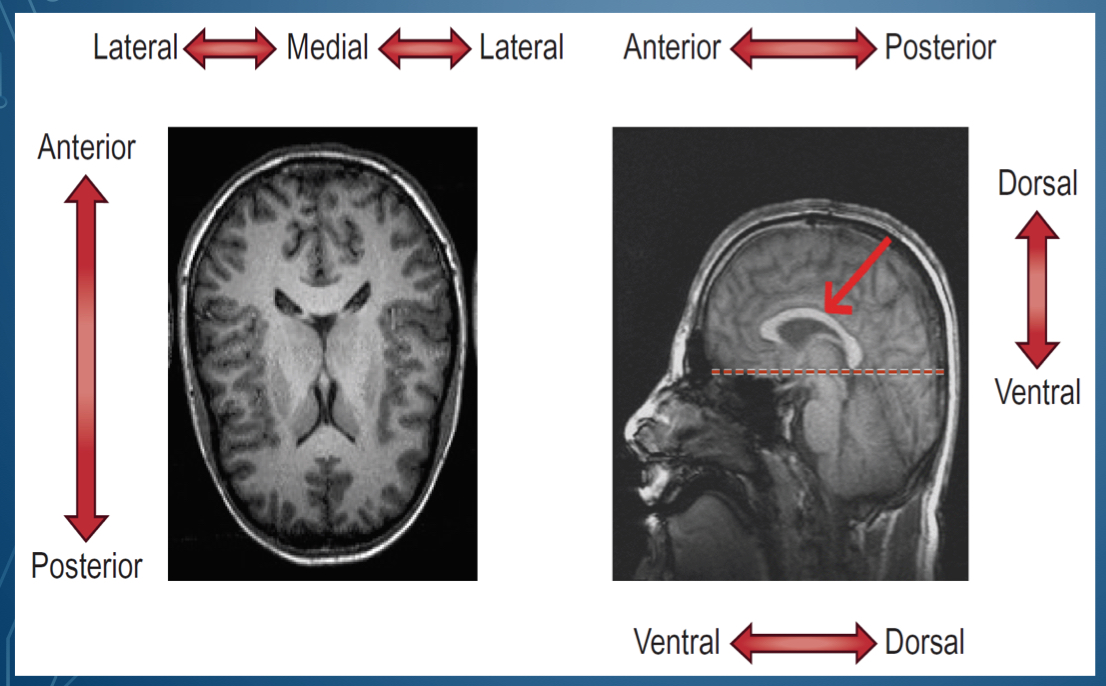
back of the head is \__________
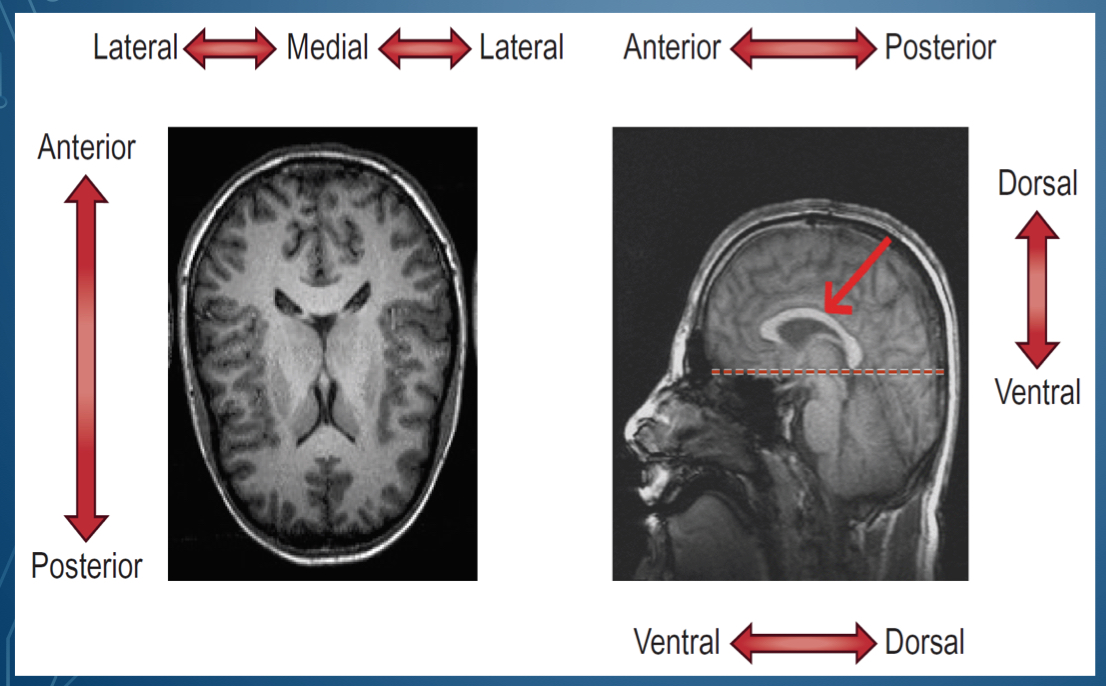
middle of the lateral sides is called
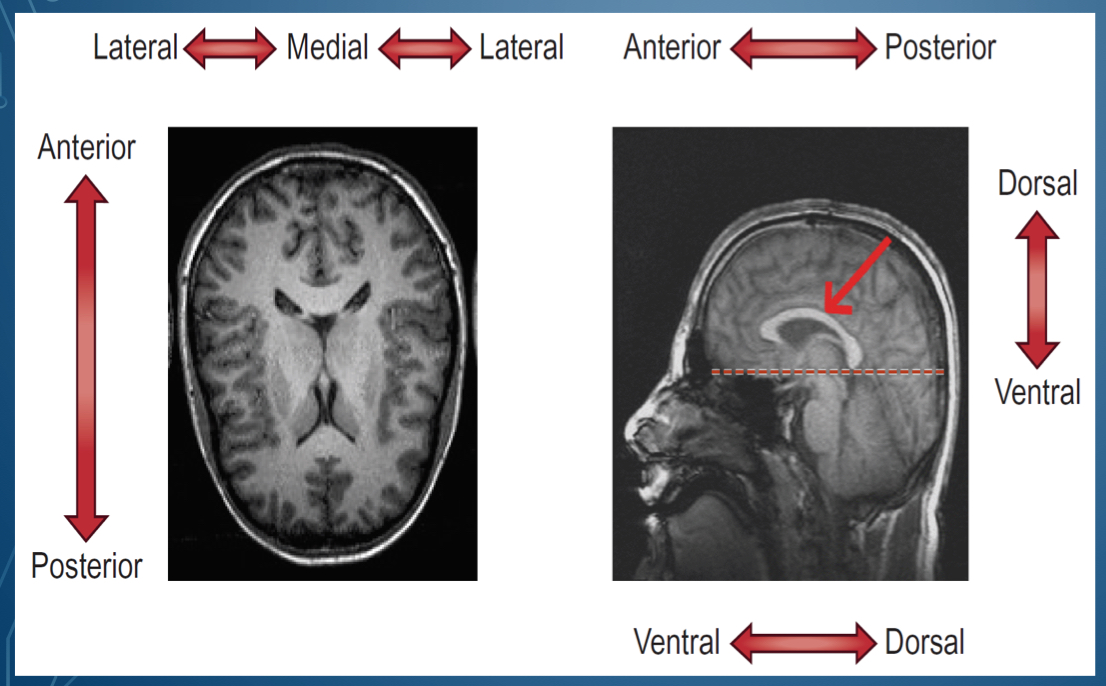
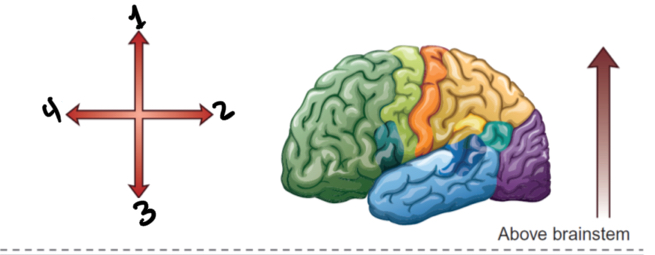
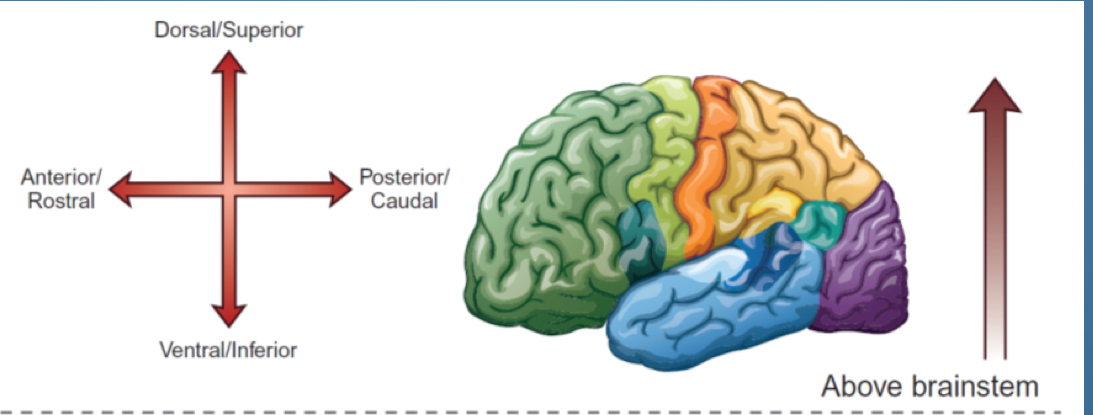
1. Dorsal/ superior
2. Posterior / caudal
3. Ventral/ inferior
4. Anterior/ rostral
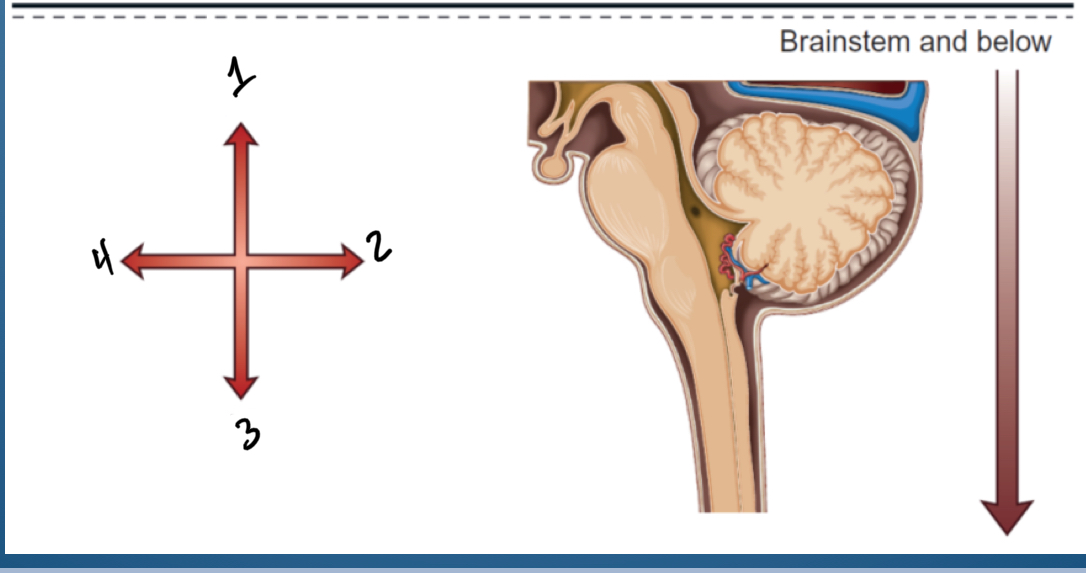
1. Superior , cephalad, rostral
2. Posterior dorsal
3. Inferior, caudal
4. Anterior ventral
Surface
Wrinkles:
Brain ( cerebrum)
Surface
Bulges:
Gyri
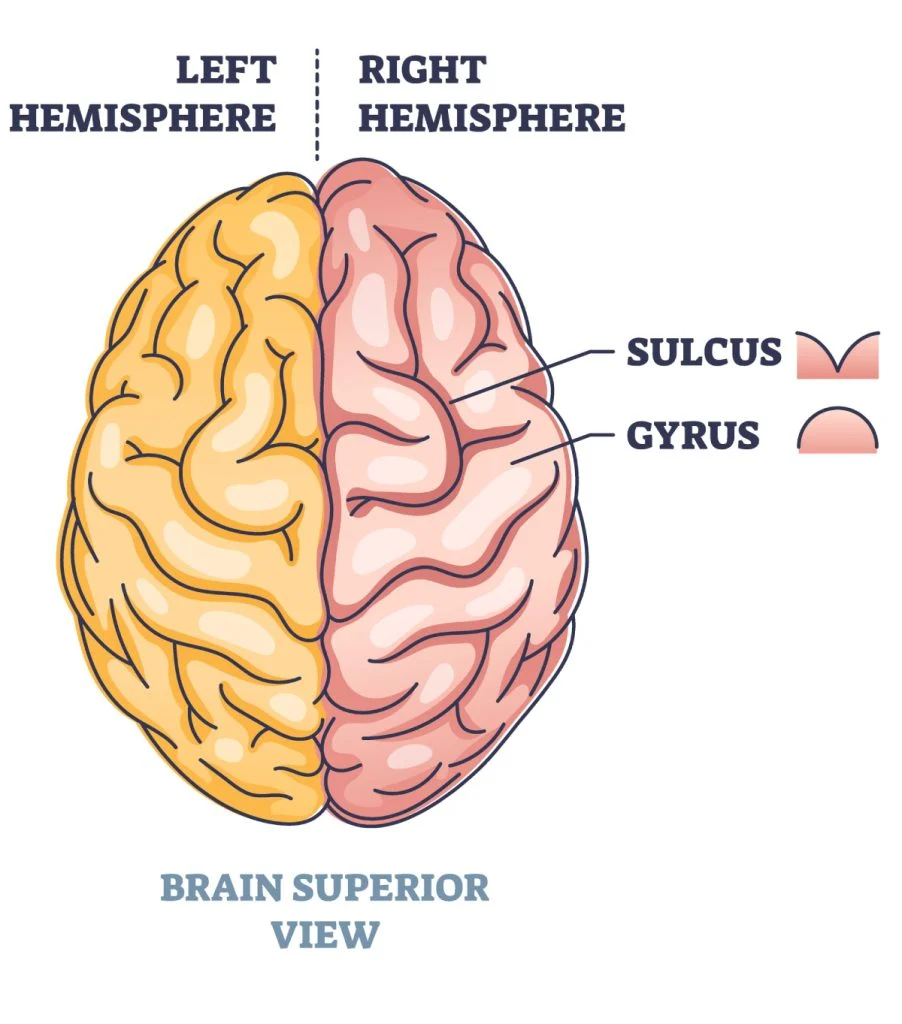
Surface
Cortex gray cell bodies (nucleus) have how many layers
Surface
What is white matter in the surface of the brain
Brain ( cerebrum)
Surface
Ventricles are
Little belly like cavities
Liquid filled cerebral spinal fluid
Aka less white and more volume
Two halves
Separated by groove
Connected
Two halves
What is the groove separates the 2 hemispheres
Surface
How are the 2 hemispheres connected
Brain ( cerebrum)
Building units
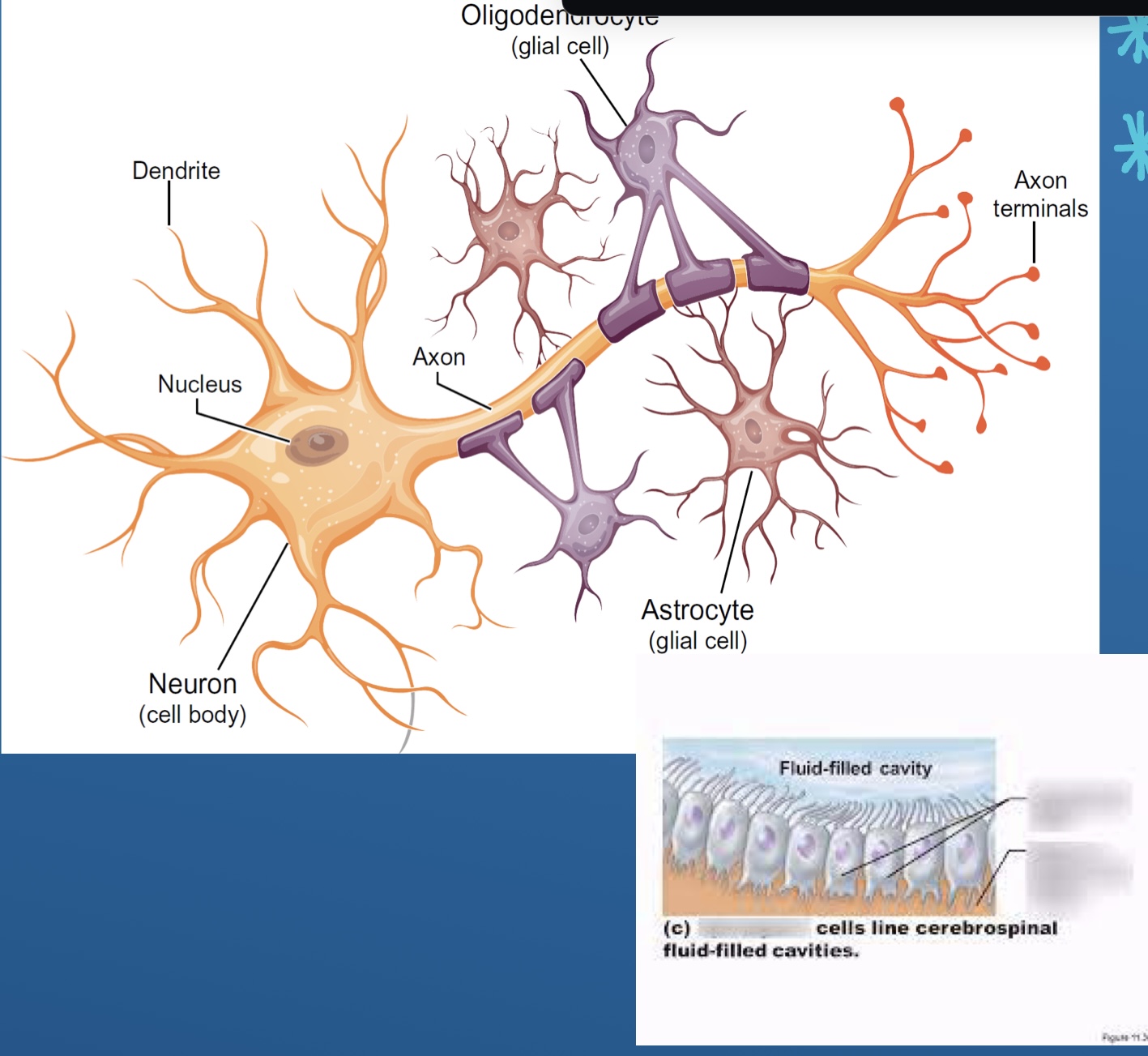
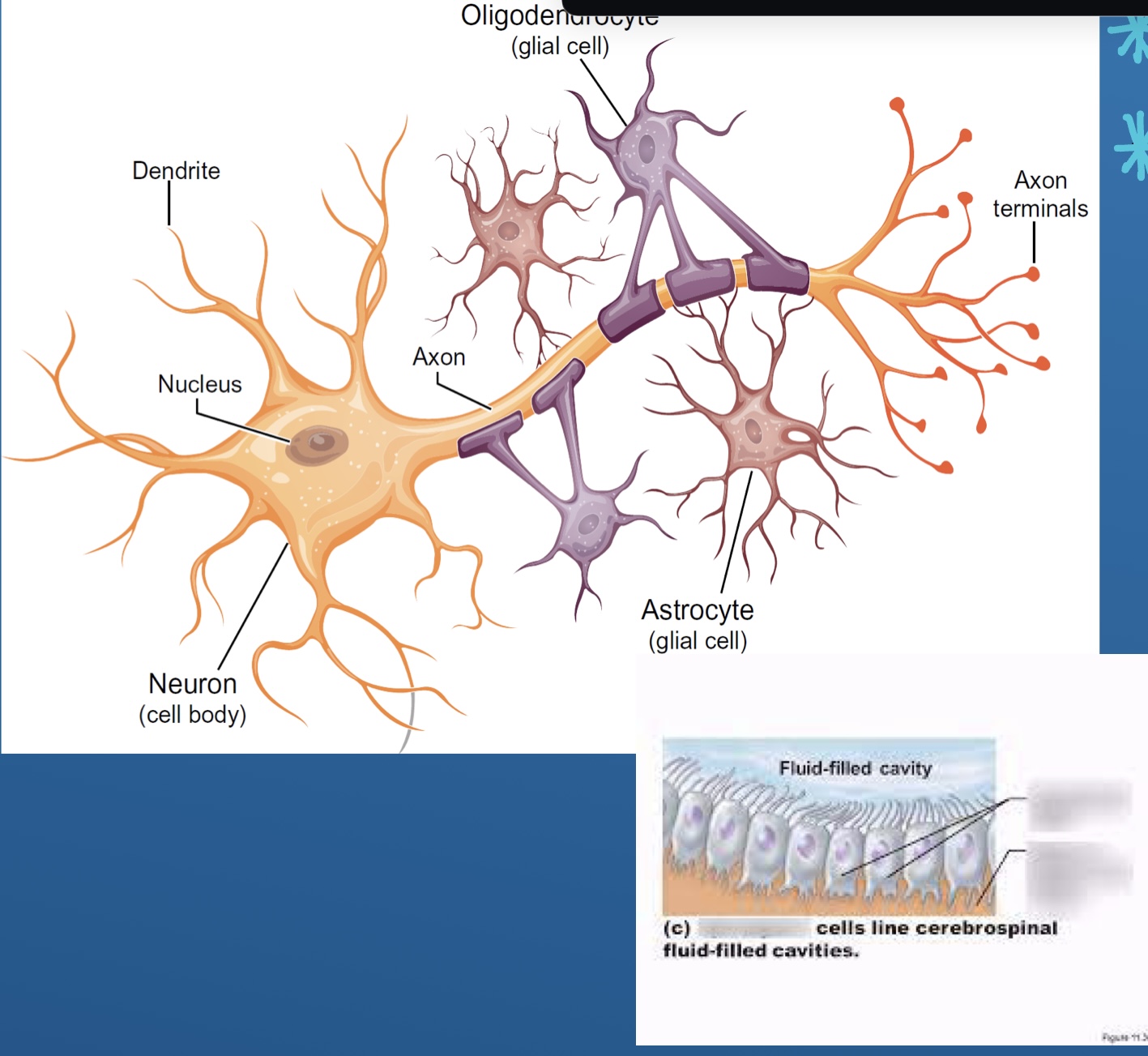
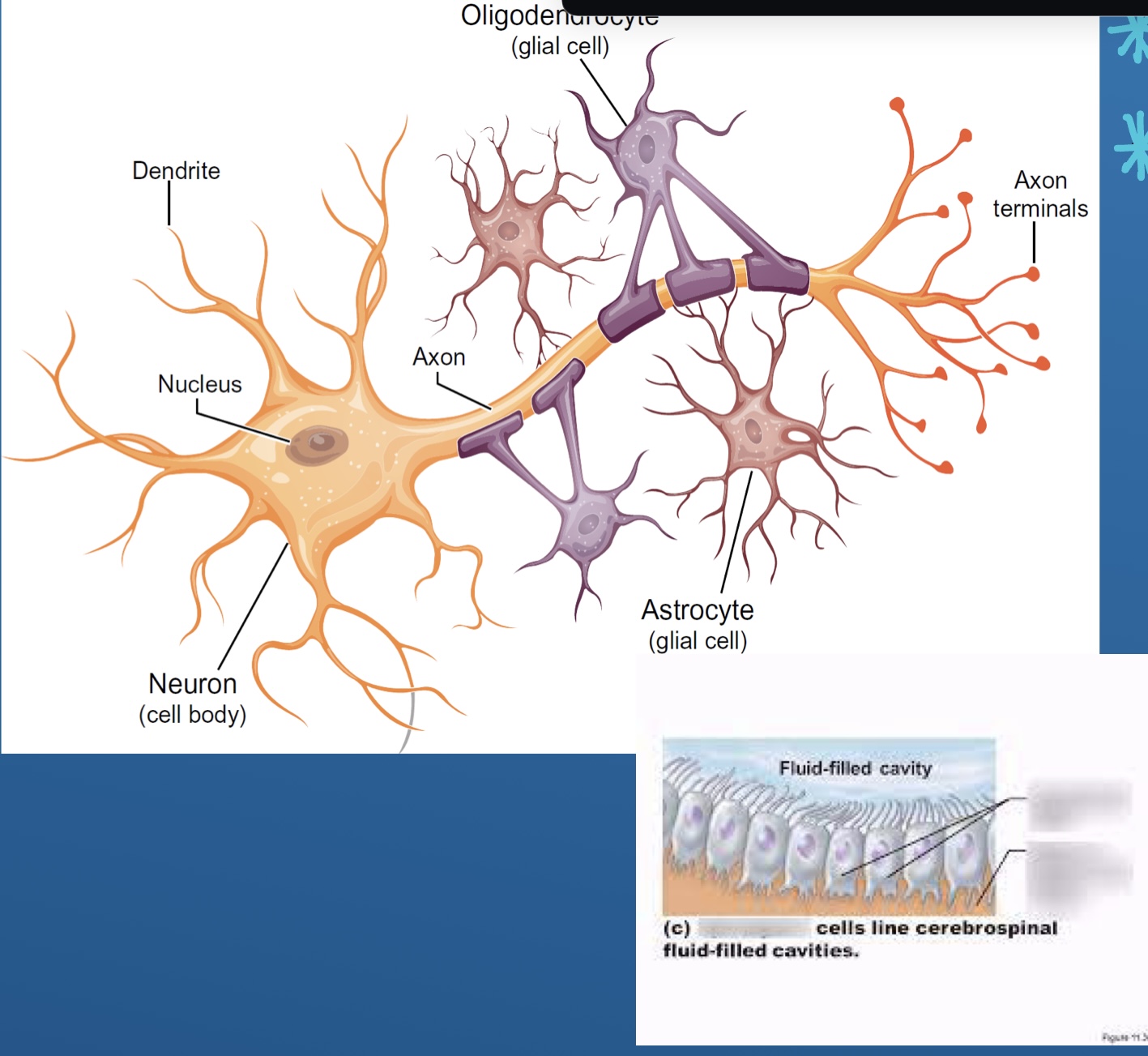
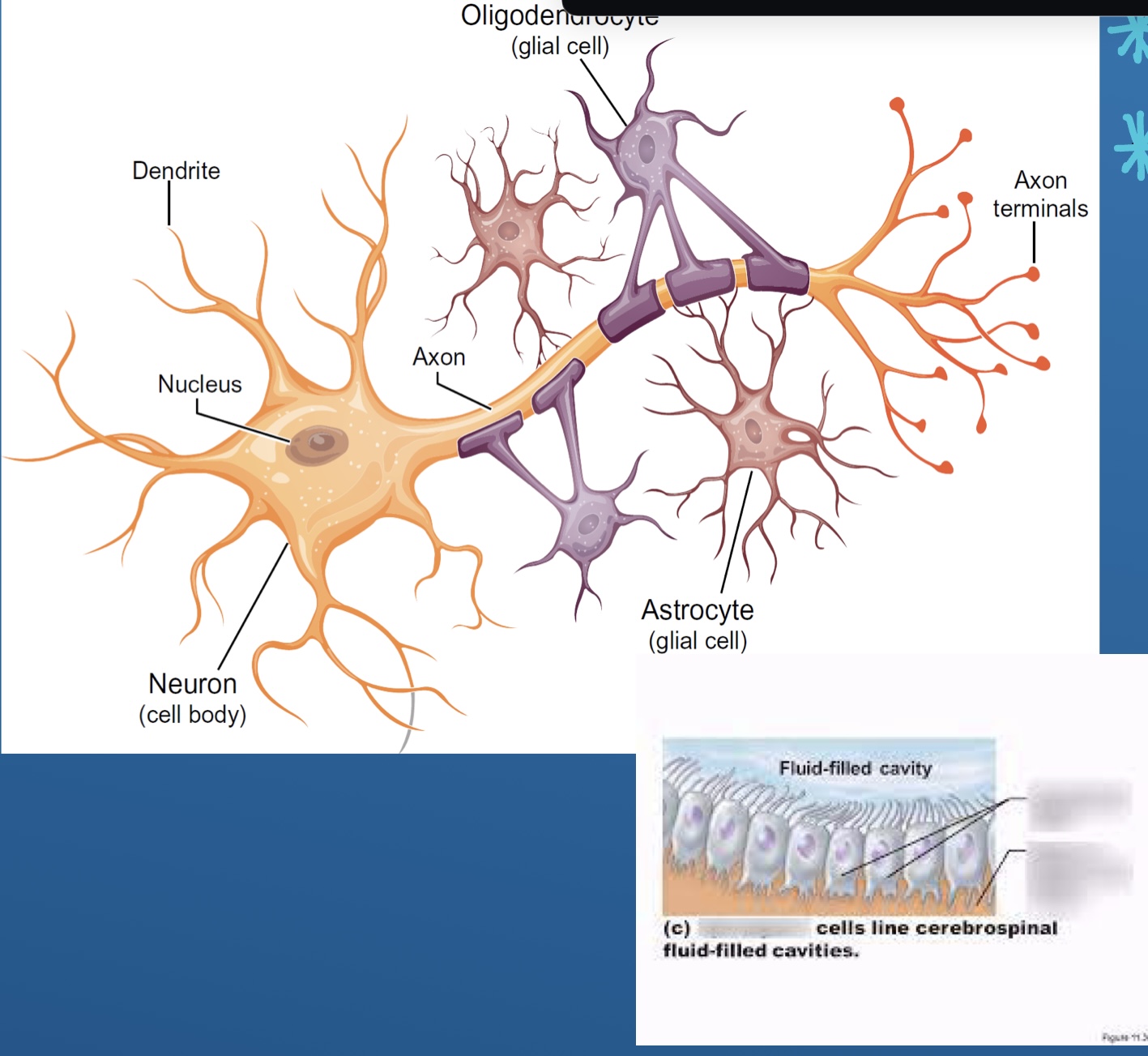
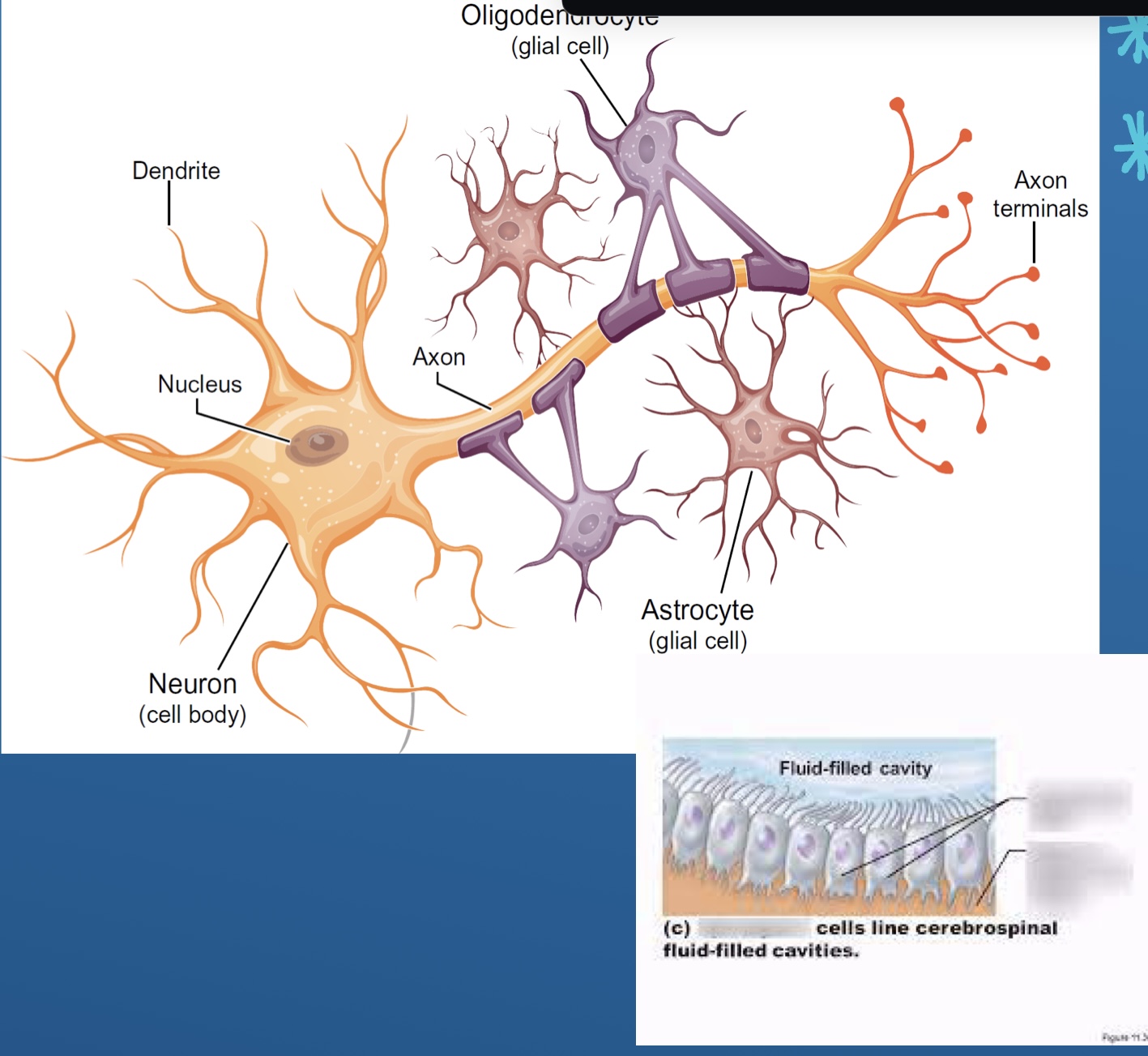
Neurons and glia
Building units
What are neurons
Cell body (gray)
Axon (white)
Building units
What does glia do
Provide structure to keep the brain together
Provide nutrition for the neurons to keep them alive
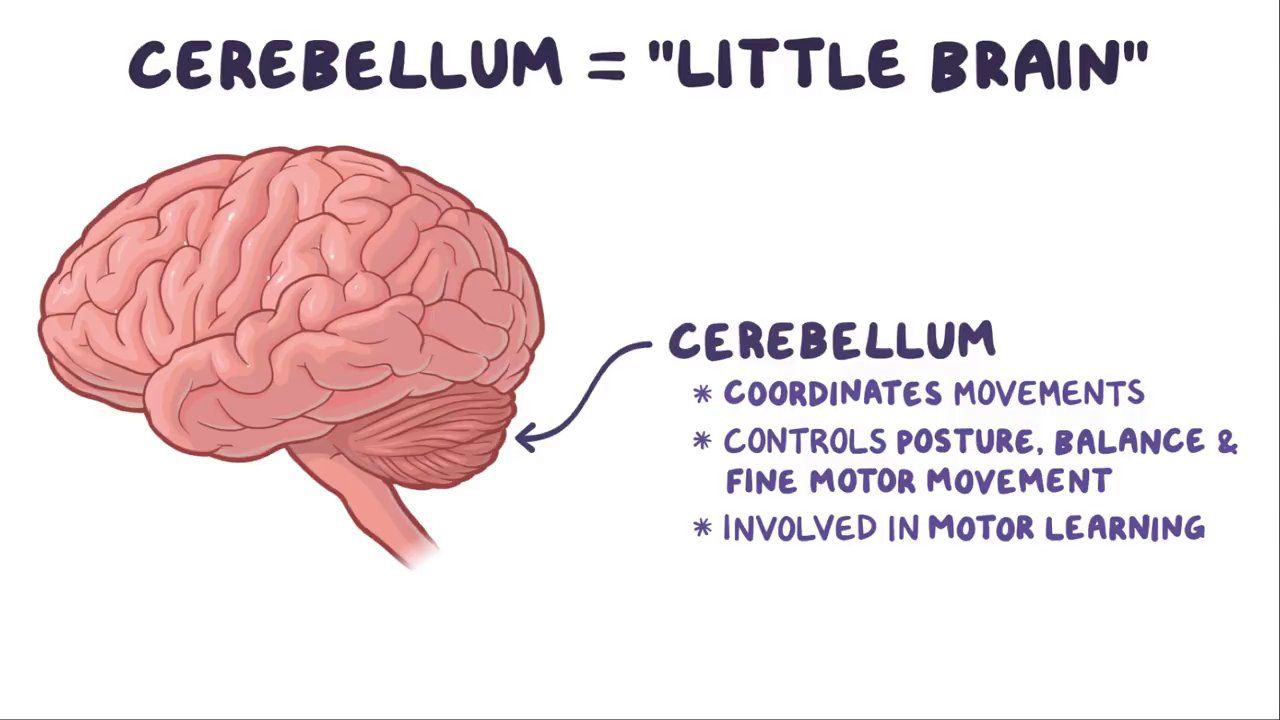
What is cerebellum
Mini brain
-muscle control, including balance and movement. It also plays a role in other cognitive functions such as language processing and memory.
Signaling cells
Their is multiple types
Non signaling cells
\
And ependymal cells
Nervous system cells
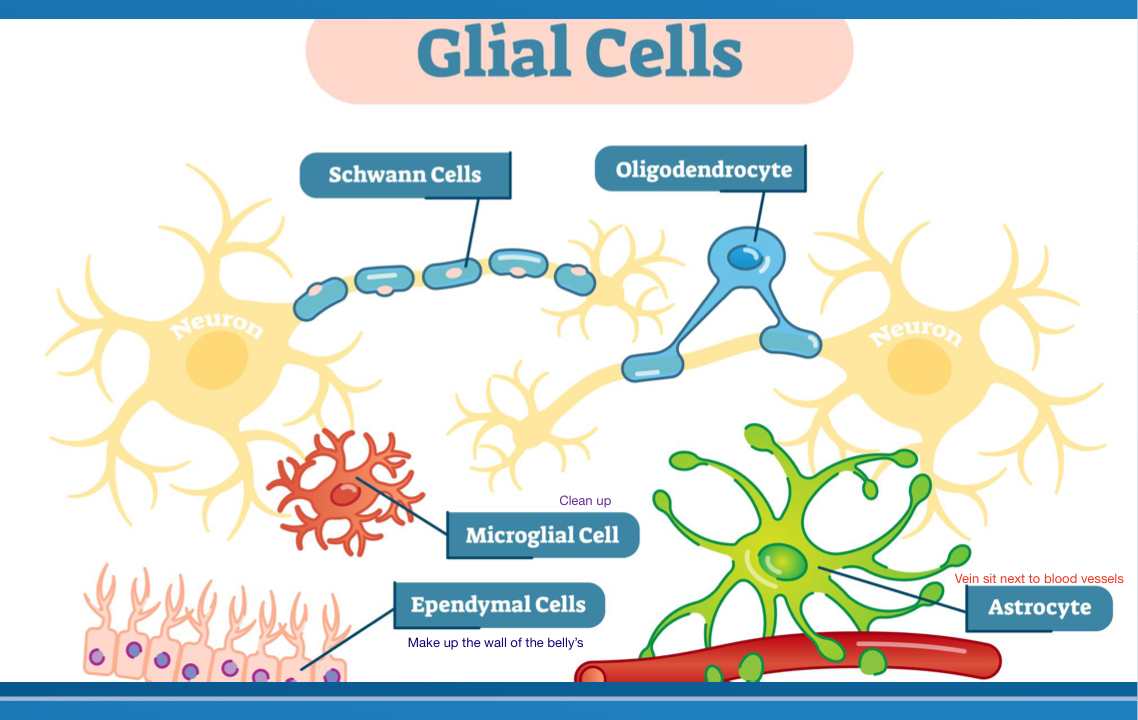
Name 4 of the glial cells (non signaling cells ) and Ependymal
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Schwann cells
Ependyma
Is there only one non signaling cells that is ependymal
What’s the name
Ependyma
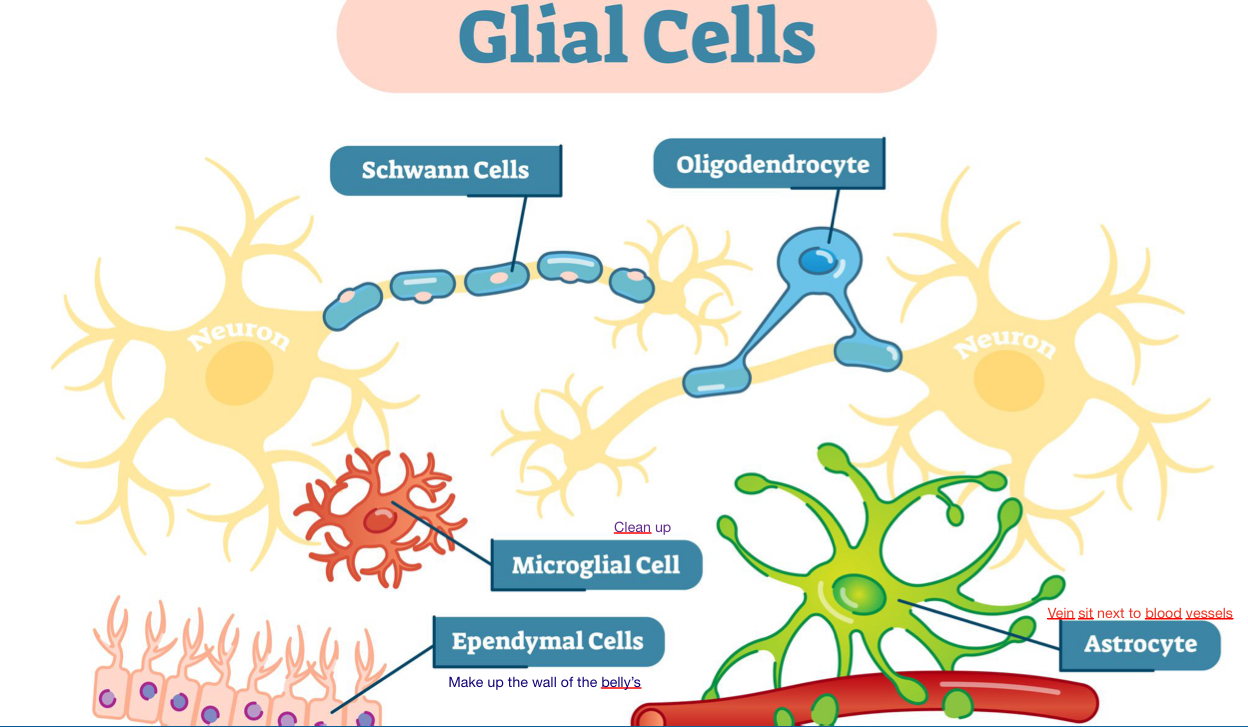
Name all the glial cells (4)and Ependymal cell
Astrocytes
Oligodendrocytes
Microglia
Schwann cells
Ependyma cells
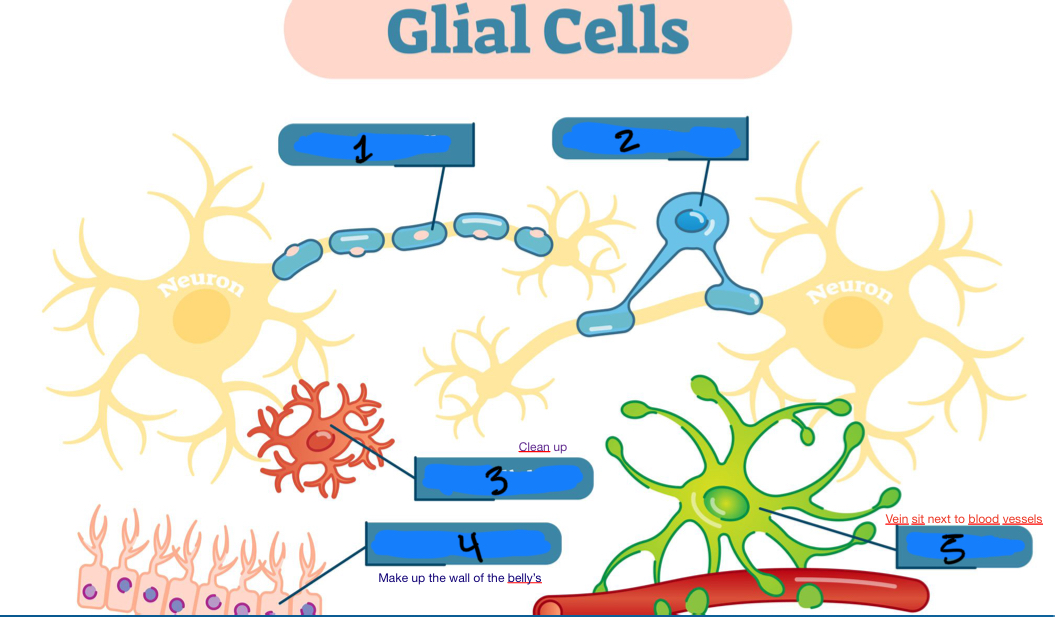
1. Schwann cell
2. Oligodendrocyte
3. Microglial cell
4. Ependymal cells
5. Astrocyte
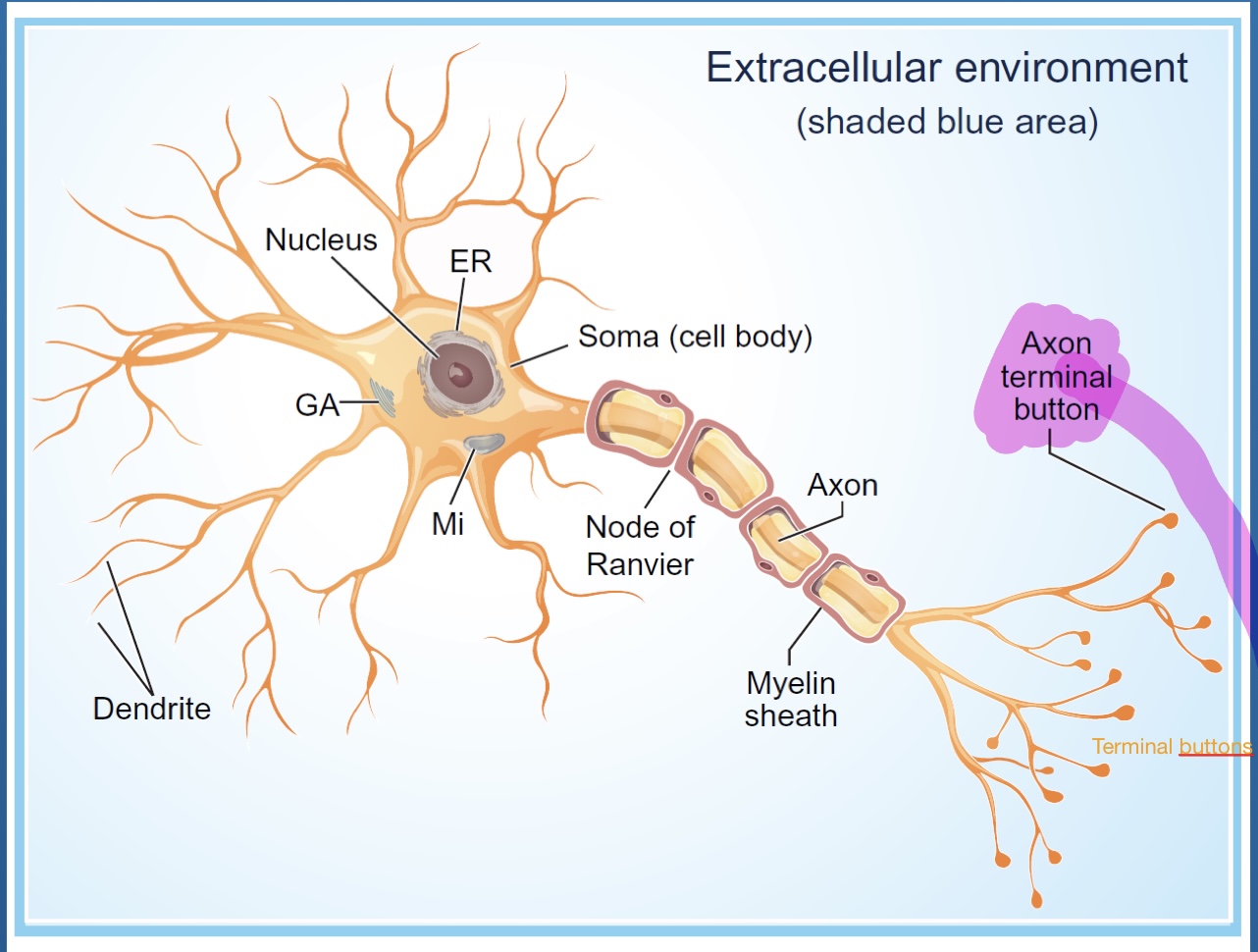
Neurotransmitter (transmits signal) transported from the cell body to terminal buttons
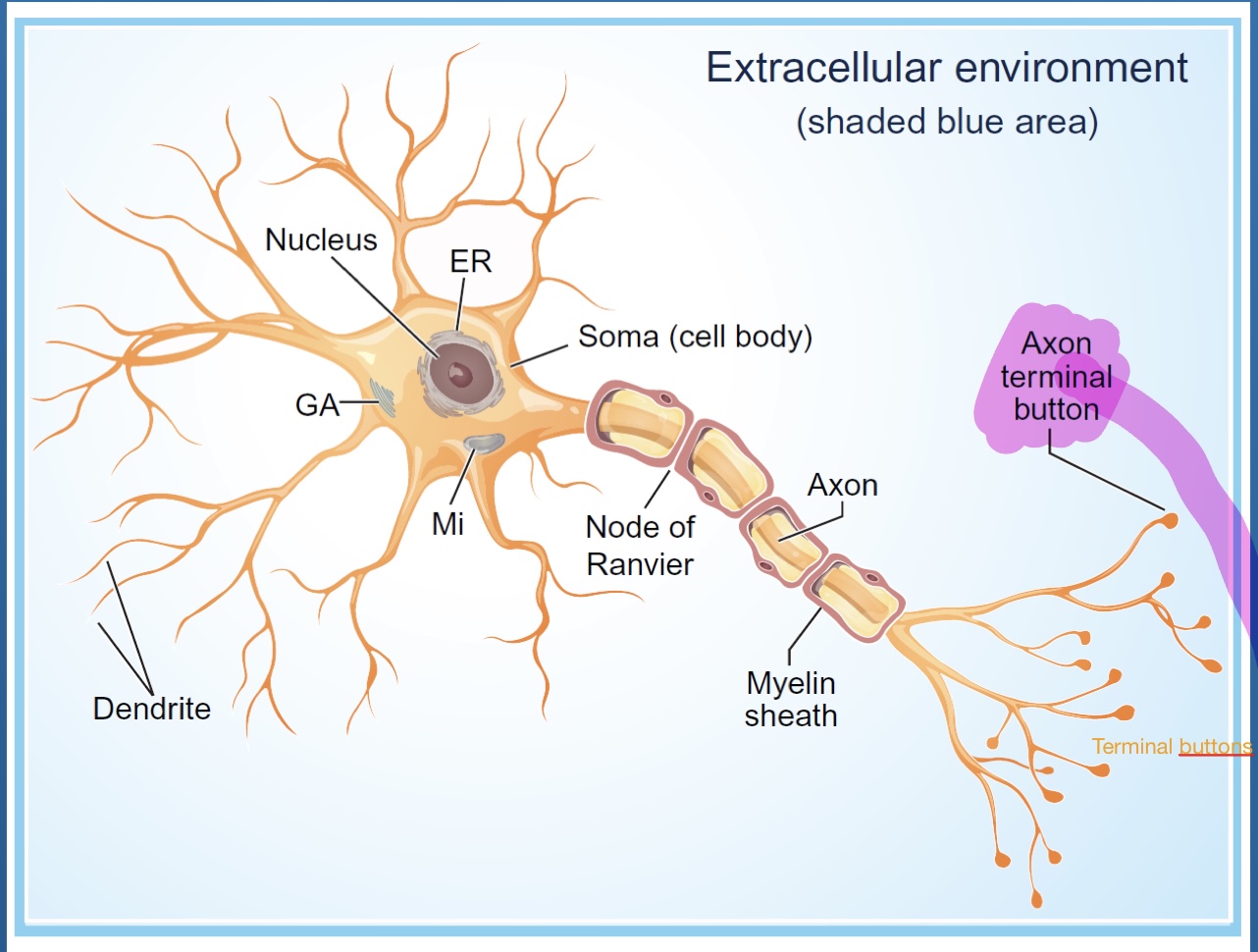
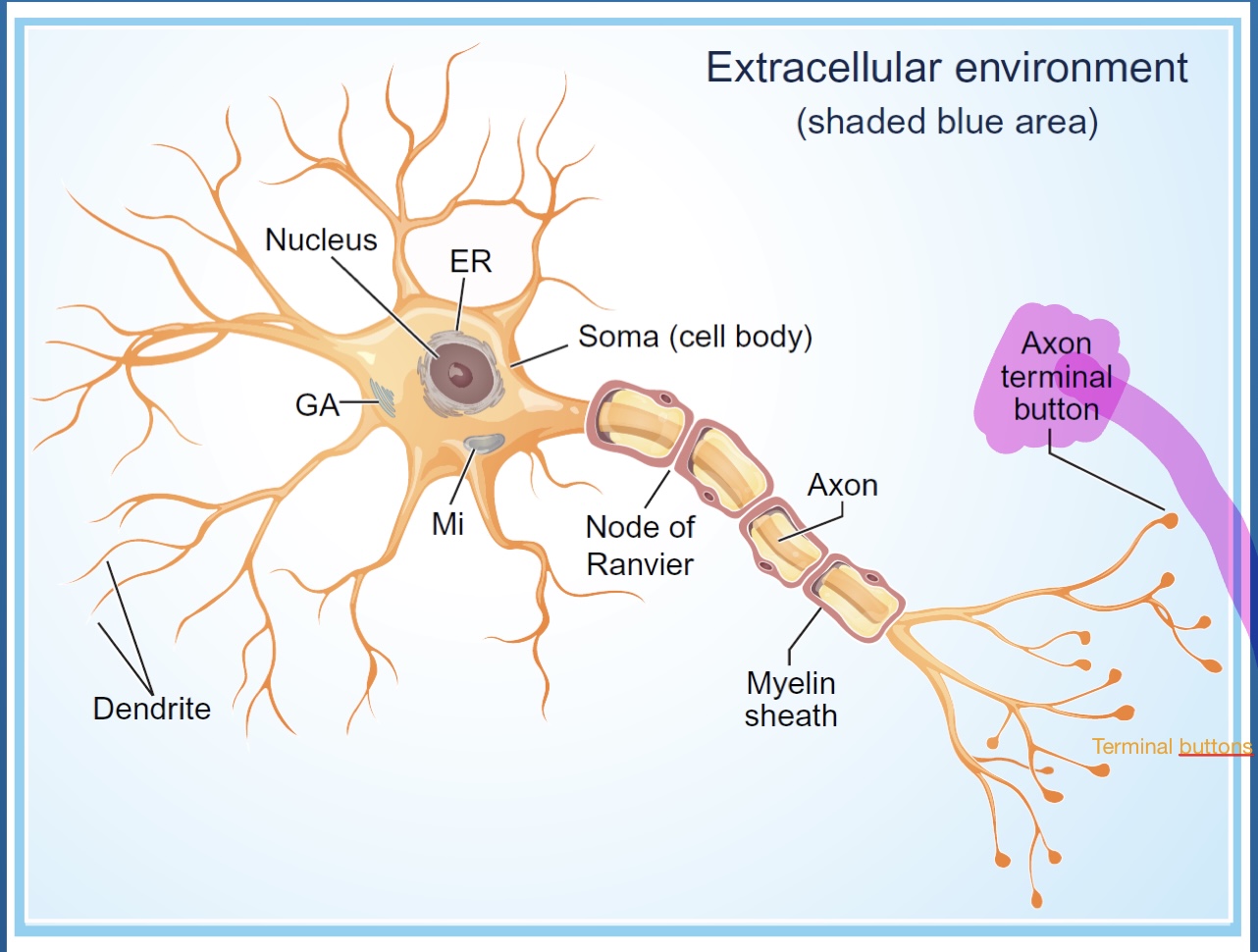
What does glial cells do for neurons?
They are structure support for neurons
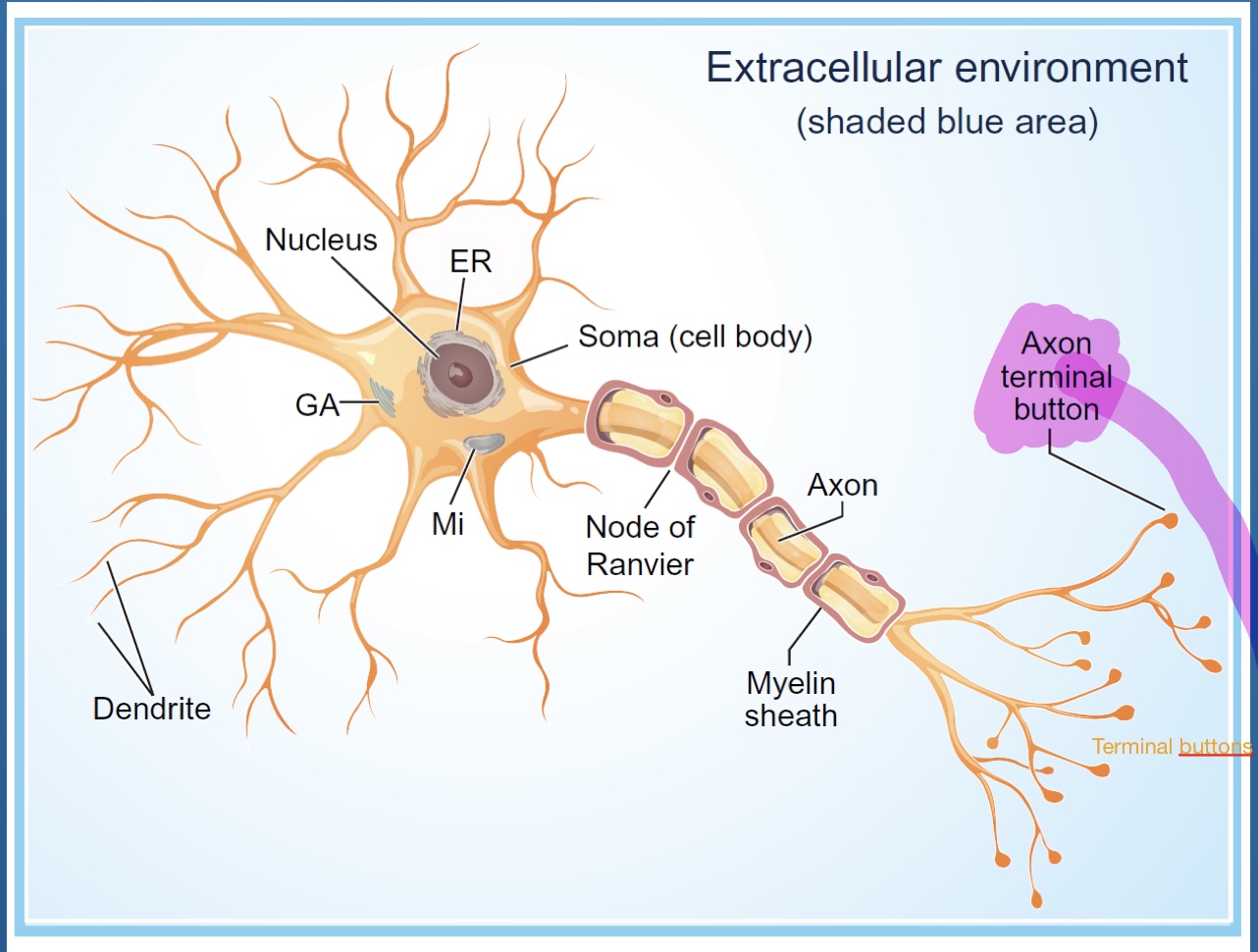
Name each Glial cell? (5)
Oligodendrocytes (CNS)
Schwann cells
Astrocytes
Microglia
Apendymal cells
\
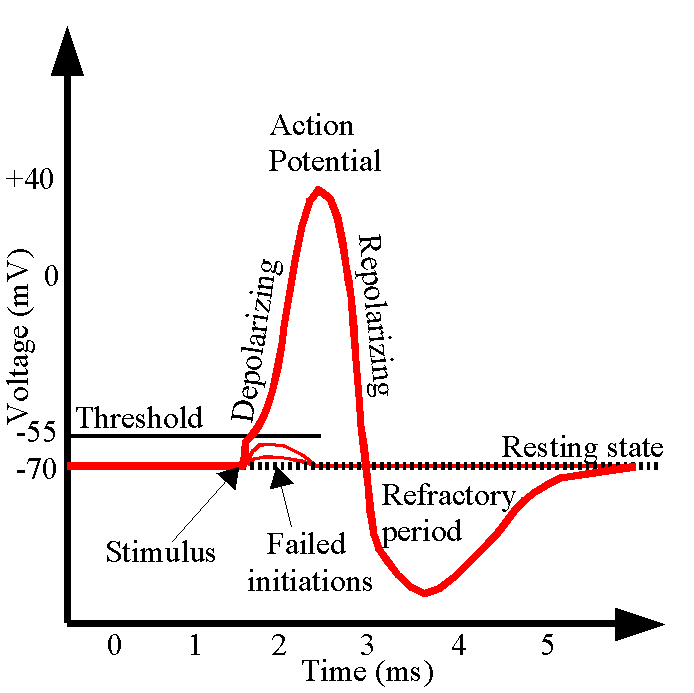
What happens when channels in the membrane allow NA+ (sodium) ions to pass into the cell?
Makes its charge more positive
What is it called when NA+ (sodium) ions rush into the cell and the “neuron fires”
Depolarazing
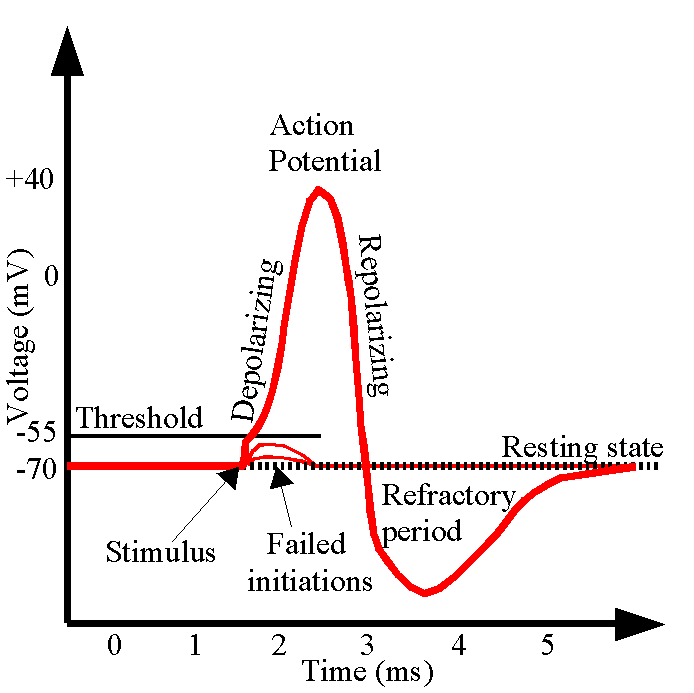
For a short time if the potentioal goes below the resting potential
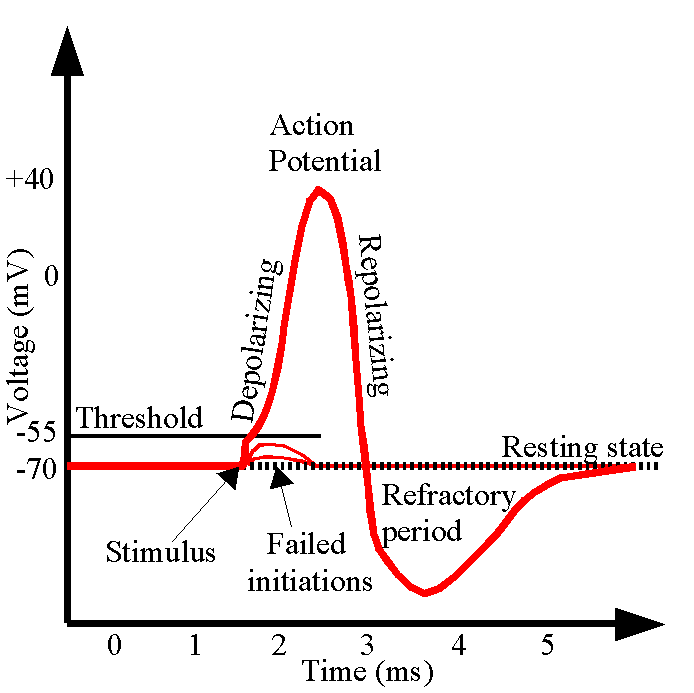
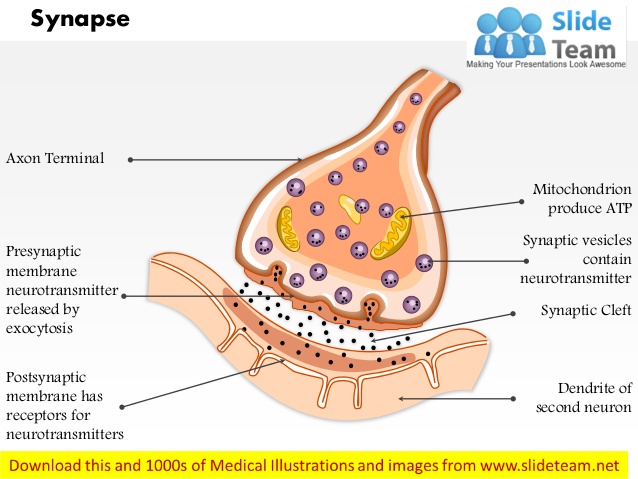
What is Presynaptic membrane?
Terminal button of peripheral motor nerve
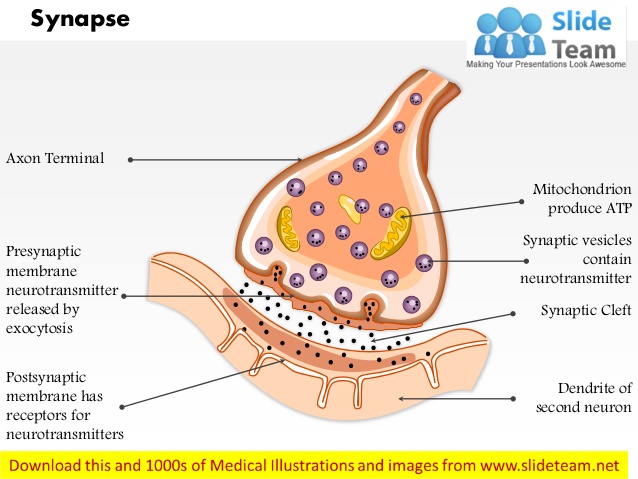
What is Postsynaptic membrane?
motor end plate
(HINT glial cell)
a mixture of proteins and lipids, that help conduct signals and protect axons
Lateralized function is _______
Asymmetric
dominant function
the view that distinct brain regions perform certain functions.
ex: L dominant hemisphere : language
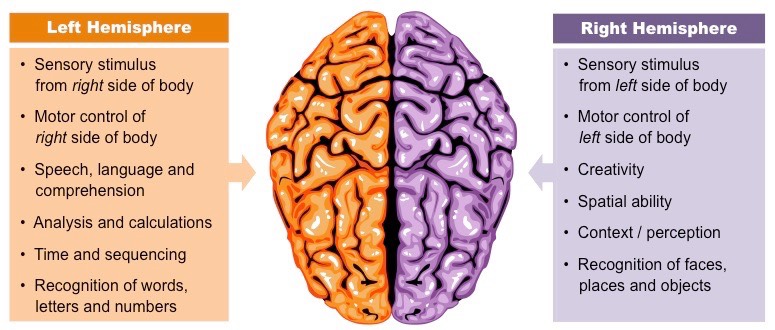
autonomic (Automatic)
skeletal
breathing for speech
aka organs
special