AQA A-Level PE Paper 1 Topics
1/302
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
303 Terms
fitness
the ability to cope with the demands made during an individual day to day life
cardiac output
The volume of blood pumped out from the hearts left ventricles in one minute. stroke volume x heart rate
stroke volume
the volume of blood pumped by the left ventricle in each contraction
heart rate
number of beats per minute
bradycardia
resting heart rate below 60bpm
venous return
the volume of blood returned to the hearts right atrium per min via the veins
max heart rate
220-age
starlings law
greater stretch leads to the greater the force of contraction, the greater the ejection faction/stroke vol
cardiac hypertrophy
increased cardiac muscle mass
cardiac conduction system
a group of specialised cardiac muscle cells in the walls of the heart that send signals to the heart tissue
sinoatrial node
pacemaker of the heart
atrioventricular node
where the impulse pauses in the cardiac conduction system
sympathetic
'Fight or flight' - speeds up heart rate
Parasympathetic
Maintains heart rate at rest - slows down heart rate
Anticipatory Rise
Increase in heart rate in anticipation of an event
Myogenic
generated within muscle tissue
vascular shunting
Blood can be redistributed to body parts
Chemoreceptors
Detect changes in chemicals eg CO2, lactic acid
medulla oblongata
In the brain, where Cardiac control centre and respiratory control centre are found
tidal volume
Amount of air that moves in and out of the lungs per breath
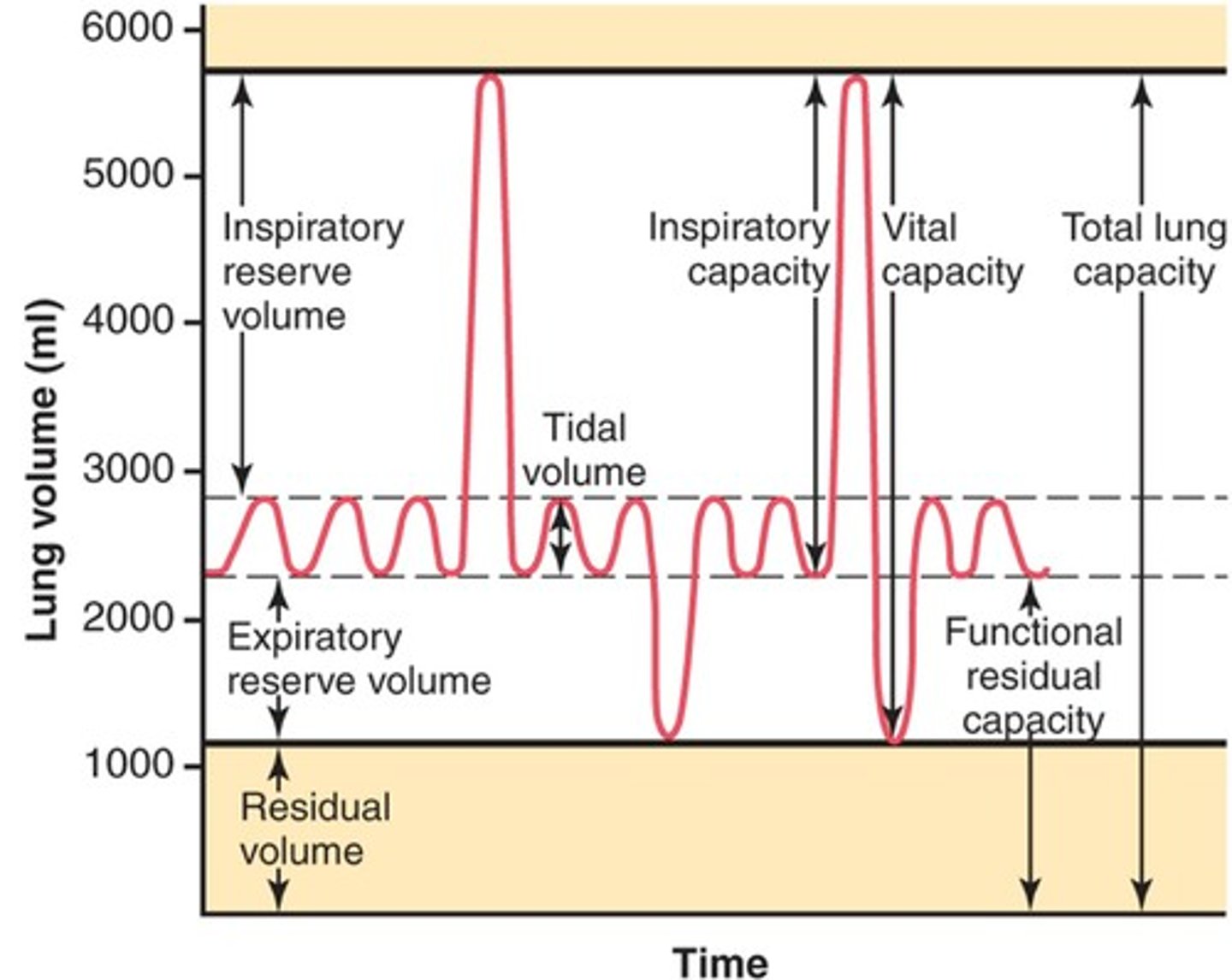
inspiratory reserve volume
maximum amount of air that can be forcebly inspired in addition to tidal volume
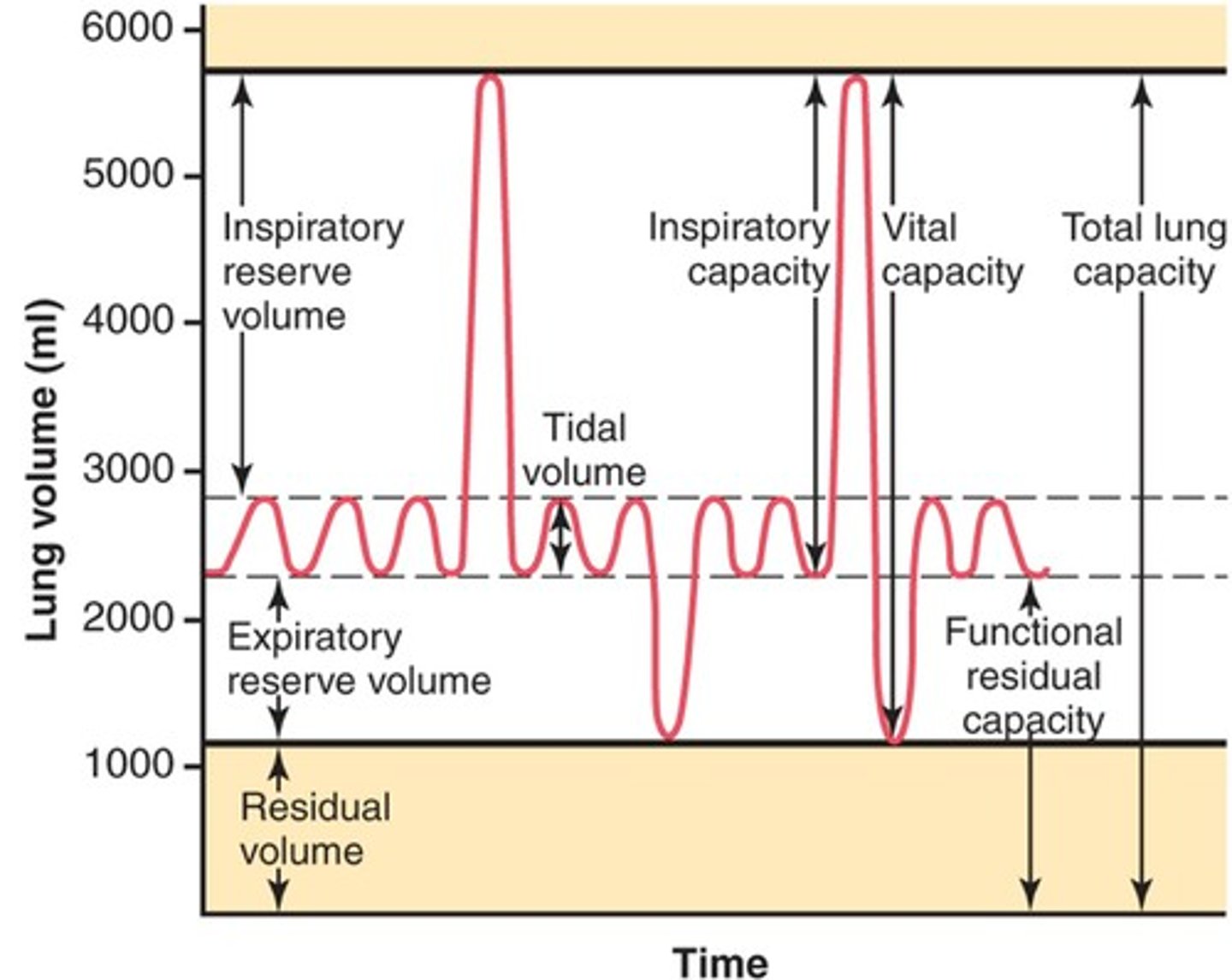
expiratory reserve volume
maximum amount of air that can be forcibly expired in addition to tidal volume
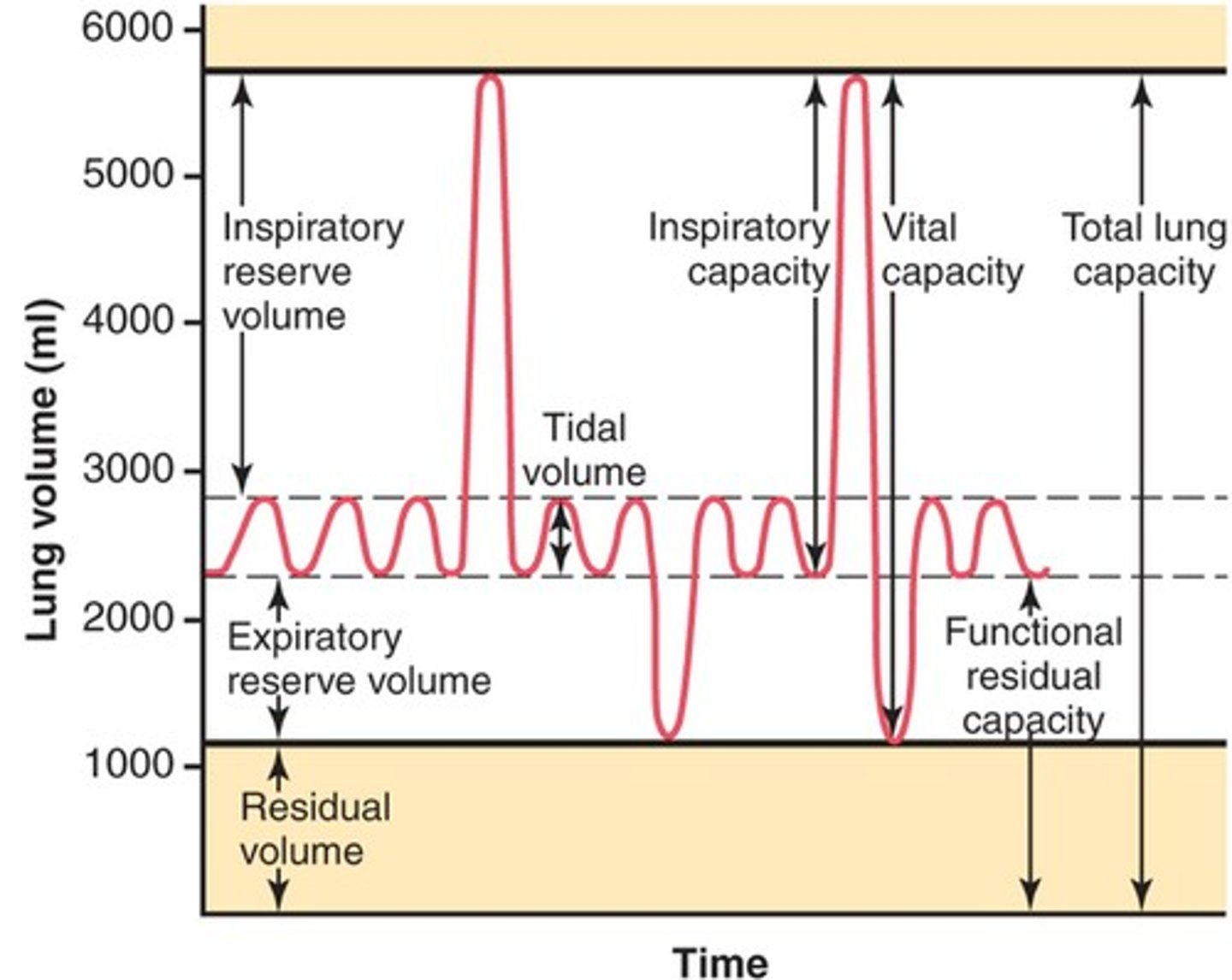
vital capacity
Maximum volume of air exhaled after a maximal inspiration
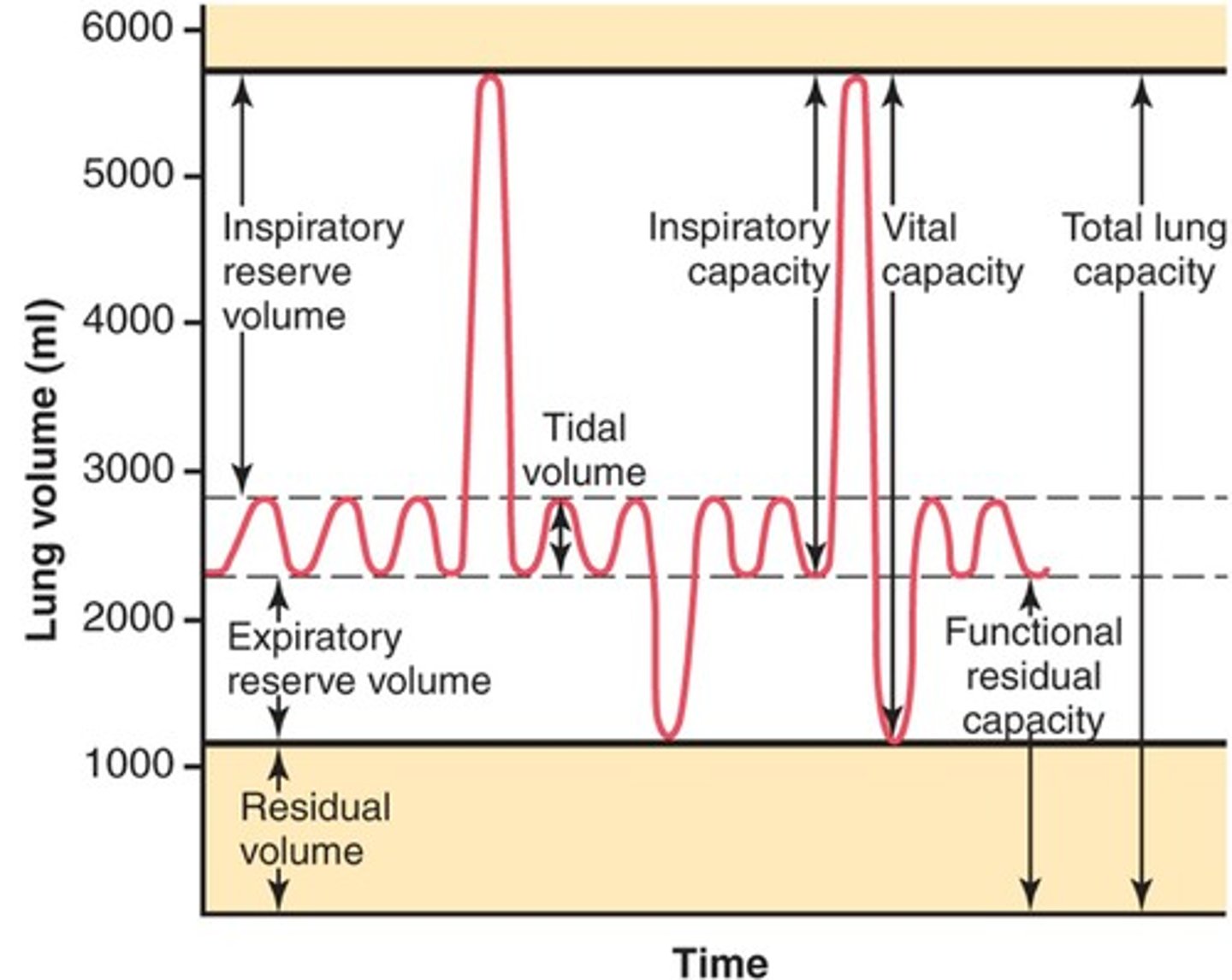
residual volume
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a maximal expiration
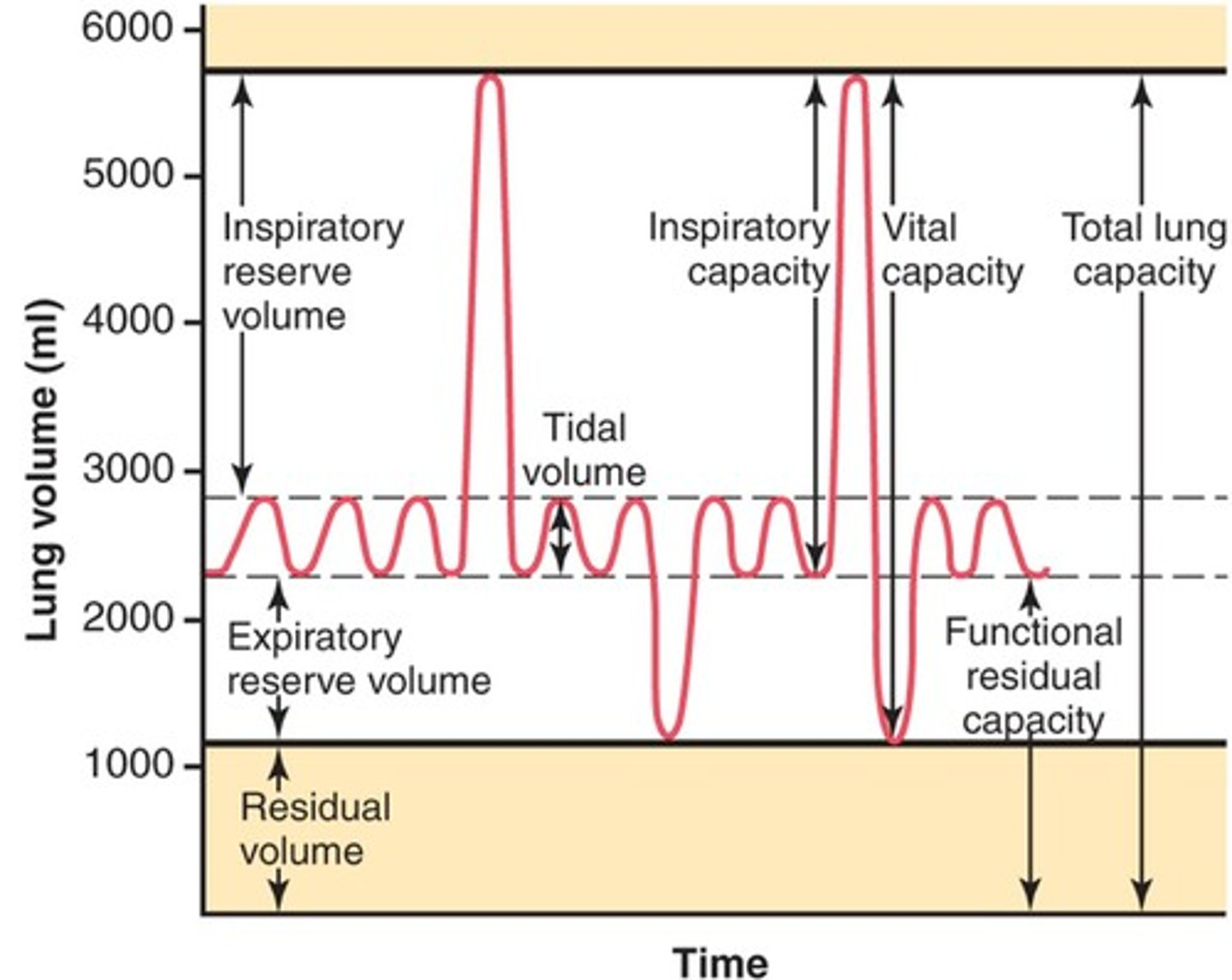
total lung capacity
vital capacity + residual volume
minute ventilation
The amount of air moved in and out of the lungs per min
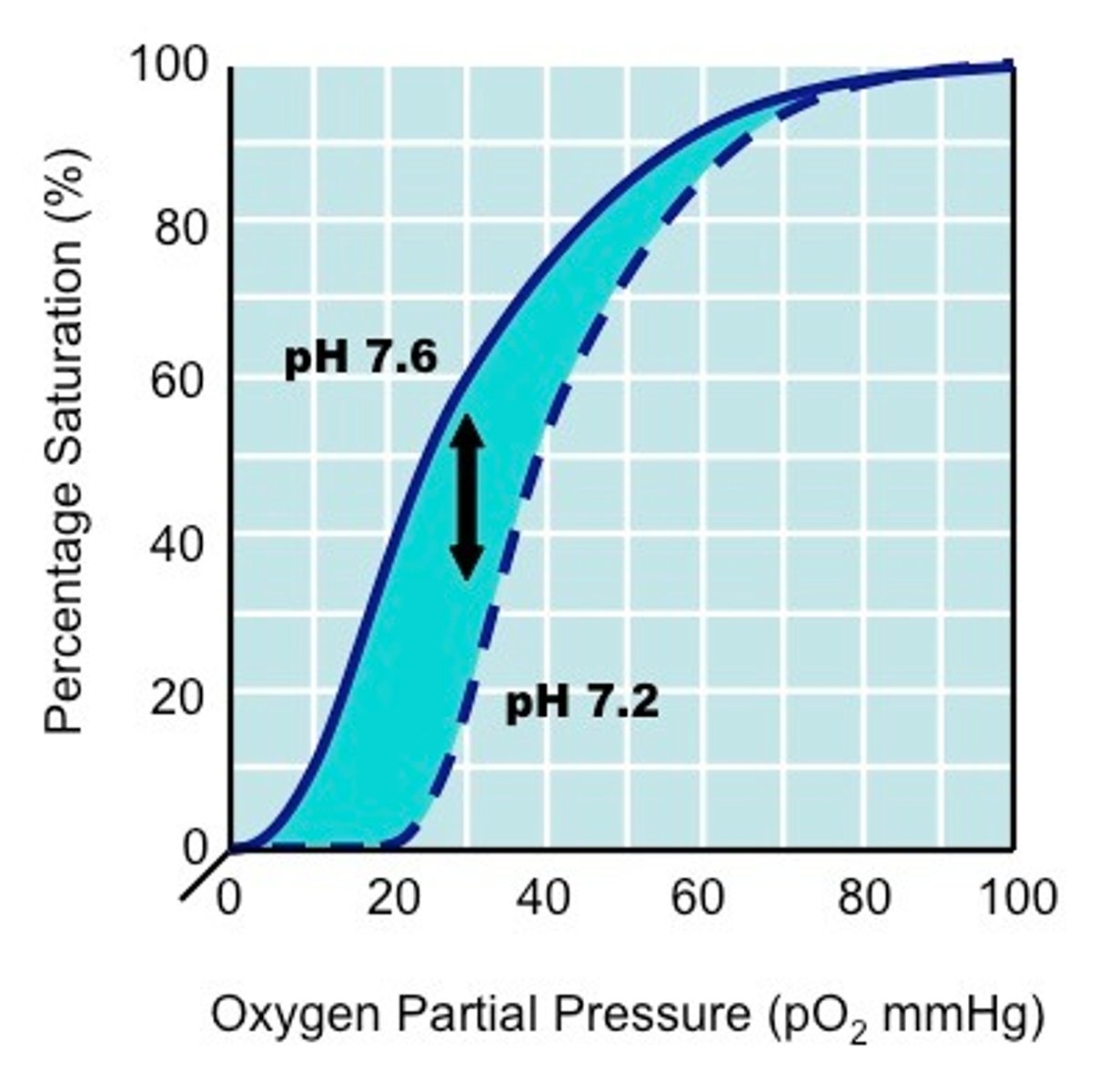
bohr shift
when an increase in CO2 acidity and temperature results in a reduction of the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen. graph shifts to the right.
role of the inspiratory centre
responsible for inspiration and expiration
role of the expiratory centre
stimulates the expiratory muscles during exercise
The order of neural/chemical control for increased inspiration during exercise is:
Receptors - medulla oblongata - phrenic nerve - inspiratory muscles (diaphragm, external intercostals, scalenes and pectoralis minor)
The order of neural/chemical control for expiration during exercise is:
Receptors - medulla oblongata - intercostal nerve - abdominals and internal intercostals
ball and socket
a joint that allows movement in every direction
hinge joints
a joint that that allows movement in only one direction
sagittal plane
a vertical plane that divides the body into a right and left half elbow and knee
frontal plane
a vertical plane dividing the body into the front and back.
transverse plane
a horizontal plane which divides the body into upper and lower halves
agonist
The muscle responsible for the movement that is occurring
antagonist
the muscle that works in opposition to the agonist
Name the agonist & antagonist in elbow flexion
agonist - Biceps
antagonist - Triceps
Name the agonist & antagonist in elbow extension
agonist - Triceps
antagonist - Biceps
Name the agonist & antagonist in ankle plantar-flexion
agonist - Gastrocnemius
antagonist - Tibialis anterior
Name the agonist & antagonist in ankle dorsi-flexion
agonist - Tibialis anterior
antagonist - Gastrocnemius
Name the agonist & antagonist in knee flexion
agonist - Hamstrings
antagonist - Quadriceps
Name the agonist & antagonist in knee extension
agonist - Quadriceps
antagonist - Hamstrings
Name the agonist & antagonist in Hip flexion
agonist - Hip flexors
antagonist - Gluteals
Name the agonist & antagonist in Hip extension/hyper-extension
agonist - Gluteals
antagonist - Hip flexors
Name the agonist & antagonist in hip adduction
agonist - Adductors
antagonist - Tensor fascia latae/gluteals
Name the agonist & antagonist in hip abduction
agonist - Tensor fascia latae/gluteals
antagonist - Adductors
Name the agonist & antagonist in hip horizontal adduction
agonist - Adductors
antagonist - Tensor fascia latae/gluteals
Name the agonist & antagonist in hip horizontal abduction
agonist - Tensor fascia latae/gluteals
antagonist - Adductors
Name the agonist & antagonist in shoulder flexion
agonist - Anterior deltoid
antagonist - Latissimus dorsi
Name the agonist & antagonist in shoulder extension/hyper-extension
agonist - Latissimus dorsi
antagonist - Anterior deltoid
Name the agonist & antagonist in shoulder horizontal abduction
agonist - Latissimus dorsi
antagonist - Pectorals
Name the agonist & antagonist in shoulder horizontal adduction
agonist - Pectorals
antagonist - Latissimus dorsi
Name the agonist & antagonist in shoulder adduction
agonist - Latissimus dorsi/posterior deltoid
antagonist - medial Deltoid/supraspinatus
Name the agonist & antagonist in shoulder abduction
agonist - medial deltoid/supraspinatus
antagonist - Posterior deltoid/Latissimus dorsi
concentric contraction (Isotonic)
when a muscle shortens under tension
eccentric contraction (Isotonic)
when a muscle lengthens under tension
Isometric contraction
when a muscle contracts without lengthening or shortening
partial pressure
the pressure exerted by a gas within a mixture of gases
pressure gradient
the relative difference between the pressure within along a pressure gradient
Gaseous exchange
The movement of oxygen from the air into the blood, and carbon dioxide from blood into the air
diffusion
the net movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration along a pressure gradient
what is the partial pressure of oxygen in the alveoli
100mmHg
identify structural features of alveoli & why
Thin walls (1 cell thick) - short diffusion pathway
Large surface area - greater opportunity for uptake of oxygen
extensive capillary network surround alveoli
what is the partial pressure of oxygen in the capillaries
40mmHg
low-density lipoprotein (LDL)
bad cholesterol - transports cholesterol in blood to tissues
High-density lipoprotein (HDL)
good cholesterol - transports excess cholesterol in the blood back to the liver
Atherosclerosis
hardening and narrowing of the arteries - clogged up by fatty deposits
ischaemic strokes
occur when a blood clot stops the blood supply to the brain
Haemorragic stroke
occur when a blood vessel supplying the brain bursts
2 types of stroke
ischaemic and hemorrhagic
Stroke
Supply of blood to the brain is cut off
Order the in which cardiac impulse travels
SAN - impulse through atria - atrial systole - AVN - Bundle of His - Purkinje fibres - ventricular systole
Explain cardiovascular drift
Increases heart rate - decreases stroke volume - occurs after 10 min (in warm conditions) - caused by thickening of blood/loss of water through sweat - reduced venous return - therefore HR increases to maintain/increase cardiac output
vasodilation
widening of blood vessels
vasoconstriction
narrowing of blood vessels
veins
carry blood to the heart
Arteries
carry blood away from the heart
Capillaries
The smallest blood vessels, and the site of exchange of chemicals and water between the blood and the tissues
pulmonary ventilation
breathing
systole
contraction of heart
diastole
relaxation of heart
The skeletal muscle pump
when muscle contract, they squeeze against nearby veins causing a pump effect
the respiratory pump
when muscle contract & relax during breathing, pressure changes in the thoracic cavities compress the nearby veins and assist in pumping blood
pocket valves
ensures blood flows in 1 direction & prevents back flow
Gravity (in venous return mechanism)
Blood above the heart is assisted by gravity
what % of oxygen is dissolved in the plasma?
3%
what % of oxygen combines with haemoglobin
97%
when oxygen combines with haemoglobin it creates what
oxyhemoglobin
Arterio-venous difference (A-V02diff)
the difference in oxygen content of the arterial blood arriving at the muscles and the venous blood leaving the muscle
Myoglobin
stores oxygen in the muscles and delivers it to mitochondria
Tidal volume will change in what way during exercise
increase
Min Ventilation will change in what way during exercise
Big increase
Inspiratory reserve volume will change in what way during exercise
decrease
Expiratory reserve volume will change in what way during exercise
slight decrease
Residual volume will change in what way during exercise
no change
adrenaline
the hormone that increases the breathing rate in preparation for exercise
Smoking causes:
irritation of trachea and bronchi
reduced lung function & increased breathlessness due to swelling and narrowing of lungs airways
damage to the cells lining the airways - leading to the build-up of mucus
reduction in efficiency of gaseous exchange
Functional characteristics of muscle fibres
Contraction speed
Motor neurone conduction capacity
Force produced
Fatigability
Aerobic capacity
Anaerobic capacity
Myosin ATPase enzyme activity