PPT16 (Child Meningitis, ADHD)
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Meningitis
spinal meningitis
an inflammation of the meninges (the membranes that line the brain & spinal cord)-- (“__” )
usually caused either by a virus or by bacteria that travel through the bloodstream from an infection in another part of the body
can occur at all ages but it is commonest in infancy
more common males than females
person-to-person; respiratory droplets
close & prolonged contact
2-10 days
Transmission: (Meningitis)
bacterial transmission from __ thru __
__ & __ (e.g. sneezing & coughing on someone, living in close quarters, sharing eating or drinking utensils, etc.)
incubation period: __ days
skipping vaccinations
age; 5; 20
living in a community setting; meningococcal meningitis
pregnancy; listeria bacteria
weakened immune system; spleen
Risk factors (Meningitis)
__ (Risk rises for anyone who hasn't completed the recommended childhood or adult vaccination schedule).
__ (Most cases of viral meningitis occur in children younger than age __ years. Bacterial meningitis is common in those under age __).
__ (College students living in dormitories, personnel on military bases, and children in boarding schools and child care facilities are at greater risk of __ meningitis). This is probably because the bacterium is spread through the respiratory route, and spreads quickly through large groups.
__ (It increases the risk of an infection caused by __ bacteria, which also may cause meningitis). The infection increases the risk of miscarriage, stillbirth and premature delivery.
__ (AIDS, alcohol use disorder, diabetes, use of immunosuppressant drugs and other factors that affect your immune system increase the risk of meningitis). Having a __ removed also increases risk. People without this organ should get vaccinated to lower the risk.
altered consciousness
bulging fontanelles
photophobia
Opisthotonos
Brudzinski’s sign
Kernig’s sign
S/Sx (NB): (Meningitis)
__/ apnea
severe headache/ __
__ (intolerance to light)
__(spasm of the muscles causing backward arching of the head, neck & spine) (sev. Stiffneck)
__ (flexing the pt’ s. neck causes flexion of the hips & knees)
__(flexing the pt’ s. hip 90 degrees then extending the pt’ s. knee causes pain)
SEE:
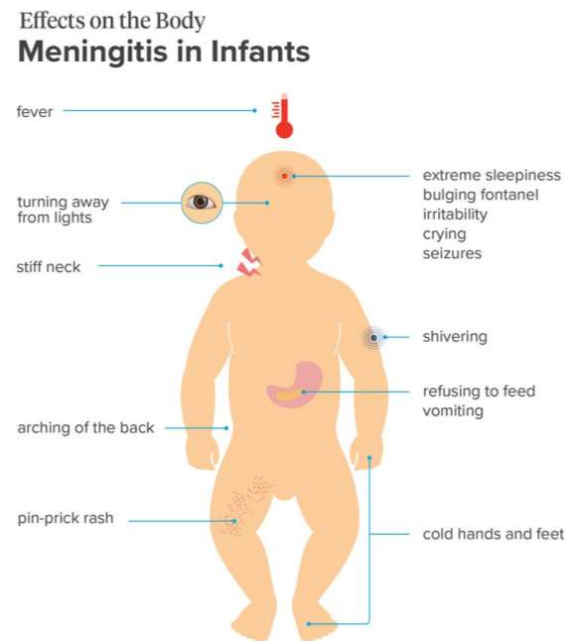
Sudden high fever.
Confusion or trouble concentrating.
Sleepiness or trouble waking.
Skin rash in some cases, such as in meningococcal meningitis.
S/Sx (>2y.o.): (Meningitis)
(Early meningitis symptoms may be similar to the flu. Symptoms may develop over several hours or over a few days).
(SCSS)
Bacterial meningitis
Viral meningitis
Chronic meningitis
Fungal meningitis
Parasitic meningitis
CAUSES (Meningitis)
(BVCFP)
Bacterial Meningitis
caused by an ear or sinus infection, a skull fracture, or — rarely — some surgeries
streptococcus pneumoniae
(the most common cause of bacterial meningitis in infants, young children and adults) more commonly causes pneumonia or ear or sinus infections. A vaccine can help prevent this infection.
Neisseria meningitidis (Meningococcus)
(This bacterium causes a bacterial meningitis called meningococcal meningitis). It commonly cause an upper respiratory infection but can cause meningococcal meningitis when they enter the bloodstream. This is a highly contagious infection that affects mainly teenagers and young adults. It may cause local epidemics in college dormitories, boarding schools and military bases.
Haemophilus influenzae; Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib)
this bacterium was once the leading cause of bacterial meningitis in children. But new Hib vaccines have greatly reduced the number of cases of this type of meningitis.
Listeria monocytogenes
(These bacteria can be found in unpasteurized cheeses, hot dogs and lunchmeats). People who are pregnant, newborns, older adults and people with weakened immune systems are most susceptible. During pregnancy, listeria can cross the placenta. Infections in late pregnancy may be fatal to the baby.
Viral meningitis
enteroviruses
herpes simplex virus (HSV), HIV, mumps virus, west nile virus
is usually mild and often clears on its own. Most cases are caused by a group of viruses known as (1)__ (shed in respiratory secretions and stool and sometimes are present in the blood and cerebrospinal fluid of infected patients). Viruses such as (2)__, __, __, __ and others also can cause this type of meningitis.
chronic meningitis
mycobacterium tuberculosis
2 weeks
long-lasting — can be caused by slow-growing organisms such as fungi and (1)__. They invade the membranes and fluid surrounding the brain.
develops over (2)__ weeks or more. Symptoms are similar to acute meningitis, which is a sudden, new case. They include headache, fever, vomiting and mental cloudiness.
fungal meningitis
fungal spores
cryptococcal meningitis
It may mimic acute bacterial meningitis. It's often contracted by breathing in (1)__ that may be found in soil, decaying wood and bird droppings.
isn't spread from person to person. (2)__ is a common fungal form of the disease. It affects people with weakened immune systems, such as from AIDS. It can cause death if not treated with an antifungal medicine. Even with treatment, this type of meningitis may come back.
parasitic meningitis
eosinophilic meningitis
amoebic meningitis
Parasites can cause a rare type of meningitis called (1)__. Parasitic meningitis also can be caused by a tapeworm infection in the brain or cerebral malaria. (2)__ is a rare type that is sometimes contracted through swimming in fresh water and can quickly become life-threatening.
The main parasites that cause meningitis typically infect animals. People are usually infected by eating foods contaminated with these parasites. This type of meningitis isn't spread between people.
bacterial meningitis
GBS & gram
purulent
CHON
<70 mg/dl
>1000cells/microL
+
More dangerous
Fatal if not treated quickly with antibiotic (AB)
__ – bacilli (found in intestines, vagina or rectum)
CSF clear to __
Elev. __
Dec. glucose: __
WBC ct. __
CSF gram stain & culture: often __ for a sp. organism
viral meningitis
7-10
polio, MMR, HSV, rabies, HIV
cloudy
CHON
glucose
<500 cells/microL
no organism
More common
Less serious (usually clears up on its own in __ days)
Enterovirus (__, __, __, __, __)
CSF clear to __
Elev. __
Normal __
WBC ct. __
CSF gram stain & culture: __ identified
SEE:
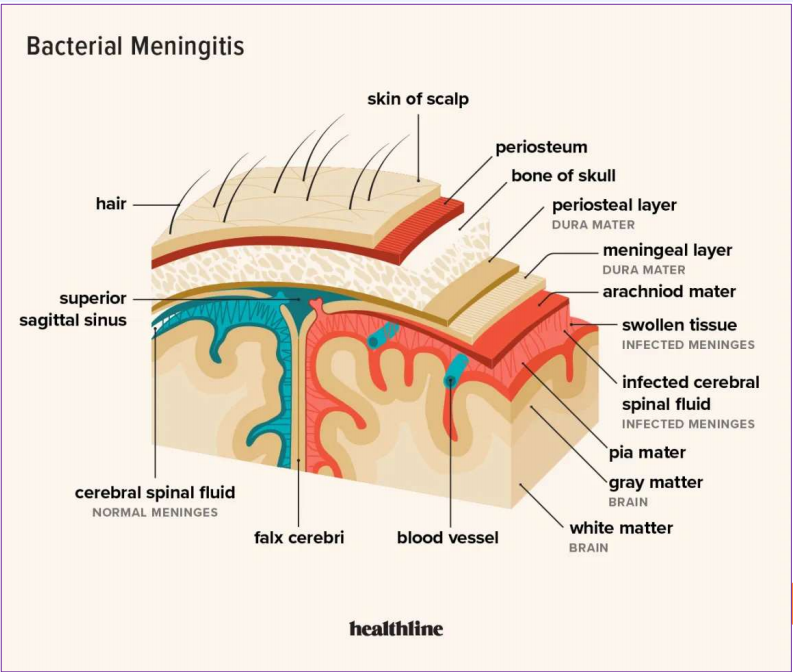
CSF study
blood culture; 80-90%; ESR
CT scan
Diagnosis: (Meningitis)
__ (Lumbar puncture is done to collect __)(analysis of __, typically reveals microorganisms on gram stain & culture)
__ (reveals up to __ of responsible bacteria) (elevation of C-reactive protein, __ differentiate bacterial from viral causes)
__ (show slit-like lateral ventricle & areas of low attenuation)
Treatment:
3 rd gen. Cephalosporins (Cefotaxime; Ceftriaxone)
Penicillin G or Meropenem
Ampicillin
Acyclovir (anti-viral)
Oseltamivir
Corticosteroids (Dexamethasone)
Prevention:
Practice good hygiene
Vaccination
H. influenza
S. pneumoniae
Antibiotic prophylaxis
Complication:
Sensori-neural hearing loss (SNHL)
(MENINGITIS)
Treatment:
__ (__; __)- for Bacterial M.
__ - alternate to Ceftriaxone
__ - for Listeria M.
__ (anti-viral)- for Viral Meningitis-- HSV (herpes simplex virus)
__ - for influenza
__ (__)- for children > 6wks. Old
Prevention:
__ (hand washing; Don't share drinks, foods, straws, eating utensils, lip balms or toothbrushes with anyone else; avoid cheeses made from unpasteurized milk, choose cheeses that are clearly labeled as being made with pasteurized milk )
__
(__ @ 2 months of age)
(__ @ 2 months (initial)
__ of susceptible at-risk contacts
Complication:
__- inner ear is affected
Opisthotonos
Kernig’s Sign
Brudzinski’s neck sign
Signs of Meningeal Irritation (OKB) / Triad Sign
ADHD (Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder)
5%
frontal, parietal, temporal, occipital LOBES
7
a developmental delay (has (1)__ smaller brain); these type of brains have low levels of a neurotransmitter called norepinephrine.
smaller, less active, less developed brain regions (impaired activity in four functional regions of the brain--(2) __, __, __ and __ lobe)
abnormal cognitive, behavioral, and motivational functioning (affect the regulation of moods, emotions, and brain cell connections)
a disorder that appears in early childhood
signs & symptoms typically appear before the age of (3)__
symptoms are typically at most prominent during elementary grades
usually continues into adulthood
Inattentive ADHD
Hyperactive-Impulsive ADHD
Combined ADHD
types of ADHD (IHC)
Inattention
S/Sx (ADHD):
>daydreams, has a hard time paying attention
>trouble listening to what’s being said
>easily distracted from tasks & play
>doesn’t follow through on obeying instructions
>disorganized
>loses important things
>forget things
>doesn’t want to do things that require ongoing mental
effort
>has trouble understanding information quickly &
accurately
Hyperactivity
S/Sx (ADHD):
> fidgets or squirms
> talks too much
> has trouble playing quietly
> often runs about or climbs in situations where it’s inappropriate
Impulsivity
S/Sx (ADHD):
> blurts out inappropriate comments or answers before the entire question has been asked
> can’t wait for things
> trouble taking turns or standing in line
> acts without thinking
> can’t control emotions
> interrupts others
neurotransmitters; Nor-epi, Dopamine
genetic; 20-25%
preservatives & artificial food coloring; red dye 40-; sodium benzoate
cigarette, alcohol
Contributing Factors: (ADHD)
a deficiency in the __ (__ & __) in the brain
__(if 1 child has ADHD, the chances of a sibling having it are __)
__ (__ a synthetic food dye made from petroleum; preservative __)
__ & __ use of mother during pregnancy
developmental pediatrician
medical and social history
vision. hearing
memory, problem-solving, listening
Evaluation: (ADHD)
evaluated by a __
___ (about pregnancy, family members with ADHD, emotional difficulties)
__ & __ test
__, __ & __ skills
family therapy (parent training)
behavioral therapy
cognitive behavioral therapy
medication; Ritalin/ Dexedrine
Treatment:
__ (__) -best way to deal with ADHD, by learning how to handle own frustration with child’s behavior, to parent consistently & positively
__ -structuring situations at home & school so a child doesn’t become unnecessarily stimulated or distracted
helping a child to develop coping strategies for particular situations
__ -The therapist also encourages the person with ADHD to adjust to the life changes that come with treatment, such as thinking before acting, or resisting the urge to take unnecessary risks
__ -stimulants (__/ __) (it helps to regulate levels of neurotransmitters in the brain)
1.)Change the scene
2.)Reward instead of punish
3.) Being clear and consistent.
4.) Keeping a routine and a schedule.
5.) Organizing everyday items.
Prevention: (ADHD)
FOR KIDS
1.)__ (eliminate sources of overstimulation & distraction in the child’s environment)
2.)__ (praise good behavior immediately/ giving a little token that pleases a child)(reward should be something enjoyable right away because ADHD kids don’t like to wait)
3.) __. Children with ADHD need consistent rules they can understand and follow.
4.) __. Keep the same routine everyday, from wake-up time to bedtime. Include times for homework, outdoor play, and indoor activities. Keep the schedule on the refrigerator or a bulletin board. Write changes on the schedule as far in advance as possible.
5.) __. Have a place for everything, (such as clothing, backpacks, and toys), and keep everything in its place. Use organizers for school material and supplies. Stress to your child the importance of writing down assignments and bringing home necessary books.
Keeping routines.
Making lists for different tasks and activities.
Using a calendar for scheduling events.
Using reminder notes.
Prevention: (ADHD)
For Adults
A professional counselor or therapist can help an adult with ADHD learn how to organize their life with tools such as:
(KMUU)
Human sources:
· Streptococcus pneumoniae
· Neisseria meningitidis (Meningococcus)
· Haemophilus influenzae (Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) bacterium
Animal sources:
· Listeria monocytogenes
Human sources:
·
·
·
Animal sources:
·
Cerebrospinal fever
Pia Mater, Arachnoid Mater, Dura Mater
CSF
Meningitis is also referred to as
parts of meninges (PAD)
substance that carries the meninges; will appear yellowish and purulent if bacteria is present; affected if there is a hematogenous spread
subarachnoid space (between the arachnoid and pia mater)
wear PPE, mask in particular
3 feet away
1 nurse (will not cater any pt)
the location of where CSF is situated and circulated
nursing intervention for meningitis
how many feet away should a pt. with meningitis be distanced from other patients
how many nurse must be assigned to a pt. with meningitis
Pentavalent, PCV
Flu vaccine (Hib vaccine or Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine)
vaccines for meningitis:
pedia:
adult:
viral meningitis
bacterial meningitis
a type of meningitis is common in this age:
under 5 yrs old -
under 20 yrs old -
crowded places
pregnant/ pregnancy
CNS
humans
dormant
meningitis will spread faster in this type of setting
no raw & unpasteurized food must be served when __
bacteria can easily infiltrate the __
are the sources of bacteria
bacteria may appear __ in some factors/ cases
fresh water (swamps)
lethargy (pathologic sleepiness)
severe headache & bulging fontanelles
parasites are common in these areas
early sign of meningitis
late signs of meningitis
hypothalamus (regulation center)
increase in Intracranial Pressure (ICP)
trigeminal nerve
increase in ICP
hypothalamus (thermoregulation center)
reasons for S/Sx manifestation:
fevers and chills & poor feeding will manifest because the __ is affected
irritability because __
photophobia the __ is affected
Seizure because __
Shivering because __ is affected
pin-prick rash and cold hands & feet
severe S/Sx of meningitis if there is a systemic sepsis and there will be a constriction of blood vessels so it will result to little or to no supply of oxygen
↑ of ICP
4 vials
pedia: 1 ml/vial
adult: 8-40 ml/vial
Sims position/ side-lying
G16
HCP must check the ICP first before inserting the spinal manometer because there might be a possibility that there is an __ — dangerous, potentially leading to brain herniation
how many vials should be obtained for the CSF study
Vial (quantity/ age group):
pedia-
adult-
position for CSF study
gauge size
3-way stopcock
used during lumbar puncture to control the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and allow for different procedures like measuring opening pressure, collecting CSF samples, and, if necessary, therapeutic injections.
It's essentially a valve that allows you to divert fluid flow between the patient, the manometer (for measuring pressure), and a collection tube.
neutrophils (WBC)
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
CSF study
0-3 mg/L
pedia: <10 mm/hr
adult: <20 mm/hr
Sensorineural hearing loss
↑ ICP because of the release of __
presence of erythrocyte (RBC)
test to differentiate bacterial from viral causes
definitive test for meningitis
CRP NV
ESR NV for pedia & adult
is manifested because the trigeminal nerve is affected
Ma’am: neck, spine, back
Google: neck, back, and lower extremities (legs)
opisthotonos sign affected areas
overstimulation
in persons who has ADHD, __ is not allowed (activity)
norepinephrine
dopamine
neuropsychologist
newborn screening
fight-or-flight hormone; for memory
feel-good hormone
doctors for adults (ADHD)
test for infants (ADHD)
Occupational Therapist
Ritalin
partner of a developmental pediatrician for ADHD
DOC that can/will increase Norepinephrine & Dopamine
direct spread
hematogenous spread
modes of transmission for Meningitis:
- skin, nose, anatomical defect (s. bifida, skull fx)
- blood stream
spinal manometer
CSF pressure is typically measured during a lumbar puncture using a __
Eosinophilic meningitis; Angiostrongylus cantonensis
amoebic meningitis; Naegleria Fowleri
__ high levels of eosinophils (WBC) in the CSF. the most common cause globally is infection with the__
also known as primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM), is a rare type but almost always fatal caused by __
is a rare type that is sometimes contracted through swimming in fresh water and can quickly become life-threatening.
rifampin
ciprofloxacin
ceftriaxone
azithromycin
24 hrs
antibiotic prophylaxis:
a common and effective option, especially for infants (4 oral doses for 48 hrs)
widely used (single oral dose)
preferred for pregnant women and sometimes used as an alternative to rifampin or ciprofloxacin (single injection)
single oral dose (if resistant to ciprofloxacin)
prophylaxis should be initiated ideally within __ hrs of identifying the index patient (the person with the disease)
<15
>15
normal pressure during CSF study
abnormal pressure during CSF study
Meningococcal vaccine
Pneumococcal vaccine
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) vaccine
Vaccines:
protects against the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis — common cause of meningitis
protects against Streptococcus pneumoniae — another common cause of meningitis
protects against Haemophilus influenzae type B (Hib) — bacteria that used to be a common cause of meningitis in children but is now less common due to widespread vaccination