Unit 10: Taxonomy and Evolutionary Patterns
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
this unit has 3 different knowts! they are all posted here on knowt!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
serial endosymbiosis theory
it explains the orgins of nucleated eukaryotic cells by the merging of archaebacterial and eubacterial cells
geologic time scale
divides up the history of the earth based on organisms that existed duirng that time
precambrian time
earliest eon
precedes the cambrian perion and phanerozoic eon
the age of early life
jellyfush, soft-bodied creautures, worms
mostly uninhabited land
cambrian explosion
approx. 530 million years ago
a wide variety of animals emerged onto the evolutionary scene
most of the major animal groups started to appear
Paleozoic era
541 - 252 million years ago
diversification of fish and abundance of marine animals (trilobites, molluscs, small shelled organisms)
formation of many land forms we know of today (eg. Appalachian Mountains, creation of Pangaea)
contains the Permian, Carboniferous, Devonian, Silurian, Ordovician, and Cambrian periods
mesozoic era
251.9 - 60 million years ago
age of reptiles (dinos, crocodiles, pterosaurs)
Pangea begins to separate into the modern continents + formation of the Rocky Mountains
contains the Triassic, Jurassic, and Cretaceous periods
cretaceous
145 - 66 million years ago
last portion of the age of dinos/mesozoic era
by then end of this era, the continents look very similar to how they are today
defined by a layer of chalk formed in western Europe
first flowering trees
ends with a mass extinction (K-T or K-pg) resulting in 70% of the species being extincy
cenozoic era
66 - 0 million years ago
recent life
the age of mammals (humans and many others)
split into many epochs (Paleocene, Eocene, Oligocene, Miocene, Pliocene, Pleistocene)
mass extinction
clears the way for surviving organisms to evolve
fossil record
a collection of all the fossils found on earth, documenting the history of life on our planet
extinct/extant
extinct: no longer in existence, died out
extant: still existing, not destroyed or lost
three-domain system
a classification system that groups all cellular life into 3 domains - Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya
five-kingdom system
A classification based on things like mode of nutrition, thallus organization, cell structure, phylogenetic relationships, and reproduction.
Consists of Monera (unicellular prokaryotic organisms), Protista (protists), Plantae (plants), Fungi, and Animalia (animals)
archaea
prokaryotic (no cell membrane)
oldest species of organisms
bacteria (eubacteria)
prokaryotic (no cell membrane)
membrane posseses discyl glycerol diester lipids
single celled
plantae (plants)
all plants (living or extinct)
highest taxonomic group organisms can be grouped into
protista (protists)
a kingdom consisting of singled celled (mostly) organisims that are neither plants nor animals nor fungi
animalia (animals)
the kingdom consisting of all the animals (including humans)
analogous structures
features that are similar in function but not necessarily in structure, do not derive from a common ancestor
divergent evolution
one common ancestor species evolves into many diverse forms
convergent evolution
organisms that are different from one another develop similarities because they live in the same type of environment
amino acid sequencing
the process of identifying the arrangement of amino acids in proteins and peptides
Carolus Linnaeus
a Swedish biologist and physician
created a system of naming plants and animals, the binomial system
phylogeny
the representation of the evolutionary history and relationships between groups of organisms
phylogenetic tree
a diagram that depicts the lines of evolutionary descent of different species, organisms, or genes from a common ancestor
binomial nomenclature
the formal naming system for living things
must be written in italics, has 2 parts, genus (larger family) is written first and must be capitalized, the specific epithet (specific name) is never capitalized and must go second
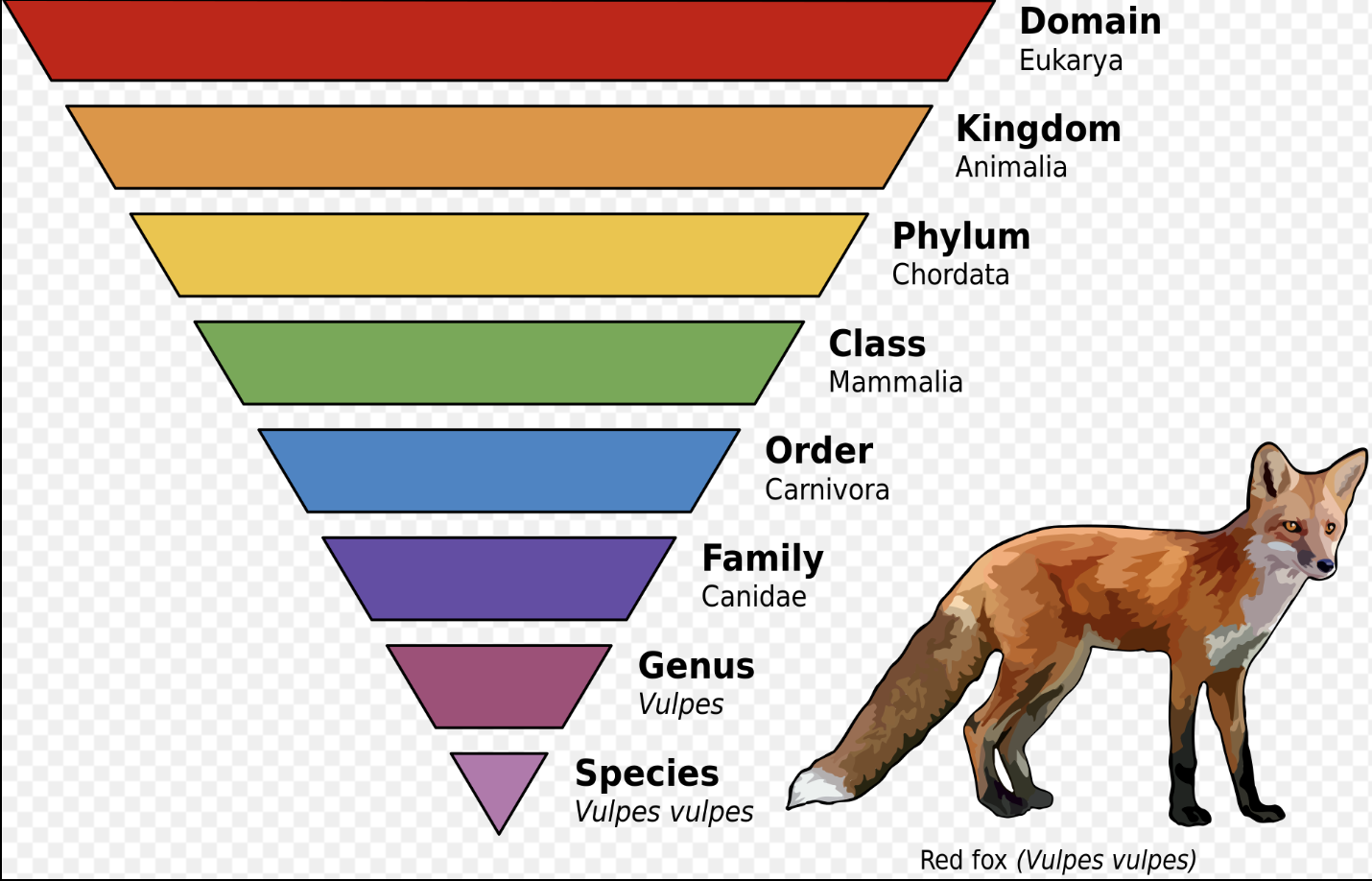
taxon/taxonomy
the science of naming, describing, and classifying organisms
cladogram
diagrams that depict the relationships between different groups of taxa called clades
taxonomic ranks
the relative level of a group of organisms (taxon) in an ancestoral hierarchy
consists of species, genus, family, order, class, phylum, kingdom, and domain