History: X-Rays, Radiation, Electromagnetic and X-ray Production
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Who first discovered X-rays?
Wilhelm Roentgen
Who worked on cathode rays at the same time as Wilhelm Roentgen?
Philipp Lenard
What did William Morgan do in 1785?
Unknowingly produced X-rays - presented a paper to Royal Society of London - describes effects of passing electrical currents through a partially evacuated glass tube, producing a glow created by X-rays
What is the linear no threshold model?
Assumes that every increment of radiation dose - no matter how small - constitutes an increased risk of cancer
What is radiation hormesis?
A little radiation is good for you - stimulates hormonal & immune response
What is a molecule?
Smallest particle of a compound possessing characteristics of the compound
What is E = mc^2 used for?
Expression of equivalence of mass and energy
What was Rutherford (1911) atomic theory?
Dense, positive nucleus is surrounded by cloud of negative electrons
What was Bohr (1913) atomic theory?
The atom was a miniature solar system
What was Schrodinger's contribution to the Atomic Theory?
Foundation of modern physics - quantum physics or wave mechanics
What are protons and neutrons made up of?
Made up of quarks
What are quarks?
The only elementary particles to experience all known forces of nature and to have a fractional electric charge
What is M theory (string theory)?
Unknown theory of everything which would combine all 5 Superstring theories and the Supergravity at 11 dimensions together - links quantum physics and relativity
How is atomic electrical stability achieved?
Maintained through equal number of protons and electrons
What is an atomic number (Z#)?
Distinguishes elements by number of protons contained by nucleus
What happens to the atomic number when there is radioactive decay?
Radium (Z# 88) emits alpha particle -> decays to radon (Z# 86)
What is an isotope?
Atoms of the same element that have the same amount of protons, but a different amount of neutrons
What is ionisation?
Process which adds or removes electrons from an atom
How does ionisation relate to X-rays?
X-ray photons can interact with atoms - results in ejection of electron and changes charges between atoms (disruption in body's metabolic relationships)
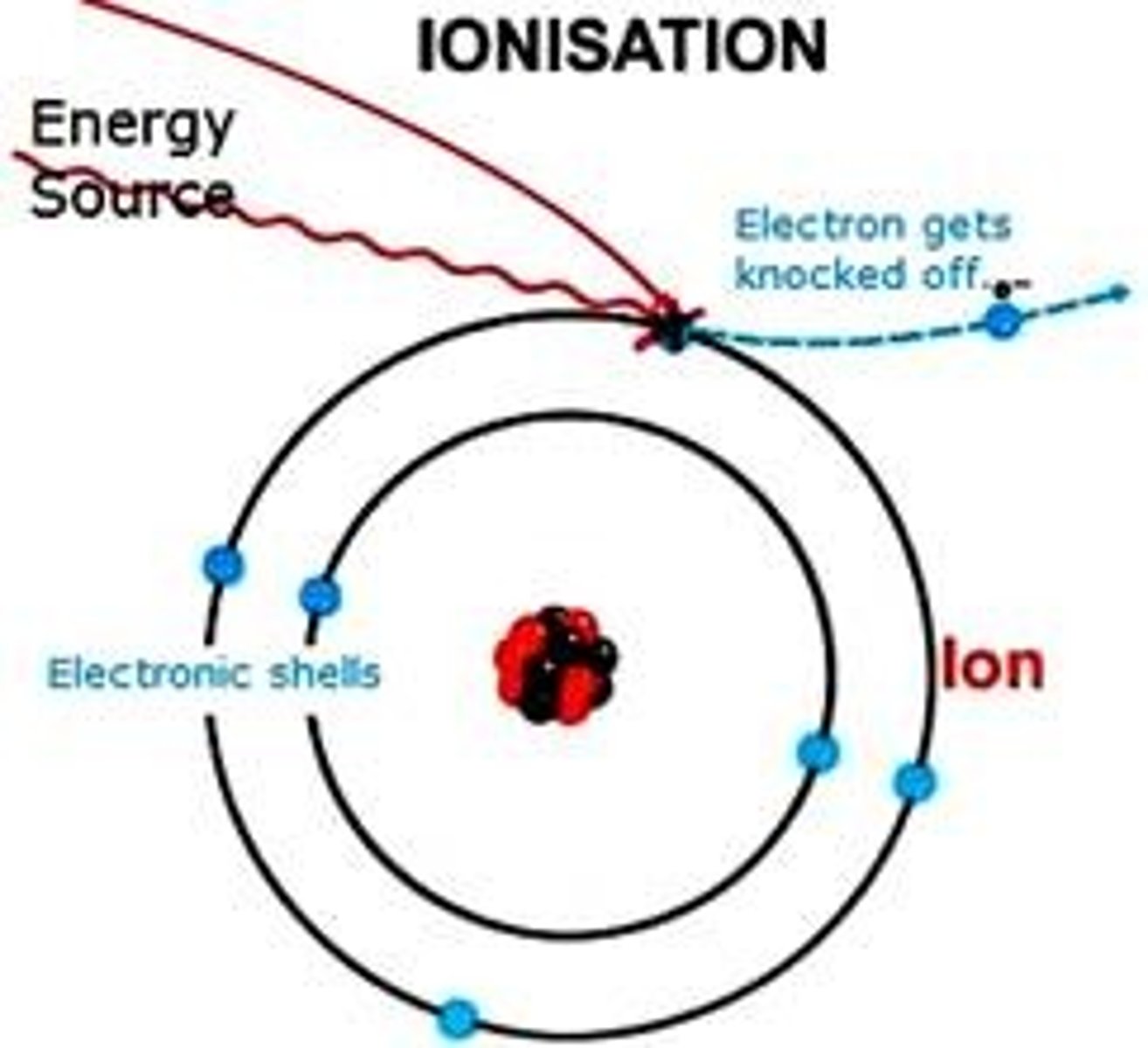
What is electron binding energy?
E(b) - energy required to eject electron from atom - related to how close electron is to the nucleus (Eb increases as Z# increases)
What is electromagnetic energy?
Combination of electric and magnetic fields travelling through space
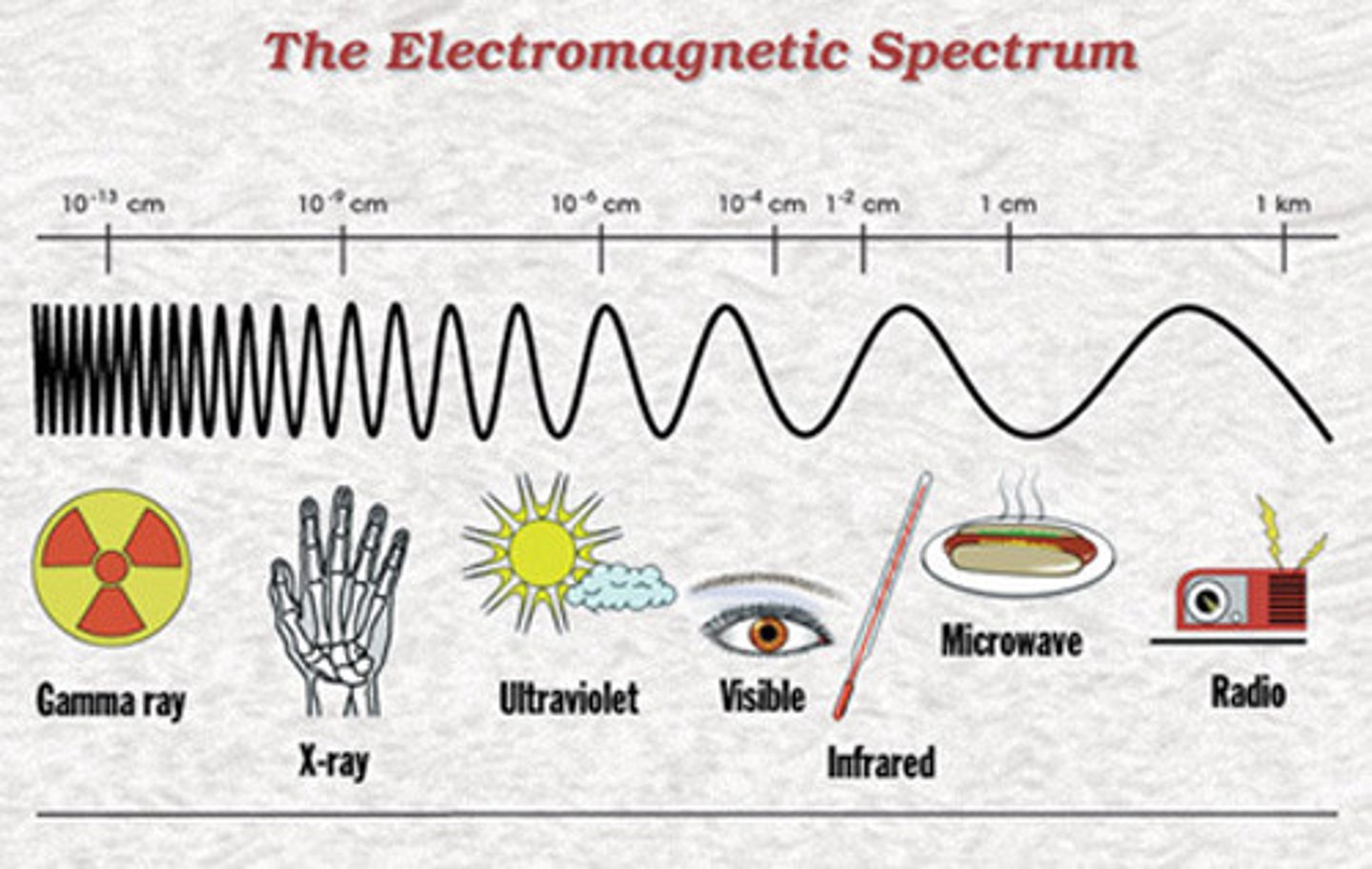
What are the characteristics of electromagnetic radiation?
- Wavelength
- Energy
- Frequency
What is non-ionising radiation?
Low frequency wavelengths DO NOT collide with electrons / transfer energy thus cannot ionise the atom
What is the X-ray tube consist of?
- Vacuum (glass 'tube')
- Metal anode +ve charge (tungsten)
- Cathode -ve charge
- Heated filaments at cathode
- Electrons (created through thermionic emission)
What does the cathode consist of?
- Filament
- Focusing cup
- Associated wiring
What does the filament consist of?
Coil of thoriated tungsten (0.1:0.2mm thick, 1: 2mm wide, 7: 15mm long)
What is the chosen filament material and why?
Tungsten - high melting point, difficult to vaporise
What are the three functions of the anode assembly?
- Target surface
- Conducts high voltage
- Serves as primary thermal conductor
What is thermionic emission?
Cathode creates electrons by sending an electrical current to heat up the cathode (based on milliamps [mA] set on control panel)
How do kiloVolts (kV) work in x-ray machines?
Electrons travel in the vacuum to the positively charged anode - the frequency (energy) of the electrons between the cathode and anode is determined by the potential difference (voltage) between them
What interactions happen when electrons hit the tungsten anode?
Brehmsstrahlung, and characteristic radiation
What is attenuation?
The reduction of the x-ray energy as it passes through matter, including absorption and compton scatter
How is the patient affected by absorption of ionising radiation?
Incoming photon is stopped by electron within the patient - which is ejected and causes ionisation of atom, creating free radicals within patient, and increases their radiation dose
How does Compton Scatter work?
Incoming photon is slowed down by interaction with electron in outer shell, changes direction with less energy
How does Compton Scatter influence imaging?
Increases grey scale on image, and degrades image quality