Micro study guide 1
1/213
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
214 Terms
What is a prokaryote?
simple, single-celled organism that lacks a nucleus and membrane bound organelles
What substance forms many bacterial walls and consists of glycosaminoglycan chains interlinked with short peptides?
peptidoglycan
What structure does penicillin target to disrupt the integrity of the bacterial cell wall?
peptide cross links
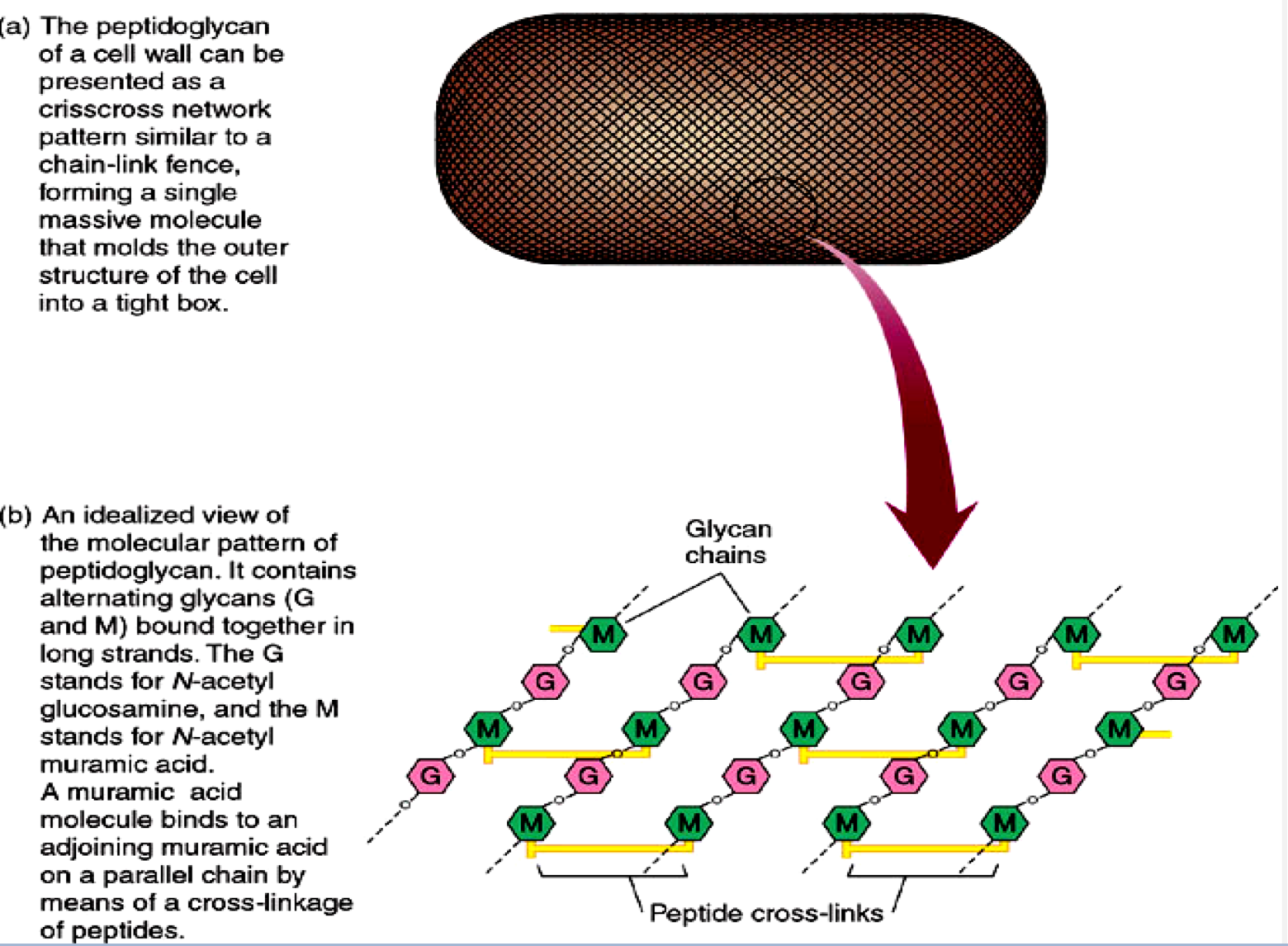
IDK just know this
What is a bacterial chromosome?
single, large, circular double-stranded DNA molecule that contains all genetic information required by a cell
What is a plasmid?
small, circular, double stranded DNA that is duplicated and passed to offspring; may encode antibiotic resistance, tolerance to toxic metals, enzymes, and toxins
Where are plasmids and bacterial chromosomes located within a cell?
both within the cytoplasm of the cell; chromosome specifically within nucleoid
What is transcription?
synthesis of mRNA from DNA
What is translation?
synthesis of proteins from mRNA
Why can transcription and translation occur simultaneously within the prokaryotic cell?
prokaryotic cells lack a membrane bound nucleus, so all components needed for synthesis are located in cytoplasm allowing cell to make proteins quickly
Briefly explain endospore lifecycle
2 phase life cycle: shifts between vegetative and endospore
Which bacterial generas produce endospores?
bacillus and clostridium
Which bacteria is known to cause outbreaks of diarrhea in hospitals and nursing homes?
Clostridium difficile
Will bleach-free disinfectants kill endospores?
naur (no)
Which type of bacteria has a thick layer of peptidoglycan that forms a single layer around the cell?
Gram positive bacteria
During a gram stain, what color will gram positive bacteria appear under a microscope? Why?
Purple; thick peptidoglycan layer retains crystal violet stain
Describe the steps involved in performing a gram stain
add crystal violet - 10 sec- rinse
add gram’s iodine - 10 sec - rinse
decolorize with 95% ethanol until colorless- rinse
add safranin - 10 sec - rinse
air dry or blot
Which step in the gram stain process if most critical and why?
third step: decolorize w/ 95% ethanol;
most affected by technical variations in timing / reagents
When viewed under a microscope, which gram-positive bacteria appear as cocci in clusters or “bunches of grapes”?
staphylococcus
When viewed under a microscope, which gram positive bacteria appear as cocci in pairs or chains?
streptococcus
How would listeria look after a gram stain when viewed under a microscope?
purple / gram positive and rod shaped
Does listeria produce spores?
naurrrr (no)
What is pleomorphism?
bacteria presents in various forms and shapes
Why is pleomorphism extreme in the mycoplasma genus of bacteria?
no cell wall- can change their shape
What are the 6 I’d of culturing microbes?
Inoculation
Incubation
Isolation
Inspection
Information gathering
Identificatoin
What is inoculation?
introduction of a sample into container of sterile media
What is incubation?
provide conditions for optimal growth, making sure you have enough microbes in sample
What is isolation?
Getting a pure culture of the microbe you’re interested in
What is inspection?
looking at colonies and microscopic characteristics of the microbe you collected
What is information gathering?
biochemical, immunologic, and genetic testing to confirm genus of microbe and identify the species
What is identification?
assigning a specific name to the microbe
What is synthetic media?
contains pure organic and inorganic compounds in an exact chemical formula
What is non-synthetic media?
contains at least one ingredient that is not chemically definable- organic extracts
What is general purpose media?
grows broad range of microbes; usually non-synthetic, nutrient agar and broth, peptone water, etc
What is enriched media?
contains complex organic substances such as blood, serum, hemoglobin, or special growth factors required by fastidious microbes
What is selective media?
contains one or more agents that inhibit growth of some microbes and encourage growth of desired microbes
What is differential media?
allows growth of several types of microbes and displays visible differences among desired and undesired microbes
Which specific medium would be best to isolate pathogenic Staphylococci?
mannitol salt agar
Describe mannitol salt agar
selective and differential; turns yellow if organism metabolizes mannitol, helping differentiate between S. aureus (yellow) and S. epidermidis (red)
Why is the growth curve in a bacterial culture closed?
they’re placed in a system with finite nutrients and space without ability to remove waste products
What are the 4 phases in the microbial growth curve?
lag phase
exponential growth (log) phase
stationary phase
death phase
Describe the lag phase of the microbial growth curve.
“flat” period of adjustment, enlargement, and synthesis of DNA, enzymes, ribosomes; little growth
Describe the exponential growth (log) phase of the microbial growth curve.
period of maximum growth that will continue as long as cells have adequate nutrients and a favorable environment
Describe the stationary phase of the microbial growth curve.
rate of cell growth equals rate of cell death- caused by depleted nutrients and O2, excretion of organic acids and pollutants
Describe the death phase of the microbial growth curve.
as limiting factors intensify, cells die exponentially in their own wastes
What is the average period of time it takes to complete the microbial growth curve?
about 4 days
Which gram positive bacteria stain like gram negative bacteria? Why?
actinomyces, corynebacterium, mycobacterium, and propionibacterium: cell walls are sensitive to breakage during cell division
bacillus and clostridium: decreased peptidoglycan during periods of growth
Which bacteria responds best to acid-fast staining?
myobacteria
Which groups of bacteria are considered obligate intracellular parasites?
rickettsias and chlamydias
How are obligate intracellular parasites different from non-obligate intracellular bacteria?
cannot serve or multiply outside of a host cell
cannot carry out metabolism on their own
List the 4 main fungal divisions (based on spore type)
zygomycota, ascomyota, basidiomycota, chytridomycota
Which fungal division does not cause human disease?
chytridomycota
Give an example of the zygomycota fungal division
rhizopus (bread mold)
Give an example of the ascomyota fungal division
penicillium, aspergillus (resp. infection), saccharomyces (yeast for bread and beer), trichiophyton (ringworm), Candida albicans, stachybotrys (toxic black mold)
Give an example of the basidiomycota fungal division
cryptococcus neoformans
What are the two morphologies in which microscopic fungi exist?
yeasts: unicellular round/oval budding cells, asexual production
hyphae: molds; long filamentous cells
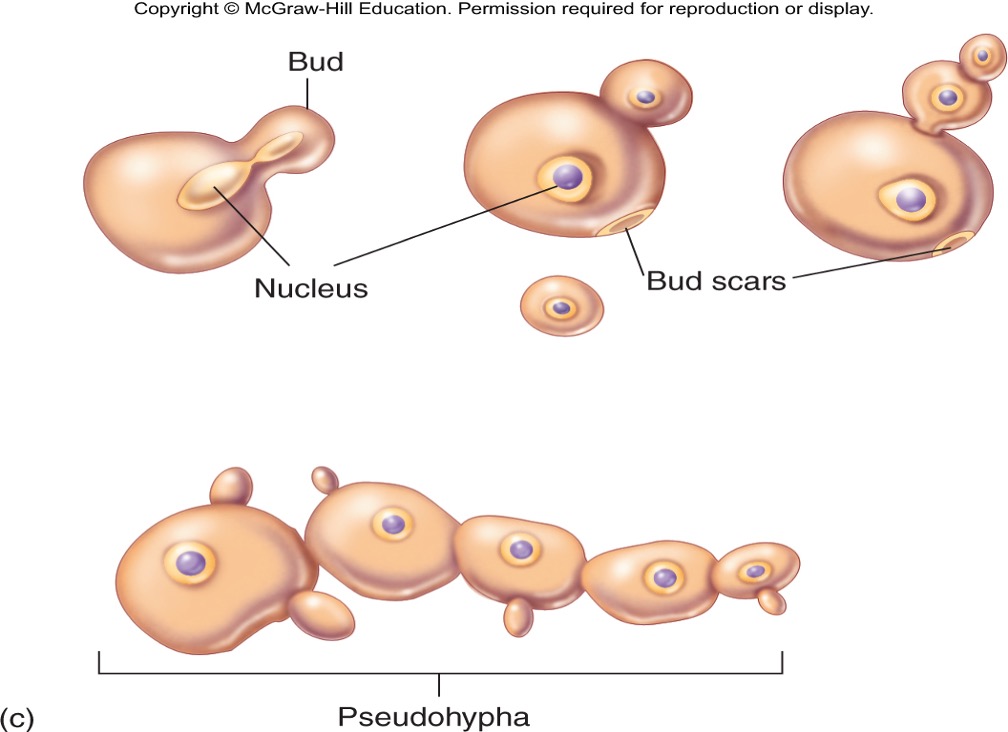
yeast
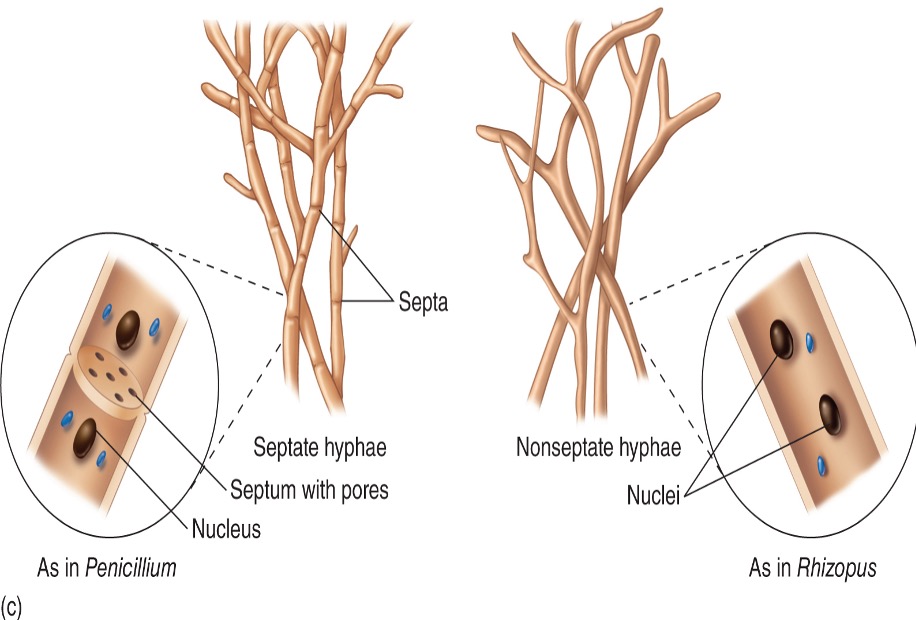
hyphae
What is the difference between primary and opportunistic fungal pathogens?
primary: can exist in both yeast and mold forms (dimorphic)
opportunistic: happen secondary to weakened immune system
Give examples of primary fungal pathogens
blastomyces, histoplasma, coccidioides, paracoccidioides, sporothrix
Give examples of opportunistic fungal pathogens
cryptococcus, candida, aspergillus, penicillium, zygomycetes, trichosporon, fusarium
List the 2 examples of marine algae toxins that can cause food poisoning and the marine life each condition is associated with.
paralytic shellfish poisoning- eating exposed clams or other invertebrates
ciguatera fish poisoning- algal toxins that have accumulated in reef fish such as barracuda and moray eel
What are the two protozoan stages?
Trophozoite- motile feeding stage
cyst- dormant resistant stage
What area the protozoan groups based on?
locomotion and reproduction
List the protozoan pathogens associated with the Mastigophora group
flagellates; trypanosoma crudi (chugs disease), leishmania, Giardia lamblia, trichomonas vaginalis
What are the two groups of parasitic helminths?
Flatworms and roundworms
Describe flatworms
parasitic helminth that is flat (thin, segmented body plan), does not have definite body cavity, digestive tract is a blind pouch, has simple excretory and nervous systems subdivided into cestodes and trematodes
List and describe the two subdivisions of flatworms
cestodes (tapeworms)- long, ribbon like
trematodes (flukes)- flat, ovoid
Describe roundworms (nematodes)
parasitic helminth that is round (elongate, cylindrical, unsegmented body plan), has a complete digestive tract, a protective surface cuticle, spines and hooks on mouth, and excretory and nervous systems are poorly developed
What type of helminth is the pinworm?
roundworm
What do enveloped viruses have that naked viruses lack?
an envelope around the capsid
What are the 6 stages of virus replication? describe each
absorption- attachment to cell surface
penetration- via fusion or endocytosis, nucleic acid is released
uncoating- release of viral capsid and RNA into cytoplasm
duplication/synthesis- take control of cell’s metabolism and machinery, causing cell to synthesize basic components of new virus
assembly- nucleocapsid and envelope are formed
release- virus bud off membrane, virion ready to infect other cells
What is a cytopathic effect?
virus-induced damage to host cells that alter their microscopic appearance
List examples of cytopathic effects caused by viruses
changes in size and shape, intracellular chages
cytoplasmic or nuclear inclusion bodies composed of damaged cell organelles or compact mass of viruses
multiple cells fuse to form one large multinucleate cell- syncytium
cell lysis/death
alter DNA to transform cells into cancerous cells
What type of infections do prions cause? How are they spread?
transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs)
direct contact, contaminated foods
What is the name of the rapidly progressive neurodegenerative human prion disease?
Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
What is a prion?
misfolded protein that does not contain nucleic acid
Which microbes have highest resistance to control?
prions and bacterial endospores (bacillus, clostridium)
What is the goal of sterilization?
destroy endospores
Define microbiostatic
any process that temporarily prevents microbes from multiplying
Define microbicide
any chemical agent that kills pathogenic organisms
Which microbicidal agent is considered a sterilizing agent?
sporicide bc it can kill endospores
Define sanitization and give an example
any cleansing technique that mechanically removes microbes;
dishwashing
Define degermation and give an example
any process that reduces number of microbes on human skin;
surgical hand scrub
define antisepsis and give an example
process that uses chemical agents on the skin to destroy or inhibit vegetative pathogens;
antibacterial soap or using iodine preoperatively
Define disinfection and give an example
any process that destroys vegetative pathogens but not endospores on inanimate objects or surfaces;
5% bleach or boiling water
Define microbial death
permanent loss of reproductive capability, even under optimal growth conditions
List the factors that can affect an antimicrobial agent’s mechanism of action
number of microbes, nature of microbes in population, temperature and pH of environment, concentration of agent, mode of action, and presence of solvents, organic matter, or inhibitors
What are the four cellular targets that antimicrobial agents aim to destroy?
cell wall, cell membrane, cellular synthetic process of proteins and nucleic acids, protein structure and function
Which antimicrobial agents are most effective for targeting cell wall and why?
antibiotics, detergents, alcohols- interfere with synthesis of cell wall
Which antimicrobial agents are most effective for targeting cell membrane and why?
surfactants- lower surface tension of cell membranes
Which antimicrobial agents are most effective for targeting cellular synthetic process of protein and nucleic acid? why?
antibiotics and chemicals- interfere with DNA and RNA function
radiation- gamma and UV cause mutations that permanently inactivate DNA
Which antimicrobial agents are most effective for targeting protein structure and function and why?
heat- coagulation by moist heat can denature proteins
chemicals- can coagulate proteins
Differentiate heat sterilization and disinfection
heat sterilization destroys endospores, disinfection does not
Is moist heat or dry heat more effective for microbial control?
moist heat
What is a common form of moist heat used in hospitals and medical offices to sterilize glass, cloth, metal, and certain cloth and rubber?
autoclave
What is desiccation? Is it an effective method of sterilization?
gradual removal of water from cells leading to metabolic inhibition
naur, not an effective microbial control- cells retain the ability to grow when water is reintroduced
Differentiate ionizing and non ionizing radiation
ionizing- deep penetrating power, breaks DNA (gamma, x-rays, high speed electrons)
non-ionizing- little penetrating power, causes DNA mutations by formation of abnormal bonds (Uv light)
What is filtration?
mechanical removal of microbes by passing a gas or liquid through a filter
Give examples of substances that are best sterilized by filtration
heat sensitive liquids like blood products, IV fluids, IV drugs
hospital isolation units through HEPA filters