Unit 7 Agriculture & Rural Land Use (Entire Unit)
1/82
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
83 Terms
Agriculture
The production of food, fiber and fuel from tending plants and livestock for the purpose of human use. (i.e. Farming)
Agriculture regions
Areas of the world where certain types of crops and animals predominate
Agribusiness
Commercial agriculture in which large corporations own and operate various steps in the production process with an emphasis on profit

Agriculture Revolutions
Different stages of advancements and invention within farming which made farming easier and more productive. Each stage has key developments.

Animal Waste
Manure - can be used as natural fertilizer

Aquaculture
The raising of fish and other aquatic species in captivity or plants for harvest.

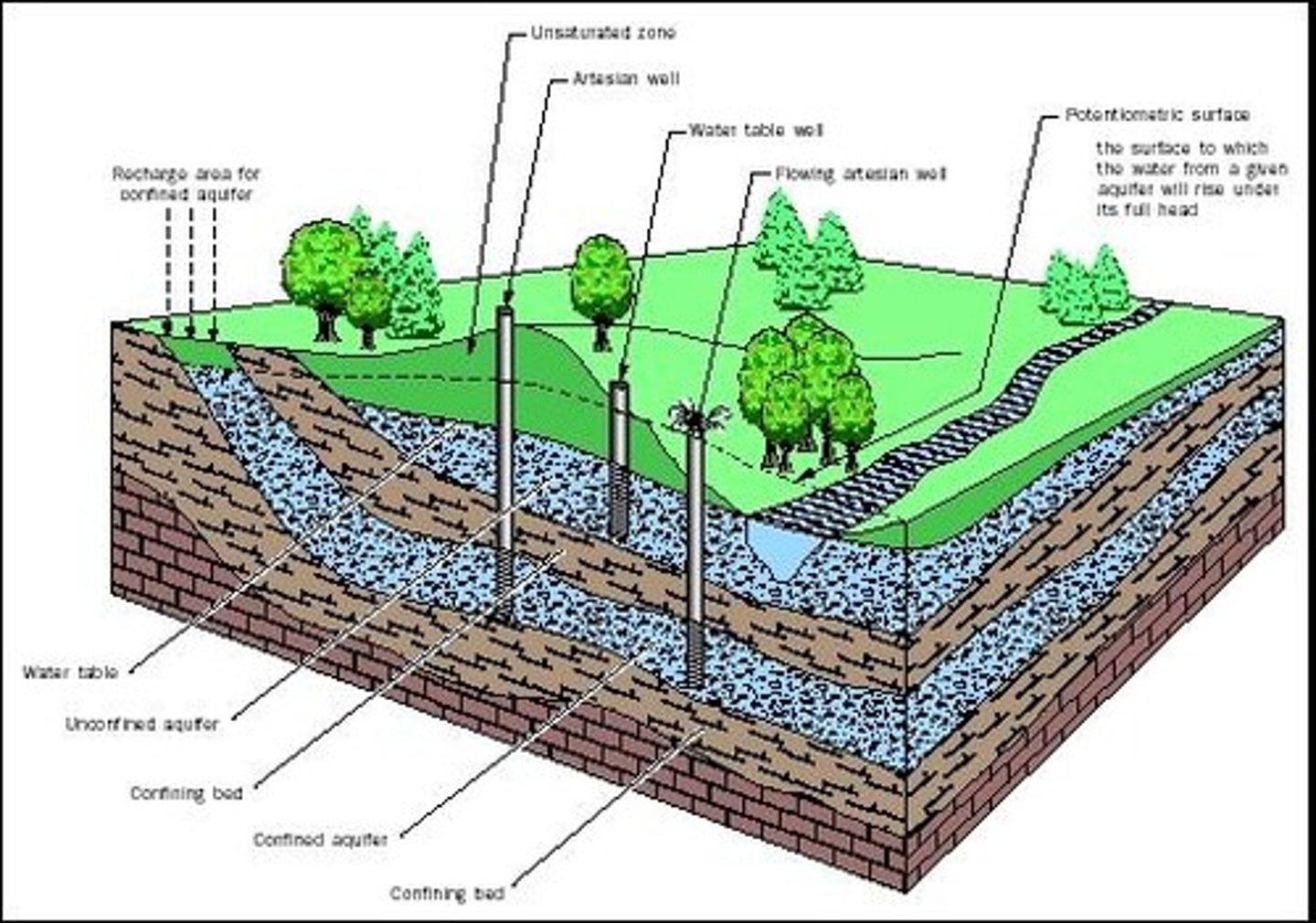
Aquifer
An underground layer of rock or sediment that holds water
Climatic Conditions/Zones
Regions where the temperatures and precipitation promote growth of certain types of plants and animals
Biodiversity
The diversity of plant and animal life in a particular habitat (or in the world as a whole)

Biotechnology
A form of science that uses living organisms, usually genes, to modify products, to make or modify plants and animals, or to develop other microorganisms for specific purposes.

Chemical farming
The application of synthetic fertilizers to the soil and herbicides, fungicides, and pesticides to crops in order to enhance yields.

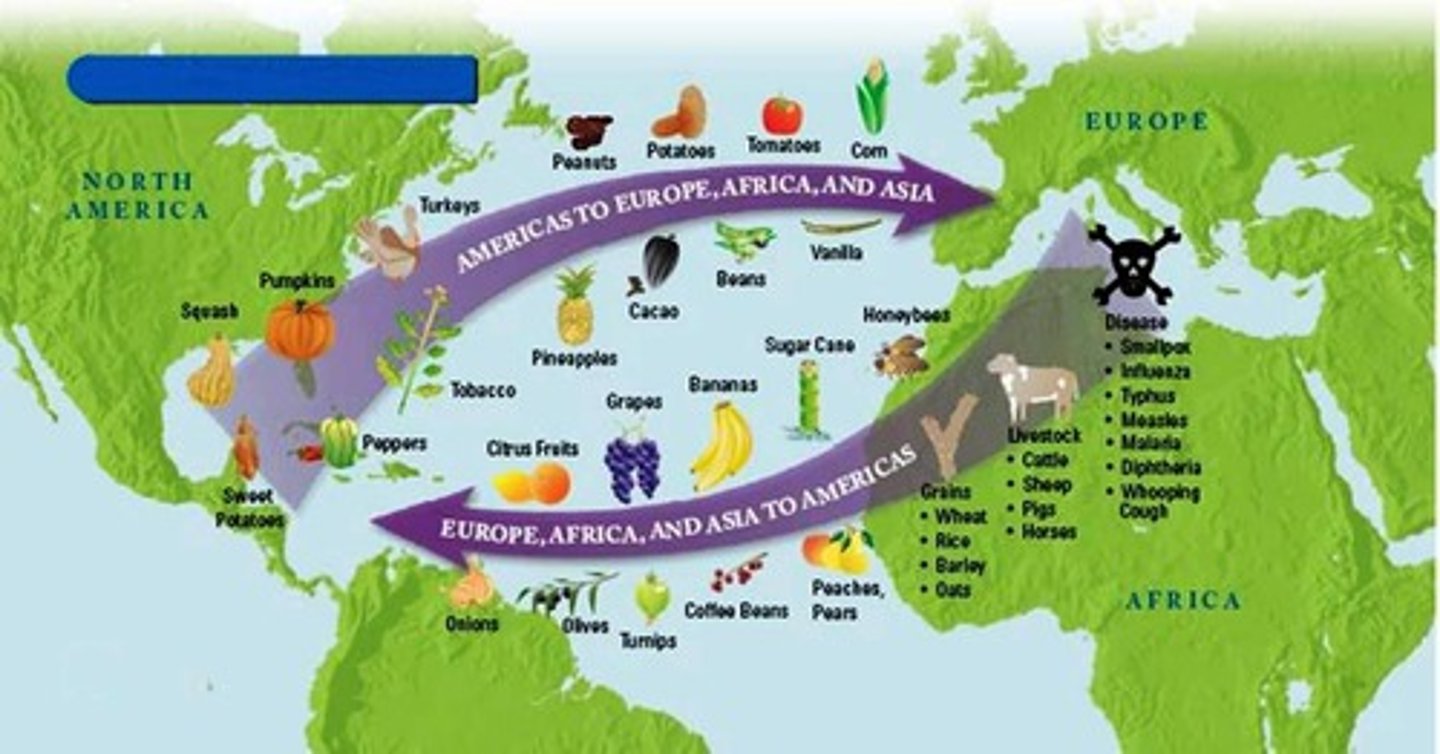
Columbian Exchange
The exchange of plants, animals, diseases, and technologies between the Americas and the rest of the world following Columbus' voyages
Commercial agriculture
the process of growing crops or raising animals to sell or trade
Deforestation
The removal of trees faster than forests can replace themselves
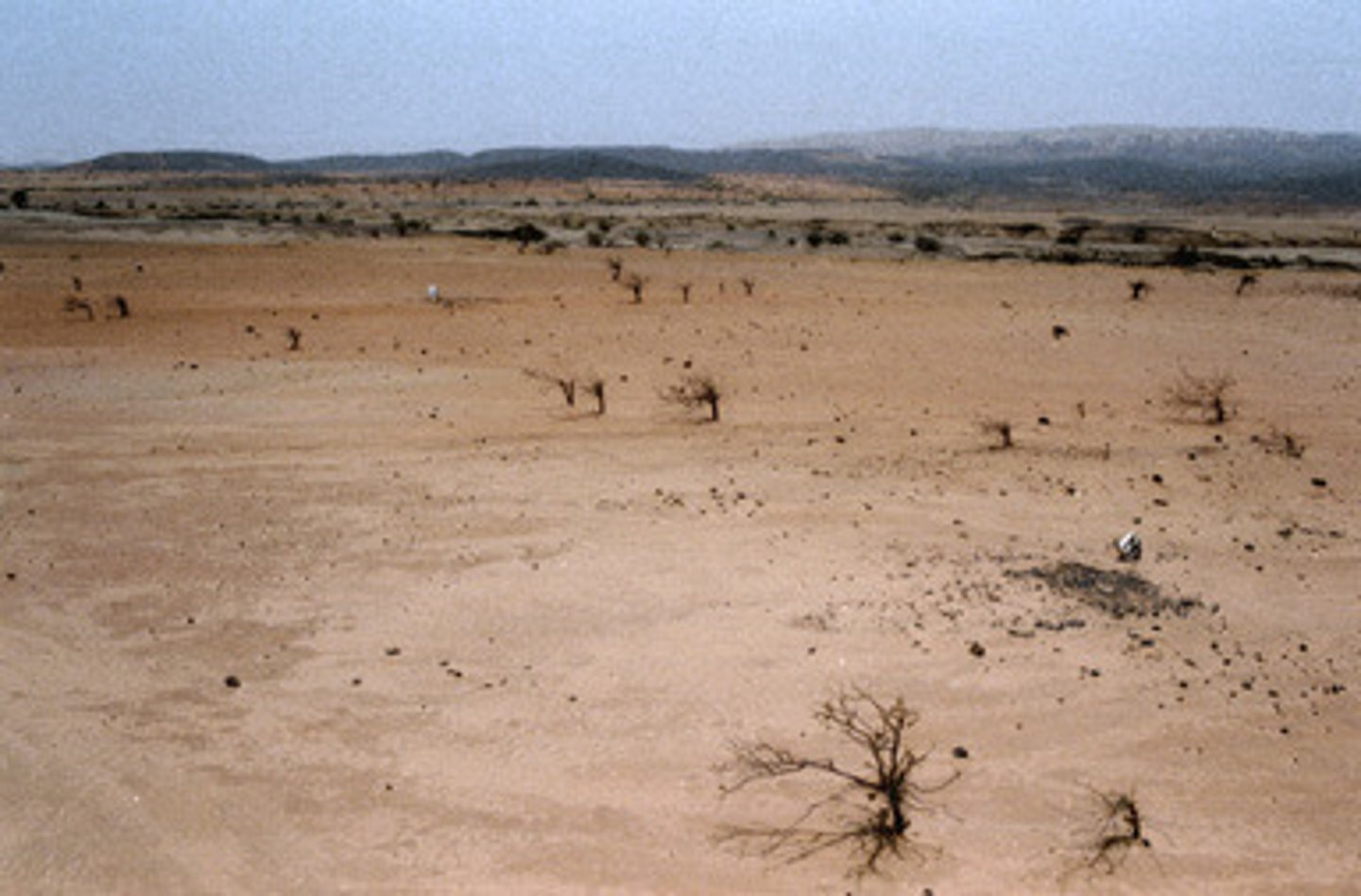
Desertification
Degradation of land, especially in semiarid areas, primarily because of human actions like excessive crop planting, animal grazing, and tree cutting

Domestication
Selective growing or breeding of plants and animals to make them more useful to humans

Diet energy consumption
the amount of food that an individual consumes
All activities of the body require energy, and all needs are met by the consumption of food containing energy in chemical form. The human diet comprises three main sources of energy: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats.
Extensive farming
A type of farming that requires large areas of land. (Don't confuse with intensive farming in a large land area.)
EXs: shifting cultivation, nomadic herding, ranching

Fair trade
A market-based approach to pay higher prices to producers of exports from LDCs to MDCs in order for the developing countries to obtain better trading conditions and promote sustainability

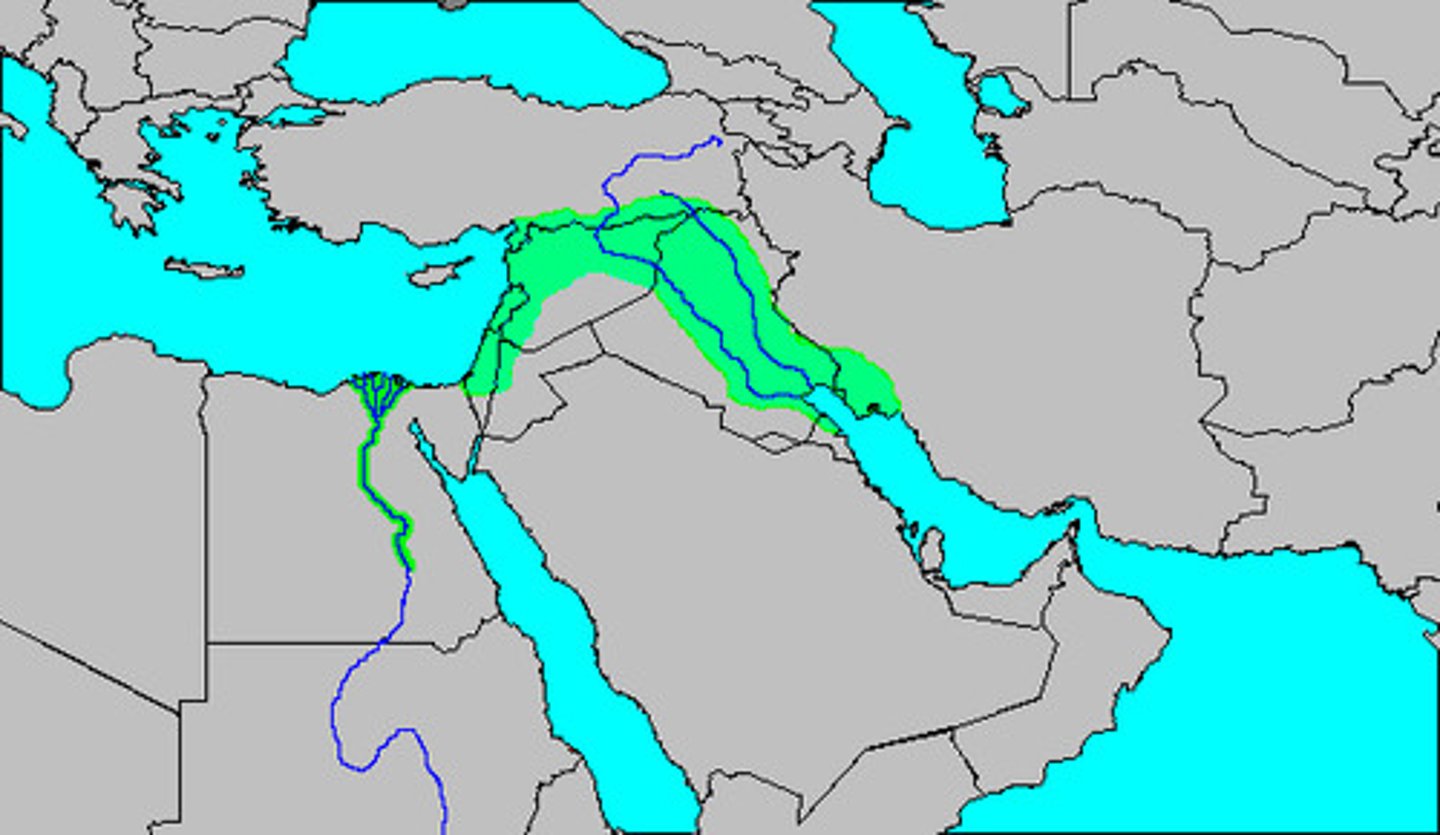
Fertile crescent
A geographical area of fertile land in the Middle East (SW Asia) stretching in a broad semicircle from the Nile to the Tigris and Euphrates
Fertilizers
A substance spread onto soil to increase its ability to support crops. Fertilizers include organic materials, such as manure, but can also be man made chemicals such as nitrates
Food deserts
urban and rural low-income areas with limited access to affordable and nutritious foods
GMOs (genetically modified organisms)
Plants and animals that have been genetically altered to contain genes they would not normally have
Green Revolution
An agricultural revolution that increased production through improved seeds, fertilizers, and irrigation; helped to support rising populations.

Herbicides
Chemicals that kill plants

High-yield seeds
Seeds that grow into plants that produce more grains per plant
Horticulture
The growing of fruits, vegetables, and flowers.
Hybrid crops
Edible plants that have been produced from cross breeding of different varieties of the same plant to produce plants with (hopefully) more beneficial traits
Intensive farming
Achieving a high yield from a small growing area - usually involves a lot of labor

Irrigation
The process of supplying water to areas of land to make them suitable for growing crops.
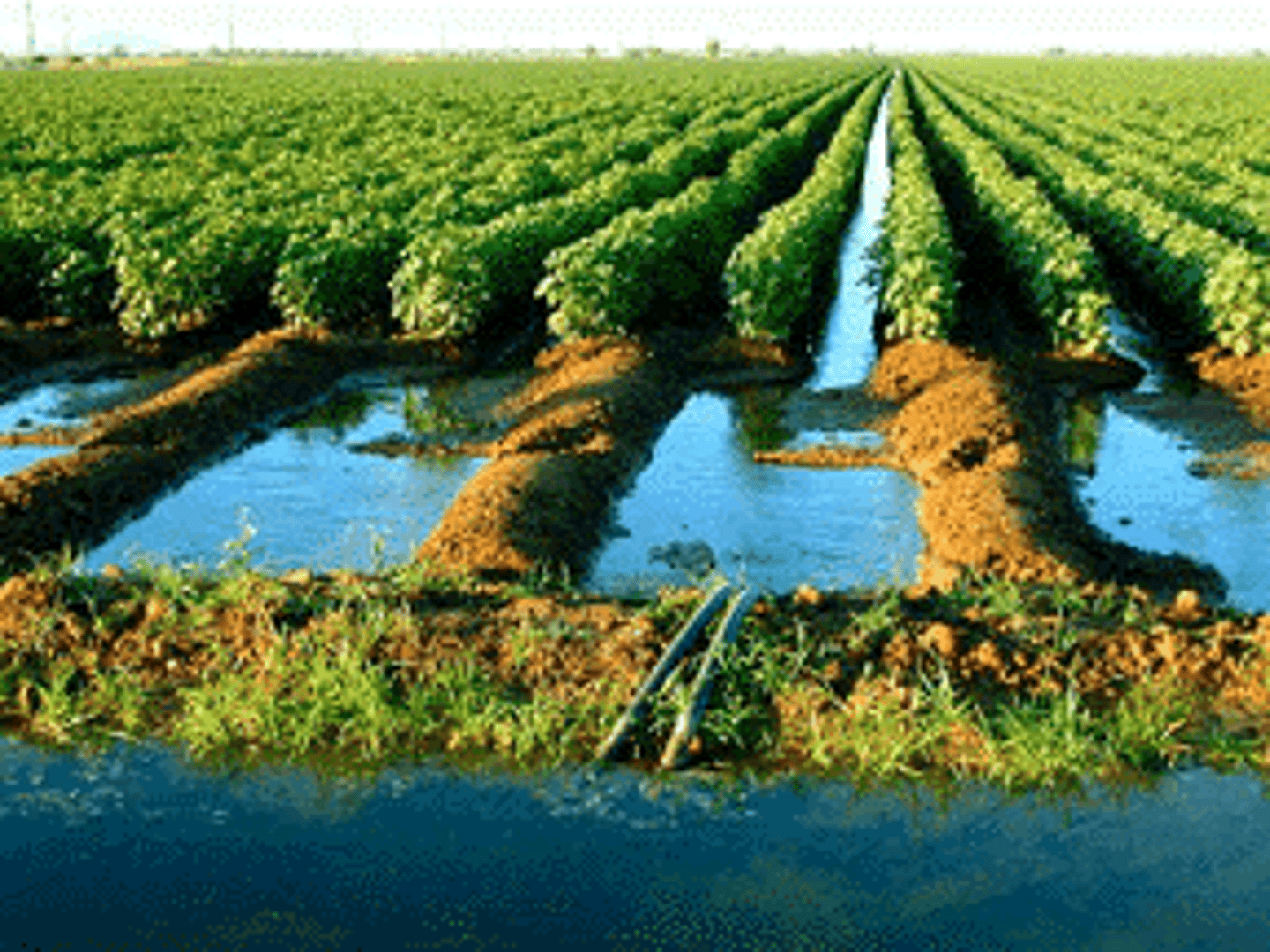

Large scale commercial agricultural operation (factory farms)
large farming for profit such as agribusiness and plantation farming
Land survey systems
surveying methods developed and used to divide the landscape into plots for sale and settling (ex: long lots, metes & bounds, township-and-range)
Local-food movements
the goal is to connect food producers and food consumers in the same area in order to develop more self-reliant and resilient food networks; improve local economies; or to have an impact on the health, environment, or community of that area
Low latitude regions
The tropics - various plants grow best here.
Market gardening
The small scale production of fruits, vegetables, and flowers as cash crops sold directly to local consumers. Distinguishable by the large diversity of crops grown on a small area of land, during a single growing season. Labor is done manually.

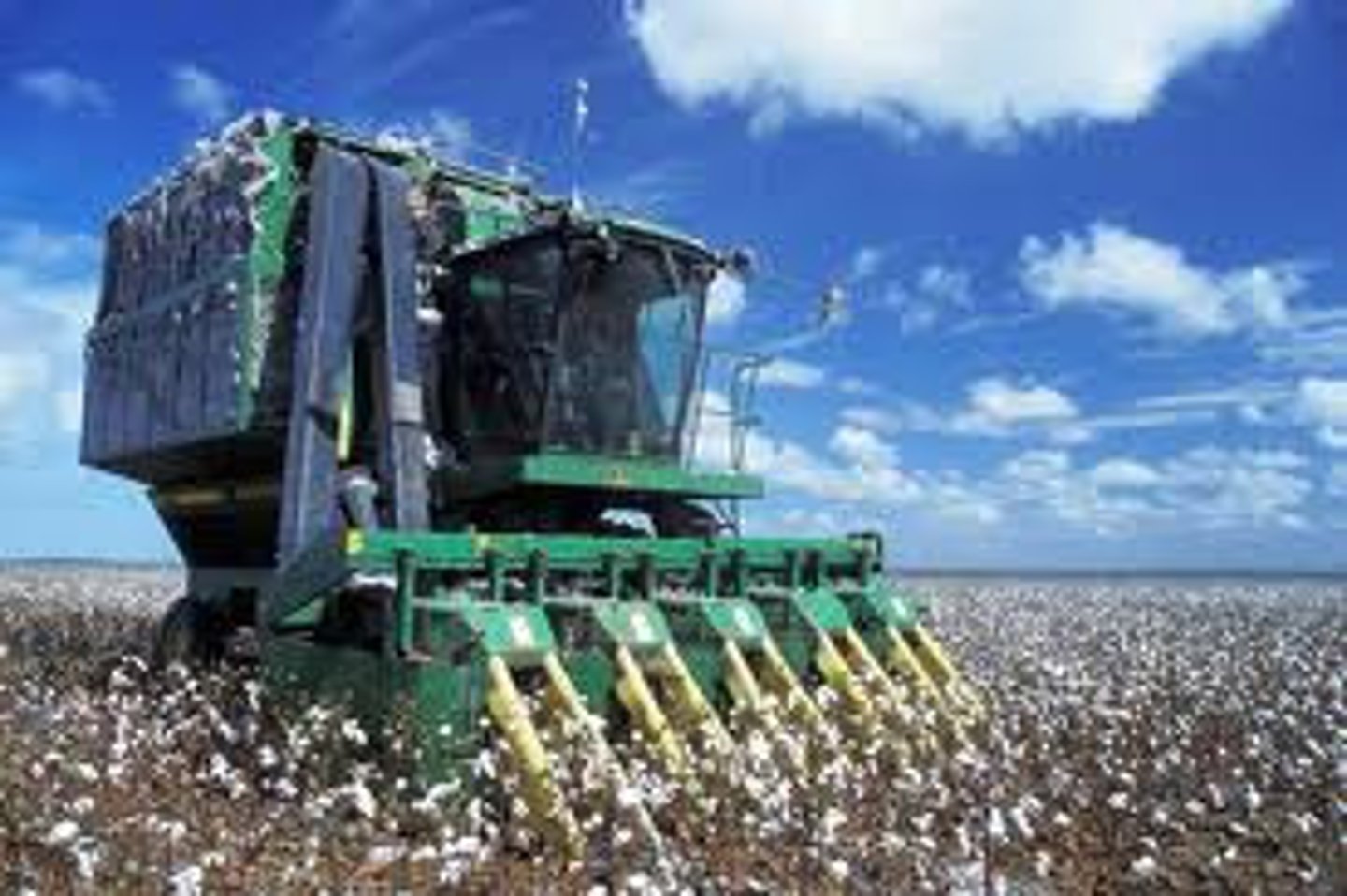
Mechanized farming
farming with machines

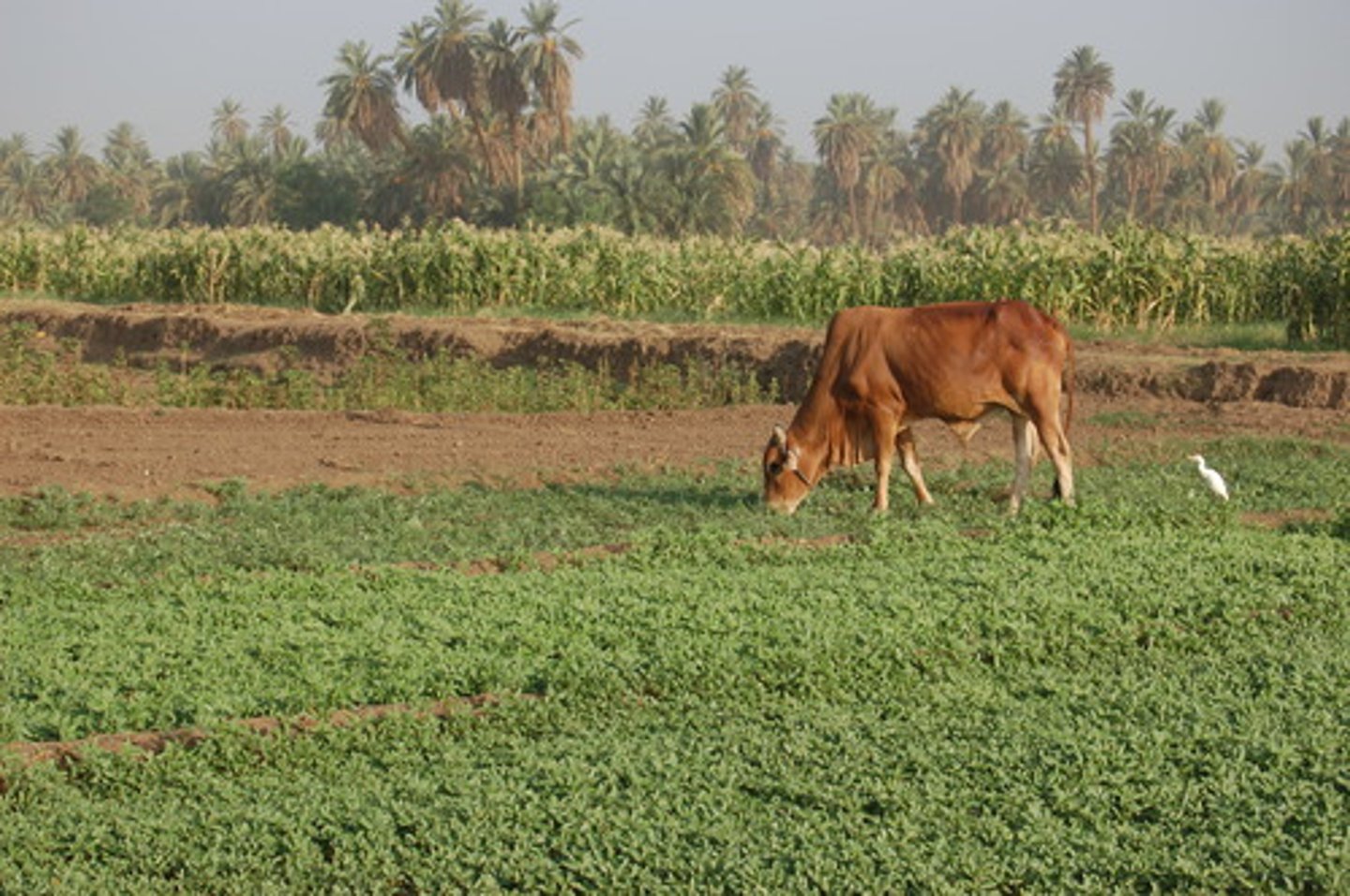
Mediterranean Climate Region
A climate marked by warms, dry, summers and cool, rainy winters - certain crops (like olives, grapes and other fruits, vegetables and tree nuts) grow best here.
Mixed crop/livestock
Smaller farms that raise both animals and a plants.

Neolithic
"Neo"means new, was a change from hunting and gathering to farming or from food gatherers to food producers

Organic farming
A method of farming that does not use artificial means such as synthetic pesticides and herbicides, antibiotics, and bioengineering
Overgrazing
Destruction of vegetation caused by too many grazing animals consuming the plants in a particular area so they cannot recover

Pastoral nomadism
A form of subsistence agriculture based on herding domesticated animals.

Pesticides
Chemicals intended to kill insects and other organisms that damage crops

Plantation agriculture
Production system based on a large estate owned by an individual, family, or corporation and organized to produce a cash crop. Almost all plantations were established within the tropics; in recent decades, many have been divided into smaller holdings or reorganized as cooperatives

Salinization
The buildup of minerals in soil, decreasing its fertility; can be caused by long-term irrigation.

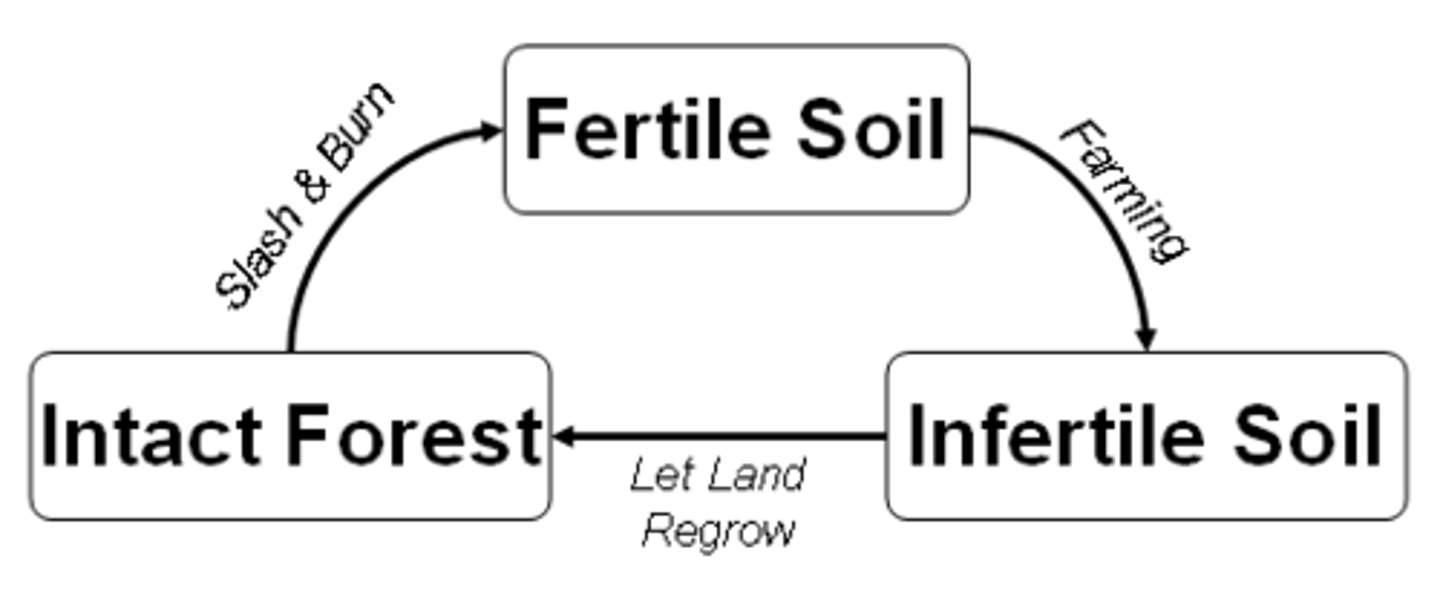
shifting cultivation
- The Practice of farming a site until the soil is exhausted, then moving on to a new site
- A form of subsistence agriculture in which people shift activity from one field to another; each field is used for crops for relatively few years and left fallow for a relatively long period.
Soil degradation
The loss of some or all of a soil's ability to support plant growth

Specialty farming (truck farming)
farmers grow crops that have increasing demand among affluent consumers such as asparagus, peppers, mushrooms, strawberries, nursery plants, etc.
Subsistence
farming in which only enough food to feed one's family is produced
Sustainability
Using resources in ways that do not harm ecological systems that support human existence

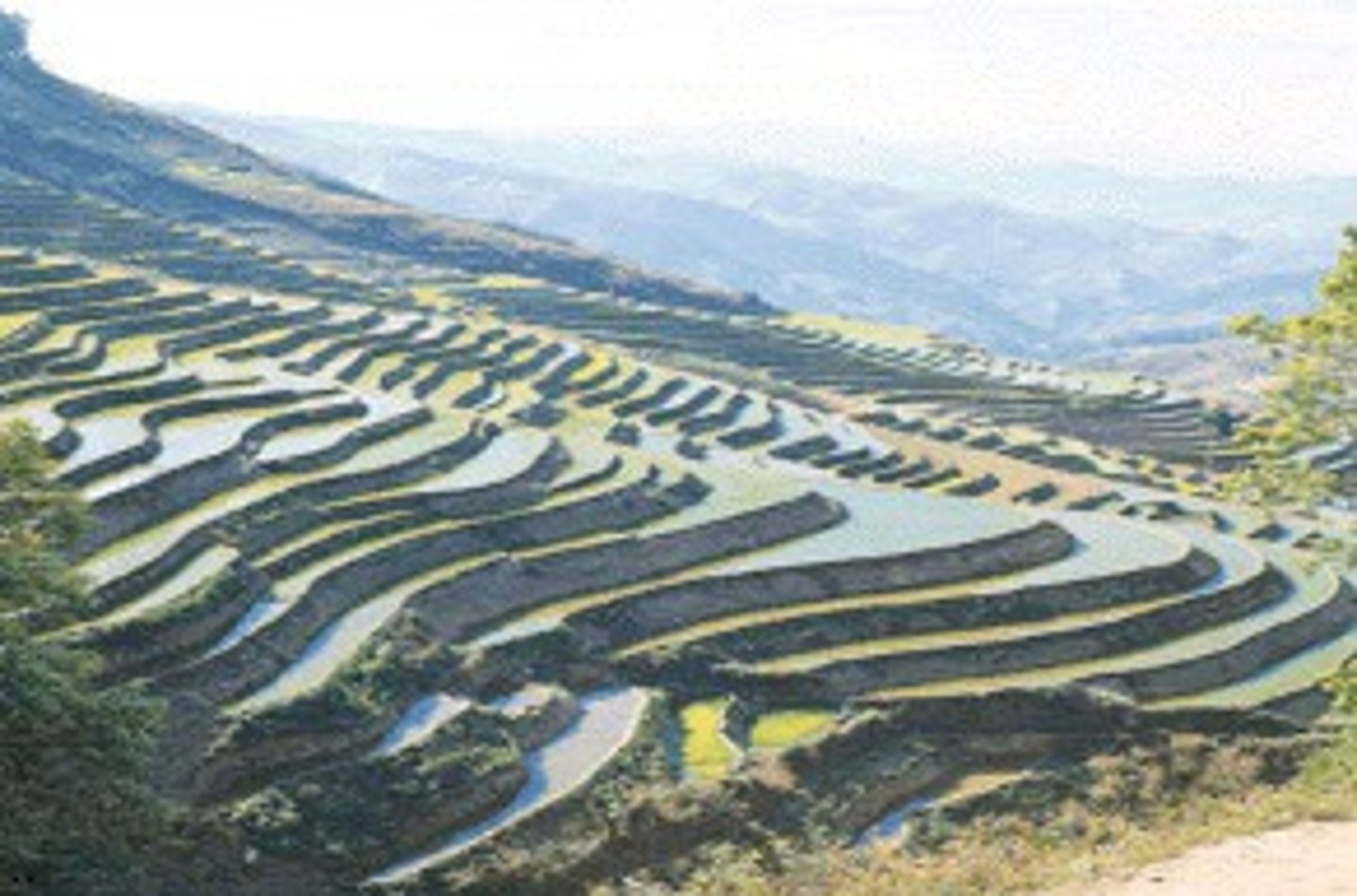
Terraces
steplike ledges cut into mountains to make land suitable for farming

Wetland destruction
When wetlands are drained and filled so the land can be used for buildings and other development

Value-added specialty crops
increasing the economic value of a commodity through particular production processes, e.g., organic produce, or through regionally branded products that increase consumer appeal and willingness to pay a premium over similar but undifferentiated products. i.e. free-range chickens, hormone-free beef
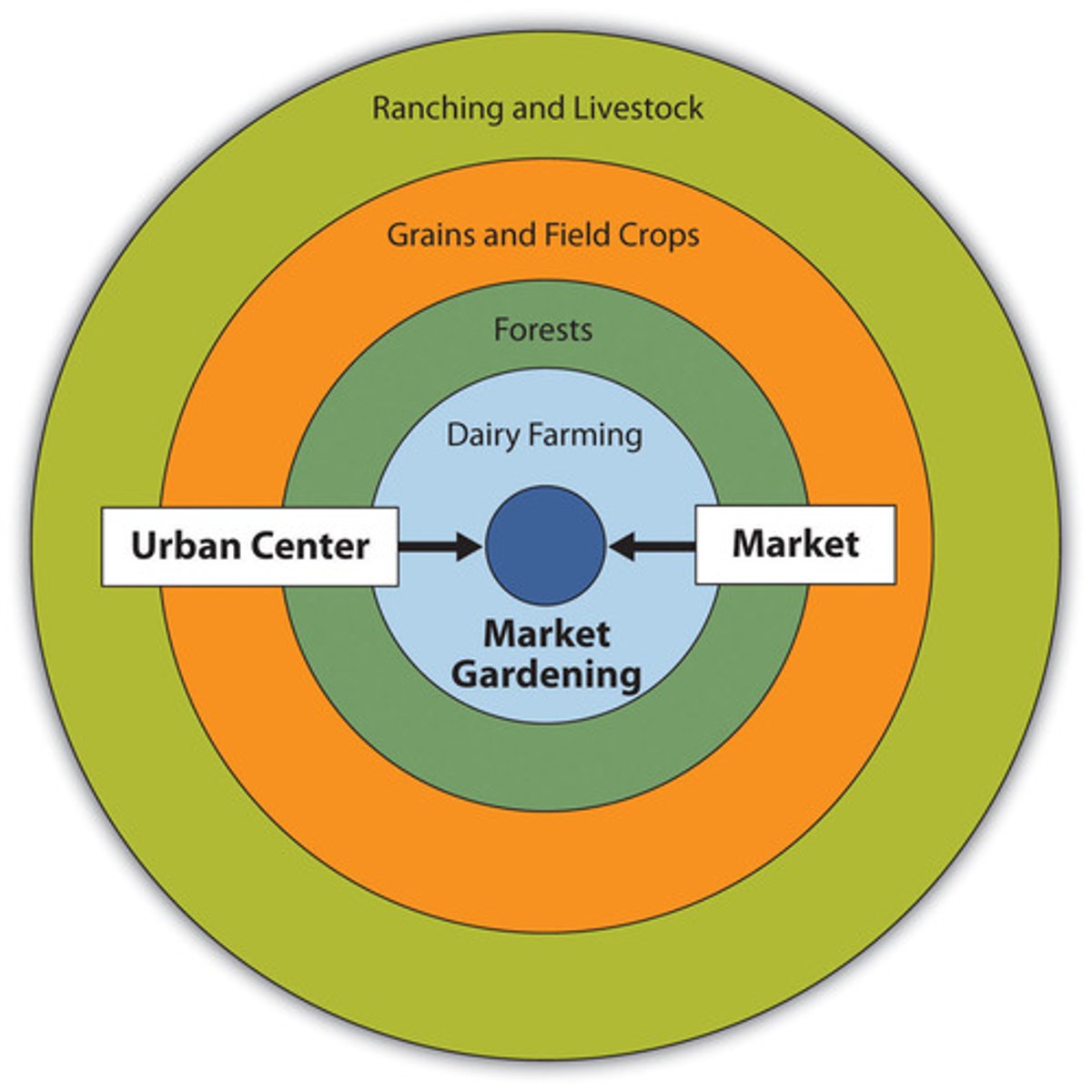
Von Thunen's Model
explains and predicts agricultural land use. more INTENSIVE land uses closer to the market place. more EXTENSIVE land farther from the market place. EX: 1st ring (intensive perishable products ), 2nd (forest resources), 3rd (mixed crop and grains), 4th (livestock grazing)
settlement patterns
the distribution of homes and farms in an area - described as dispersed, clustered and linear
Bid-Rent theory
geographical economic theory that refers to how the price and demand on real estate changes as the distance towards the Central Business District (CBD) increases
commodity chain
series of links connecting the many places of production and distribution and resulting in a commodity that is then exchanged on the world market
Community Supported Agriculture (CSA)
network between agricultural producers and consumers whereby consumers pledge support to a farming operation in order to receive a share of the output from the farming operation
conservation
the sustainable use of and management of Earth's natural resources to meet human needs such as food, medicine, and recreation
cash crop
a crop produced for its commercial value rather than for use by the grower
crop rotation
the system of growing a different crop in a field each year to preserve the fertility of the land
double cropping
growing more than one crop a year on the same land
Early Hearths of Agricultural Domestication
Agriculture originated in multiple hearths around the world, including SW Asia (Fertile Crescent), South Asia (Indus River Valley), SE Asia, and Central America
fallow
plowed but not seeded; inactive land
Intertillage
- tillage or cultivation between plants (as corn and potatoes), in contrast to tillage of the entire surface when no growing crop is on it.
- tilling the soil between the rows of a crop already planted in the soil
Land cover change
The changes that have taken place to natural environments due to a variety of natural and/or human-induced causes
Overfishing
depleting fish populations by capturing fish faster than they can reproduce; has led to the extinction of species
preservation
the activity of protecting cultural assets, nature resources or cultural landscapes from loss or danger no matter the characters of the environment it is situated in, the needs or thoughts of the community whom it belongs
subsidy
a sum of money granted by the government or a public body to assist an industry or business (Ex: Agricultural subsidy)
Swidden
A patch of land cleared for planting through slashing and burning.
tillage
the preparation of land for growing crops
Transhumance
The seasonal migration of livestock between mountains and lowland pastures.
Urban farming
The growing of fruits, herbs, and vegetables and raising animals in towns and cities, a process that is accompanied by many other activities such as processing and distributing food, collecting and reusing food waste.
wet rice farming
The practice of planting rice on dry land in a nursery and then moving the seedlings to a flooded field for growth. Labor intensive.
Monocropping (monoculture)
An agricultural method that utilizes large plantings of a single species or variety
Ranching
A form of commercial agriculture in which livestock graze over an extensive area.
Clustered rural settlement
A rural settlement in which the houses and farm buildings of each family are situated close to each other and fields surround the settlement.
Dispersed rural settlement
A rural settlement pattern characterized by isolated farms rather than clustered villages.
linear rural settlements
Farms are clustered along road, river, or dike; lots of land perpendicular to river and road inland parallel to river; lots of land parallel to original riverfront settlement (St. Lawrence river in Quebec)
metes and bounds system
A system of land surveying east of the Appalachian Mountains. It is a system that relies on descriptions of land ownership and natural features such as streams or trees. Because of the imprecise nature of metes and bounds surveying, the U.S. Land Office Survey abandoned the technique in favor of the rectangular survey system.
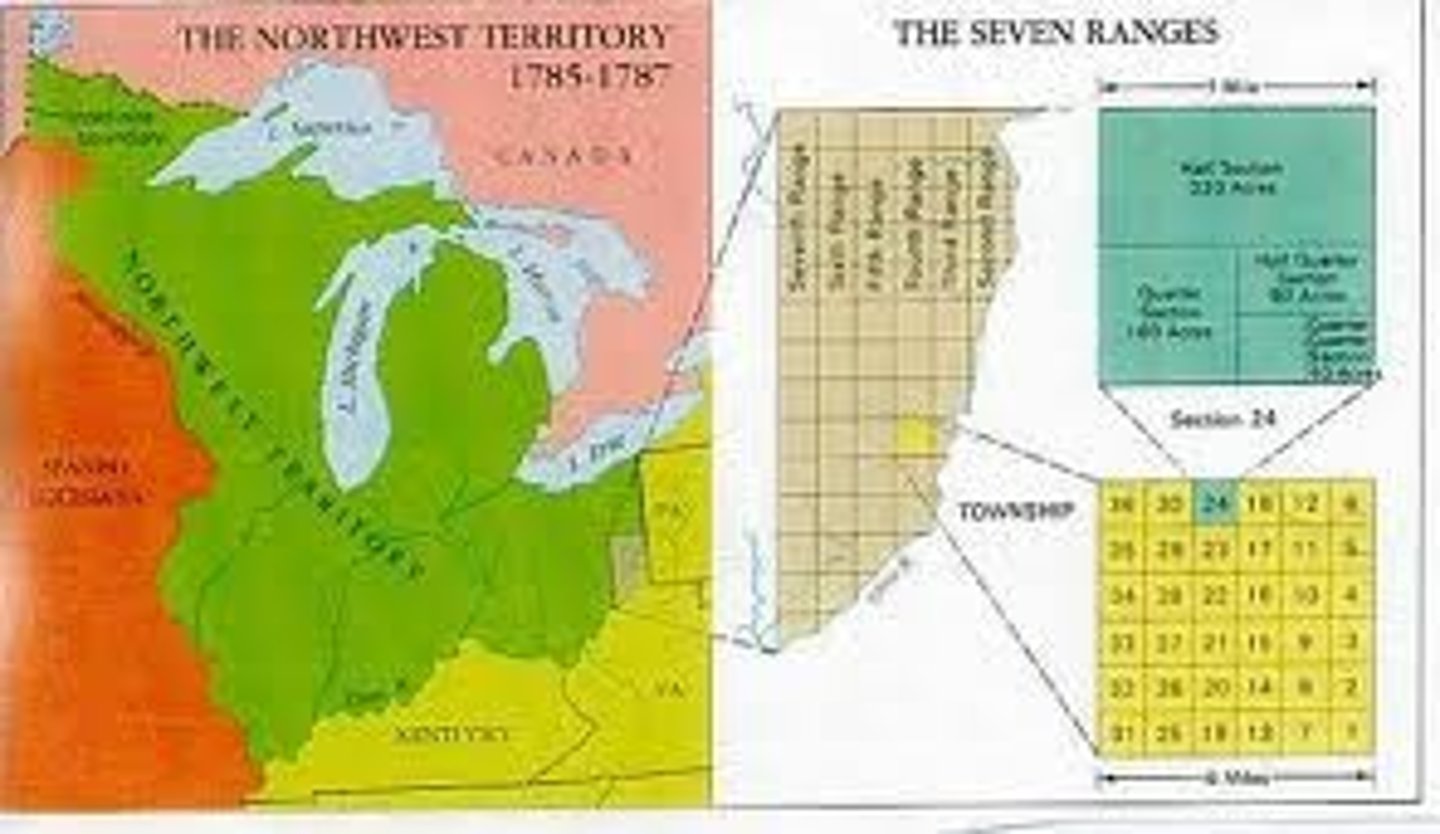
township and range system
A rectangular land division scheme designed by Thomas Jefferson to disperse settlers evenly across farmlands of the U.S. interior.
long-lot survey system
distinct regional approach to land surveying found in the Canadian Maritimes, parts of Quebec, Louisiana, and Texas whereby land is divided into narrow parcels stretching back from rivers, roads, or canals
slash and burn agriculture
Another name for shifting cultivation, so named because fields are cleared by slashing the vegetation and burning the debris.