Blood Values & Pharmacology
1/63
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
64 Terms
What is the primary function of a rapid infusion pump?
a) To slowly infuse IV medications over several hours
b) To deliver blood or fluids rapidly using a pressurized cuff, often with a fluid warmer
c) To measure blood pressure continuously during surgery
d) To regulate oxygen flow during anesthesia
b) To deliver blood or fluids rapidly using a pressurized cuff, often with a fluid warmer
A rapid infusion pump delivers blood or fluids quickly by applying external pressure with a cuff around the administration bag, sometimes including a fluid warmer to prevent hypothermia during rapid transfusions.
Type A positive blood can donate to:
a) A positive
b) B positive
c) AB positive
d) A positive and AB positive
d) A positive and AB positive
Type A positive blood can be safely given to recipients with A positive or AB positive blood types due to compatible antigens and Rh factors.
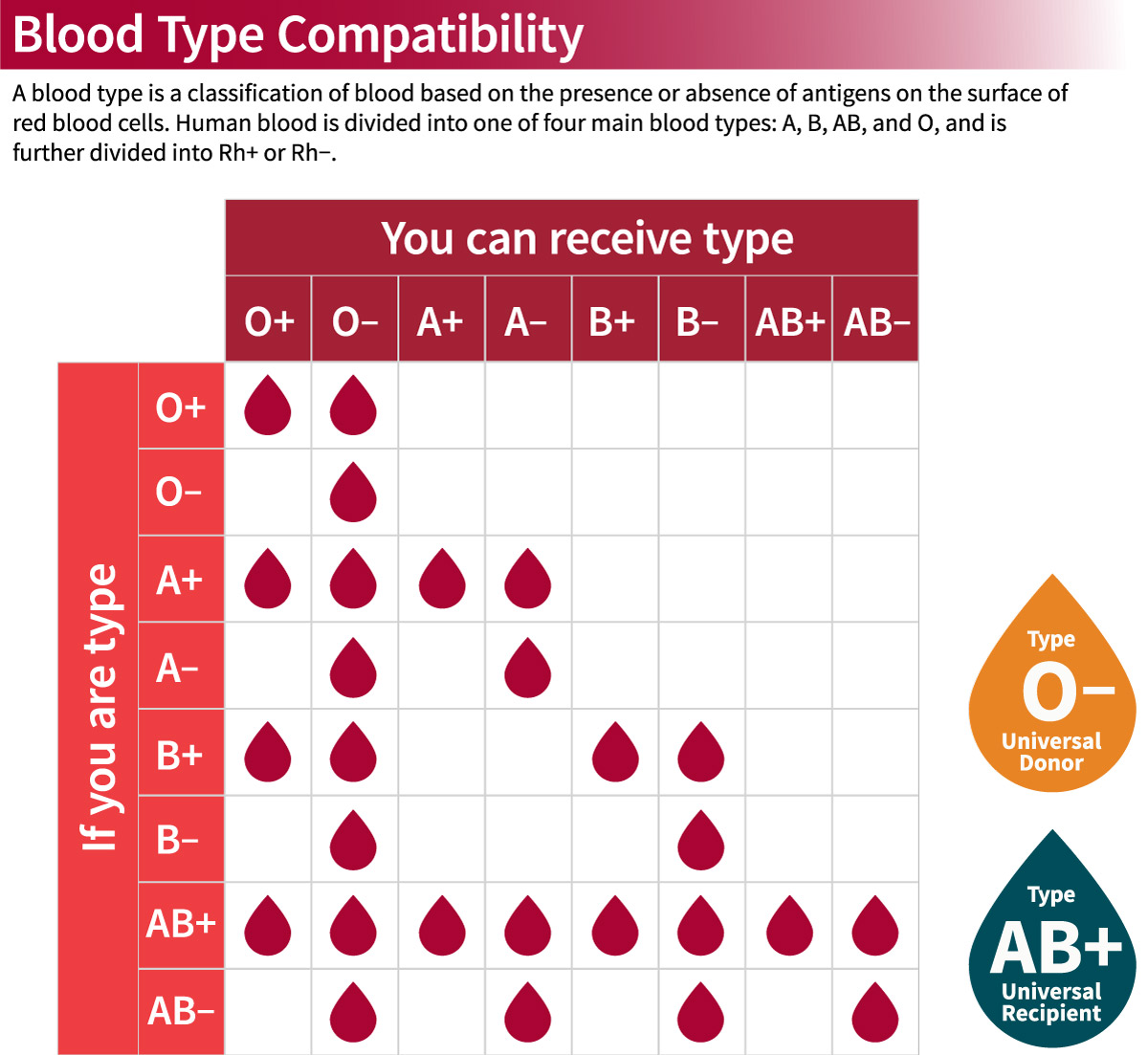
Homologous refers to:
a) one's own blood
b) donated blood
c) blood products
d) synthetic blood products
b) donated blood
Homologous blood is blood donated from another person, while one's own blood used in transfusion is called autologous.
In a normal adult, the average number of leukocytes per cubic millimeter of circulating blood is:
a) 1,000 - 4,000
b) 3,000 - 8,000
c) 5,000 - 10,000
d) 10,000 - 15,000
c) 5,000 - 10,000
A normal adult has about 5,000 to 10,000 leukocytes (white blood cells) per cubic millimeter; elevated counts usually indicate infection or inflammation.
What is the normal white blood cell count in an adult male?
a) 5.0 - 6.0
b) 5,000 - 10,000
c) 14 - 18
d) 150 - 400
b) 5,000 - 10,000
The normal white blood cell count range for adult males and females is 5,000 to 10,000 per cubic millimeter of blood.
If you are Rh positive:
a) you do NOT have the antigen on the surface of red blood cells
b) you can donate blood to all patients
c) you do have the antigen found on red blood cells
d) you CANNOT receive O negative blood
c) you do have the antigen found on red blood cells
Rh positive individuals have the Rh antigen on their red blood cells, which affects compatibility in blood transfusions.
Who is the universal plasma donor?
a) AB
b) A
c) B
d) O
a) AB
AB plasma contains no anti-A or anti-B antibodies, making it the universal plasma donor.

Cross-matching of blood:
a) determines patient's blood type
b) determines Rh factor of both patient and donor
c) determines suitability of donor by mixing donor RBC's with recipient serum
d) determines blood group of donor
c) determines suitability of donor by mixing donor RBC's with recipient serum
Cross-matching tests for compatibility by mixing donor red blood cells with recipient serum; if agglutination (clumping) does not occur, the blood is compatible for transfusion.
One ounce is equal to _ cc.
a) 60 cc
b) 1 cc
c) 30 cc
d) 10 cc
c) 30 cc
One ounce is equal to 30 cubic centimeters (cc), a common conversion in medical dosing.
An osmotic diuretic agent used to decrease cerebral edema and intraocular edema is:
a) Diuril
b) Furosemide
c) Papaverine
d) Mannitol
d) Mannitol
Mannitol is an osmotic diuretic given prophylactically to prevent renal failure and to decrease intracranial and intraocular pressure.
A drug used to reverse an overdose of an analgesic is:
a) Atropine
b) Demerol
c) Narcan
d) Protamine sulfate
c) Narcan
Narcan (naloxone) reverses opioid analgesic overdose; atropine is an anticholinergic, Demerol is an analgesic, and protamine sulfate reverses heparin.
Normal saline is used for lap pad moistening and for intraperitoneal irrigation because it is:
a) Hypotonic
b) Isotonic
c) Hypertonic
d) Hyperkalemic
b) Isotonic
Normal saline is isotonic, containing salt concentration equal to body fluids, so it does not disrupt sodium, chloride, or fluid balance.
Which of the following refer to Kortokoff's sounds?
a) The first tapping sound heard when taking a blood pressure
b) Soft whistling sound as cuff is deflated
c) Rhythmic tapping sound as the cuff is deflated
d) All of the above
d) All of the above
Kortokoff's sounds include all these phases and are used to determine blood pressure.
The most widely used local anesthetic is:
a) Carbocaine
b) Marcaine
c) Prilocaine
d) Lidocaine
d) Lidocaine
Lidocaine (Xylocaine) is potent with rapid onset and minimal local irritation; allergic reactions are rare.
The drug used to treat malignant hyperthermia is:
a) Dantrolene
b) Levophed
c) Depo-Medrol
d) Digoxin
a) Dantrolene
Dantrolene blocks calcium release in muscle cells to relieve malignant hyperthermia symptoms.
An artificial plasma-volume expander is:
a) Mannitol
b) Dextran
c) Ringer's solution
d) Uromatic
b) Dextran
Dextran expands blood volume by drawing fluid from tissues and is used in shock treatment.
An undesirable or intolerable reaction to a drug administered at the normal dosage is defined as:
a) Toxicity
b) Allergy
c) Side effect
d) Adverse reaction
d) Adverse reaction
Adverse reactions are harmful or intolerable effects occurring at normal doses.
Drugs used to reduce the reabsorption of water, causing frequent urination:
a) Anticoagulants
b) Anticholinergics
c) Diuretics
d) Colloids
c) Diuretics
Diuretics promote urine secretion to remove excess fluid.
Avitene is:
a) Hemostatic
b) Adrenergic
c) Cycloplegic
d) Mydriatic
a) Hemostatic
Avitene is a microfibrillar collagen hemostatic agent applied dry to assist clotting when conventional methods fail.
A topical antibiotic is:
a) Bacitracin
b) Ephedrine
c) Ancef
d) Keflex
a) Bacitracin
Bacitracin is used topically to prevent infection.
During general anesthesia, exhaled CO2 is absorbed by:
a) Soda lime reservoir
b) Vaporizer
c) Ventilator
d) Breathing bag
a) Soda lime reservoir
Soda lime absorbs exhaled CO2 from the anesthesia circuit.
Which of the following symptoms is not a symptom of malignant hyperthermia?
a) Muscle contraction
b) Bradycardia
c) Rigid jaw
d) Increased body temperature
b) Bradycardia
Malignant hyperthermia typically causes tachycardia, not bradycardia.
The drug used to treat ventricular arrhythmias is:
a) Lidocaine
b) Marcaine
c) Sensorcaine
d) Bupivacaine
a) Lidocaine
Lidocaine is used IV for ventricular arrhythmias; other agents are not given intravenously.
The patented name of medication is also its:
a) Chemical name
b) Proprietary name
c) Molecular name
d) None of the above
b) Proprietary name
The proprietary name is the brand or patented name given by the manufacturer.
The needed medication comes in 100 mg per 1 oz. The surgeon wants 50 mg. Your syringe will draw up ___ of the medication.
a) 0.5 cc
b) 1 cc
c) 2 cc
d) 3 cc
a) 0.5 cc
If 1 cc = 100 mg, then 50 mg equals 0.5 cc.
An example of a depolarizing muscle relaxant is:
a) Halothane
b) Fentanyl
c) Sufentanil
d) Succinylcholine
d) Succinylcholine
Succinylcholine produces depolarizing neuromuscular blockade.
The trade name for xylocaine is:
a) Pontocaine
b) Marcaine
c) Lidocaine
d) Sensorcaine
c) Lidocaine
Lidocaine is the trade (proprietary) name for xylocaine.
A drug that constricts the pupil during ophthalmic surgery is:
a) Healon
b) Miochol
c) Hyaluronidase
d) Atropine
b) Miochol
Miochol rapidly constricts the pupil during anterior segment surgery.
Which IV solution is similar to plasma, is water based and contains sodium, potassium, and calcium?
a) Dextrose 5% in water
b) Ringer's
c) Normal saline
d) Lactated Ringer's
b) Ringer's
Ringer's solution contains electrolytes similar to plasma; others differ in composition.
Compazine is:
a) Antiemetic
b) Sedative
c) Tranquilizer
d) Anticholinergic
a) Antiemetic
Compazine reduces nausea and vomiting.
Which instrument aids in positioning the endotracheal, nasotracheal, and nasogastric tubes in the trachea?
a) McGill forceps
b) Bayonet forceps
c) Transfer forceps
d) Bozeman forceps
a) McGill forceps
McGill forceps are used for tube placement in the airway or esophagus.
Nitrous oxide should never be used on which procedure?
a) Shoulder arthroscopy
b) Circumcision
c) Tympanoplasty
d) Closed fracture
c) Tympanoplasty
Nitrous oxide increases pressure in enclosed spaces, contraindicated in tympanoplasty.
Neuroleptanalgesia combines:
a) A narcotic and an anticholinergic
b) A tranquilizer and narcotic
c) An anti-inflammatory and a tranquilizer
d) A muscle relaxant and a tranquilizer
b) A tranquilizer and narcotic
This combination produces analgesia and sedation, sometimes with inhaled anesthetics.
The solutions used intravenously to replace plasma when plasma is not available is:
a) 0.9% NaCl
b) Dextrose 5% in water
c) Lactated Ringer's solution
d) Dextran
d) Dextran
Dextran is an artificial plasma volume expander used in emergencies.
Patient is receiving 1 litre of 5% dextrose in water as an IV fluid during her 1-hour surgery. The number of grams of dextrose the patient has received during this infusion is:
a) 5 g
b) 50 g
c) 500 g
d) 0.5 g
b) 50 g
5% means 5 g per 100 cc; 1 litre = 1000 cc, so 10 times 5 g = 50 g.
When the surgeon performs an intraoperative cholangiogram s/he uses:
a) Renografin
b) Conray
c) Barium sulfate
d) Gentian violet
a) Renografin
Renografin is a contrast medium used for imaging hollow organs.
Which technique can be employed to prevent pain during an operative procedure or to relieve chronic pain?
a) Local infiltration
b) Bier block
c) Nerve block
d) Field block
c) Nerve block
Nerve blocks provide anesthesia by blocking nerve conduction in targeted areas.
Another name for Anectine is:
a) Succinylcholine
b) Halothane
c) Fluothane
d) Fentanyl
a) Succinylcholine
Anectine is the trade name for succinylcholine.
Malignant hyperthermia can be triggered by:
a) Succinylcholine
b) Demerol
c) Morphine
d) Valium
a) Succinylcholine
Succinylcholine and some inhalation agents trigger malignant hyperthermia in susceptible patients.
A drug that could be used to reverse the effect of muscle relaxants is:
a) Narcan
b) Protamine sulfate
c) Prostigmin
d) Valium
c) Prostigmin
Prostigmin (neostigmine) reverses non-depolarizing muscle relaxants.
Solu-Medrol is a/an:
a) Antibiotic
b) Myotic
c) Mydriatic
d) Anti-inflammatory
d) Anti-inflammatory
Solu-Medrol (methylprednisolone) is a corticosteroid reducing inflammation.
A dissociative agent that provides complete unconsciousness and a catatonic state is:
a) Ketamine
b) Nitrous oxide
c) Versed
d) Anectine
a) Ketamine
Ketamine induces a catatonic-like dissociative anesthesia.
Benzodiazepines are categorized as:
a) Analgesics
b) Sedatives
c) Cholinergics
d) Anticholinergics
b) Sedatives
Benzodiazepines relieve anxiety and induce sedation.
During ophthalmic surgery, paralysis of the ciliary muscle is achieved by using:
a) Cycloplegics
b) Myotics
c) Mydriatics
d) Narcotics
a) Cycloplegics
Cycloplegics paralyze the ciliary muscle to facilitate surgery.
A drug that decreases the tendency of blood to clot is:
a) Warfarin sodium
b) Diazepam
c) Lorazepam
d) Midazolam HCl
a) Warfarin sodium
Warfarin is an anticoagulant that inhibits clot formation.
Each of the following agents must be applied using dry gloves or instruments EXCEPT:
a) Gelfoam
b) Collastat
c) Avitene
d) Helistat
a) Gelfoam
Gelfoam can be used wet or dry; the others must be applied dry.
A method of anesthesia in which medication is injected into the subarachnoid space, affecting a portion of the spinal cord, is called a:
a) Bier block
b) Field block
c) Nerve block
d) Spinal block
d) Spinal block
Spinal anesthesia affects lower spinal cord and nerve roots via subarachnoid injection.
Zofran is an:
a) Antiemetic
b) Sedative
c) Tranquilizer
d) Anticholinergic
a) Antiemetic
Zofran blocks serotonin receptors to reduce nausea and vomiting.
Drug effects that occur predictably, and may not cause a problem are:
a) Adverse reaction
b) Toxicity
c) Side effect
d) Therapeutic effect
c) Side effect
Side effects are expected but not harmful effects.
A sedative/tranquilizer used to reduce anxiety and apprehension of the pre-op patient is:
a) Valium
b) Marzicon
c) Anectine
d) Demerol
a) Valium
Valium is a benzodiazepine used to calm patients before surgery.
Which name is derived from the molecular formula of a drug?
a) Brand
b) Proprietary
c) Chemical
d) Generic
c) Chemical
Chemical names are based on molecular structure as standardized internationally.
The most common diuretic is:
a) Lasix
b) Pronestyl
c) Isoptin
d) Cefadyl
a) Lasix
Lasix (furosemide) is widely used to promote urine output.
An A-line is commonly inserted into the:
a) Jugular artery
b) Radial artery
c) Carotid artery
d) Brachial artery
b) Radial artery
The radial artery is commonly used for arterial line placement.
An antimuscarinic:
a) Controls pain
b) Prevents nausea
c) Limits salivation
d) Reverses muscle relaxation
c) Limits salivation
Antimuscarinics reduce secretions like saliva.
A short-acting drug useful during intubation to produce paralysis and also to produce muscle relaxation is:
a) Sublimaze
b) Valium
c) Versed
d) Anectine
d) Anectine
Succinylcholine (Anectine) rapidly induces paralysis for intubation.
A Bier block provides:
a) Anesthesia to a distal portion of an extremity
b) Anesthesia below the diaphragm
c) Anesthetic block surrounding a peripheral nerve
d) Anesthetic block to a nerve group
a) Anesthesia to a distal portion of an extremity
Bier block anesthetizes the distal limb via intravenous injection with a tourniquet.
Benzodiazepines produce ___ for up to 6 hours from the onset of the drugs action.
a) Pain relief
b) Hallucinations
c) Amnesia
d) Relief from nausea
c) Amnesia
Benzodiazepines cause temporary loss of memory (amnesia).
A bolus is:
a) A small, intermittent dose intravenously
b) A dose injected subcutaneously
c) A dose injected all at once, intravenously
d) A dose injected all at once, intravenously
d) A dose injected all at once, intravenously
A bolus is a rapid intravenous injection of medication.
Pitocin is a trademark for which hormone used therapeutically to contract the uterus after placenta delivery?
a) Prostaglandin
b) Oxytocin
c) Estrogen
d) Progesterone
b) Oxytocin
Pitocin is synthetic oxytocin, a hormone produced by the pituitary gland, used to contract the uterus and control uterine hemorrhage after delivery.
Fluothane, a widely used halogenated hydrocarbon in anesthesia, is also known as:
a) Isoflurane
b) Sevoflurane
c) Halothane
d) Desflurane
c) Halothane
Fluothane is the brand name for halothane, a nonflammable anesthetic agent that provides smooth induction.
Why must suction always be available and assistance provided to the anesthesiologist during induction?
a) To keep the patient calm
b) To prevent aspiration and ensure patient safety
c) To administer medication
d) To monitor heart rate
b) To prevent aspiration and ensure patient safety
Suction is essential during induction to clear the airway and prevent aspiration, ensuring patient safety.
Nitrous oxide is best suited for which type of surgical procedures?
a) Long, complex surgeries
b) Short procedures where muscle relaxation is unimportant
c) Procedures requiring deep muscle relaxation
d) Emergency surgeries only
b) Short procedures where muscle relaxation is unimportant
Nitrous oxide has rapid induction and recovery, ideal for short procedures without the need for muscle relaxation.
Cheyne-Stokes breathing is characterized by:
a) Rapid, shallow breathing only
b) Fast breathing followed by apnea in cycles
c) Difficulty breathing
d) Normal breathing
b) Fast breathing followed by apnea in cycles
Cheyne-Stokes breathing involves cycles of rapid breathing alternating with periods of apnea.
Steroids used in surgery to reduce tissue inflammation and postoperative swelling include:
a) Decadron and Cortisporin ophthalmic ointment
b) Lidocaine and Marcaine
c) Atropine and Neostigmine
d) Aspirin and ibuprofen
a) Decadron and Cortisporin ophthalmic ointment
Steroids like Decadron and Cortisporin are applied topically to reduce inflammation and swelling postoperatively, especially in eye and plastic surgery.