Movement into and out of cells
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is diffusion
Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
what gives particles more kinetic energy
higher temperature, faster movement
what do cells need for energy
water, mineral ions, food
why do cells need energy
for them to build cell structure
where do substances pass through in a cell
a partially permeable membrane
when to molecules stop diffusing into cells
when there is an equilibrium inside and outside the cell
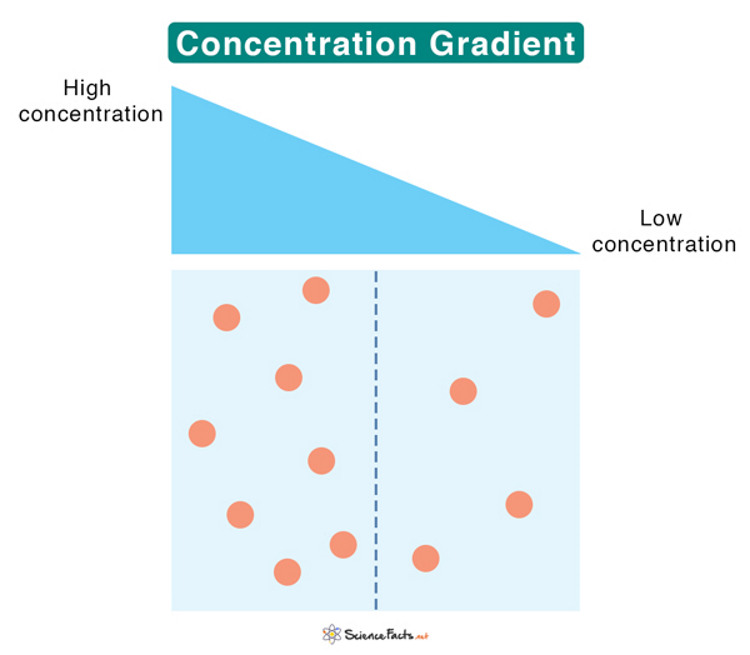
which ways of movement move down a concentration gradient
diffusion, osmosis
why do living organisms diffuse
get rid of waste, get nutrients from outside the cell
how do plants use diffusion on their leaves
to diffuse air into the leaves from outside the leaf
what is osmosis
Movement of water molecules across a partially permeable membrane from higher water concentration to lower water concentration
why is water important in the body
it in and out of cells, for chemical reactions, used as a solvent
what is the concentration gradient for osmosis
down
what is the concentration gradient for diffusion
down
what is the concentration gradient for active transport
up
where does water pass into a cell
a partially permeable membrane
what is water potential
Measure of the tendency of water molecules to move from one place to another
what is high water potential
a lot of water outside cell
what is an example of high water potential
a drink that needs to be diluted to be drinkable
what is low water potential
less water outside the cell
what is an example of low water potential
a drink that is already diluted with no need of any more water
what happens when a lot of water molecules diffuse into a cell
the cell swells and strains
do animal cells or plant cells burst when they get a lot of water in its cell
animal cells
why don’t plant cells burst
cell wall prevents that w
why do animal cells burst
the cell membrane is too weak to hold it together
what happens when the cytoplasm is too concentrated
it strains and could burst
what happens when the cytoplasm is not concentrated enough
loses water cell becomes smaller
what is it called when a cell swells
turgid
what is it called when a cell loses too much water
flaccid
what does turgid mean
a plant cell that is tight and firm
what is turgid pressure
the pressure of the water pushing outwards on a plant cell wall
what does flaccid mean
a plant cell that is soft and shrunk
what happens to the cytoplasm and vacuole when a cell become flaccid
they shrink
what else happens to the cell when it becomes flaccid regarding the cell wall and cytoplasm
cytoplasm and cell membrane pull away from the cell wall
what does Plasmolysed mean
a cell in which the cell membrane tears away from the cell wall
what is active transport
movement of molecules through the cell membrane from a region of lower concentration to high concentration
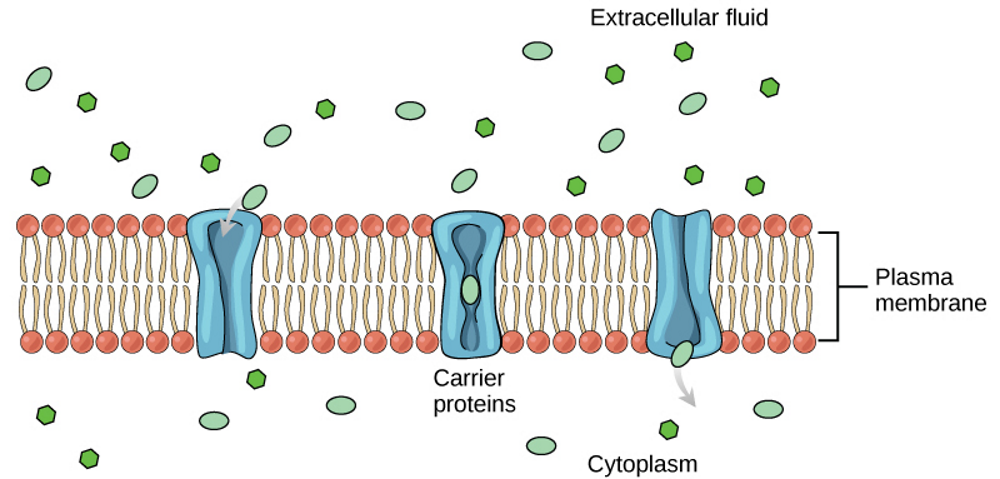
what are the blue structures
carrier Proteins
what are carrier proteins
Proteins embedded in the cell membrane that pick up specific molecules and transport them into the cell.