iCEV Slides - The Skeletal System: Skeletal Tissue
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards and fill-in-the-blanks from iCEV's course on the skeletal system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Skeletal system
The body’s framework of bones, providing structural support to the body and protecting vital organs
Types of skeletal tissue
Bone, cartilage, and ligaments
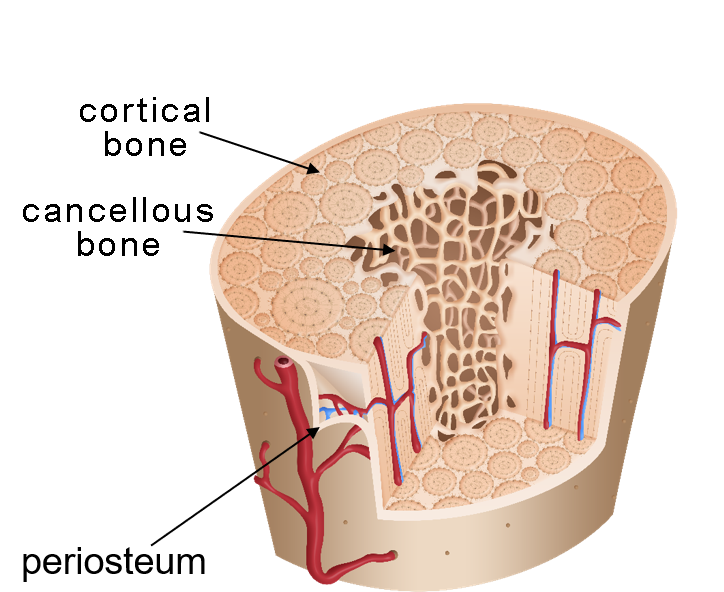
Types of bone
Cortical (compact) and cancellous (spongy)
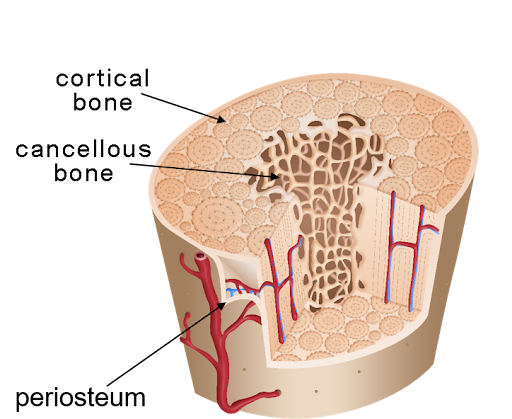
Cortical bone (compact bone)
The hard, dense outer layer of a bone
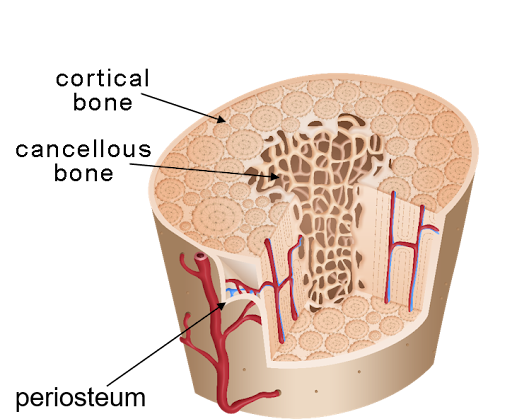
Cancellous bone (spongy bone)
The lighter, porous inner layer of a bone
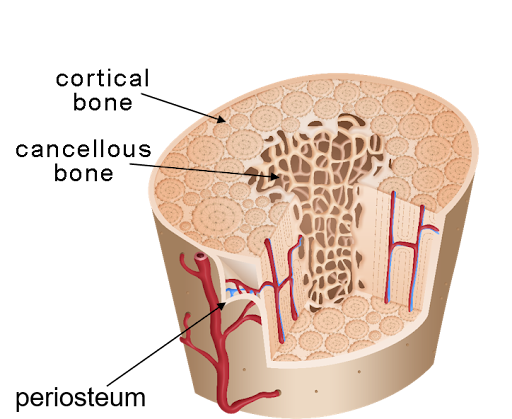
Periosteum
The thin outer layer of a bone
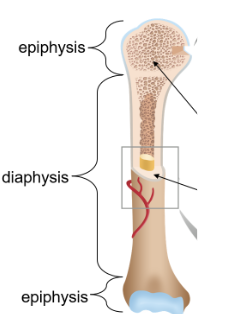
Diaphysis
The shaft extending throughout the middle of the bone containing the medullary cavity lined with endosteum
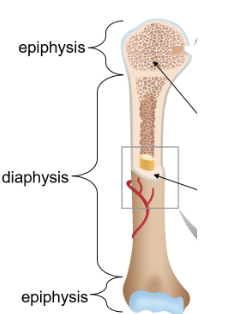
Epiphyses
Ends containing cancellous bone covered with hyaline cartilage for growth
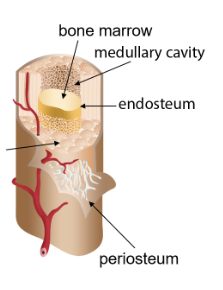
Bone marrow
Cells in the medullary cavity which can become platelets or red or white blood cells
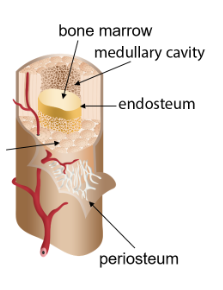
Medullary cavity
Cavity in the diaphysis (middle) of a bone that holds the bone marrow
Types of bone cells
Osteoblasts, osteocytes, and osteoclasts
Osteoblasts
Cells that develop bone matrix through ossification
Osteocytes
Mature, inactive osteoblasts incorporated into mature bone
Osteoclasts
Cells that break down old or damaged bone
Types of bones
Long, short, flat, irregular, and sesamoid (classified by shape and function)
Long bones
Hard, dense bones which provide strength, structure, and mobility—have a diaphysis and two epiphyses; types invlude the humuerus, radius and ulna, femur, and tibia and fibula
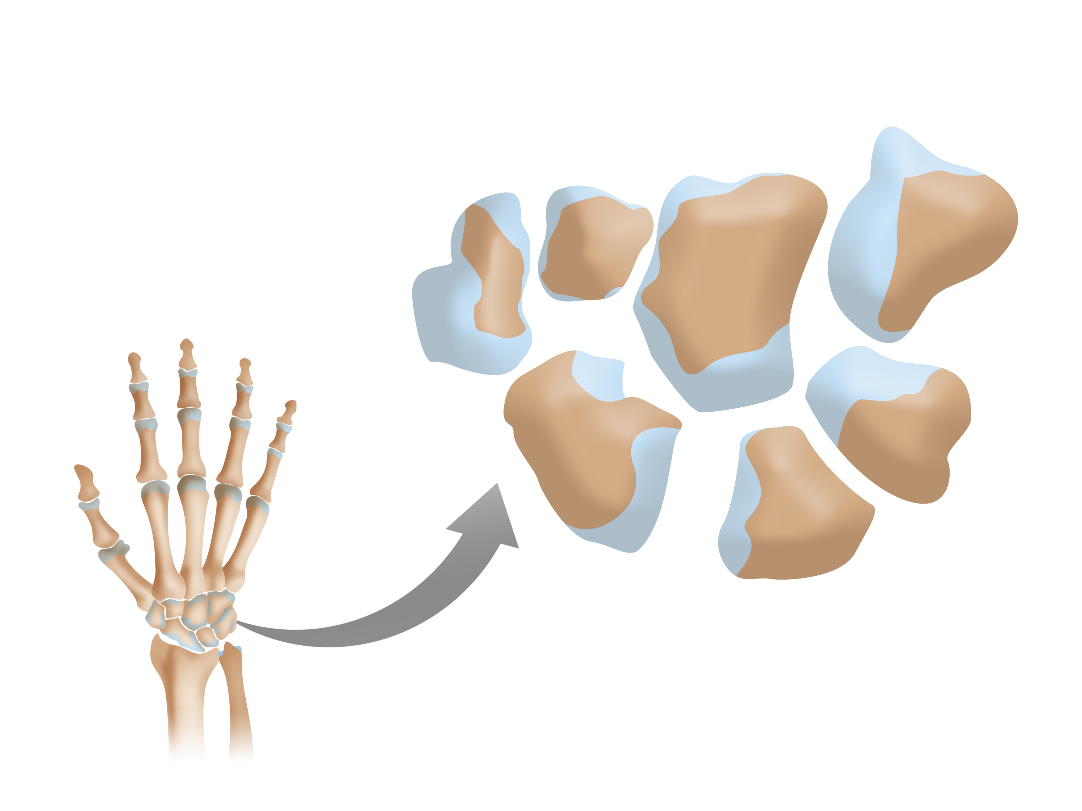
Short bones
Cube-like bones that do not contain a diaphysis and contain almost entirely cancellous (spongy) tissue; includes carpals and tarsals
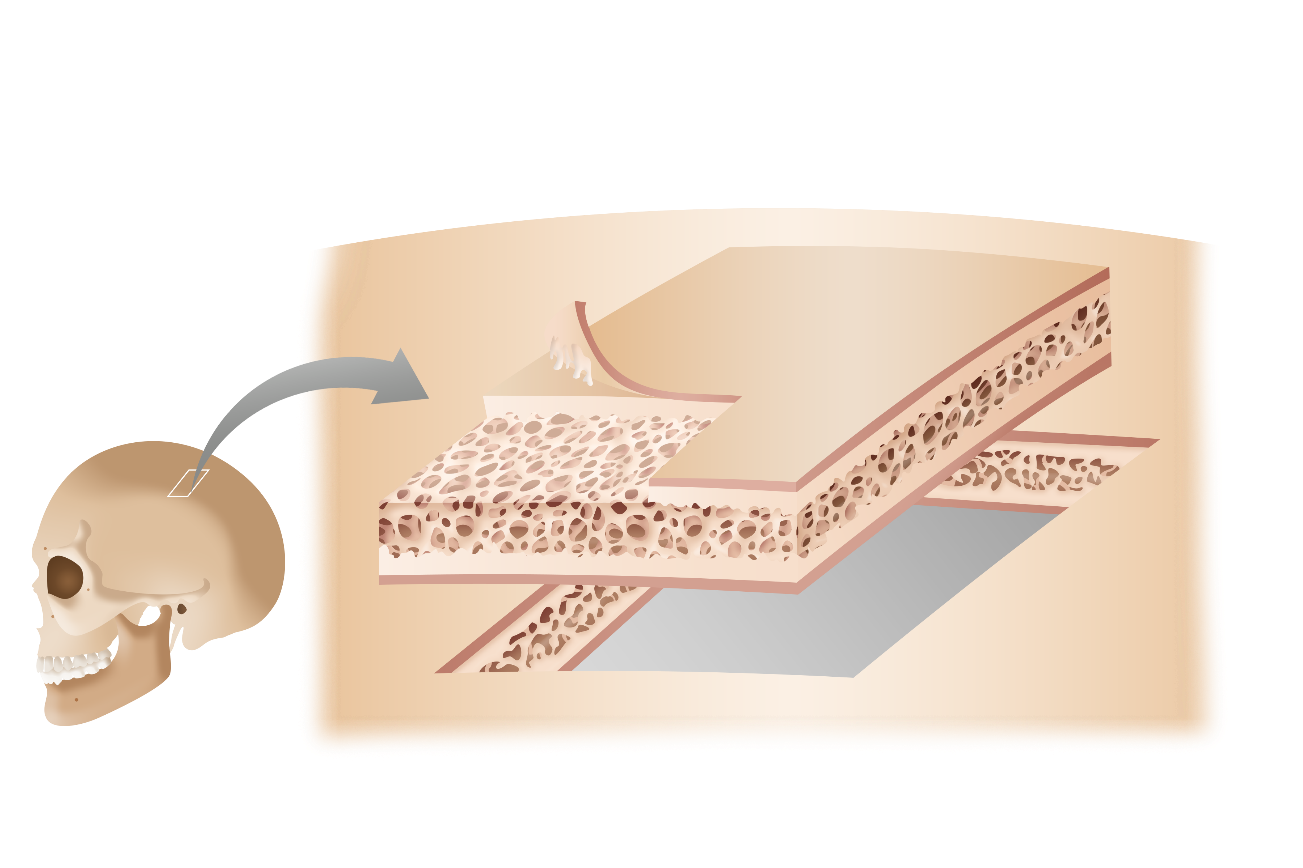
Flat bones
Thin, broad, and often curved bones with a cancellous bone layer sandwiched between two layers of cortical bone; protects internal organs and allows for attachment
Types include the skull, sternum, and ilium
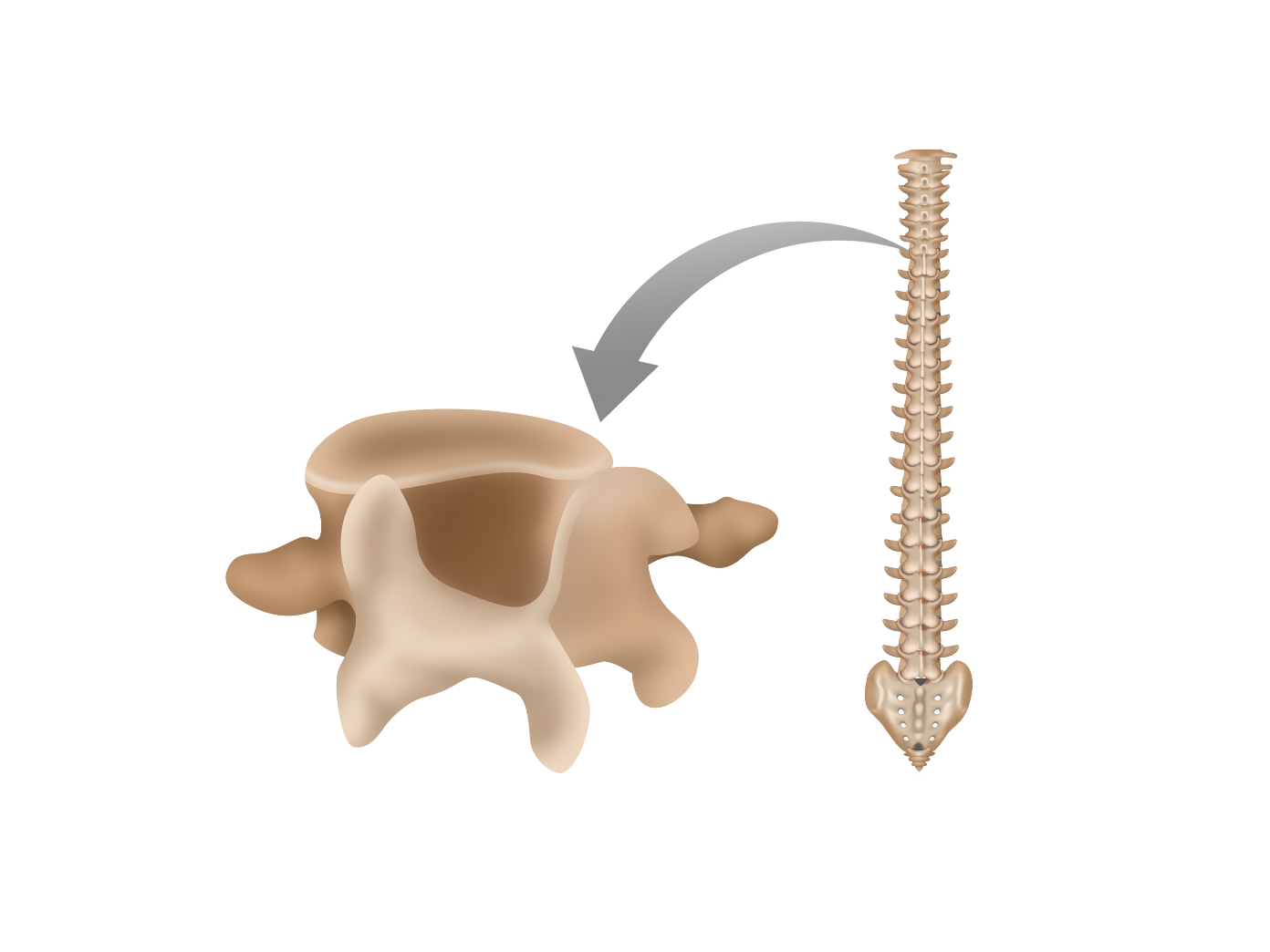
Irregular bones
Bones that are not uniform in shape with different types of surfaces; includes the vertebrae, sacrum, and coccyx
Sesamoid bones
Bones developed and embedded inside tendons that vary in shape and serve to protect the tendons
Tendons
Tough, flexible connective tissue connecting bones to muscles
Articulation
Where two bones meet
Head
The rounded surface of an articulation
Crest
A ridge on a bone
Condyle
A rounded surface on a bone
Projection
A raised marking on a bone
Process
A prominent feature on a bone
Fossa
A shallow depression on a bone
Foramen
A hole in a bone
Cartilage
A flexible connective tissue found in elbows, knees, and ankles, enhancing bone strength and providing support for the joints
Hyaline cartilage
Glassy cartilage which reduces friction and absorbs shock on most joint surfaces
Fibrocartilage
The strongest type of cartilage which provides ridigity and absorbs shock; lines bony grooves
Elastic cartilage
The most flexible type of cartilage; it provides shape and support and is found in the ears, nose, and parts of the respiratory system
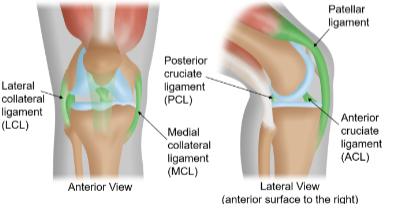
Ligaments
Tough, dense, and fibrous connective tissue that form connections among bone and cartilage to stabilize joints