EPSS 9 - Solar Systems and Planets Final
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/139
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
1
New cards
Olber's Paradox
A paradox pointing out that if the universe were infinite in both age and size, then the sky would not be dark at night. ( the universe is finite)
2
New cards
Archmides
10^63 grains of sand to fill universe, proved exponential math ( the universe is large)
3
New cards
1 AU
The distance from the Earth to the Sun
4
New cards
Parallax
the apparent change in position of an object when seen from different places
5
New cards
Cepheid variables
A variable star that brightens and dims regularly, or pulses, and whose distance can be determined from its period of pulsation
6
New cards
Edward Hubble
used Cepheid variables to obtain distances. Things moving away = reddening of light. Farther things move faster ( the universe is expanding)
7
New cards
Hubble constant
the rate of expansion of the universe 1/time ( velocity versus distance)
8
New cards
Doppler effect
lengthening of wavelength due to motion and velocity
9
New cards
Super Nova
a star that suddenly gets very bright and explodes
10
New cards
Age of universe
~13 billion years ( hubble constant slope: age/rate of expansion)
11
New cards
volume
4/3 pi r^2
12
New cards
velocity
distance/time
13
New cards
Kepler Telescope
Help see that we are not the only solar system and that other solar systems are different than ours
14
New cards
Aristotle
Earth was prime mover causing astronomical motions, planets closer to horizon = closer to sun
15
New cards
Ptolemy
tried to explain retrograde motion using epicycles from a geocentric system
16
New cards
Epicycles
along with orbiting earth, each planet had its own cycles around another fixed point along the orbit
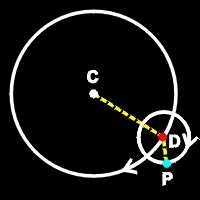
17
New cards
Retrograde
Earth's orbit moves faster than orbits of other planets, makes it seems like other planet is moving backwards for a while
18
New cards
Copernicus
proposed heliocentric model, earth around sun once yearly; all planets have circular orbits; retrograde motion was only apparent
19
New cards
Galileo
early adopter of telescope; planets are disks; venus has phases; moons of jupiter; sunspots; moon craters
20
New cards
Tycho Brahe
Saw new star, nova, made planet position error bars smaller
21
New cards
Kepler
proposed elliptical orbits; planets sweep equal area in equal time.
22
New cards
Kepler's First Law
The orbit of each planet around the Sun is an ellipse with the Sun at one focus.
23
New cards
Kepler's Second Law
As a planet moves around its orbit, it sweeps out equal areas in equal times. closest to star = perihelion, farthest to star = aphelion. T^2 = R^3
24
New cards
Kepler's Third Law
The square of the orbital period of a planet is directly proportional to the cube of planets avg distance from sun. P = sqroot(r^3/A)
25
New cards
Newton
Introduced 3 new laws of motion. Proposed force between all objects in universe with mass ( gravity )
26
New cards
Newton's laws
Everything in motion remains in motion, force = mass*acceleration, action => equal and opposite reaction
27
New cards
force between two objects is proportional to product of their mass
f = G mM/r^2
28
New cards
Stellar Nursery
gaseous pillars of star formation
29
New cards
rotational motion
planetary systems form in disks, planets turn counter clockwise
30
New cards
plane of the ecliptic
The plane of Earth's orbit around the Sun
31
New cards
Obliquity
The tilt of the planet's axis
32
New cards
inner planets
Small, rocky planets that orbit closest to the sun including Mercury, Venus, Earth, & Mars
33
New cards
outer planets
Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, & Neptune made of gases and ices with irregular satellites
34
New cards
asteroid
planetesimals broken and reassembled by multiple collisions
35
New cards
Comets
small icy bodies from far reaches of solar system with a gas tail pointing away from sun, dust tail curves from orbit
36
New cards
angular velocity
2 pi / T(time of one orbit)
37
New cards
Angular momentum
lies within the planets due to molecular cloud viscosity and friction. Inner disk slows down, outer disk speeds up
38
New cards
Isotope
same number of protons, different number of neutrons
39
New cards
Safronov
planetesimal hypothesis: dust to planetesimals, planetesimals to protoplanets, protoplanets to planets
40
New cards
N-body simulation
Approximates the motion of particles that are interacting with one another through physical force (usually gravity)
41
New cards
Isolation Mass
feeding zone mass
42
New cards
Pebble Accretion
material slow down and spiral into planetesimal; inside gaseous protoplanetary disk
43
New cards
Hutton and Lyell
said earth was formed by regular processes rather than catastrophic events
44
New cards
Kelvin
calculated earth was molten for 20-40 million years; didn't consider convection
45
New cards
Becquerel
discovered radioactivity (through uranium)
46
New cards
Joly
measured salt in ocean to estimate earth to be 90-100 million years old
47
New cards
Rutherford
suggested used radioactivity as geological clock
48
New cards
Boltwood
said lead is final product of Uranium decay
49
New cards
Holmes
got age of 3 bys from coniferous samples
50
New cards
Patterson
measured minerals in meteorites and first established age of earth and solar system
51
New cards
Age of Solar System
4.567 billion years old
52
New cards
Mass spectrometry
a technique that separates particles according to their mass
53
New cards
Titius- Bode law
predicts regular spacing b/w planets in solar system; led to discovery of Uranus; suggested asteroid belt is exploded planet
54
New cards
1 Ceres
Largest body in the main asteroid belt; 1/3 total mass of all asteroids. Discovered 1801, never melted, malleable, spherical
55
New cards
Kirkwood gaps
gaps in the asteroid belt
56
New cards
E-type asteroids
chondrite
57
New cards
S-type asteroids
ordinary chondrites
58
New cards
C-type asteroids
Carbonaceous asteroids...they are the most common variety, forming around 75% of known asteroids.
59
New cards
JAXA Mission
evidence for rubble pile concept
60
New cards
Dawn Mission
got good pictures of Vesta and Ceres
61
New cards
4 Vesta
made of basalt and shown to have been once melted, metal core, spherical. Like HED meteorites
62
New cards
white spots on Ceres
salt
63
New cards
Cryovolcano
saltwater, mud, ice volcano driven by liquid water and ammonia
64
New cards
Pysche
M type asteroid- Metal, represents metal core with silicate worn away
65
New cards
Heat to melt asteroids
radioactive decay. Heat from accretion not enough
66
New cards
Harold Urey
proposed decay of Al 26 as source of heat within planets
67
New cards
Comet IP / Halley
elliptical orbit, short period comets from Kuiper belt
68
New cards
Jan Oort
proposed comets reside in cloud of icy/rocky material (oort clout)
69
New cards
Tempel 1
It was the target of the Deep Impact space mission. shown to have equal rocky and ice
70
New cards
chondrites
a stony meteorite containing small mineral granules
71
New cards
chondrules
a spheroidal mineral grain present in large numbers in some stony meteorites. Melted and help date universe
72
New cards
undifferentiated meteorites
never melted, preserve proportions of silicate and metal inherited from solar nebula
73
New cards
Fireballs
very bright meteors, can help track meteorite's orbit
74
New cards
SNC meteorites
Meteorites that appear to have formed on Mars and have managed to make their way to a variety of locations on the Earth. May show signs of life on mars (small bacteria)
75
New cards
Moon composition
silicate crust, mantle, maybe core
76
New cards
Imbrium Basin
ridges and groves on near side of moon
77
New cards
simple crater
small, bowl-shaped craters with a fairly uniform blanket of ejecta distributed around the rim
78
New cards
complex crater
A crater that has central peaks and ejecta thrown out in long rays
79
New cards
Tycho
youngest large impact crater on moon's nearside
80
New cards
lunar cataclysm
Nice model suggested that planets migrate largely, causing increased scattering of planetesimals that impacted the moon
81
New cards
second suggestion for lunar craters
just the end of planet formation
82
New cards
Porcellarum
rift volcano basin on moon
83
New cards
Formation of moon
Earth and Theia collision
84
New cards
SPLAT
a second moon plastered itself to far side, creating a thicker crust there
85
New cards
Moon and Tides
Moon pulls on Earth and slows down rotation of earth, increasing lunar orbit speed
86
New cards
snow line
liquid water within, solid water outside
87
New cards
light and gravity
1/r^2
88
New cards
Tranquility
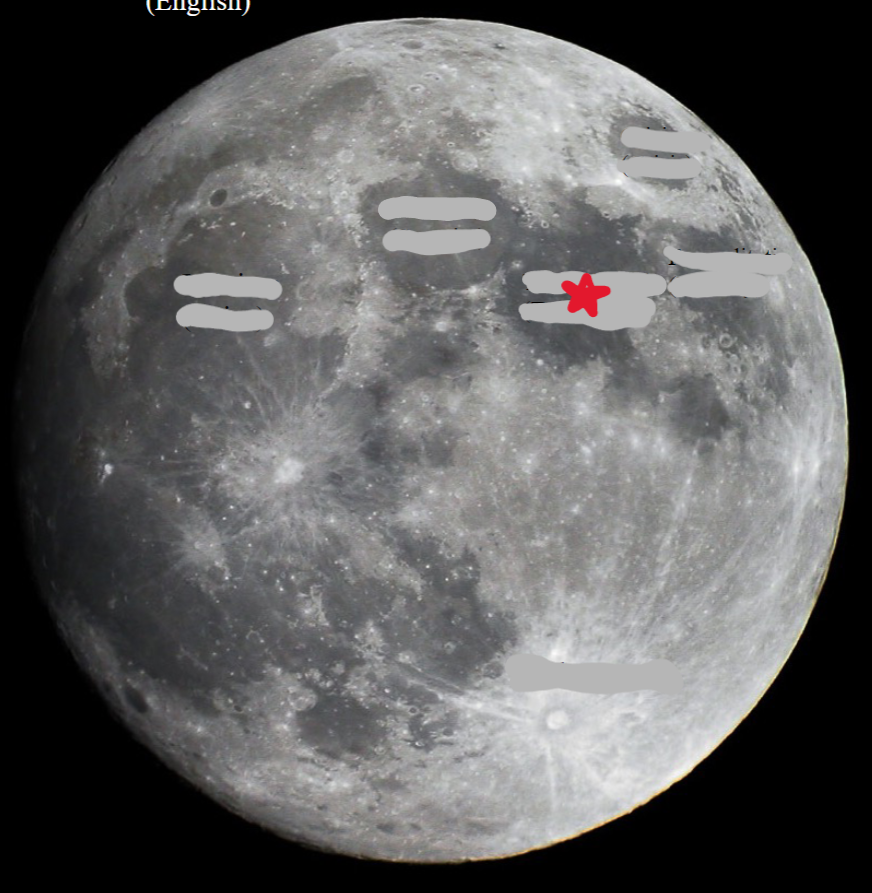

89
New cards
Serenity
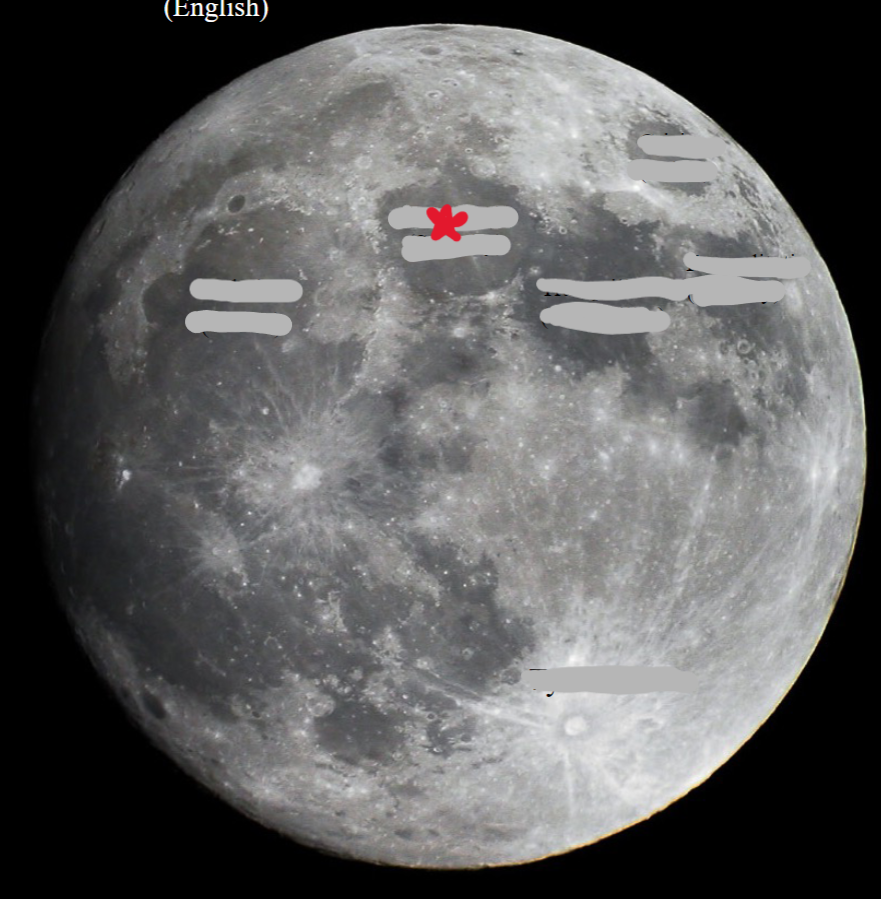

90
New cards
Imbrium
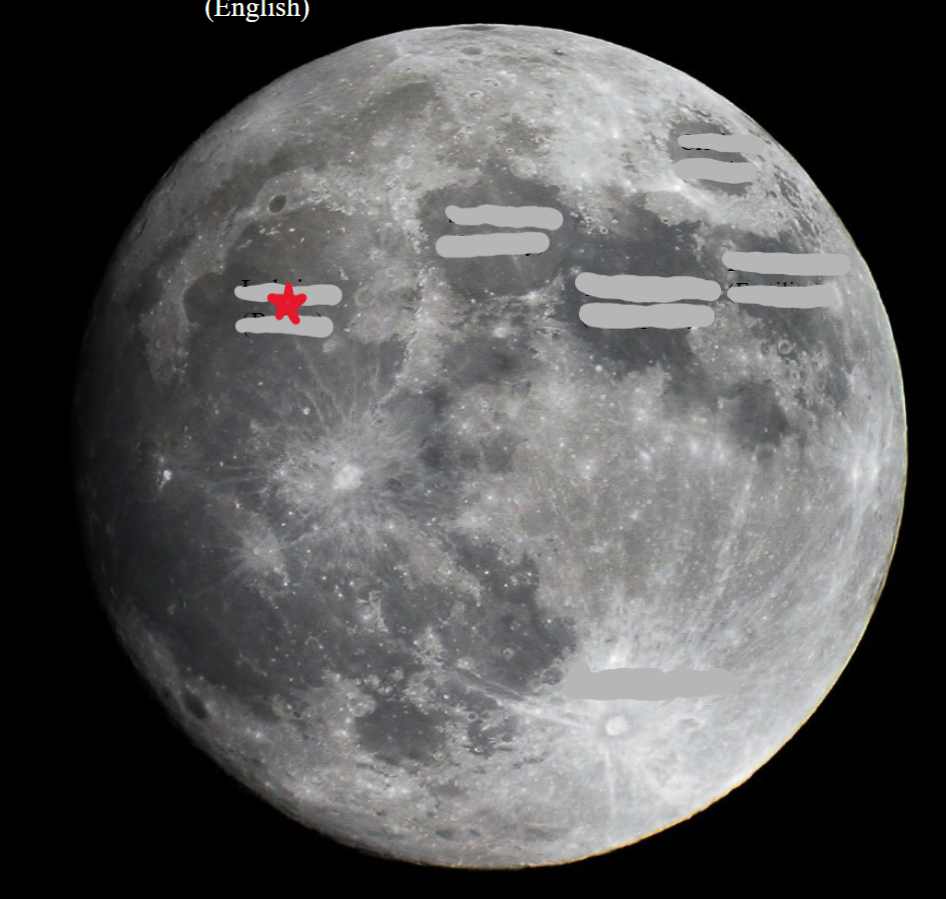

91
New cards
Crisium
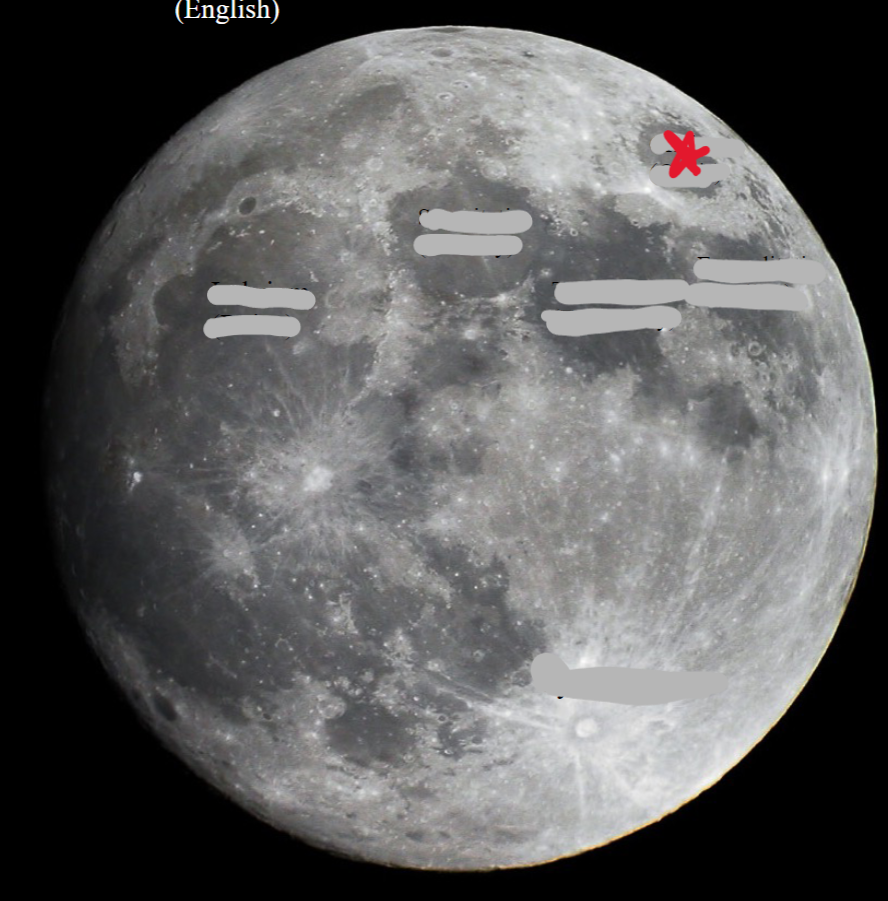

92
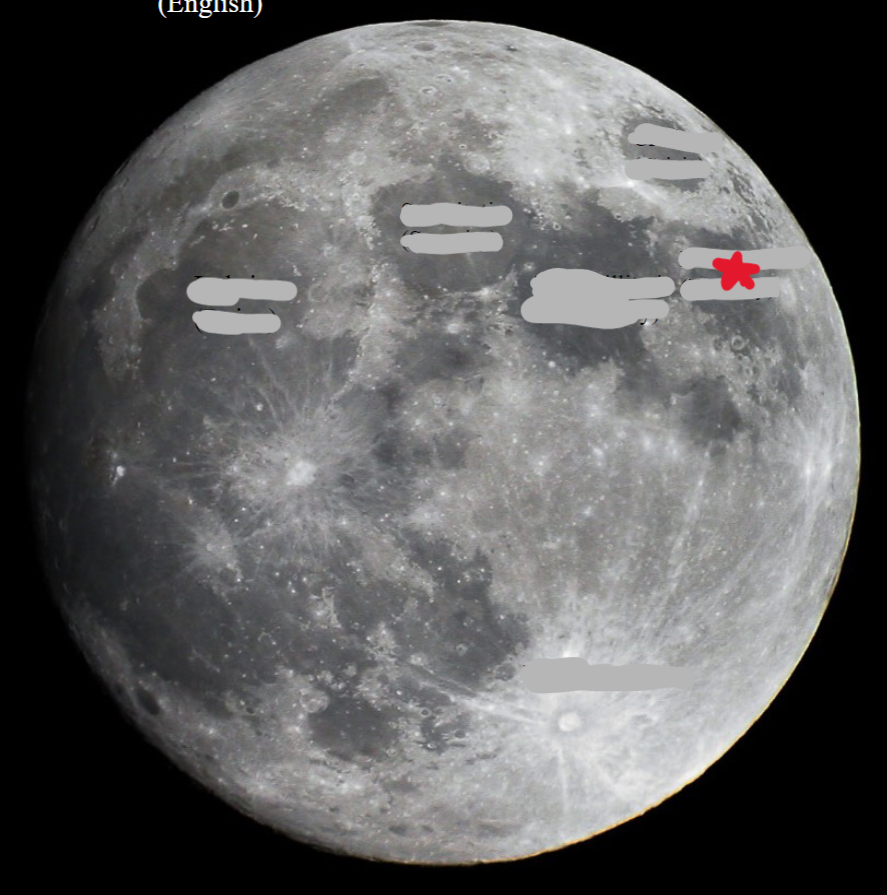
New cards
Fertility

93
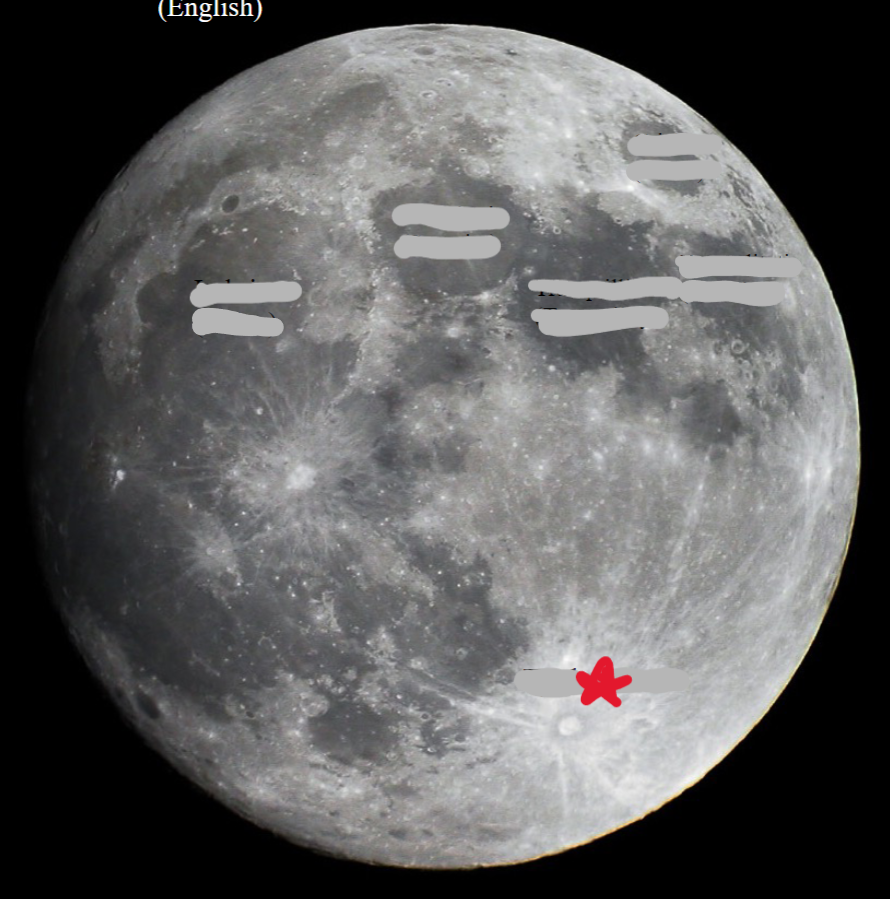
New cards
Tycho crater

94
New cards
Mercury
dense with no atmosphere, most models dont make this planet, dramatic topography range; 59 moons; larger than moon
95
New cards
Mercury's spin orbit resonance
3:2
96
New cards
Caloris Basin
big impact feature on Mercury filled with Lava; chaotic terrain on other side of planet shows effect of shock wave; sun is attracted to this side.
97
New cards
Venus
Planet in retrograde rotation; large, sulphuric atmosphere. Intense volcanism.
98
New cards
Surface of venus
has basalt and continental terrain
99
New cards
how old is the surface of venus
young ( very low cratering ), no magnetic field
100
New cards
Tessera terrain
contains a strike slip fault and corona volcanic flows, pancake domes