Year 10 Bio - DNA and Genes
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What are the subunits of DNA called?
Nucleotides.
What are the three parts of nucleotides called?
Phosphate, sugar, base.
What nucleotides join to make a single strand of DNA, what type of bond?
Phosphate and sugar make up single strand of DNA, joined by covalent bond which is stronger than a hydrogen bond.
What DNA nucleotides join to make a double strand DNA, what type of bond?
Complementary base pairs join to make a double strand of DNA, joined by hydrogen bonds, which are weaker than covalent bonds.
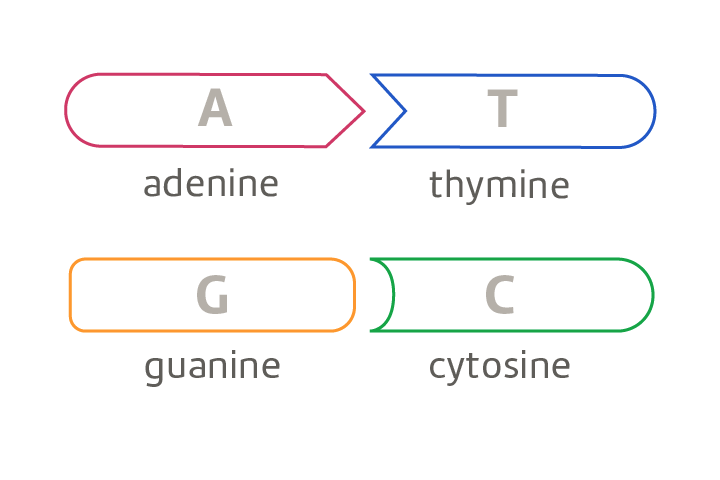
How do DNA molecules encode genetic information?
Encoded through sequence of their nucleotides, the bases. The order determines the instruction for building proteins which determine a lot of characteristics and genetic traits.
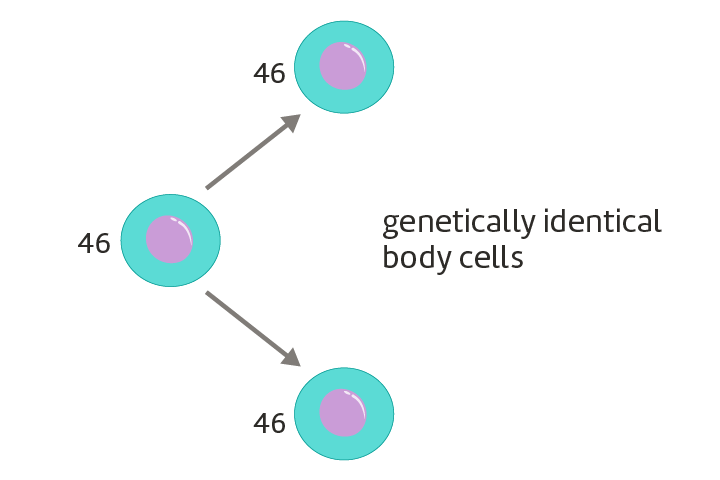
What is Mitosis?
Cell division/replication. One cell splits to create two identical daughter cells, used for growth and repair.
What are the stages of Mitosis in order?
Interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, cytokinesis. I (PMAT) C
During interphase…
The cell is resting and carrying out it’s normal job. Chromatin are dispersed.
During prophase…
Centrioles form. DNA condense in to visible chromosomes. Nuclear membrane breaks down. Cell Prepares to split (Pmat)
During metaphase…
Chromosomes line up in the Middle (pMat). Centriole spindle fibres attach to chromosomes.
During anaphase…
Spindle fibres retract pulling chromosomes Away (pmAt) to each side.
During telophase…
Cell membrane starts to pink, nuclear membrane forms, Two new nuclei form (pmaT).
Cytokinesis
Splitting of one cell into two. Cytoplasm splits in to two, resulting in two daughter cells (in Mitosis).
What is Meiosis?
A type of cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, producing four genetically diverse gametes. Meiosis consists of two rounds of division, meiosis 1 and meiosis 2.
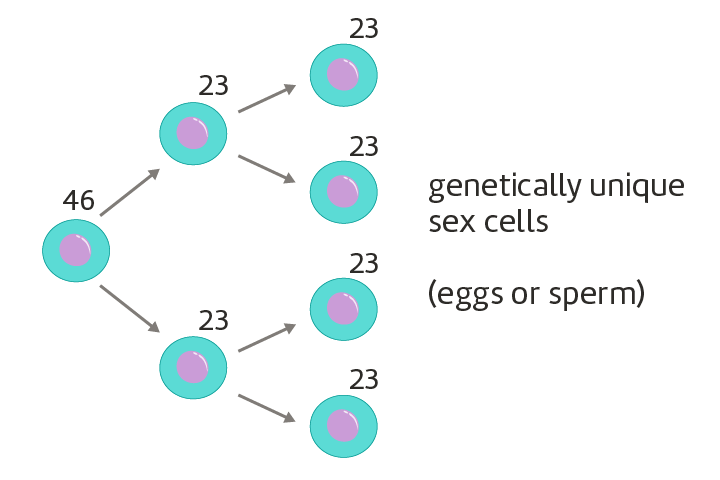
What are the stages of Meiosis in order?
Interphase, Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I, followed by Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, and Telophase II.
In Prophase 1…
Chromosomes condense and do crossing over, swapping parts of DNA.
What is a gene?
A section of DNA that carries the code to make a protein, composed of specific sequences of DNA causing a characteristic.
What is a genome?
Complete set of DNA contained in haploid (half) set of an organism’s chromosomes. All pieces of DNA within an organism.
What is loci (in genes)
Location of a gene.
What is the meaning of haploid?
Half the amount of DNA (found in sex cells). Haploid, Hafloid.
What is the meaning of diploid?
Full set of DNA (found in body cells), 2 sets of chromosomes (from both parents).
What is an allele?
A variation of the same gene, 1 from father one from mother. Ect alleles for eyes: blue eyes vs brown eyes.
What is a genotype?
A combination of particular alleles within DNA that causes a characteristic.
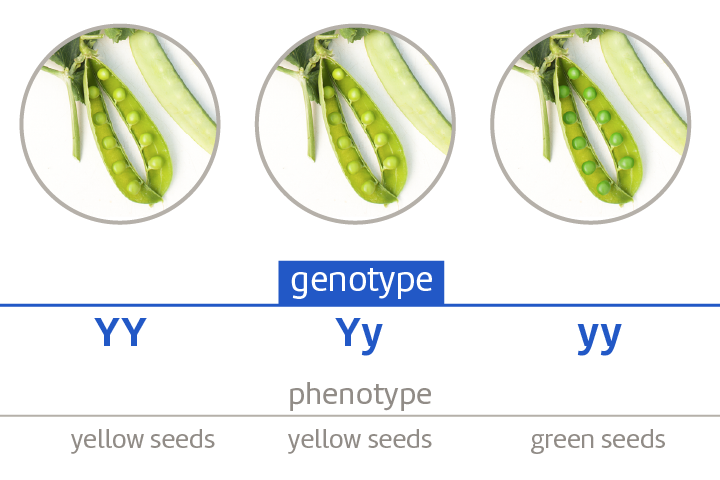
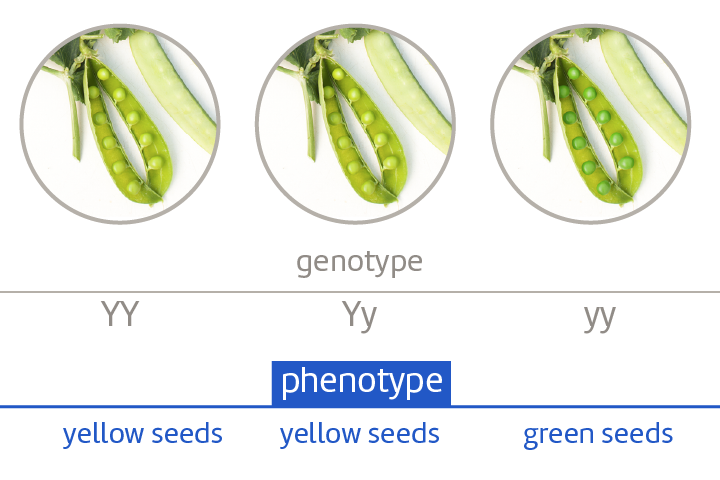
What is a phenotype?
The observable/physical characteristic caused by the genotype/alleles.
What is the meaning of a homozygous gene?
A gene that has two identical alleles, ect. CC or cc. Can show dominant or recessive phenotype.
What is the meaning of a heterozygous gene?
A gene that has two different alleles, ect Cc. Heterozygous genes can only show the dominant phenotype.
What is a gamete?
The scientific word for sex cell, sperm/egg, have haploid number of chromosomes.
What is a Somatic cell?
Scientific word for body cells, that have diploid number of chromosomes (a full set)
What is the meaning of hemizygous?
Only one copy of the gene. Ect: Males only have one X chromosome.
What is the meaning of autosomal?
Chromosomes that are not sex chromosomes. Every chromosome but the sex chromosome.
What is autosomal dominant inheritance?
Inheritance of dominant traits that are not on the sex chromosome.
What is autosomal recessive inheritance?
Two unaffected parents can have an affected child if they’re both carries. Trait can skip generations.
What is X linked inheritance?
Both male and female can be affected by a disease carried on the X chromosome. (Mothers can only pass on X chromosome, male can pass on X or Y.)
What is Y linked inheritance?
Only males can be affected by a disease carried on the Y chromosome, as only males have a Y chromosome.
What is a mutation?
A mutation is an alteration of the genetic composition of a cell or organism.