BIOL 1021 Bowling lab final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
1
New cards
what did caffeine and ethanol do to the heart rate of Daphnia?
caffeine- speeds up
ethanol- slows down
ethanol- slows down
2
New cards
important aspects of the anatomy of a daphnia (diagram)

3
New cards
major parts of the dissecting scope
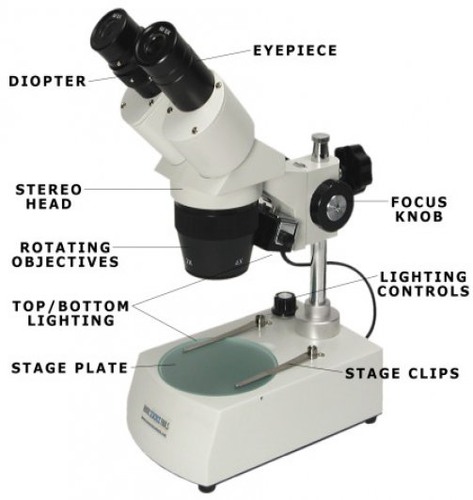
4
New cards
independent variable
One or more factors that the scientist varies during the experiment. (In the example below, the independent variables are exercise and diet.)
5
New cards
dependent variable
A feature that the scientist measures in order to determine if it changes in response to the independent variables. (In the example below, the dependent variable is the amount of blood cholesterol).
6
New cards
mean
where you add up all the numbers and then divide by the number of numbers.
7
New cards
Median
is the "middle" value in the list of numbers from least to greatest.
8
New cards
Mode
is the value that occurs most often
9
New cards
range
is just the difference between the largest and smallest values
10
New cards
what solutions were used to test for the 4 types of organic molecules?
water, glucose, sucrose, starch, onion juice, (unknown)
11
New cards
The Biuret Test: turns violet
protein or long peptide
12
New cards
The Biuret Test: turns pinkish
short peptide
13
New cards
functional groups
hydroxyl group (X-OH)
aldehyde, carbonyl (X-C-H) || O
carbonyl (X-C-X) || O
carboxyl group (X-COOH)
amino group (X-NH2)
sulfhydryl group (X-SH)
phosphate group (X-PO4H2)
methyl group (X-CH3)
aldehyde, carbonyl (X-C-H) || O
carbonyl (X-C-X) || O
carboxyl group (X-COOH)
amino group (X-NH2)
sulfhydryl group (X-SH)
phosphate group (X-PO4H2)
methyl group (X-CH3)
14
New cards
54 km = ?
54,000 m
5,400 m
54,000 mm
0.054 m
5,400,000 mm
54,000 m
5,400 m
54,000 mm
0.054 m
5,400,000 mm
54,000 m
15
New cards
54 mm = ?
5,400 m
0.000054 km
0.54 m
540 cm
540 μm
5,400 m
0.000054 km
0.54 m
540 cm
540 μm
0.000054 km
16
New cards
75,400 = ?
7.54 x 10^3
754 x 10^1
75.4 x 10^4
7.54 x 10^-4
7.54 x 10^4
7.54 x 10^3
754 x 10^1
75.4 x 10^4
7.54 x 10^-4
7.54 x 10^4
7.54 x 10^4
17
New cards
82 dm = ?
8.2 x 10^3 mm
1.64 x 10^-2 mm
82 x 10^4 mm
82 x 10^-2 mm
8.2 x 10^-2 mm
8.2 x 10^3 mm
1.64 x 10^-2 mm
82 x 10^4 mm
82 x 10^-2 mm
8.2 x 10^-2 mm
8.2x10^3 mm
18
New cards
16 μl = ?
1.6 x 10^-6 l
8.0 x 10^6 l
1.6 x 10^6 l
1.6 x 10^5 l
8.0 x 10^6 l
1.6 x 10^-6 l
8.0 x 10^6 l
1.6 x 10^6 l
1.6 x 10^5 l
8.0 x 10^6 l
1.6 x 10^5 I
19
New cards
8.4 mg = ?
8.4 x 10^3 μg
8.4 x 10^4 g
4.2 x 10^3 μg
8.4 x 10^6 kg
4.2 x 10^3 g
8.4 x 10^3 μg
8.4 x 10^4 g
4.2 x 10^3 μg
8.4 x 10^6 kg
4.2 x 10^3 g
4.2 x 10^3 g
20
New cards
6.4 x 10^3 μm = ?
6.4 x 10^-3 dm
6.4 x 10^-6 m
3.2 x 10^1 mm
3.2 x 10^-1 cm
6.4 x 10^0 mm
6.4 x 10^-3 dm
6.4 x 10^-6 m
3.2 x 10^1 mm
3.2 x 10^-1 cm
6.4 x 10^0 mm
6.4 x 10^0 mm
21
New cards
Surface Area: A rectangle is 10 meters by 6 meters; what is its area?
60 m^2
16 m^2
32 m
32 m^2
60 m^2
16 m^2
32 m
32 m^2
60 m^2
22
New cards
Surface Area: A rectangle is 2 cm by 6 cm. What is its area?
1.2 x 10^0 cm^2
8 x 10^0 cm^2
1.2 x 10^1 cm^2
12 x 10^1 cm^2
1.2 x 10^0 cm^2
8 x 10^0 cm^2
1.2 x 10^1 cm^2
12 x 10^1 cm^2
1.2 x 10^1 cm^2
23
New cards
Surface Area: A rectangle is 3.0 x 10^3 mm by 3.0 x 10^2 cm. What is its area?
3.0 x 10^5 m^2
9.0 x 10^2 m^2
9.0 x 10^5 cm^2
9.0 x 10^4 mm^2
3.0 x 10^5 m^2
9.0 x 10^2 m^2
9.0 x 10^5 cm^2
9.0 x 10^4 mm^2
9.0 x 10^0 m^2
24
New cards
Volume: A box is 3 m long by 2 m wide by 2 m high. What is its volume?
10 m^3
12 m^3
7 m
7 m^3
10 m^3
12 m^3
7 m
7 m^3
12 m^3
25
New cards
Volume: A paper strip is 2 m long by 3 cm wide by 2 mm thick. What is its volume?
1.2 x 10^-4 m^3
1.2 x 10^1 mm^3
1.2 x 10^1 cm^3
1.2 x 10^4 mm^3
1.2 x 10^-4 m^3
1.2 x 10^1 mm^3
1.2 x 10^1 cm^3
1.2 x 10^4 mm^3
1.2 x 10^-4 m^3
26
New cards
Volume: 6.4 x 10^15 μm3= ?
6.4 x 10^9 m^3
6.4 x 10^33 m^3
6.4 x 10^3 m^3
6.4 x 10^-3 m^3
6.4 x 10^9 m^3
6.4 x 10^33 m^3
6.4 x 10^3 m^3
6.4 x 10^-3 m^3
6.4 x 10^-3 m^3
27
New cards
Surface Area: 5.4 x 10^-6 km^2= ?
5.4 x 10^3 μm^2
5.4 x 10^12 μm^2
5.4 x 10^6 μm^2
5.4 x 10^18 μm^2
5.4 x 10^3 μm^2
5.4 x 10^12 μm^2
5.4 x 10^6 μm^2
5.4 x 10^18 μm^2
5.4 x 10^12 μm^2
28
New cards
102 °F = ?
38.9 °C
212 °C
74.4 °C
70 °C
38.9 °C
212 °C
74.4 °C
70 °C
38.9 °C
29
New cards
-40 °C = ?
-72 °F
-14.4 °F
-8 °F
-40 °F
-72 °F
-14.4 °F
-8 °F
-40 °F
-40 °F
30
New cards
degree conversions
°F = 9/5(°C) + 32°
°C = 5/9 (°F - 32°)
°C = 5/9 (°F - 32°)
31
New cards
Water freezes at what temperature?
0 degrees Celsius and 32 degrees Fahrenheit
32
New cards
Water boils at what temperature?
100 degrees Celsius or 212 degrees Fahrenheit
33
New cards
Human body temperature
37°C
34
New cards
compound scope magnification equation (eyepiece mag x objective mag)
eyepiece (ocular) lenses (10X); these are constant objective lenses; there are 3 lenses: low power (4X) medium power (10X) high power (45X or 40X)
35
New cards
Resolution equation
Resolution = (.61)(wavelength λ)/Numerical Aperture
36
New cards
Using a compound microscope with a 15X eyepiece lens and a 40X objective lens produces a final magnification of ?
60X
55X
400X
600X
60X
55X
400X
600X
600X
37
New cards
Using a compound microscope with a numerical aperture of 0.22 gives a resolution of R = ?
0.22 μm
1.5 μm
2.8 μm
0.33 μm
0.22 μm
1.5 μm
2.8 μm
0.33 μm
1.5 μm
38
New cards
A cell takes up about 1/4 of the field of view in your microscope on medium power (diameter of field = 1800 μm). What is the approximate width of the cell?
7200 μm
1800 μm
450 μm
This cannot be determined without knowing the numerical aperture.
7200 μm
1800 μm
450 μm
This cannot be determined without knowing the numerical aperture.
450 μm
39
New cards
A family has 10 children with these ages: 24, 21, 21, 21, 17, 17, 14, 11, 8, 6. What is the mean age of these children?
16
14.4
18
17
21
16
14.4
18
17
21
16
40
New cards
A family has 10 children with these ages: 24, 21, 21, 21, 17, 17, 14, 11, 8, 6. What is the mode age of these children?
16
14.4
18
17
21
16
14.4
18
17
21
21
41
New cards
A family has 10 children with these ages: 24, 21, 21, 21, 17, 17, 14, 11, 8, 6. What is the range of ages of these children?
16
14.4
18
17
21
16
14.4
18
17
21
18
42
New cards
A family has 10 children with these ages: 24, 21, 21, 21, 17, 17, 14, 11, 8, 6. What is the median age of these children?
16
14.4
18
17
21
16
14.4
18
17
21
17
43
New cards
what is the compound scope magnification equation?
eyepiece mag x objective mag
44
New cards
major parts of the compound scope
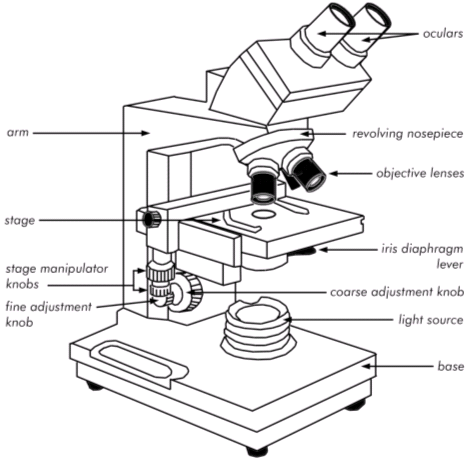
45
New cards
40X (low power)
4500 um (4.5 mm)
46
New cards
100X (medium power)
1800 um (11.8 mm)
47
New cards
450X or 400X (high power)
400 or 450 um (.4 or .45 mm)
48
New cards
LAB 4 LOOK AT CELLS ON MANUAL
.
49
New cards
How does temperature affect the rate of diffusion?
The higher the temperature, the faster the rate of diffusion. This is because the particles have more energy so they move around faster.
50
New cards
How does molecular weight affect the rate of diffusion?
Heavier molecules move more slowly; therefore, they diffuse more slowly. The rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to square root of its inverse of its molecular weight.
51
New cards
active transport
the net movement of a substance, often against a gradient, that requires an input of energy and a carrier protein
52
New cards
Diffusion
the net movement of particles down a concentration gradient
53
New cards
osmosis
the net movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane
54
New cards
dynamic equilibrium
the point where 2 solutions (or other situations) are such that no net movement of molecules will occur
55
New cards
Hypertonic
when comparing 2 solutions, it is the solution that has the higher concentration of solute particles
56
New cards
Hypotonic
when comparing 2 solutions, it is the solution that has the lower concentration of solute particles
57
New cards
lab 5 look at hand-in for lab results
.
58
New cards
What are enzymes?
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions; living organisms depend on them; act as catalysts
59
New cards
what do enzymes do?
make reactions occur faster by lowering the activation energy of the reactants so that the final products are produced at a faster rate
60
New cards
What are the substrates of lab 6?
catechol, hydroquinone, and p hydroxybenzaldehyde
61
New cards
What is the product of lab 6?
benzoquinone
62
New cards
what affects the rate of a chemical reaction?
temperature and pH
63
New cards
does lower or higher temperature affect an enzyme?
higher
64
New cards
Without an enzyme, most reaction rates will either increase continually as pH is___1___ or will increase continually as the pH is ___2___.
1. lowered
2. raised
2. raised
65
New cards
Alcoholic fermentation produces _______________________ for every molecule of glucose that undergoes glycolysis.
2 molecules of ethanol, 2 molecules of CO2, and 2 molecules of ATP
66
New cards
In lactic acid fermentation _______________________________ are produced for every molecule of glucose that undergoes glycolysis.
2 molecules of lactic acid and 2 molecules of ATP
67
New cards
Oxygen is present in ____1_____ and not present in __2____.
1. aerobic respiration
2.fermentation
2.fermentation
68
New cards
lab 7- What does it mean in the Bromthymol blue experiment if the color is Blue?
no CO2
69
New cards
lab 7- what does it mean In the Bromthymol blue experiment if the color is Green?
some CO2
70
New cards
lab 7- what does it mean In the Bromthymol blue experiment if the color is Yellow?
a lot of CO2
71
New cards
Chromatography
A laboratory technique used to separate mixtures of molecules
72
New cards
How does chromatography work?
Chromatography paper has fibers of a certain size. Molecules, such as pigments, are able to migrate along the paper if they are soluble in an appropriate solvent.
73
New cards
what pigments were separated in lab 8?
accessory pigments from spinach leaves
74
New cards
What is fluorescence?
the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation.
75
New cards
How is fluorescence caused?
occurs when a molecule reflects a ray of light at a higher wavelength than the original light that was shone onto it
76
New cards
which color is least useful in photosynthesis?
green
77
New cards
which colors are most useful for photosynthesis?
red, violet, blue
78
New cards
reflected light
color that is seen; light that is thrown back or bounced off an object
79
New cards
absorbed light
converted to energy and transmitted light moves through the material
80
New cards
what is starch made of?
carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
81
New cards
where is starch stored?
plant's vacuole
82
New cards
does light affect starch storage?
no
83
New cards
how does measuring O2 levels relate to photosynthesis?
Plants produce oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis
84
New cards
Stages of Mitosis
interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
85
New cards
pictures of stages of mitosis
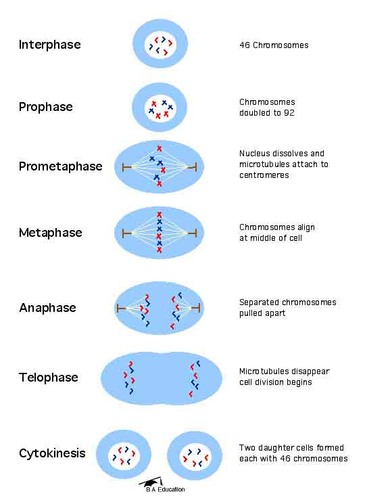
86
New cards
meiosis 1 stages
Prophase 1, Metaphase 1, Anaphase 1, Telophase 1
87
New cards
meiosis 1 pictures
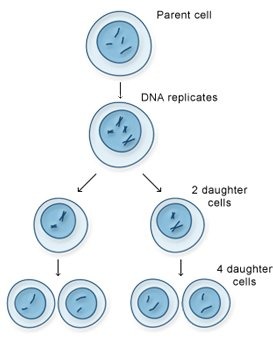
88
New cards
Meiosis II stages
Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II, Telophase II
89
New cards
Meiosis II picture
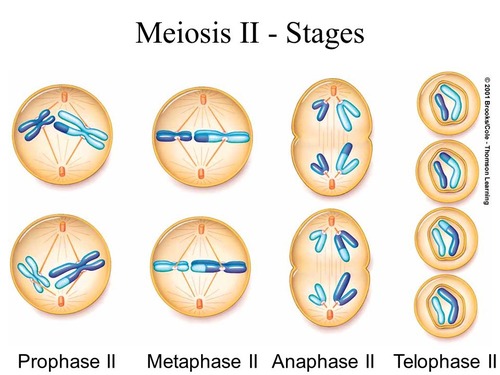
90
New cards
diploid cell
A cell containing two sets of chromosomes (2n), one set inherited from each parent.
91
New cards
haploid cell
A cell containing only one set of chromosomes (n).
92
New cards
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms; produces 4 haploid cells
93
New cards
Mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes; produces 2 diploid cells
94
New cards
look at charts on lab 9
.
95
New cards
homozygous dominant
AA
96
New cards
homozygous recessive
aa
97
New cards
Heterozygous
Aa
98
New cards
allele
variations of a trait
99
New cards
genotype
genetic makeup of an organism; AA, Aa, aa
100
New cards
phenotype
An organism's physical appearance, or visible traits.