Functional anatomy Intro video Q & A
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
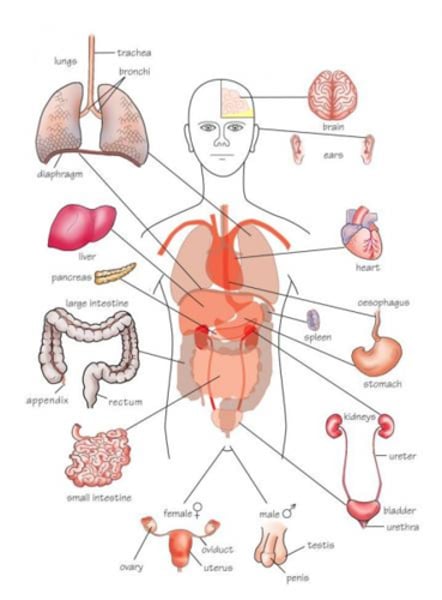
Four body systems that work together to allow for athletic endeavors.
Skeletal
Muscular
Respiratory
Circulatory
Base structure needed to handle loads of sport and allow for movement
skeletal structure
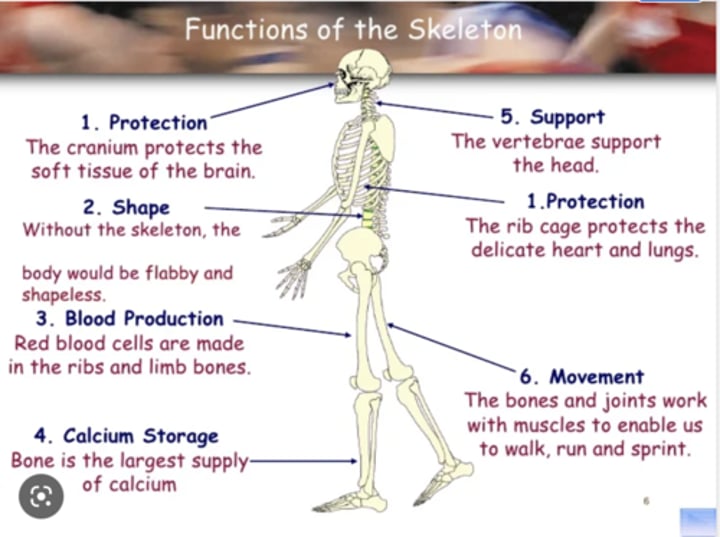
Functions of the skeleton
1. Rigid framework
2. Protection of organs
3. Allows for Movement (Joints are an attachment site for muscles and tendons)
4. Store and release minerals
5. Blood cell production
How many bones in an adult?
206
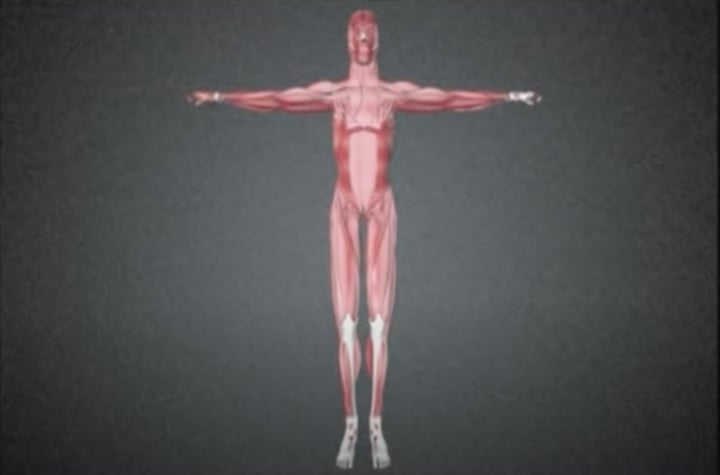
Function of muscles
movement
Stability.
Posture. ...
Circulation. ...
Respiration. ...
Digestion. ...
Urination. ...
Childbirth.
Thermoregulation
Vision
Organ protection
How is muscle force production controlled
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dtwow0BXW5c&t=183s
Length tension:
https://youtu.be/FT7OABz8I5k?t=110
Force Velocity:
https://youtu.be/zQwSPwHQB28?t=99
1. rate coding (frequency of nerve signal)
2. Fiber type
3. Total number of muscle cells
4. Angle of pull
5. Muscle Temperature
6. length tension relationship
7. Force velocity relationship
8. # of motor units recruited
9. Elasticity
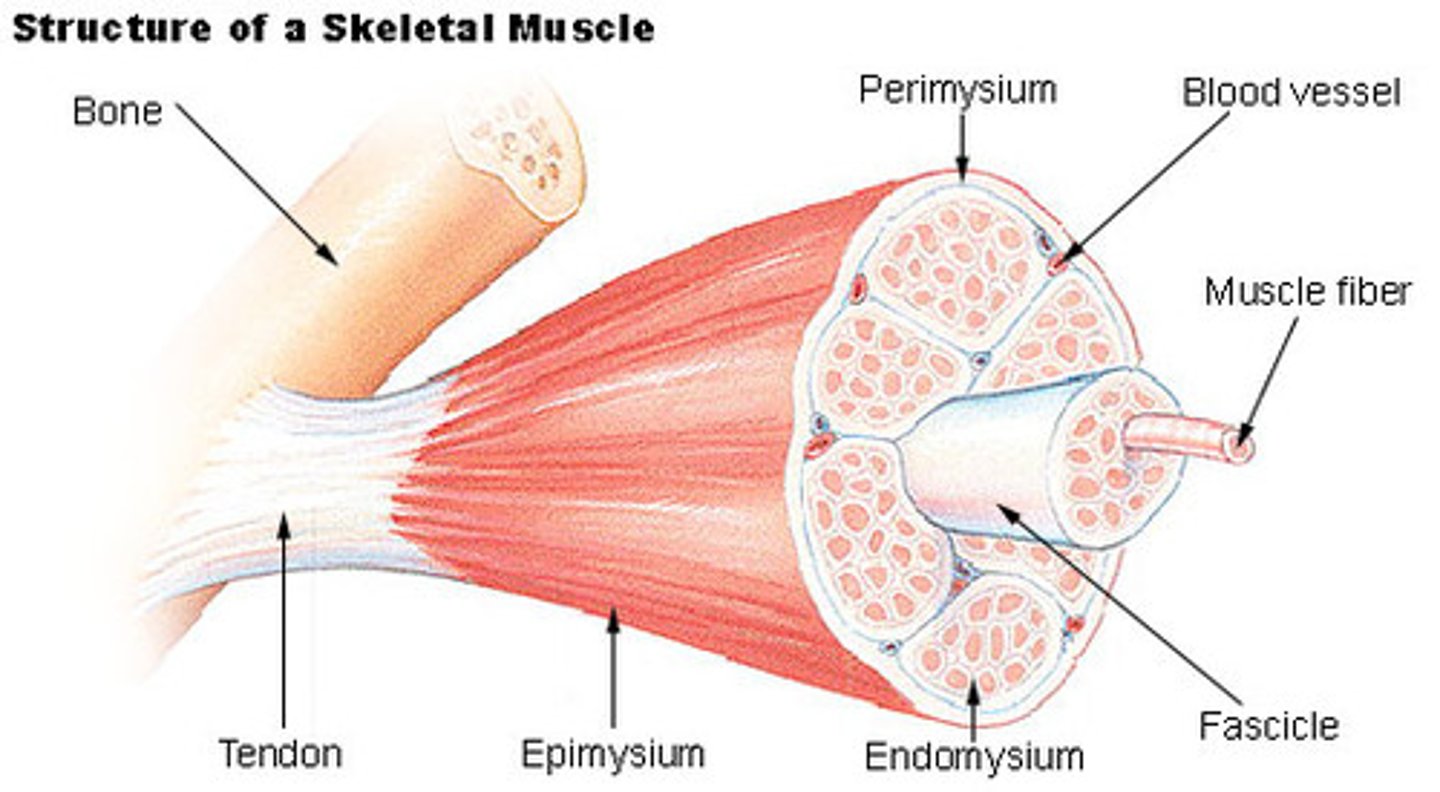
Grouped or packed tubes of myofibrils
Muscle Bundle AKA fasciculus
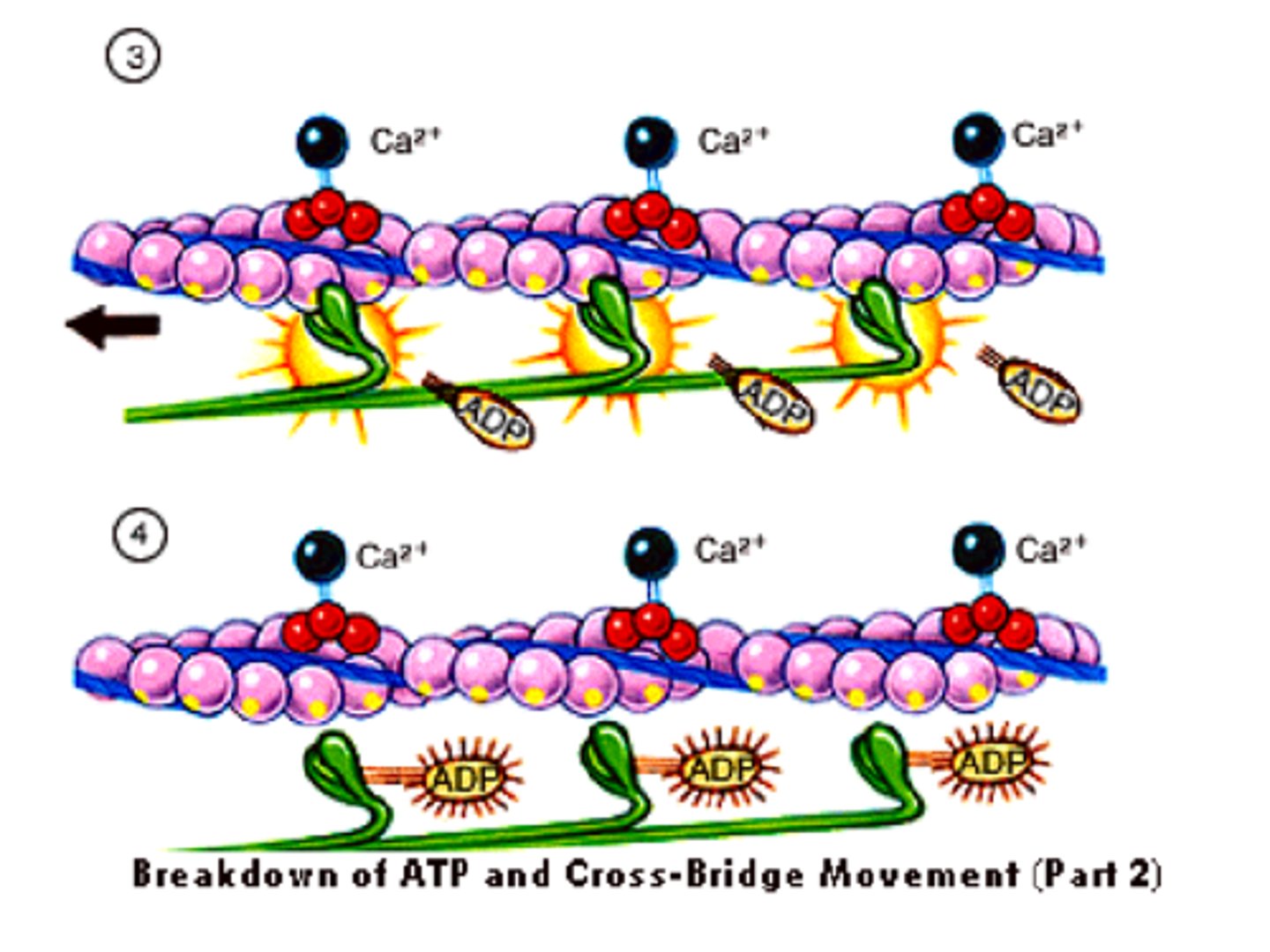
Describe briefly how a muscle contracts
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nTZnBdeIb5c
The muscle bundle shortens from the sum effort of a large group of muscle cells pulling simultaneously through a ratcheting mechanism of their small protein filaments (Actin & Myosin).
AKA - Sliding Filament theory
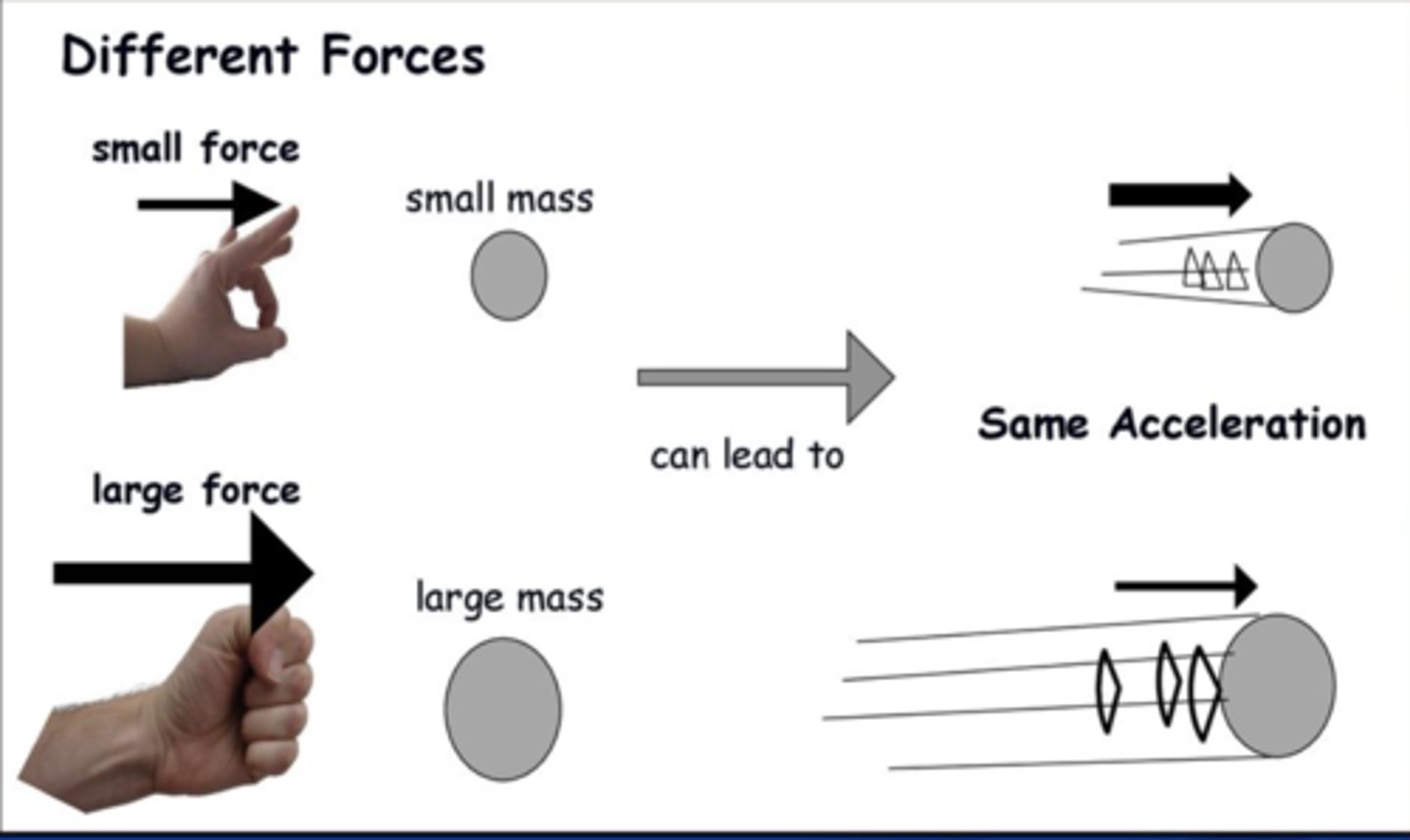
How does the brain differentiate between small force and large force requirements
selective Stimulation/recruitment of various amounts of motor units based on need.

what effects the ratio of slow to fast twitch fibers in humans?
Genetics

elite sprinters have a ratio of ___________ fast to ___________ slow twitch
80% Fast
20% Slow
why is oxygen so important
Essential ingredient for energy production. (oxidative phosphorylation)

How many Alveoli are in our lungs?
Millions

What is the combined surface area of the lungs Alveoli?
80 square meters
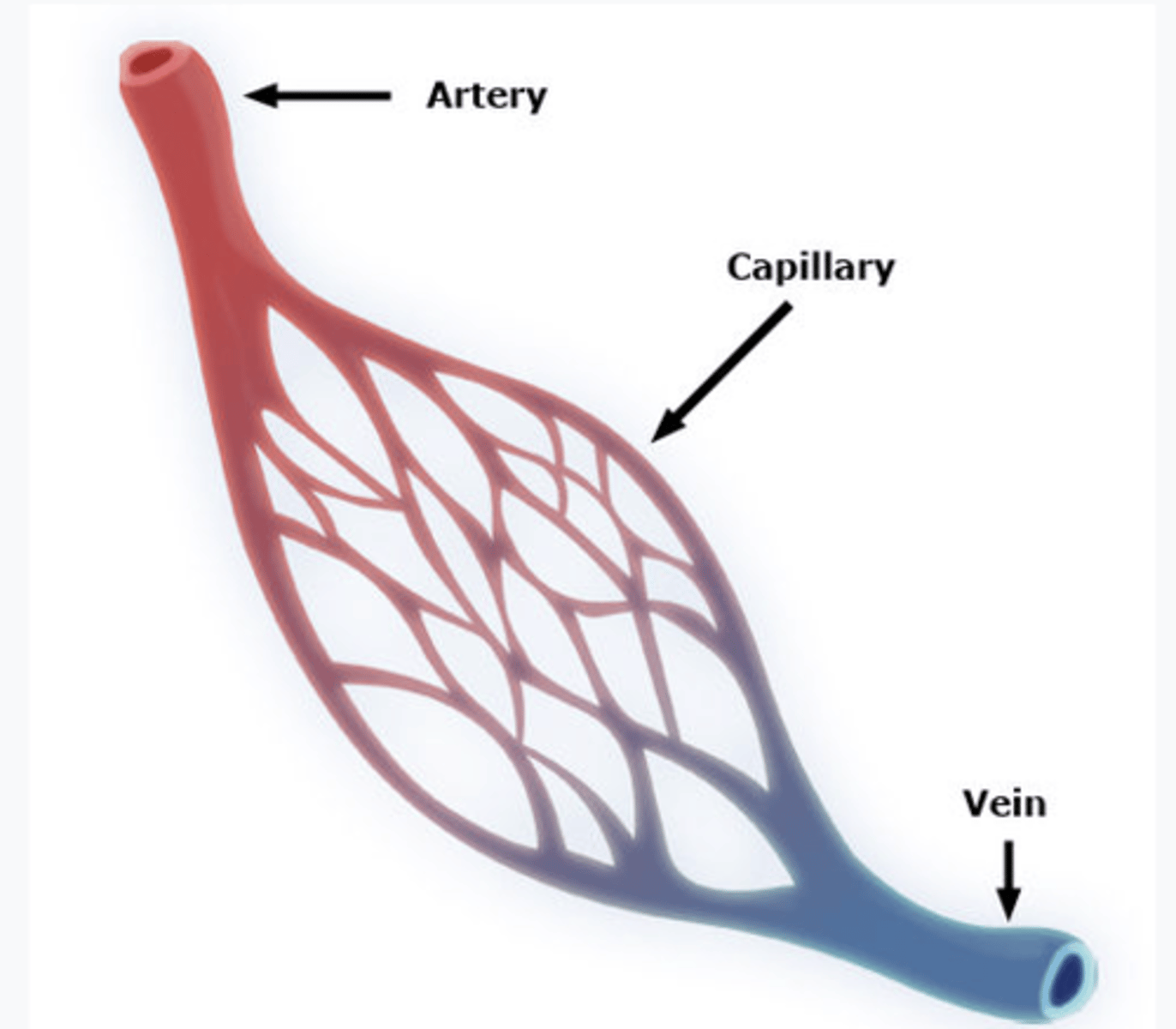
The smallest branch of the closed circulatory system, where the arteries converge with the veins.
capillary
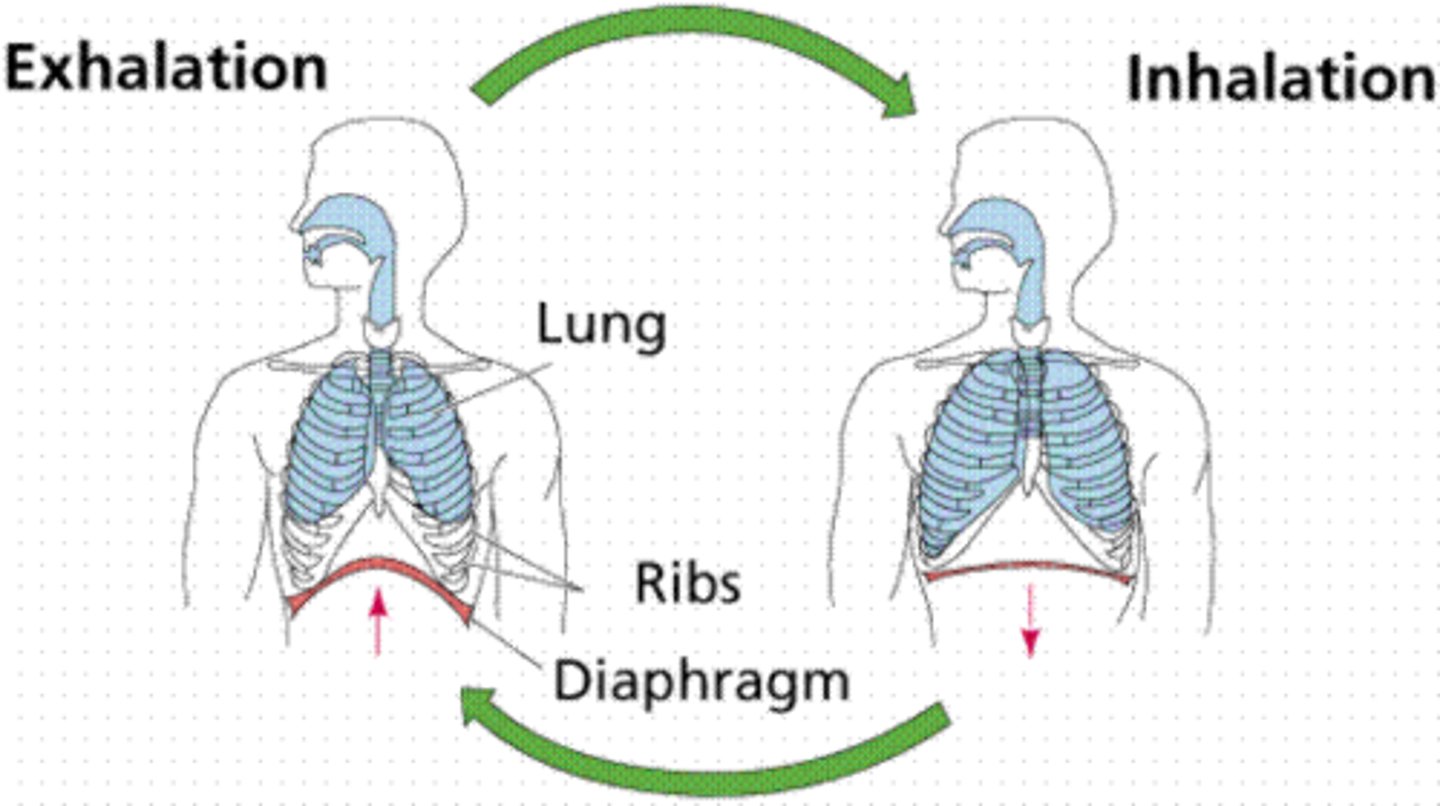
exchanging of gases from the body via the lungs and heart.
respiration

average resting respiration rate
12-18/min
respiration rate during cardiovascular demands?
35/min

Main function of the circulatory system
Transport and Distribution
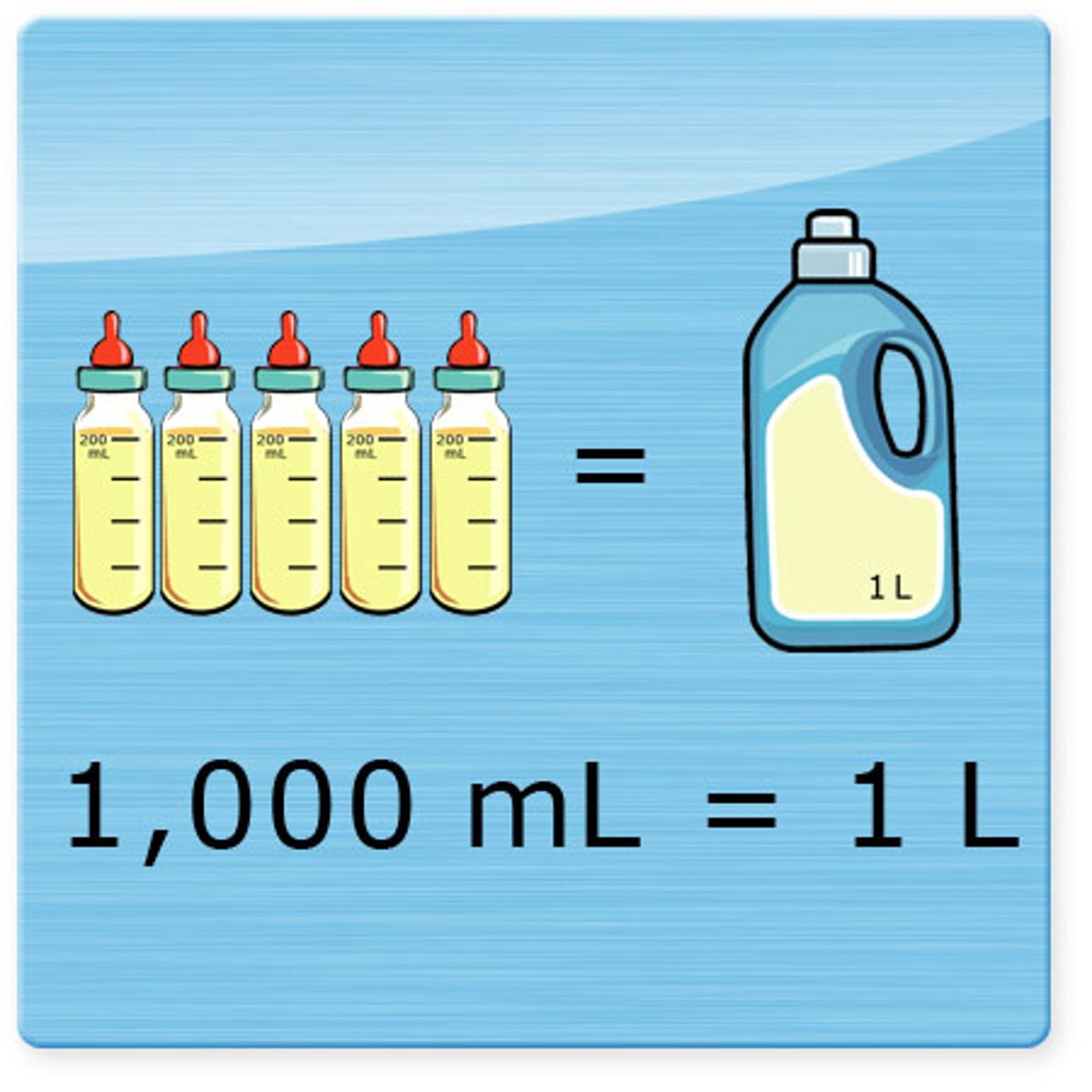
volume of blood in a human
4-5 liters
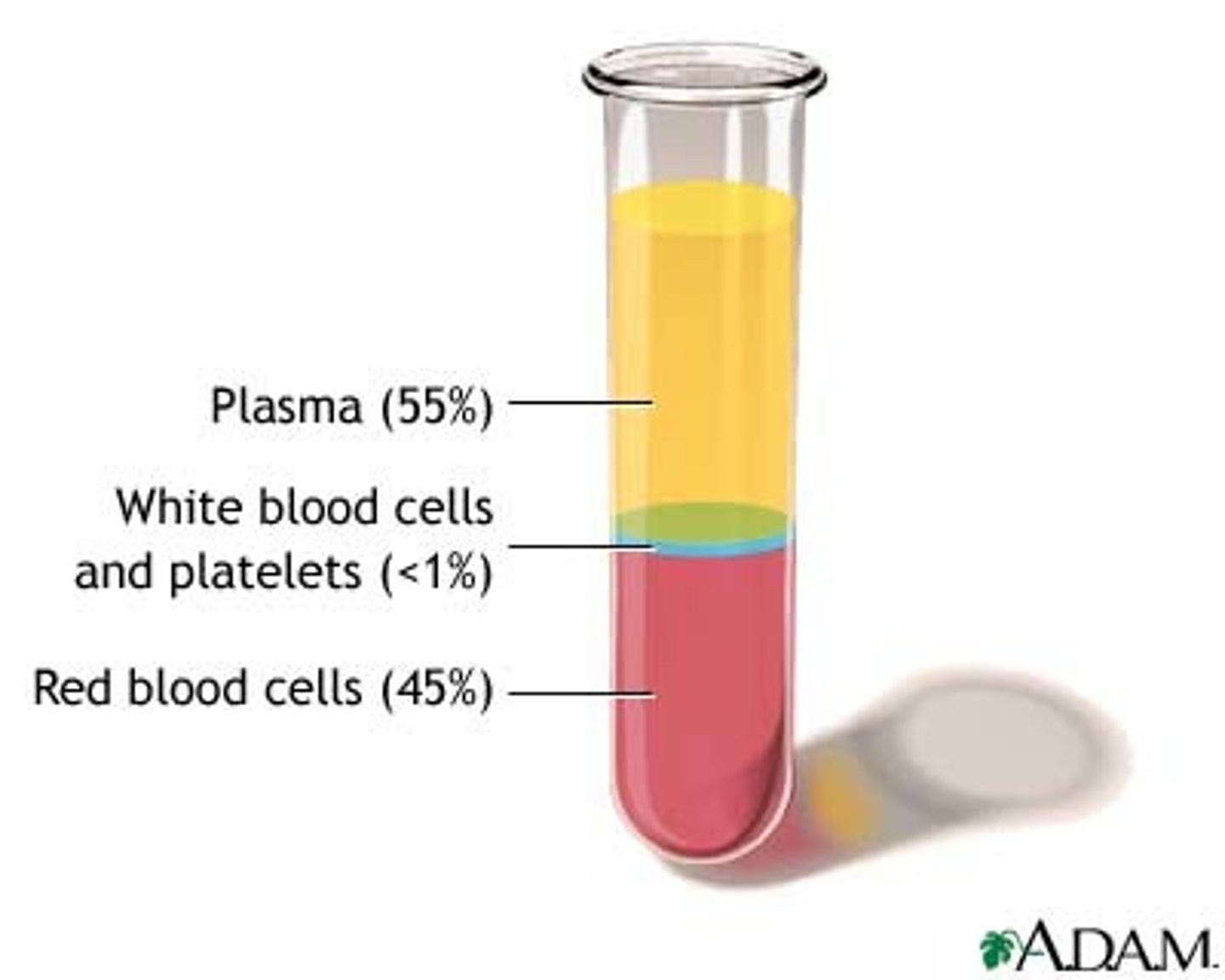
Types of blood cells include:
Platelets, WBC, RBC
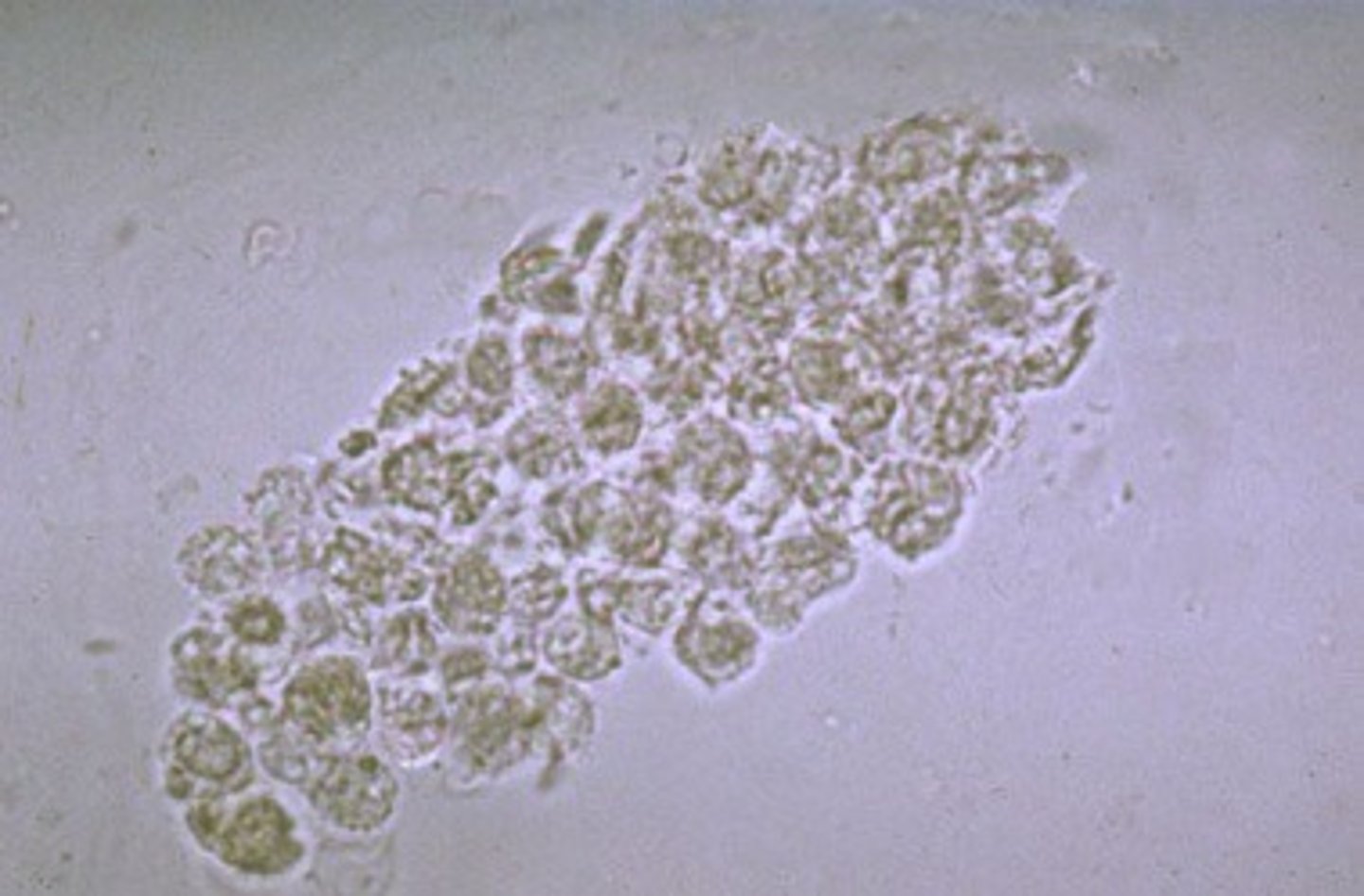
Helps fight infection
WBC
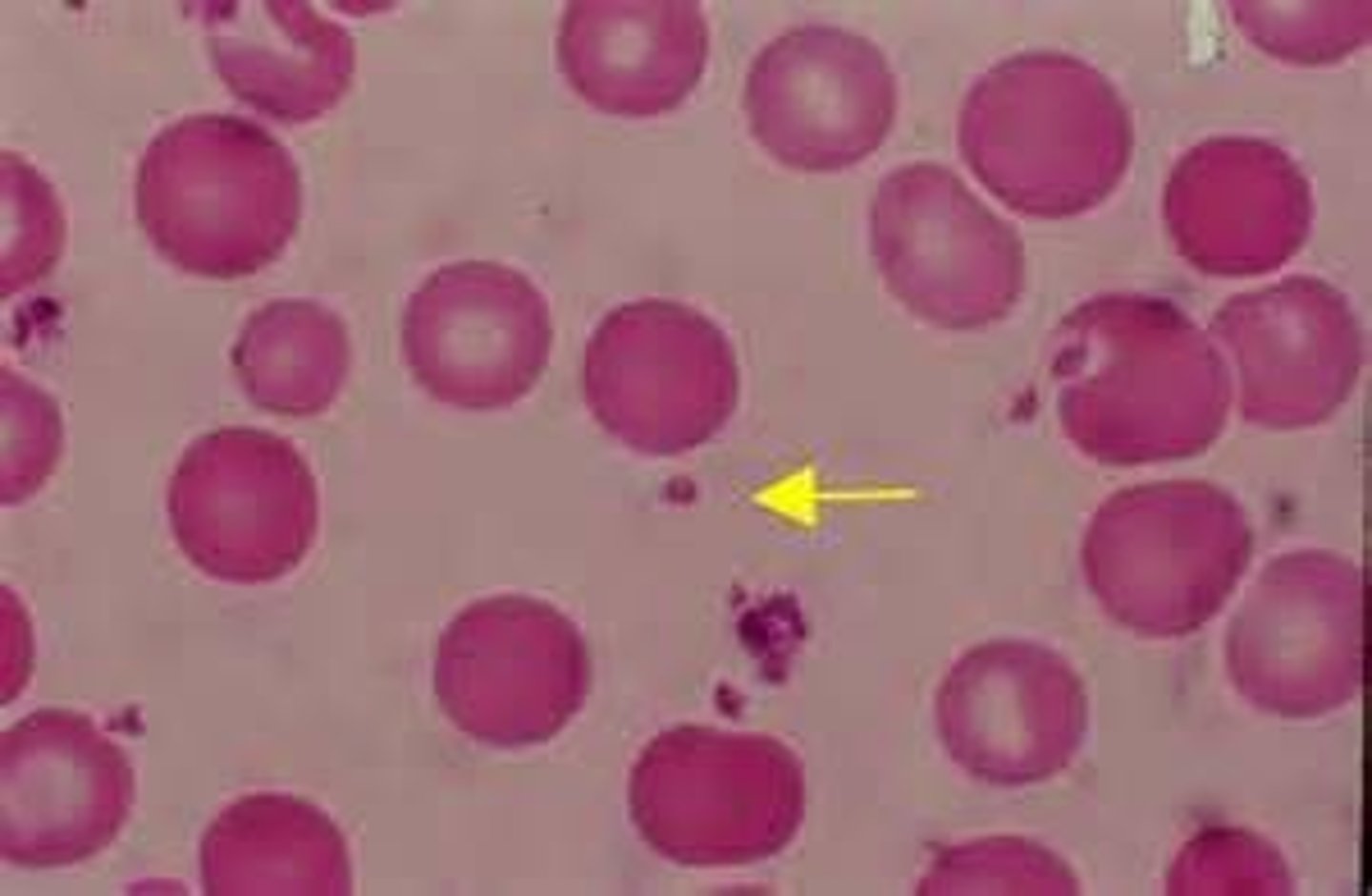
Helps form blood clots for healing
Platelets
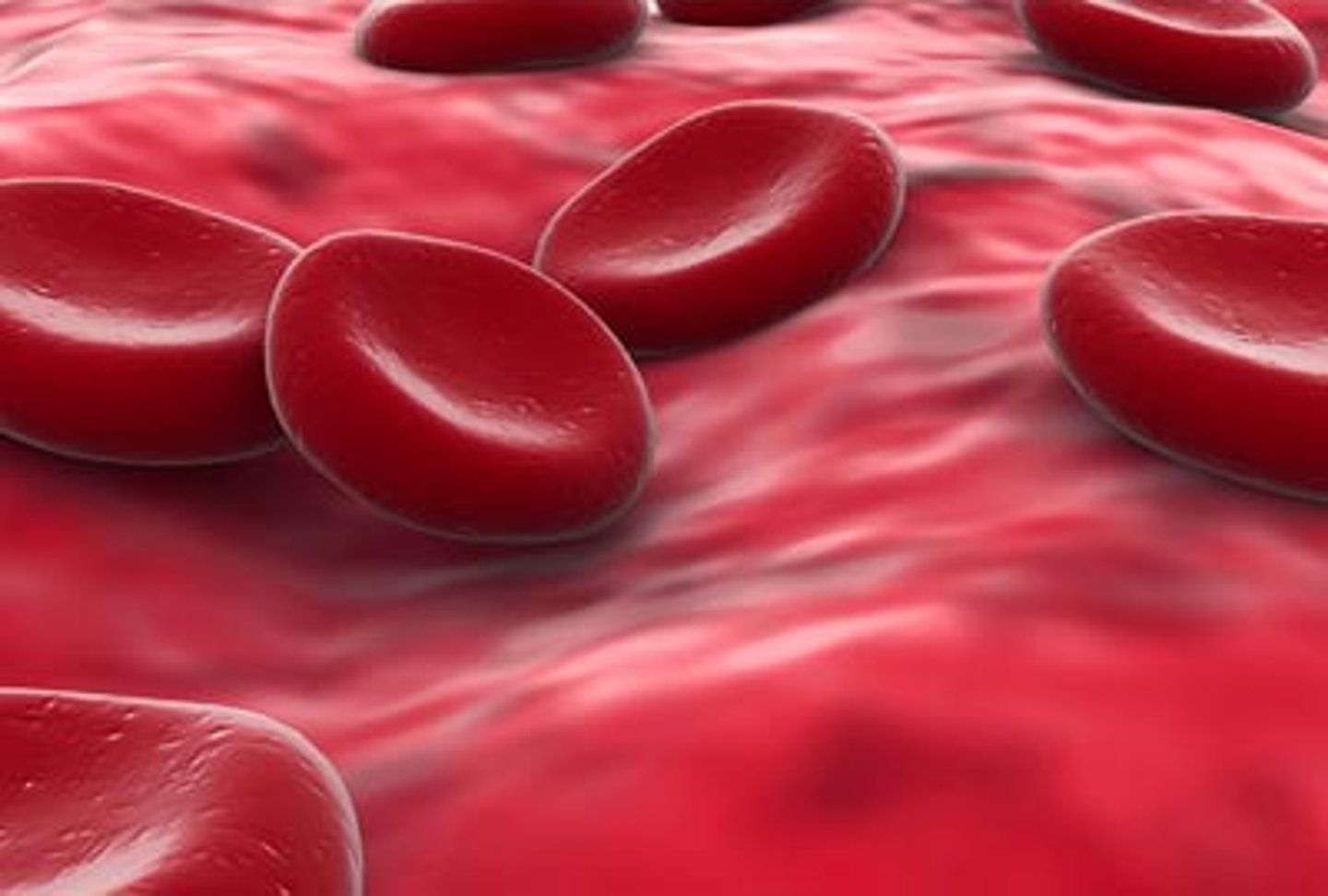
Carry oxygen
RBC
Blood plasma is made of __________% water?
90%
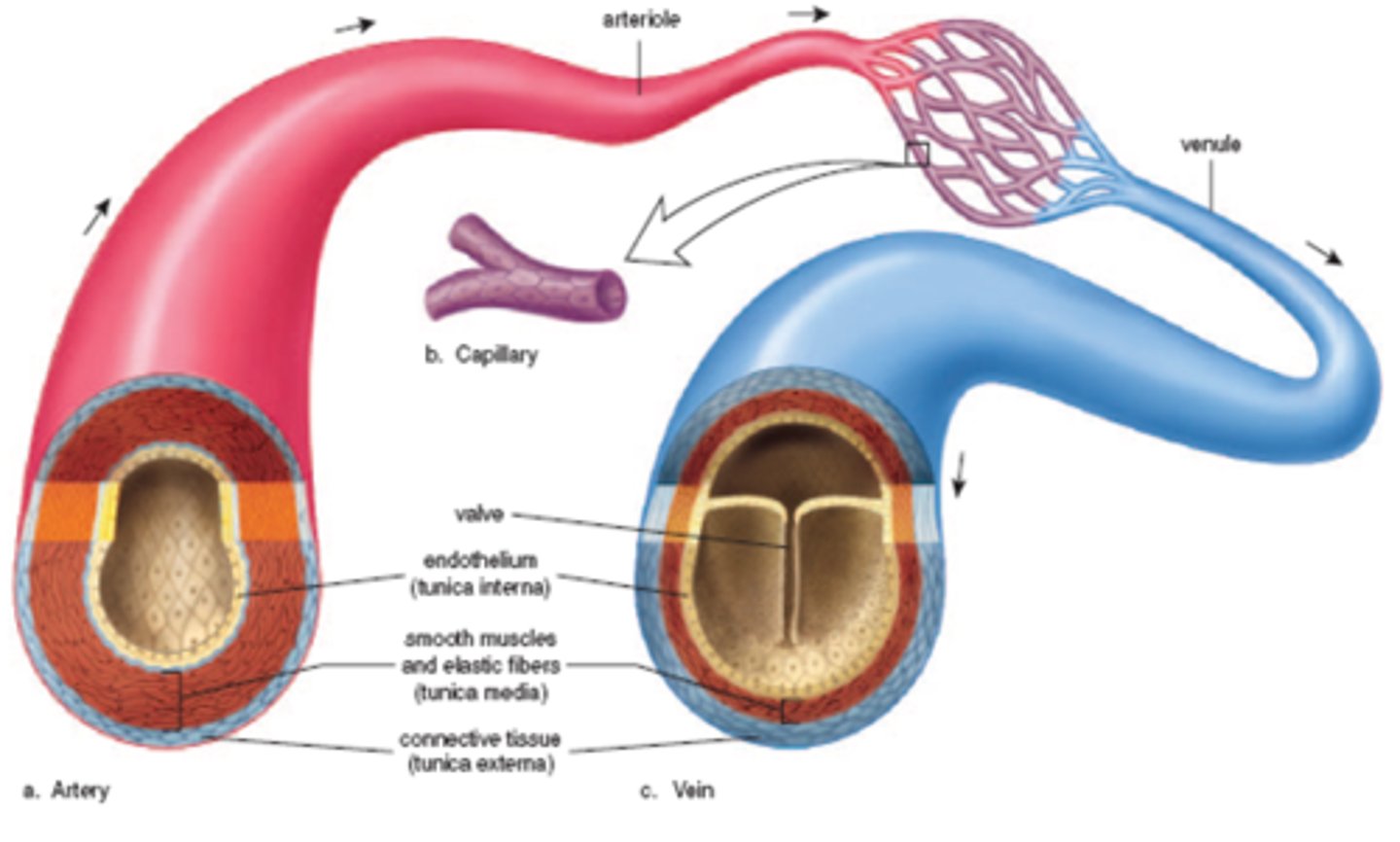
Carries blood away from the heart
Arteries
largest blood vessels are located
Near the heart
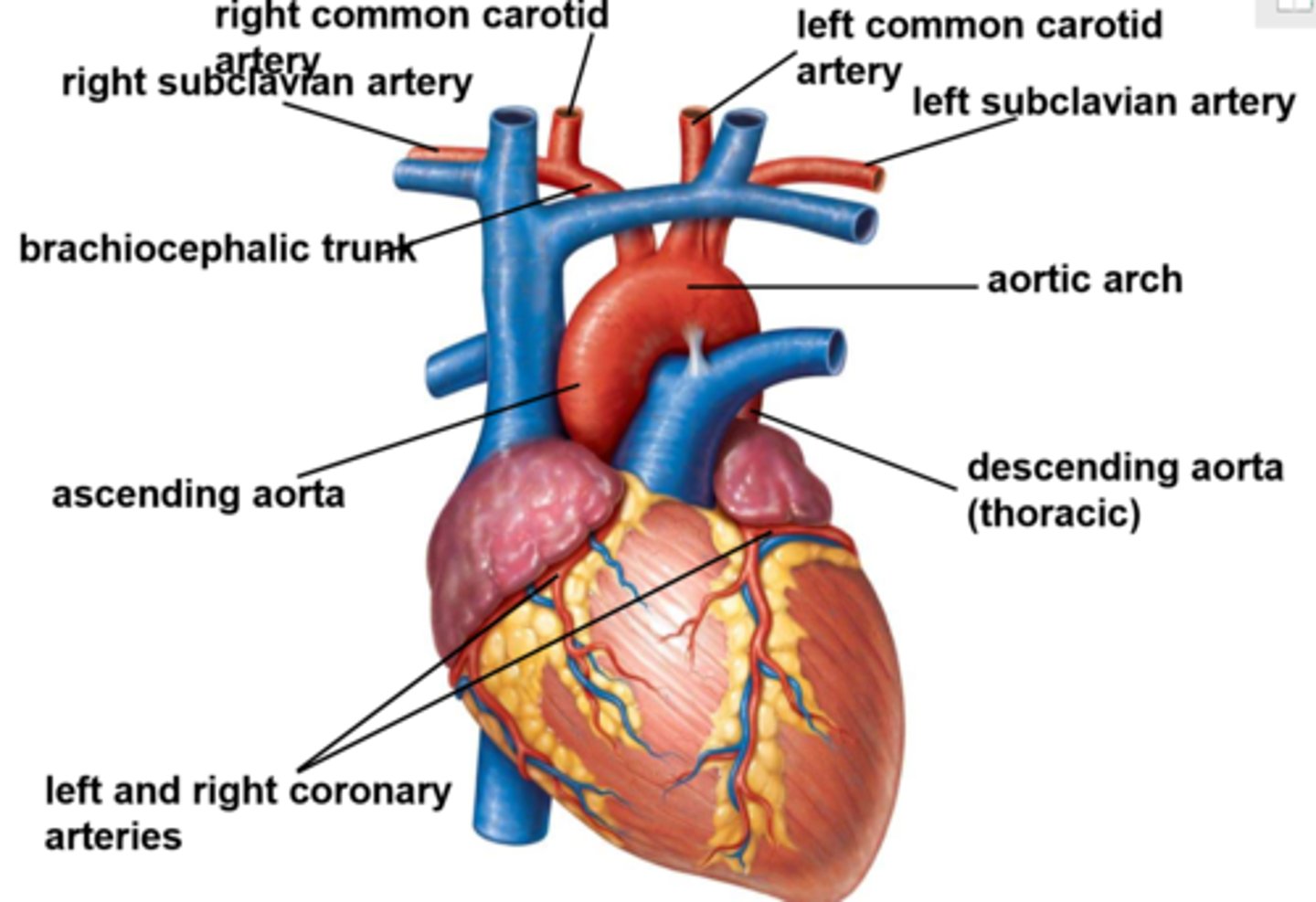
How long does it take for blood to travel a complete loop in the circulatory system
20-30seconds

Resting heart rate =
60-80 BPM
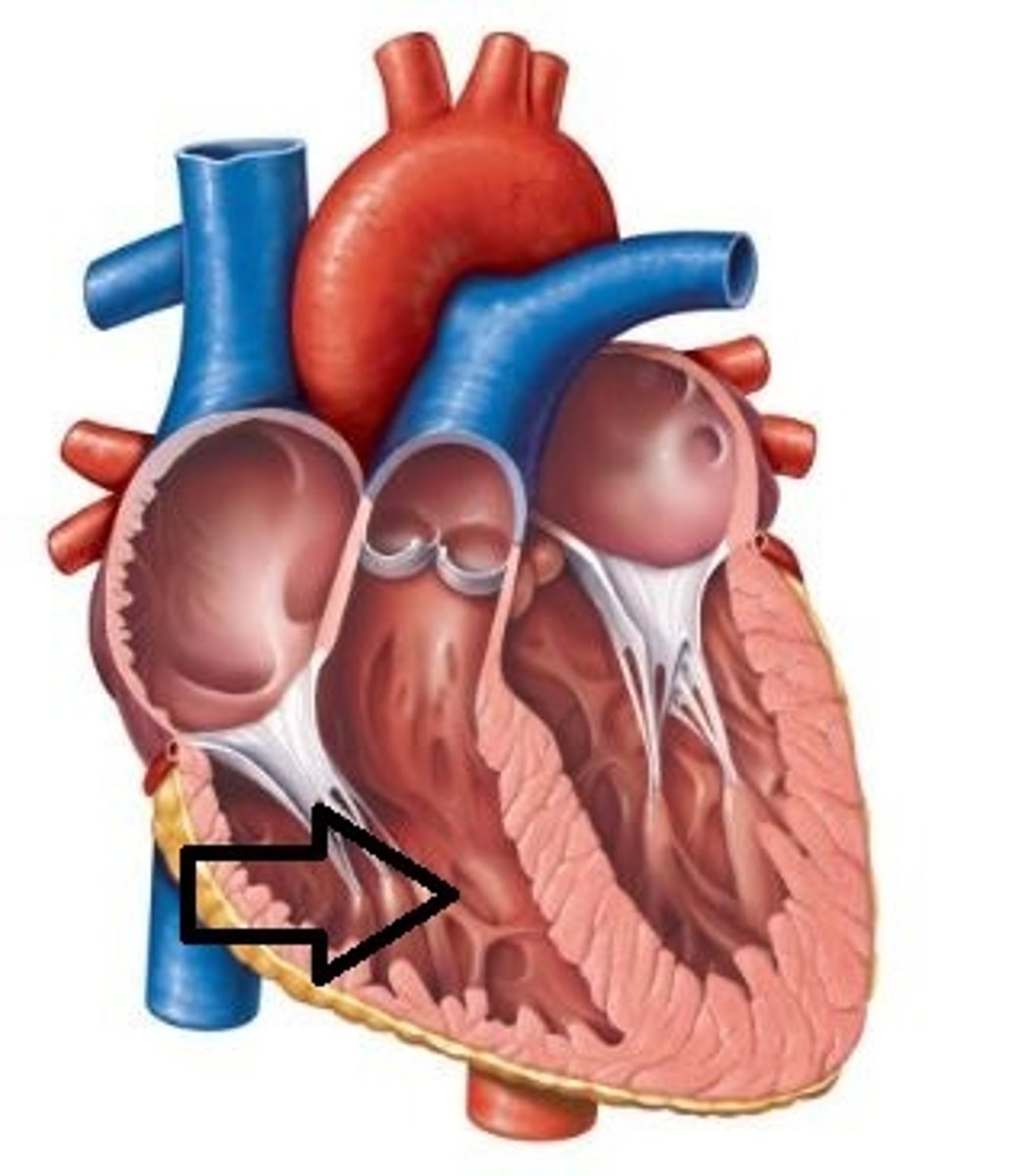
Deoxygenated blood enters the ________ side of the heart.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dX9SAgzLwXk&t=504s
right atrium
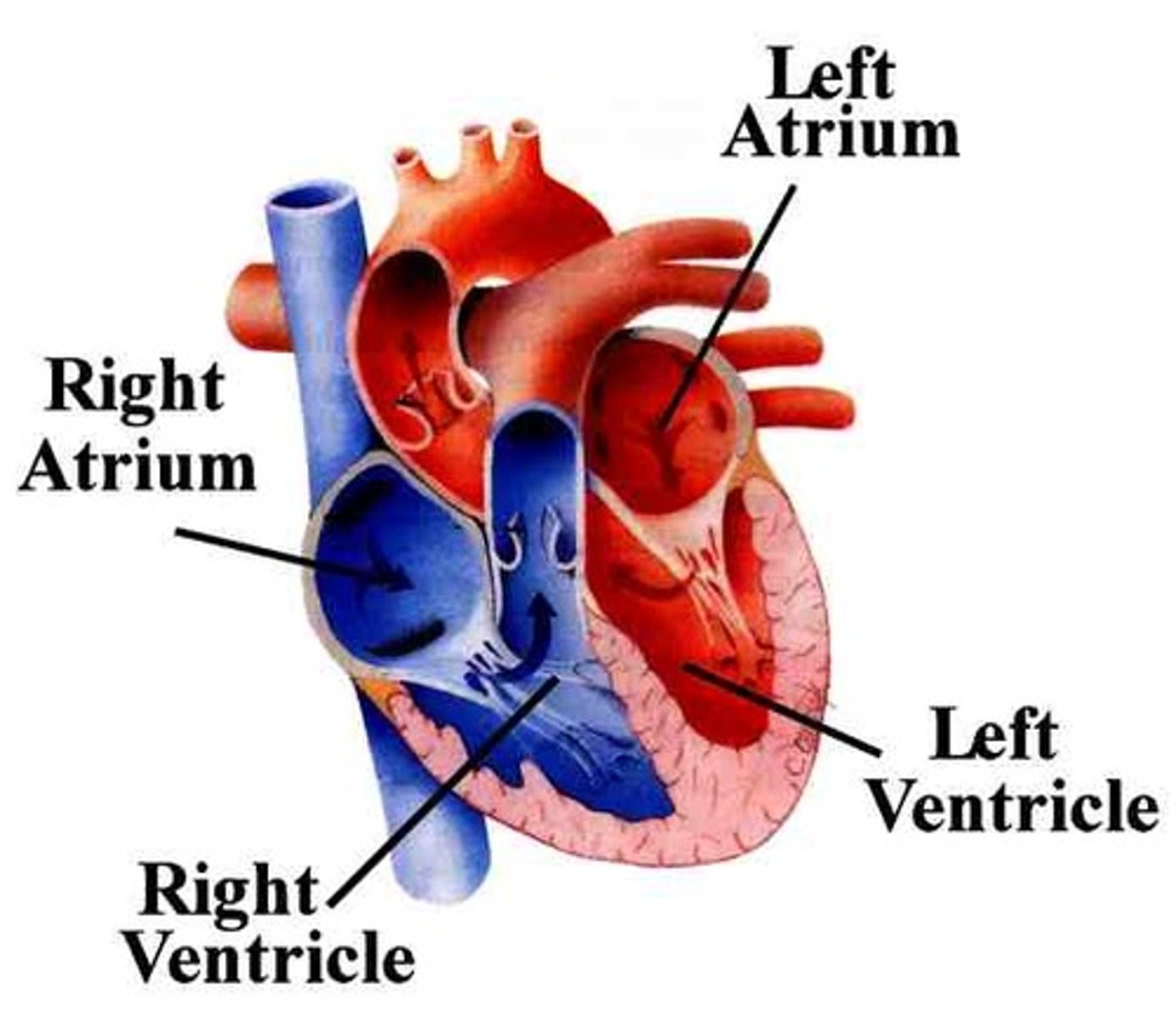
oxygnated blood leaves the heart from the _________
left atrium
HR during intense exercise can reach
120 - 200 BPM
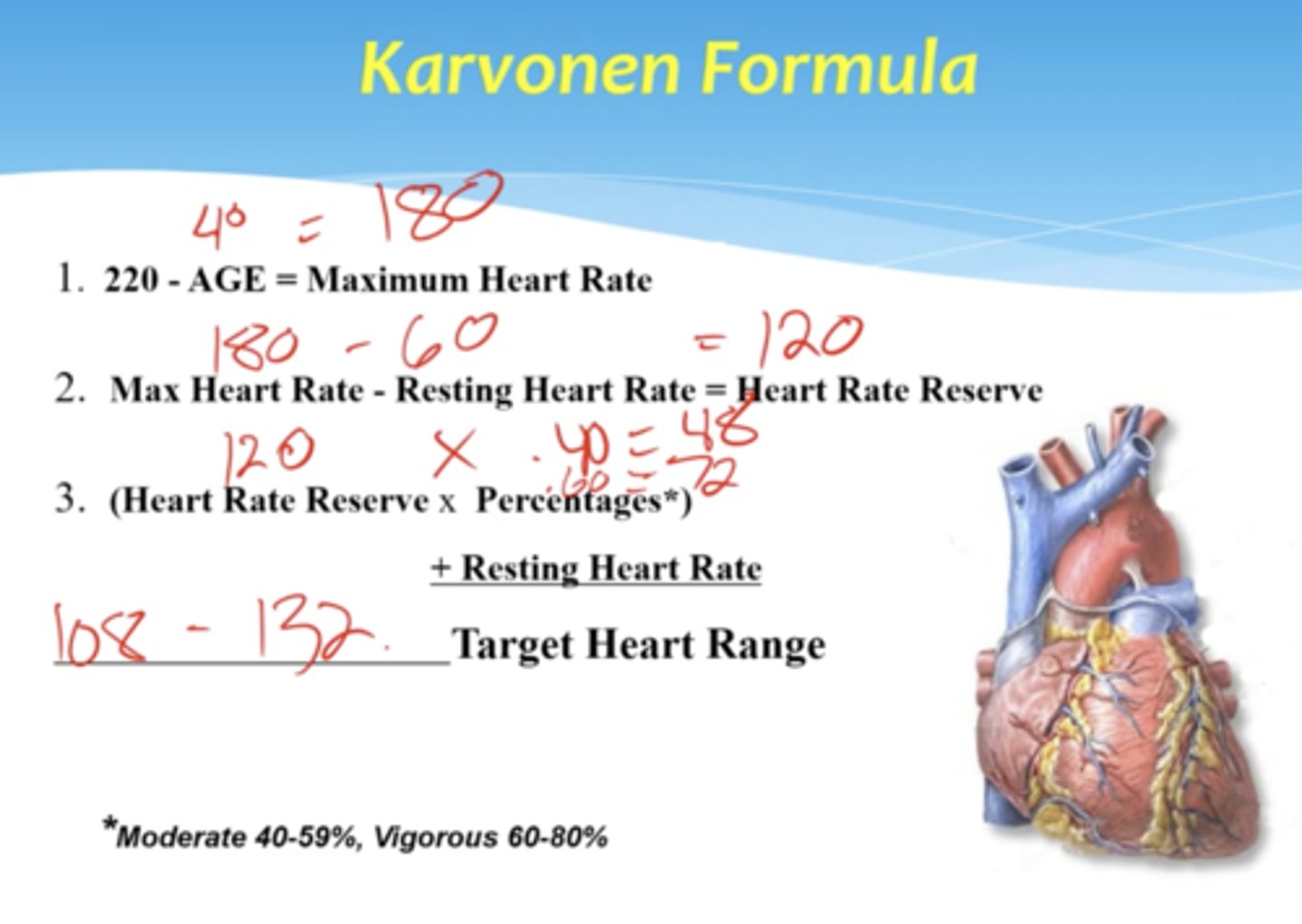
Formula for determining your Max target HR
220 - age

What is HRR
Heart rate recovery
What does HRR measure
how much your heart rate drops (recovers) after 1 minute of rest
IOW: heart health
How is HRR calculated
1. Work out to your targeted HR range & record the Target HR # (THR)
2. Rest for 1 minute and measure the HR (RHR1')
3. Do the math: THR - RHR1' = HRR
Peak heart rate – heart rate after one minute = heart rate recovery
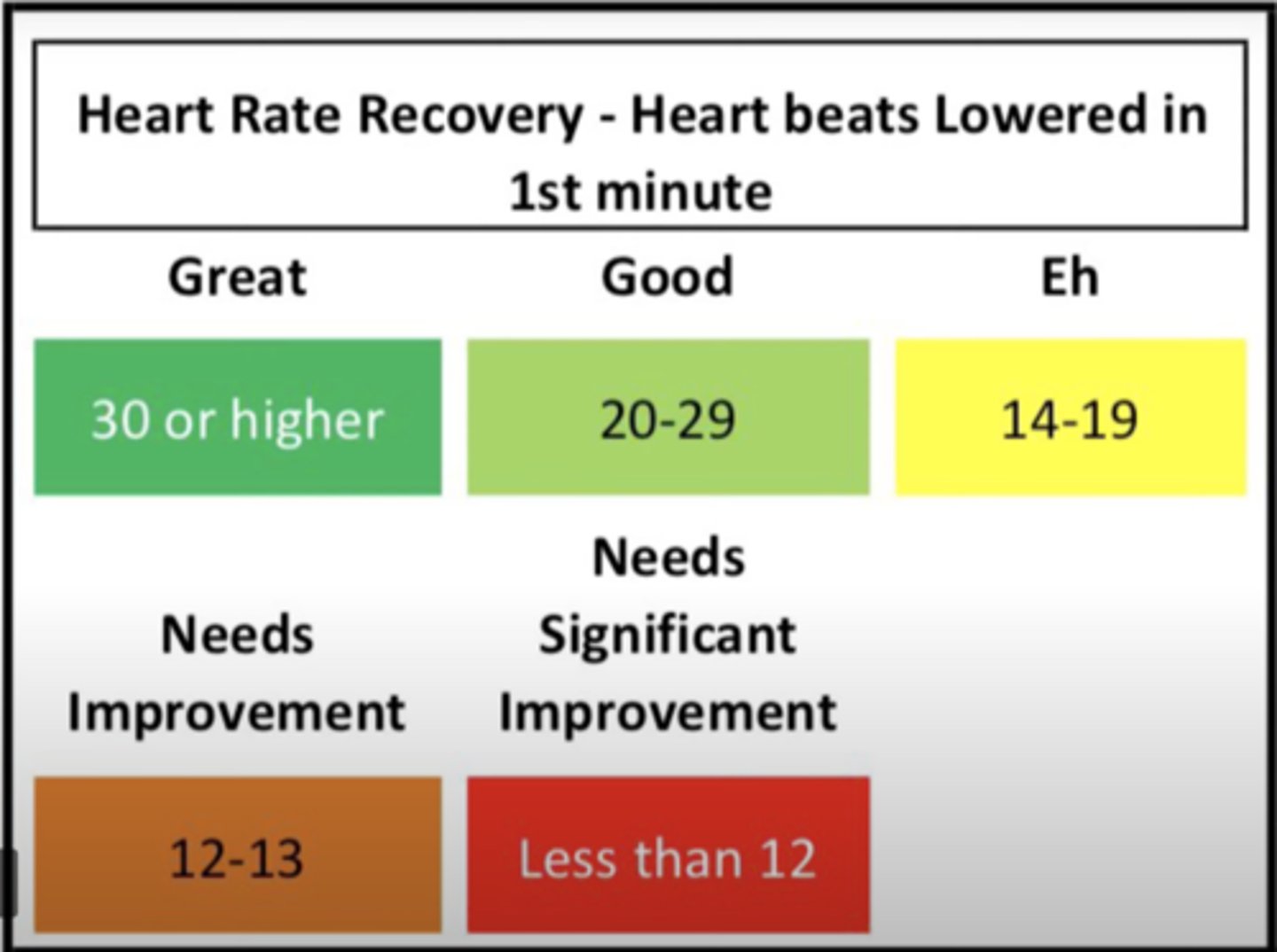
What is a great, good and bad HRR?
Great: 30
Good: 20-29
Bad: less than

Can the heart adapt?
How?
Yes, through training loads (weight training & cardiovascular work)
What decisions might one considered when wanting to compete in sport?
Genetics

whats more important?
1. technique and drive
2. Genetics?
Hard work beats talent when talent doesn't work hard

How many bones does a newborn have
305

Why do you suppose a child's bones are softer than an adult?
Less likely to brake as they develop the proprioceptive system.
Fitting through the birth canal
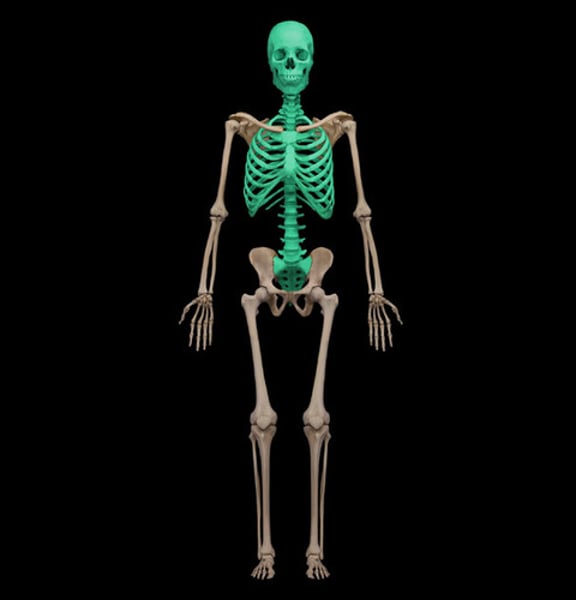
Name the portion of the skeleton
Axial skeleton
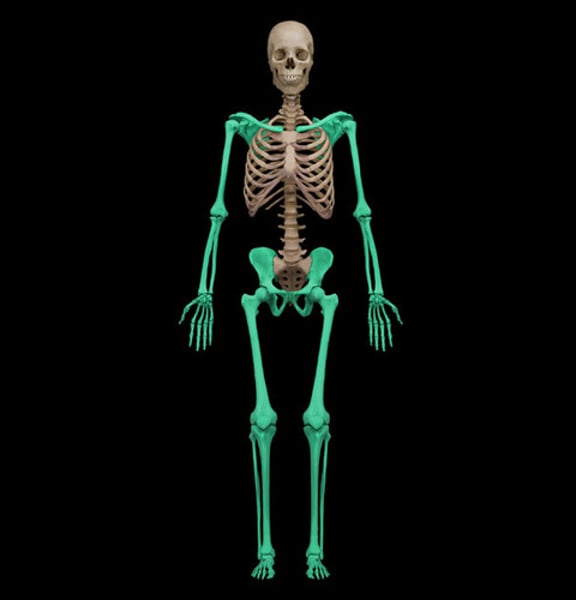
Name the portion of the skeleton
Appendicular skeleton
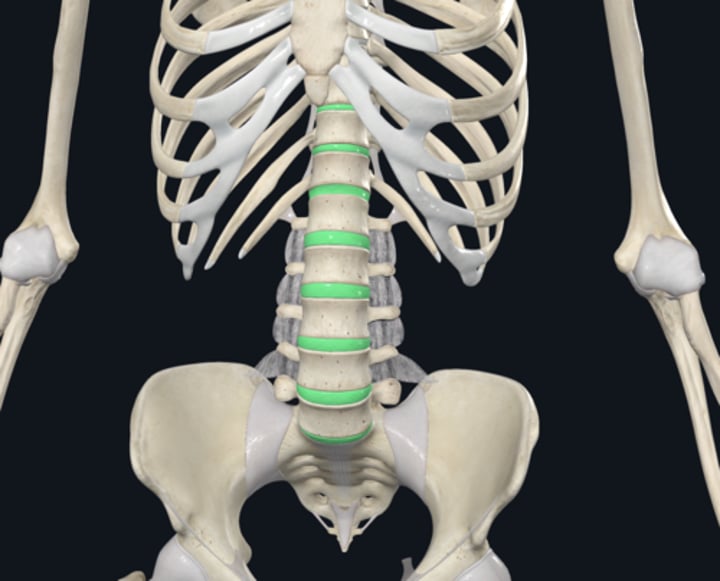
Name the body part in the image highlighted green
Intervertebral Discs

What is the function of the disc
Shock absorption
Flexibility

What is the function of the long bones of the appendicular skeleton
Levers for force/power production
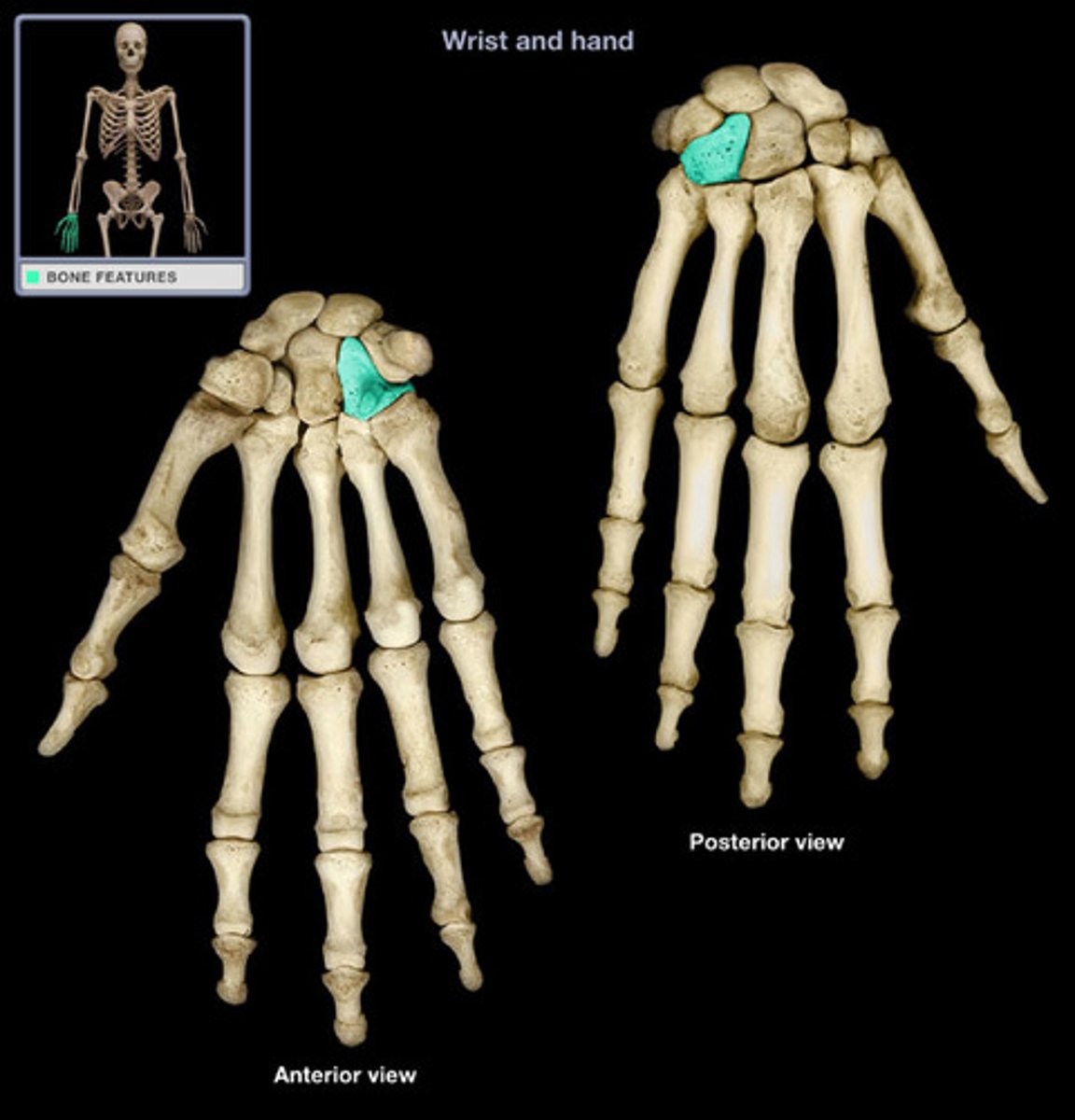
How many bones are in the hands
54

Why are the carpal bones small
IOW: what is their function based on their design?
1. Flexibility for small movements tasks
2. Absorb impact
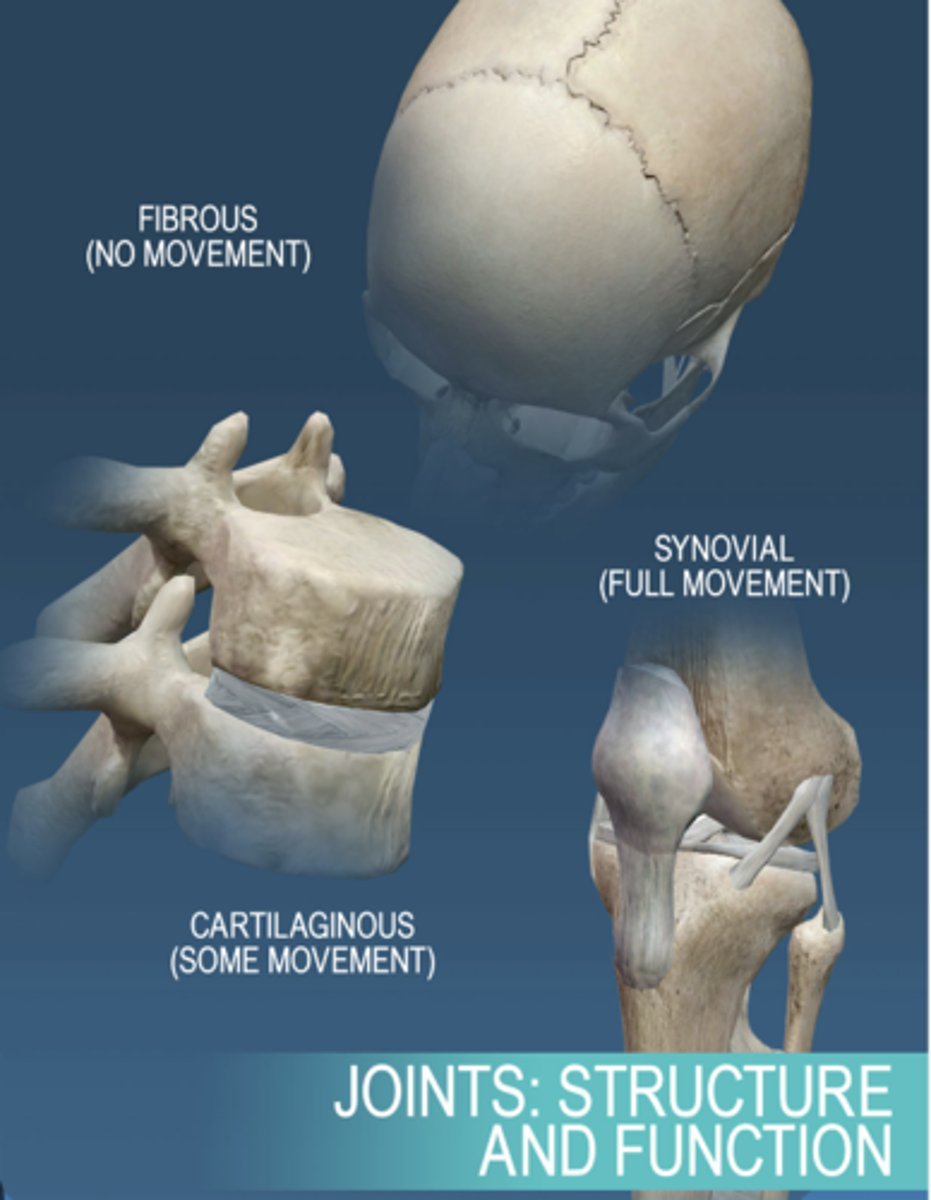
What are the three types of skeletal joints
1. Fibrous
2. Cartilaginous
3. Synovial
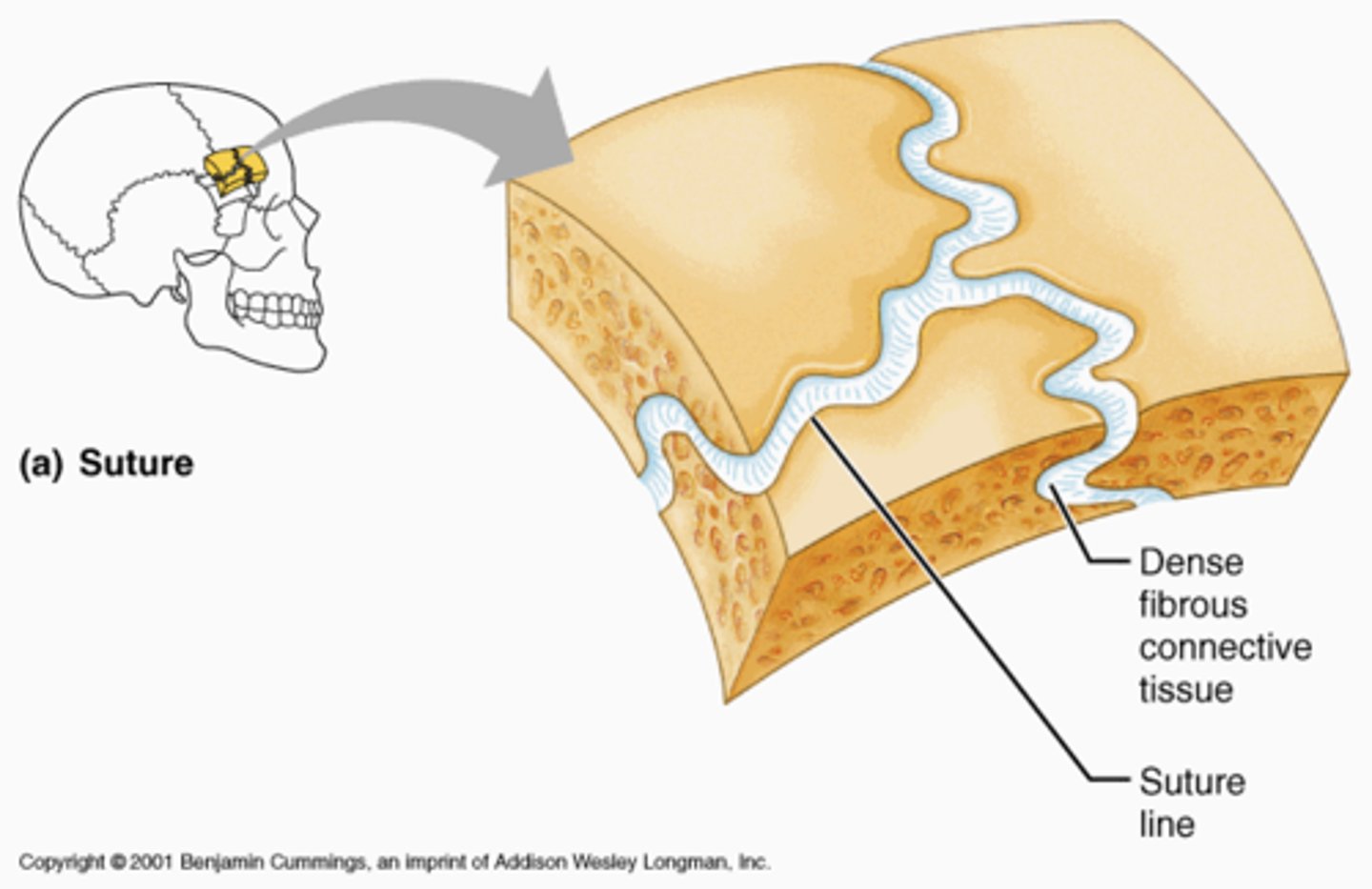
Immovable joints
fibrous joints
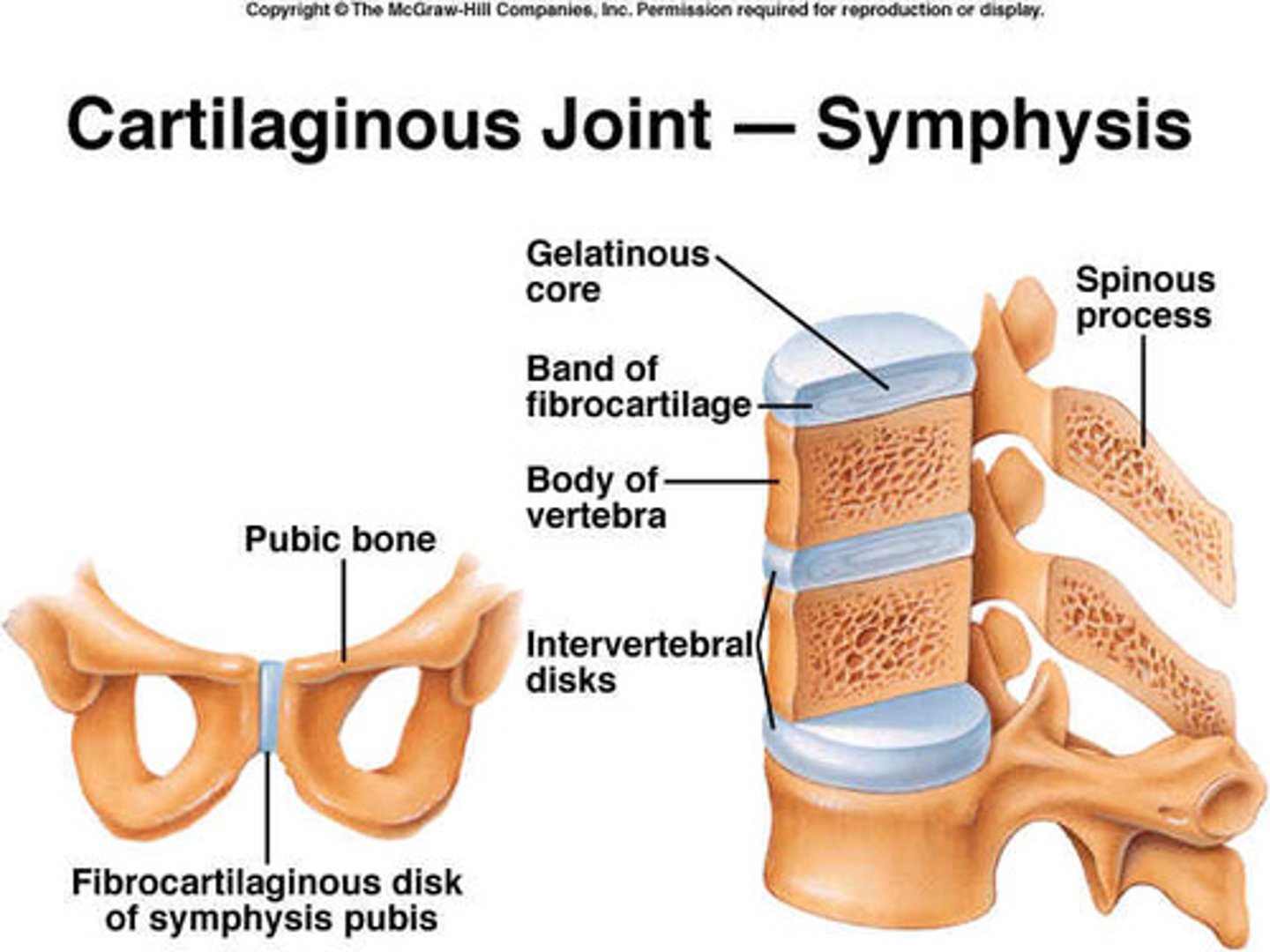
cartilaginous joints
partially moveable joints
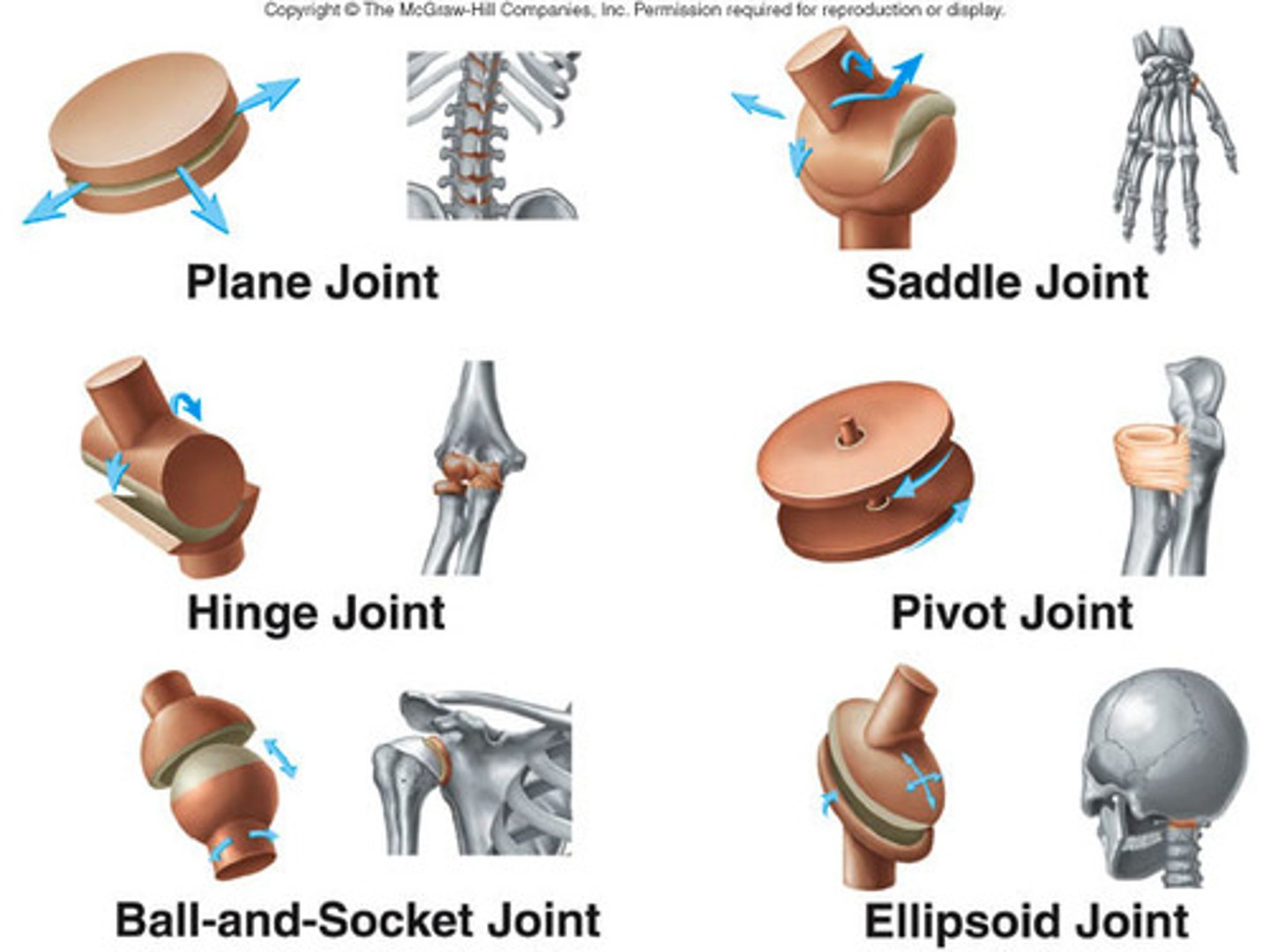
Synovial Joints
freely movable joints
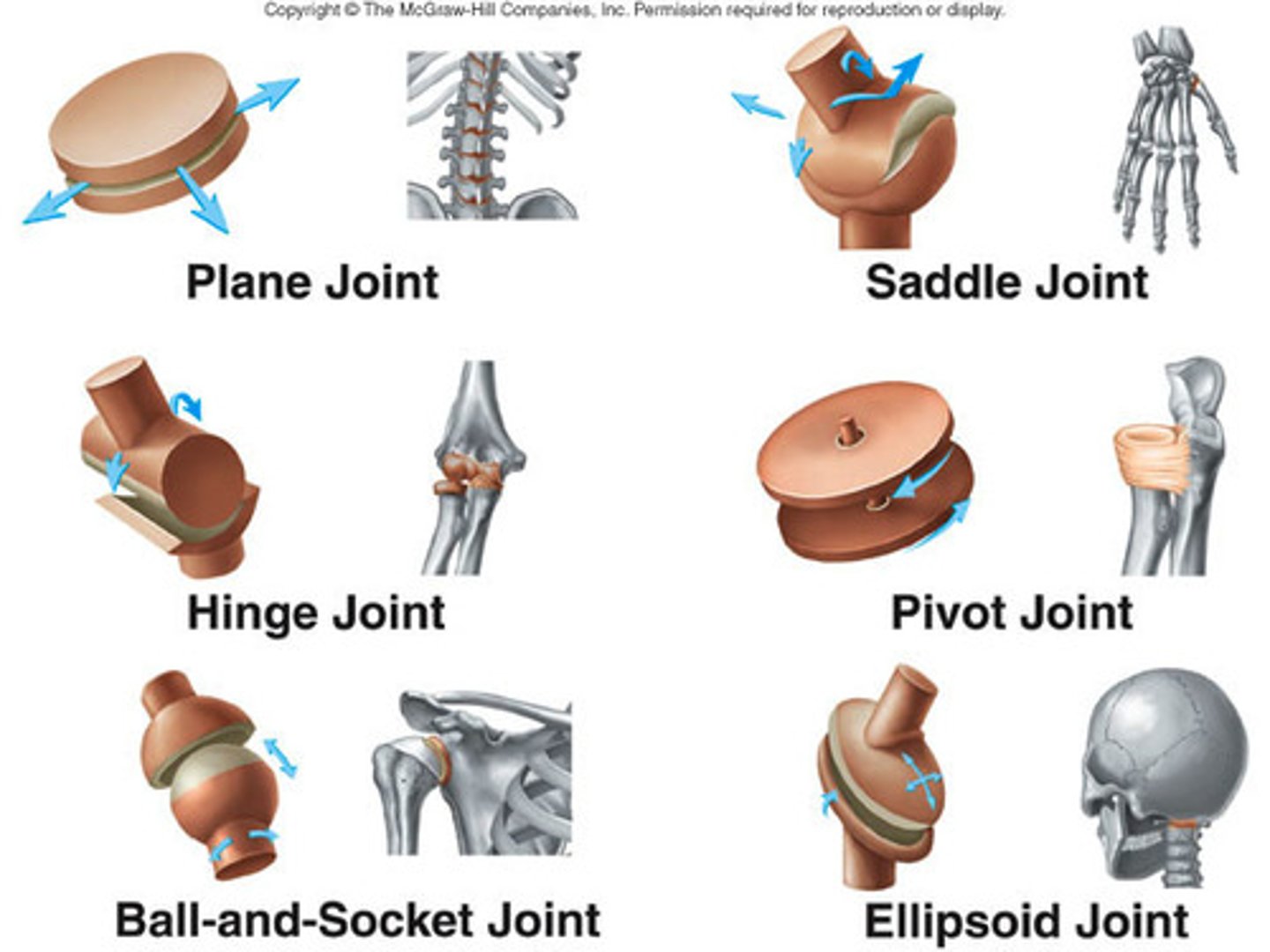
6 types of synovial joints
ball and socket
gliding
ovoid
Saddle
Hinge
Pivot

Why are the ball and socket and hinge joint so important for sport?
they allow for a large Range Of Motion (ROM)

Of the 6 types of synovial joints, which are crucial for sport performance
Ball and socket
Hinge
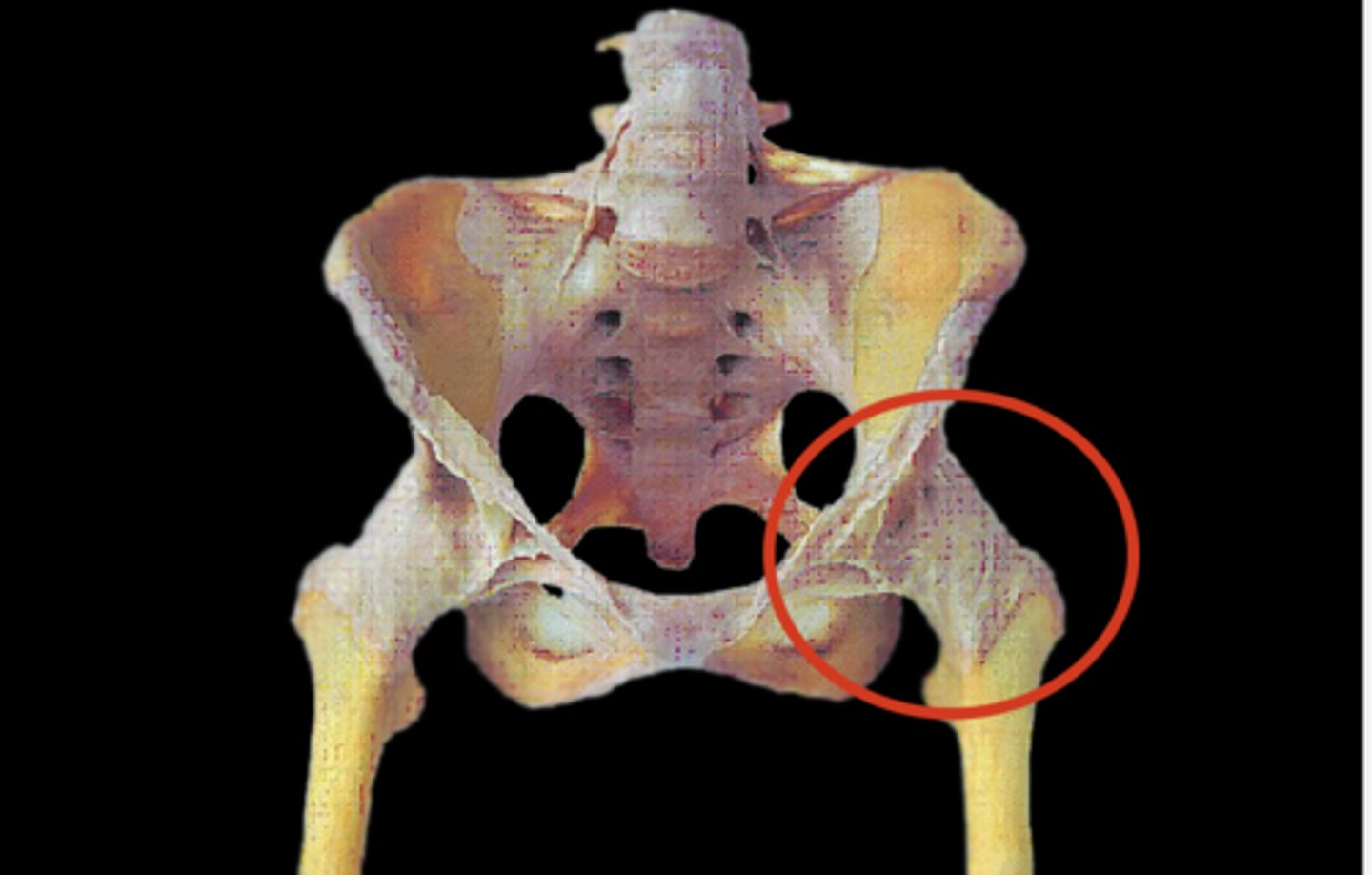
What aids in keeping the ball and socket joint's stable
Labrum
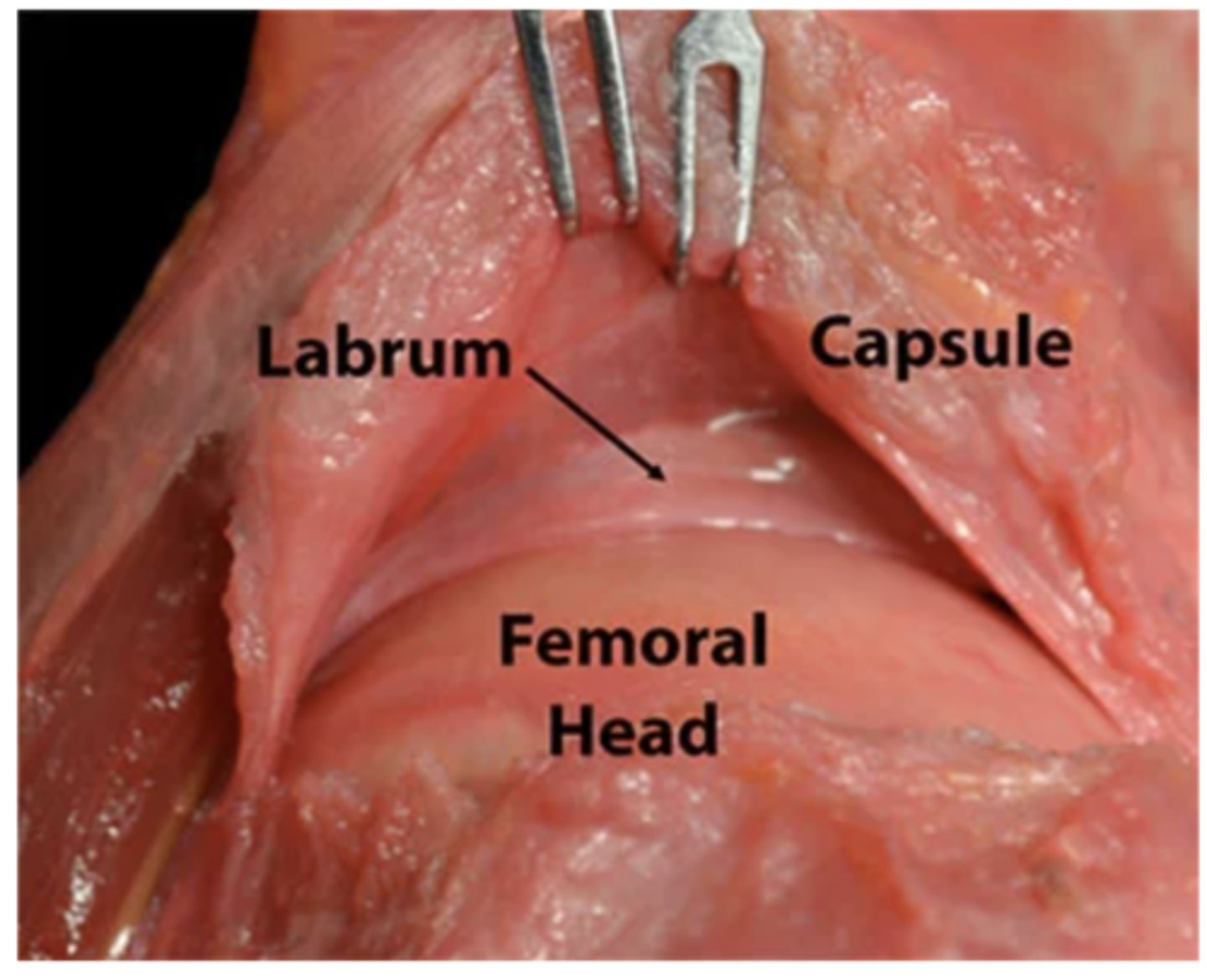
What is the Labrum
a soft circumferential tissue extension of the bone (ligament) made of tough fibrous tissue

Hinge joint's allow movement how?
One plane only

How many muscles in the human body
about 600 with some variances
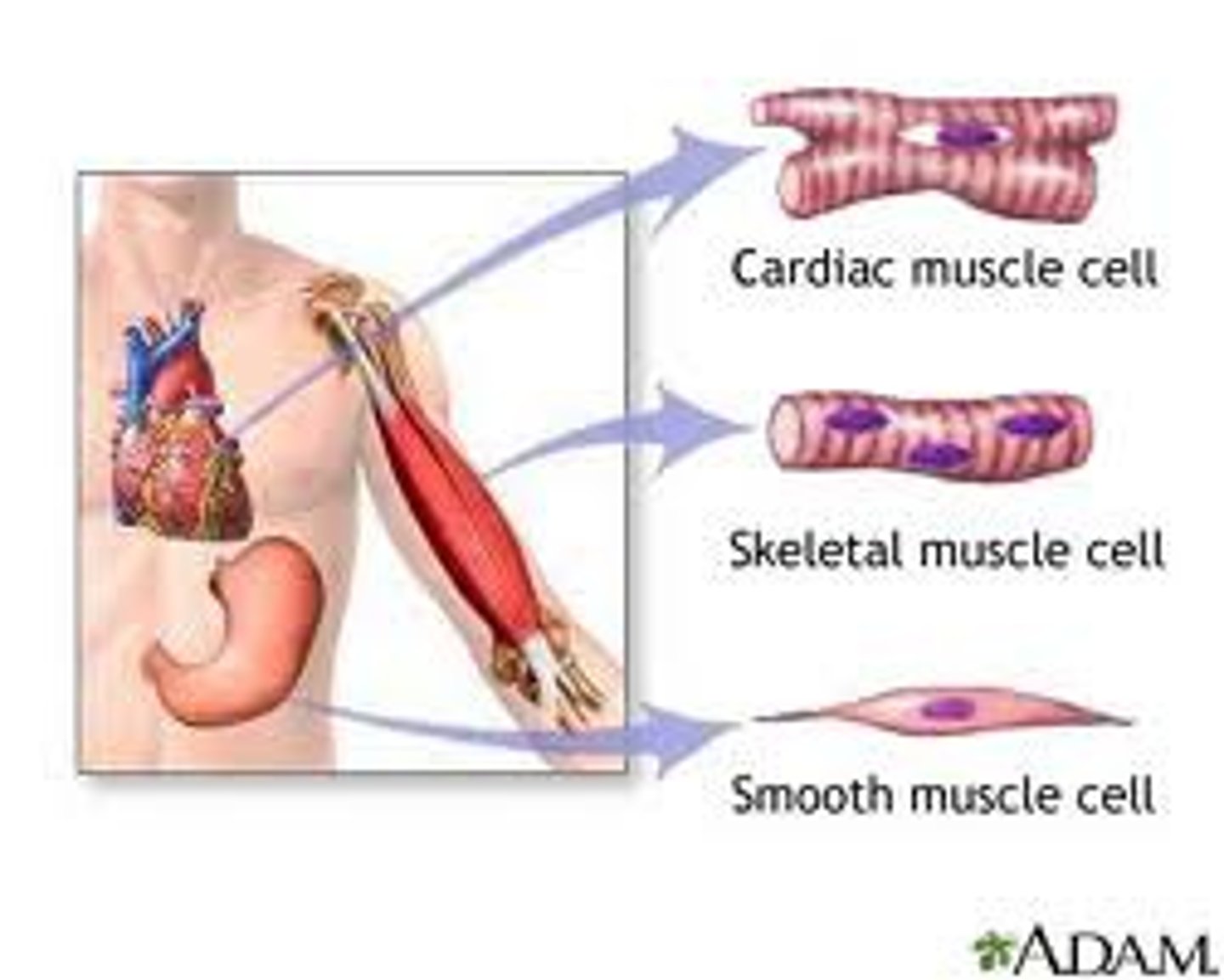
Voluntary (Somatic) muscles
skeletal muscle

Involuntary (Autonomic)
cardiac & Smooth muscle (Organ, etc)

T/F - Muscle cells are either on (full Force) or off
True
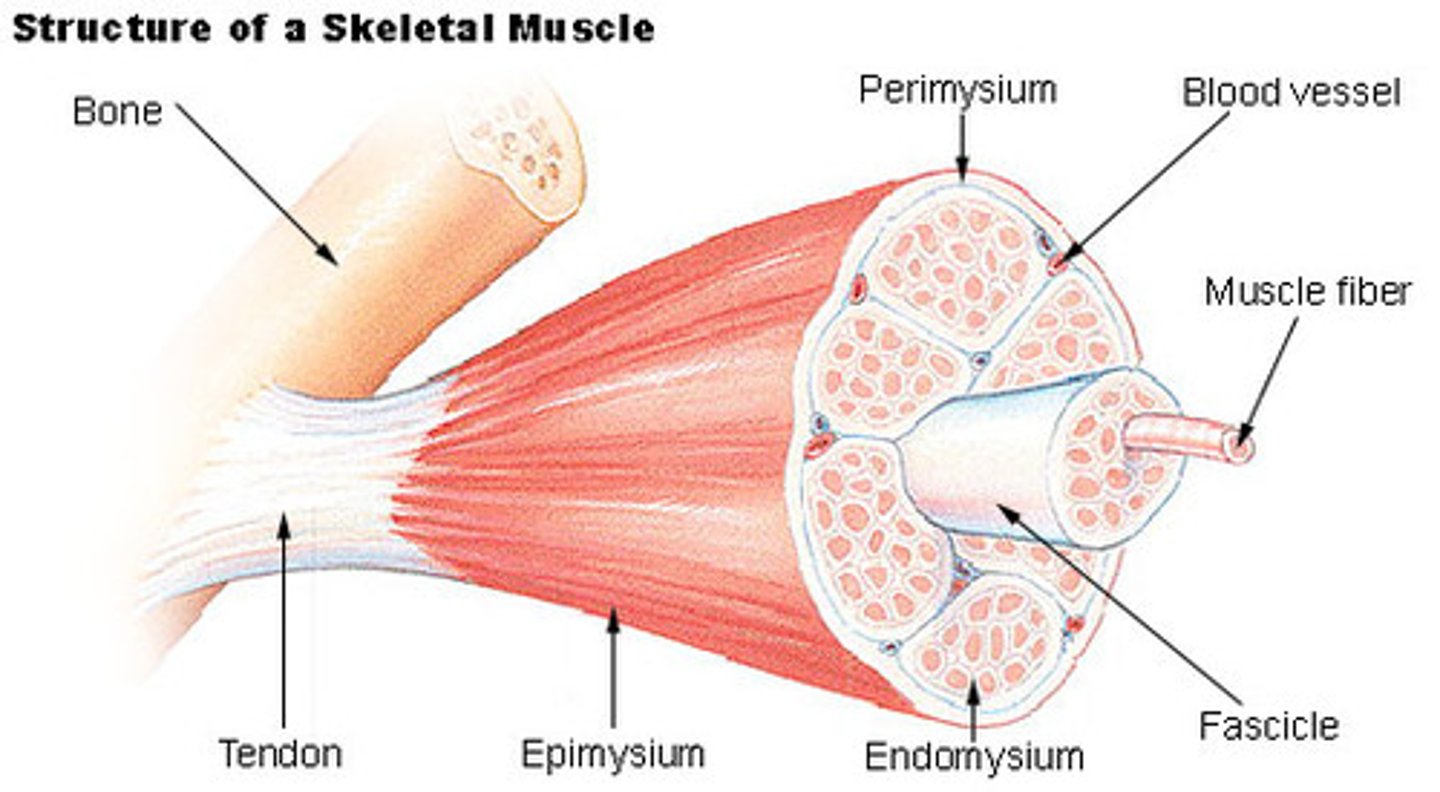
Describe the architecture of a muscle belly
tubes within parallel tubes (bundles), until you get to the muscle cell fiber itself.
All encased in connective tissue (fascia)
33:39
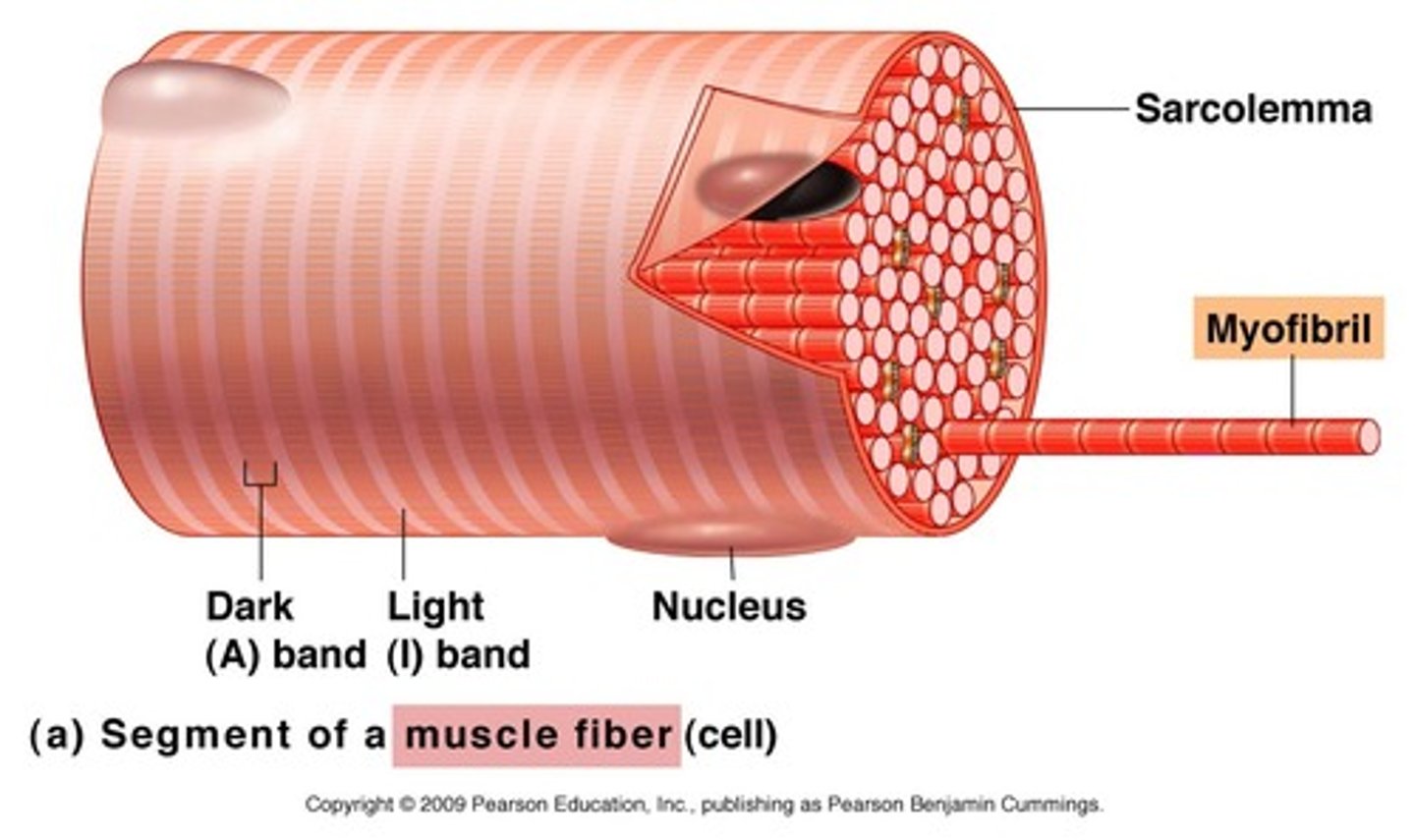
A series of muscle protein filaments joined end to end
Myofibrils
When does a muscle relax
When the nerve impulse from the brain stops
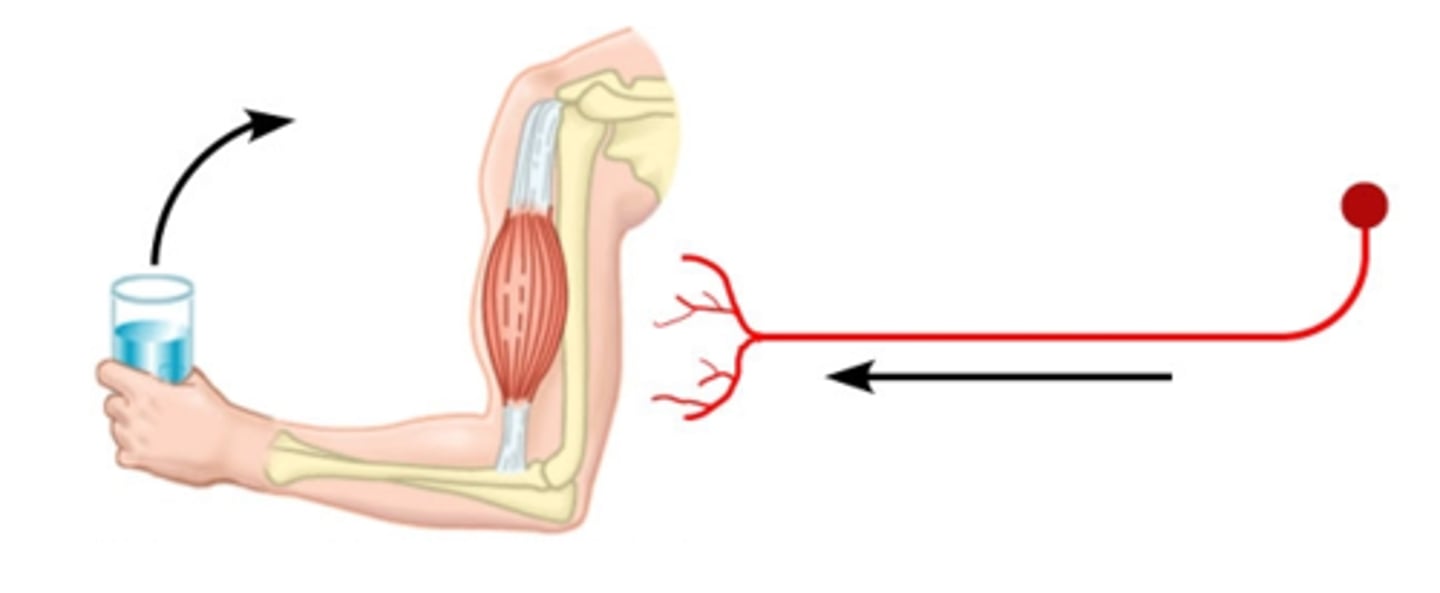
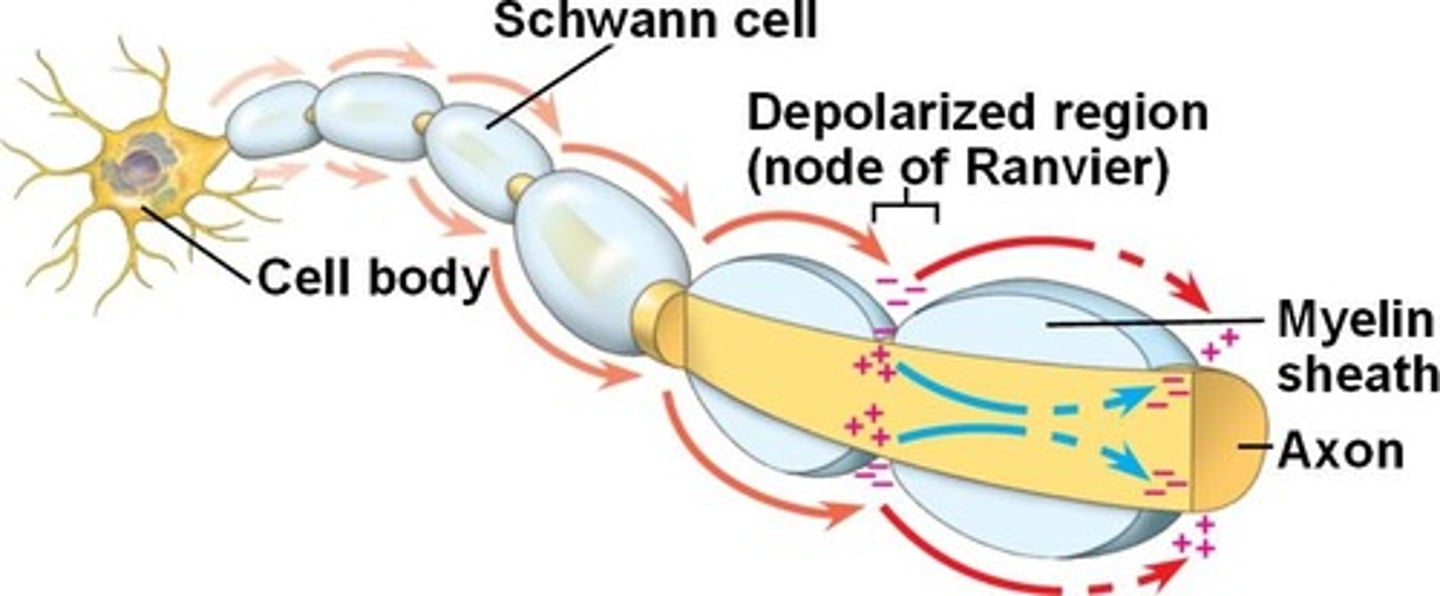
What structure (wire) sends the signal to the muscle from the brain
Motor Neuron
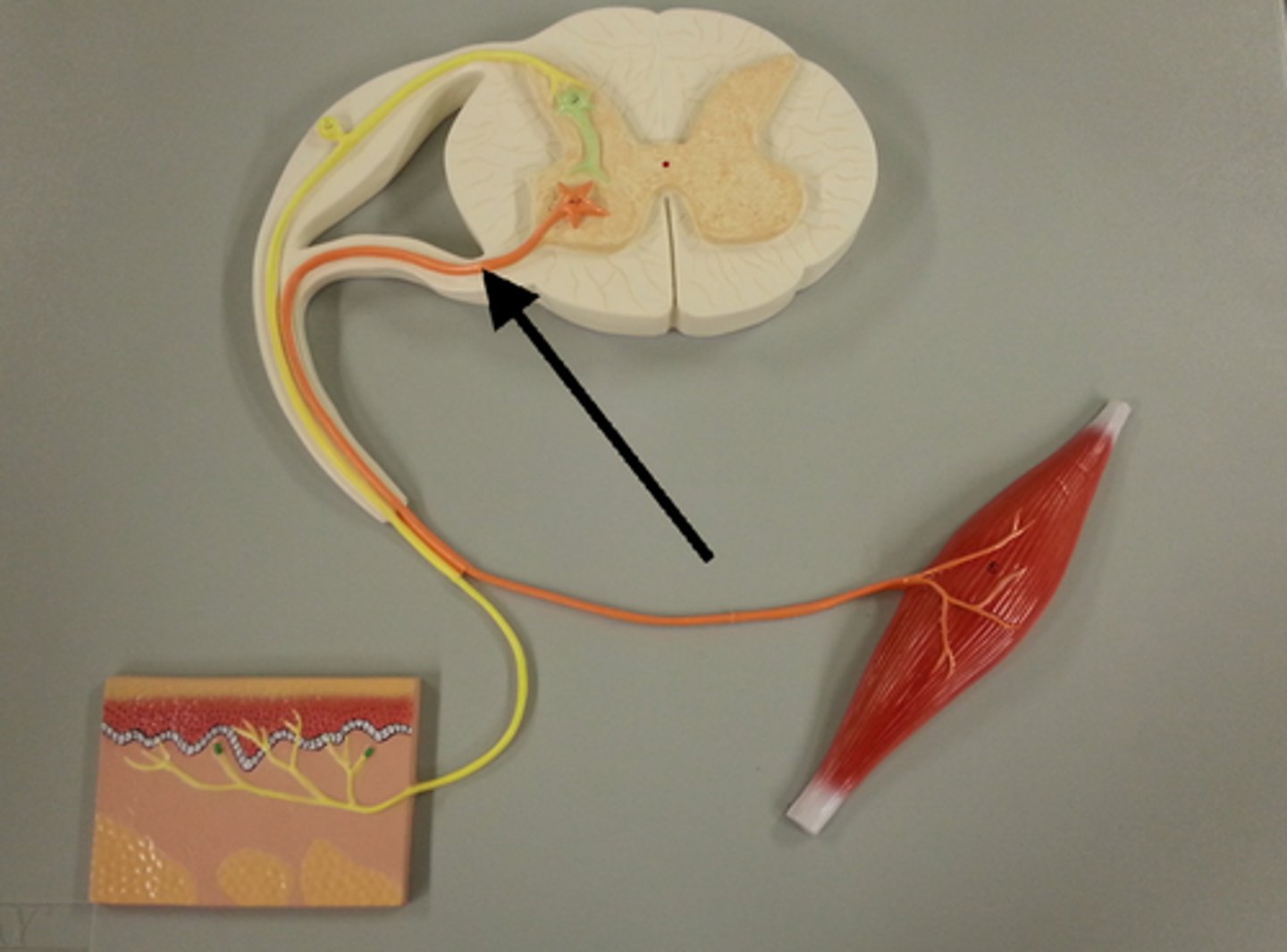
1 motor neuron serves .......
a small number of muscle fibers (10-100)
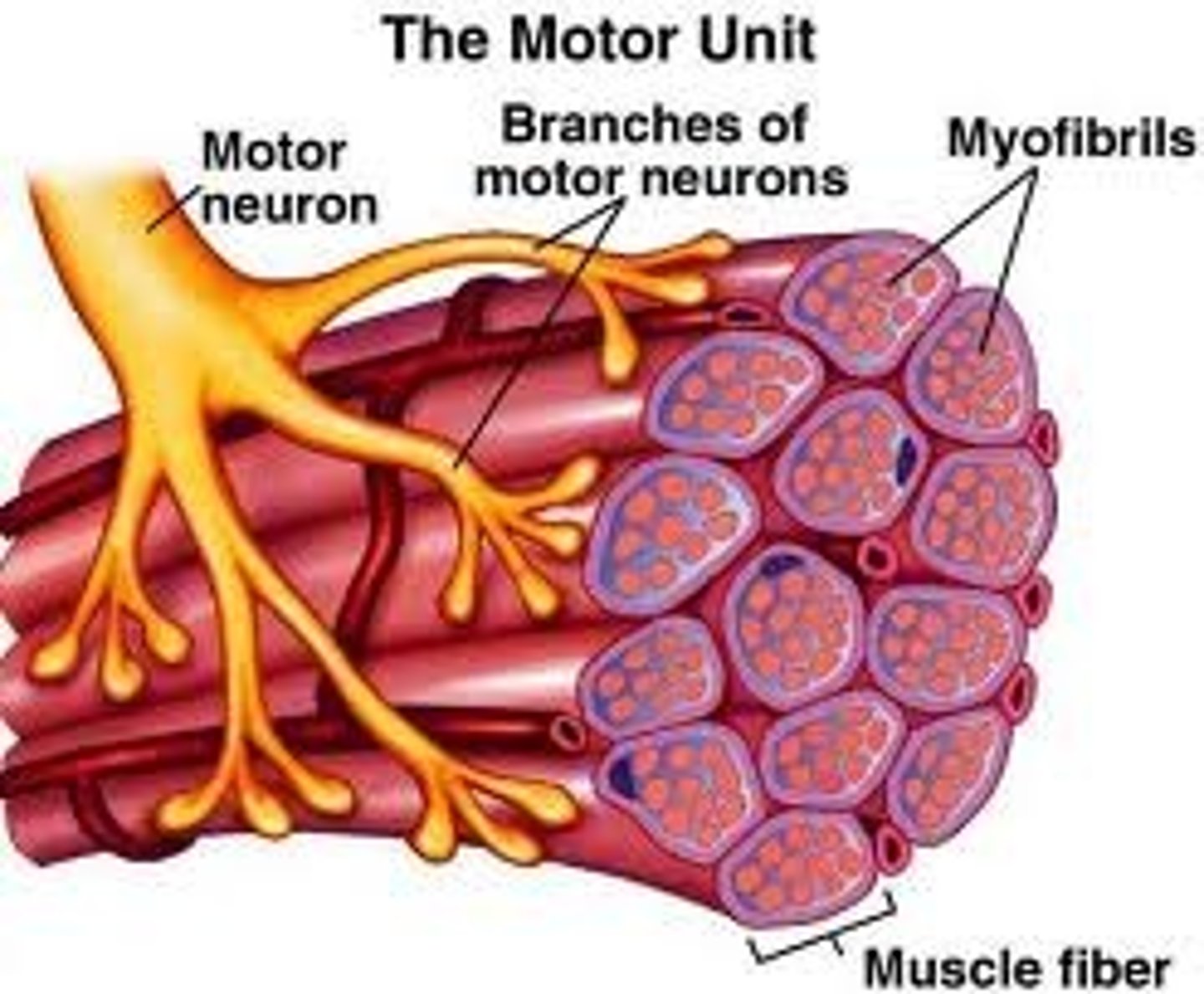
The motor neuron and all the fibers it connects to
Motor unit
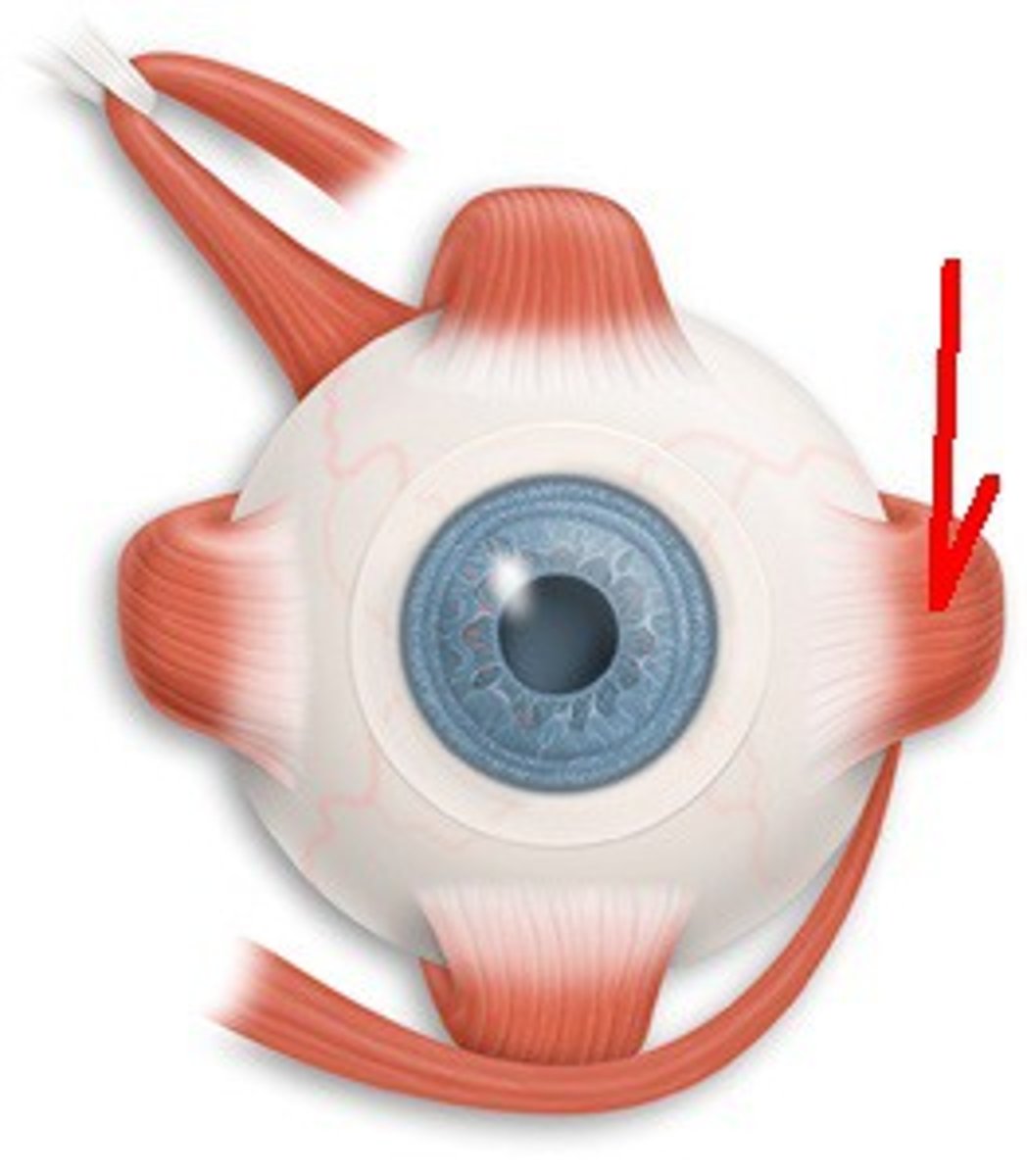
What allows for more precise motor control in the eyes and hands?
small motor units
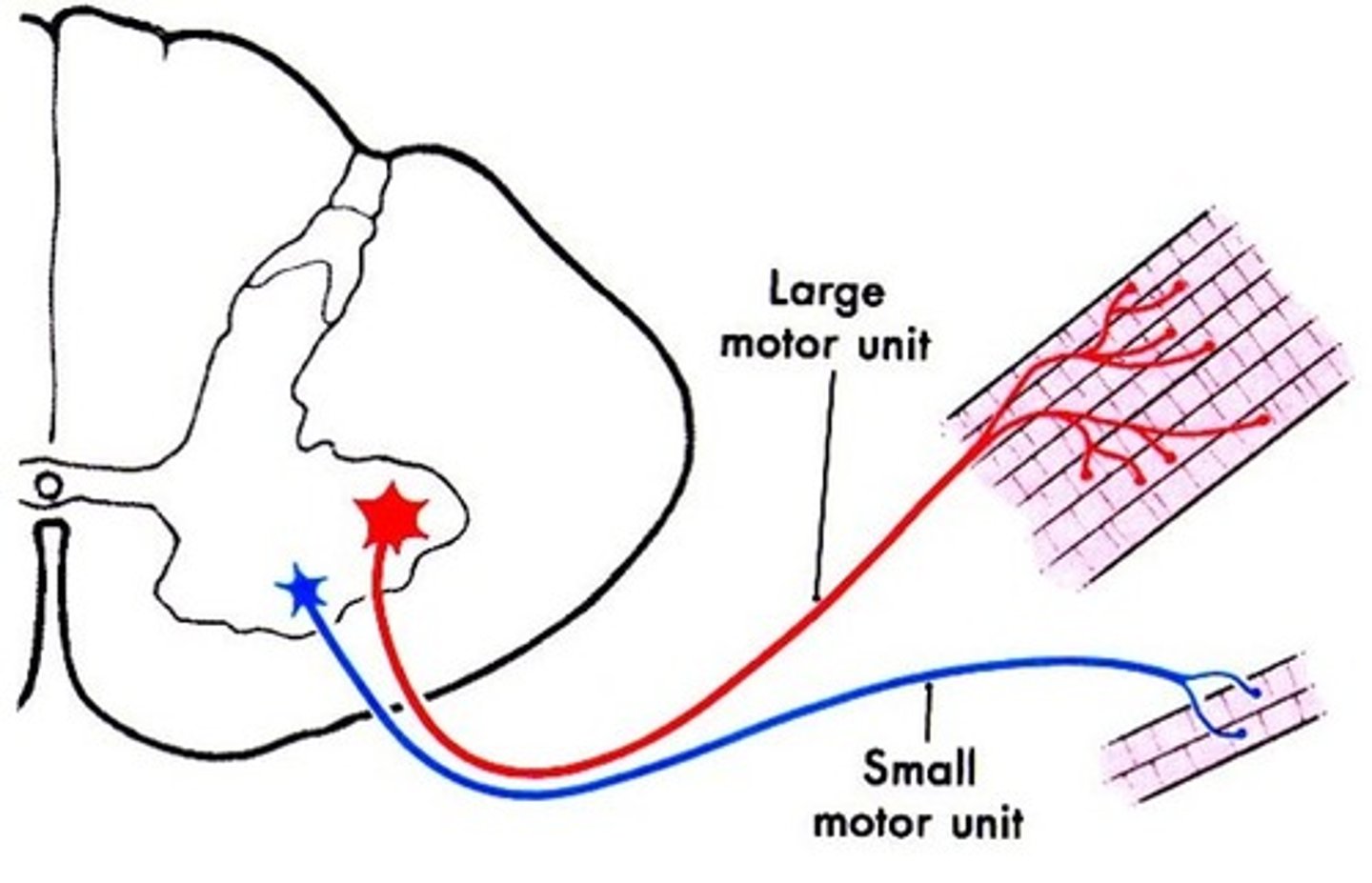
What is a small motor unit
A single motor neuron supplying a small number of muscle fibers in a muscle bundle
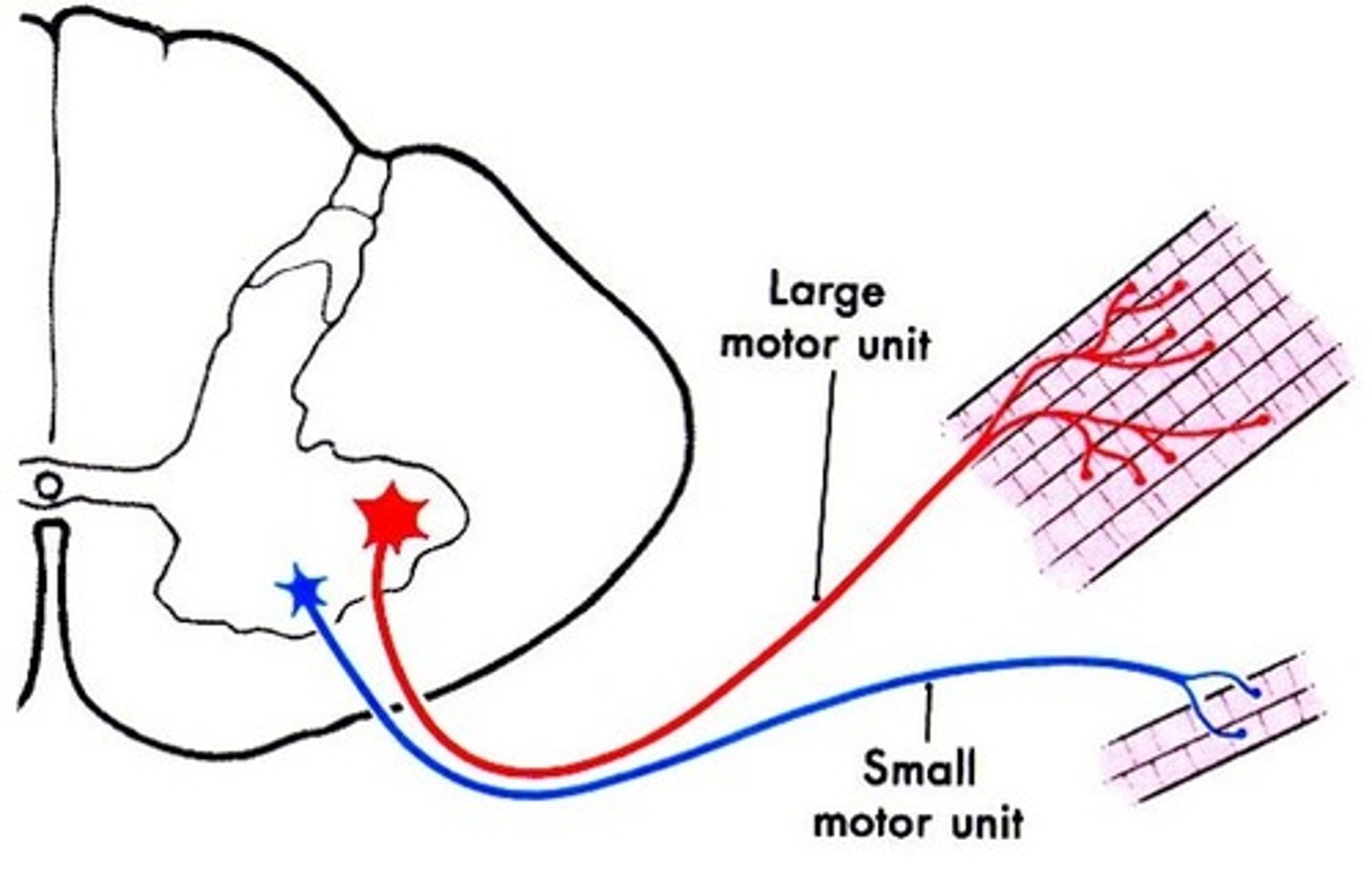
What is a large motor unit
a single motor neuron supplying large numbers of muscle fibers

Why are maximal muscle contractions short lived?
Energy supply (ATP) diminishes quickly
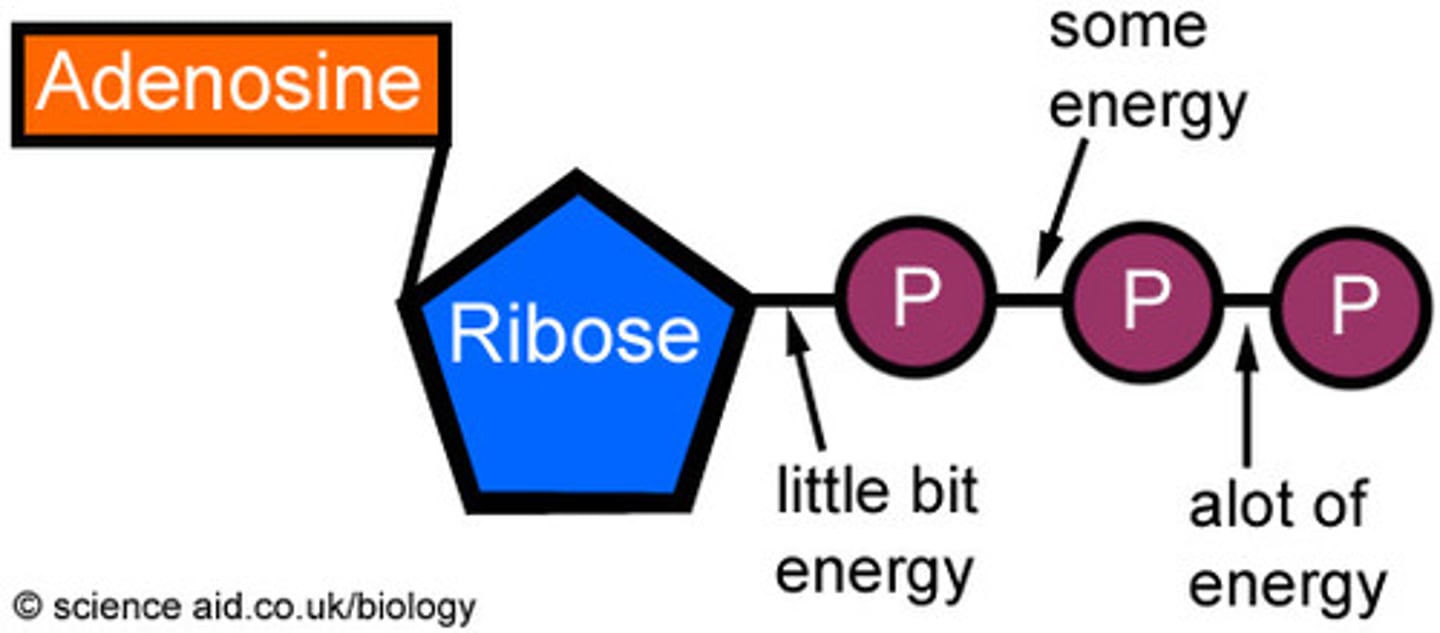
What is ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
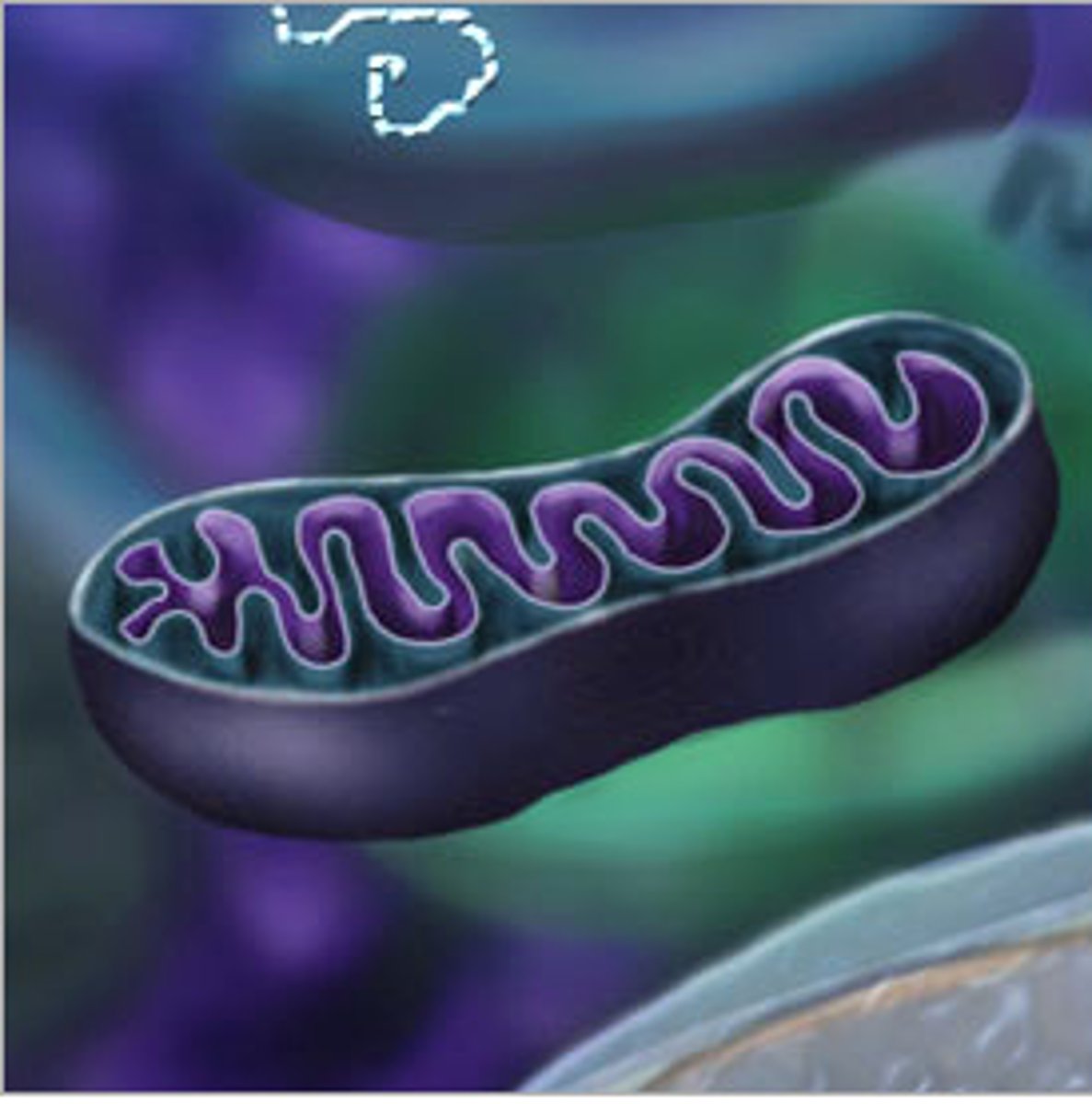
Where is ATP stored
Mitochondria

Two types of Skeletal muscles are .....
Fast and slow twitch fibers
What activities require fast twitch fibers
Explosive sports

What activities require slow twitch fibers
endurance sports

The average human has roughly _______ % fast twitch fibers
60%

The average human has roughly _______ % slow twitch fibers
40%
Muscle force is transmitted to bones via
Tendons

describe the shape of the muscle transition to tendon
tapered
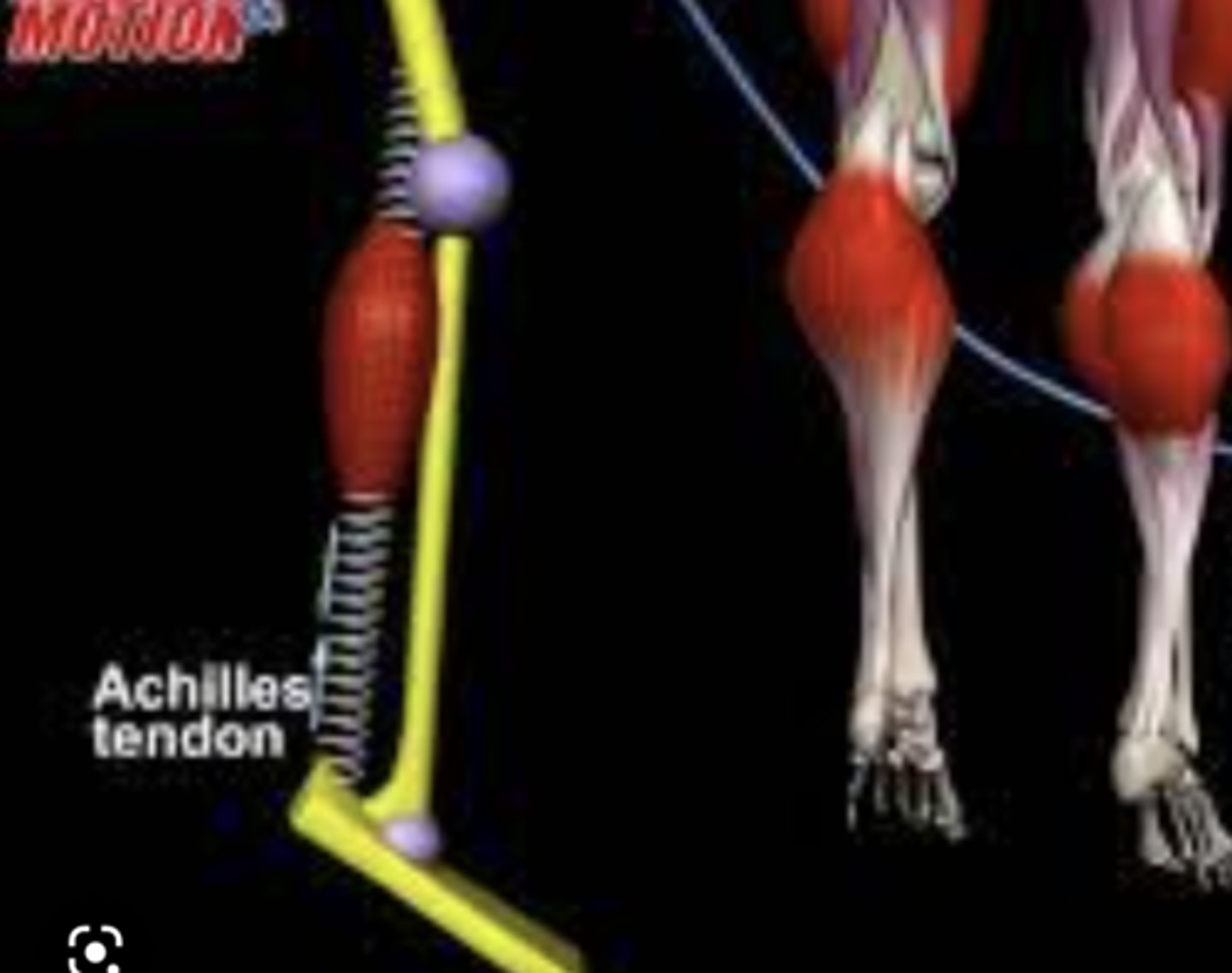
Tendons are strong and slightly elastic, stretching by about ______%
5%

Why is tendon elasticity important.
Shock absorption & tear prevention

Muscles can stretch to about ______ % of their resting length
130%
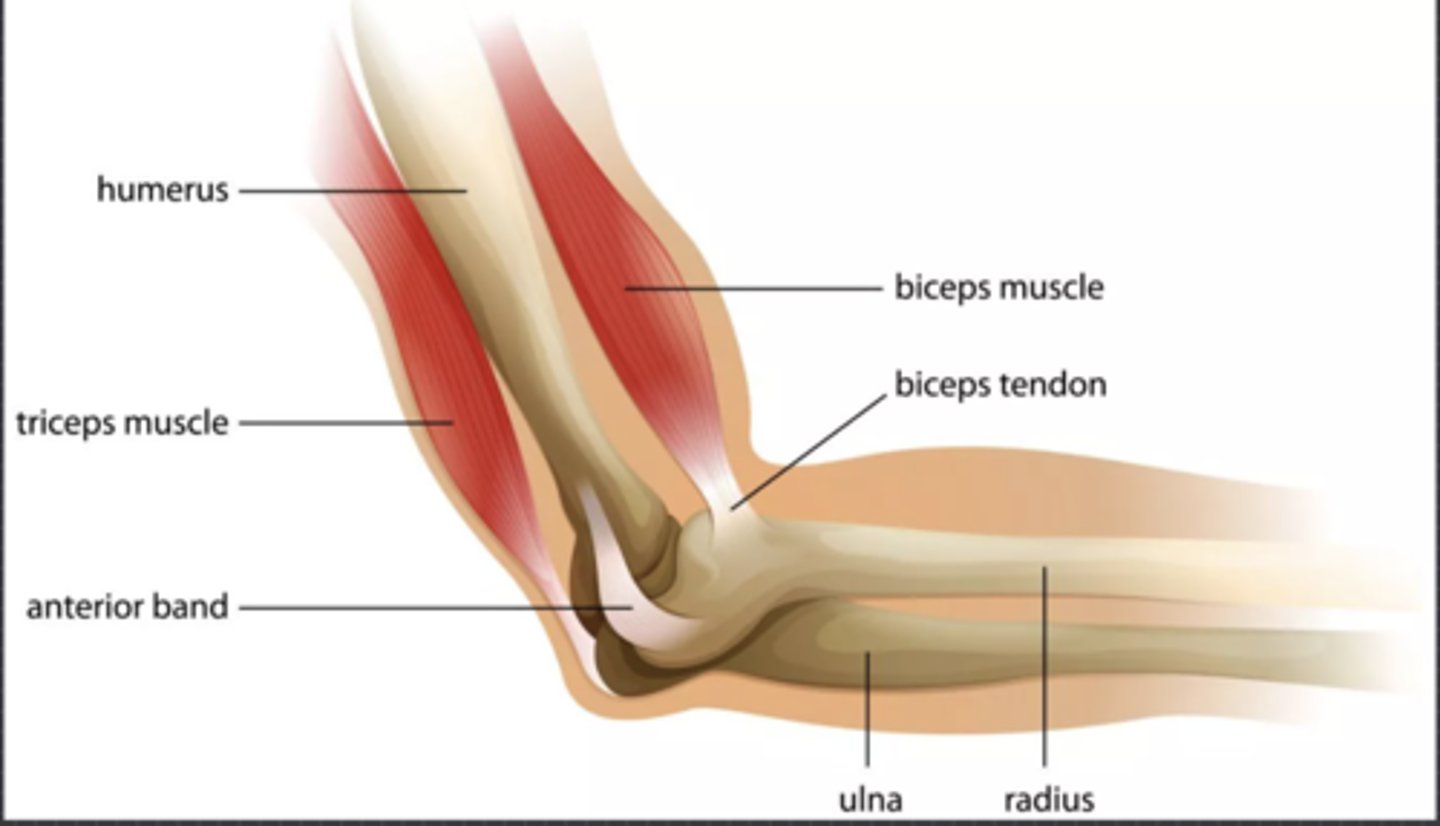
To produce movement, a muscle must
cross a joint and attach to different bones
the two names for where a tendon attaches to a bone
Origin
Insertion

Muscles only ever _______
pull
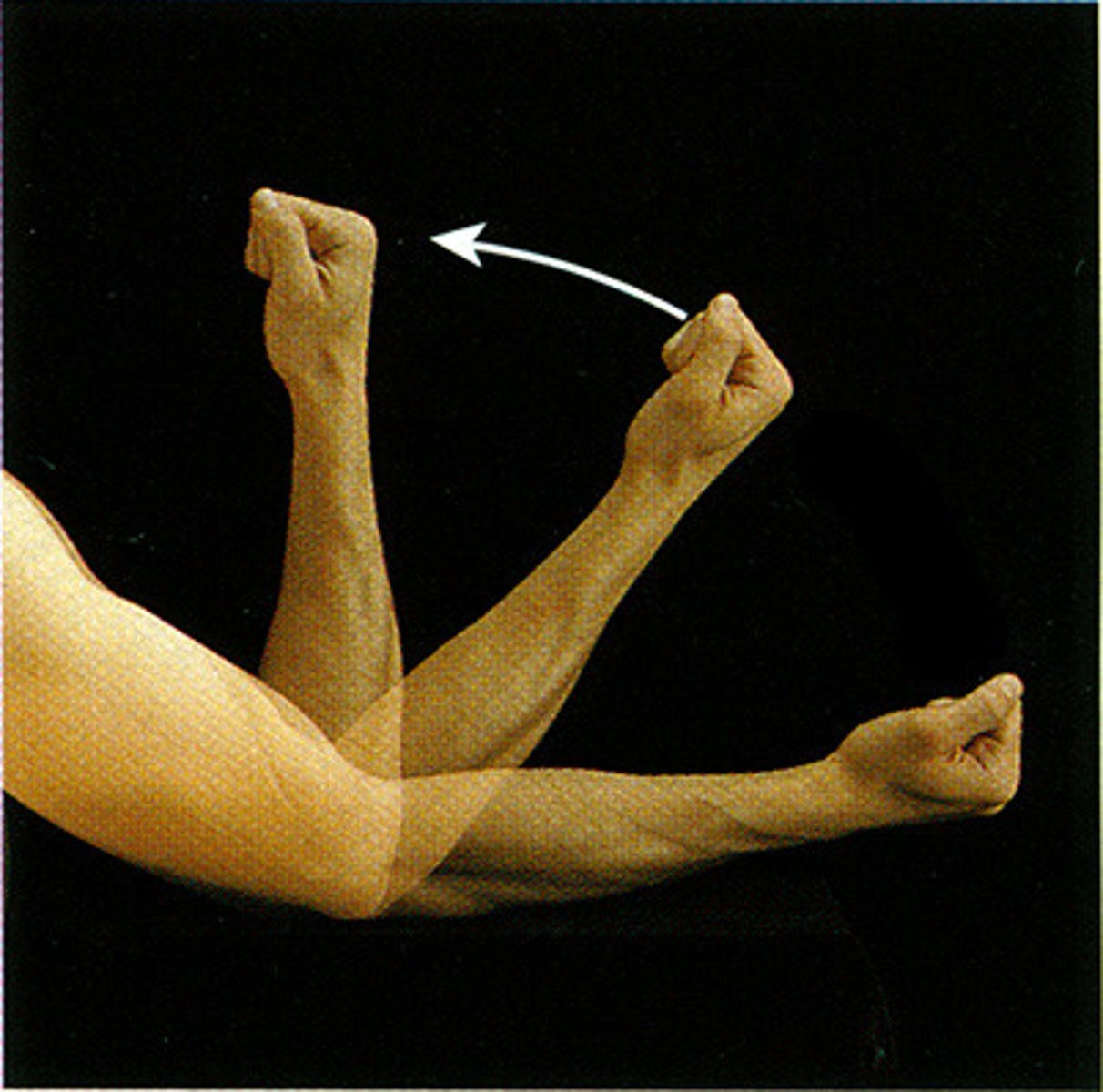
Flexion
joint angle decreases
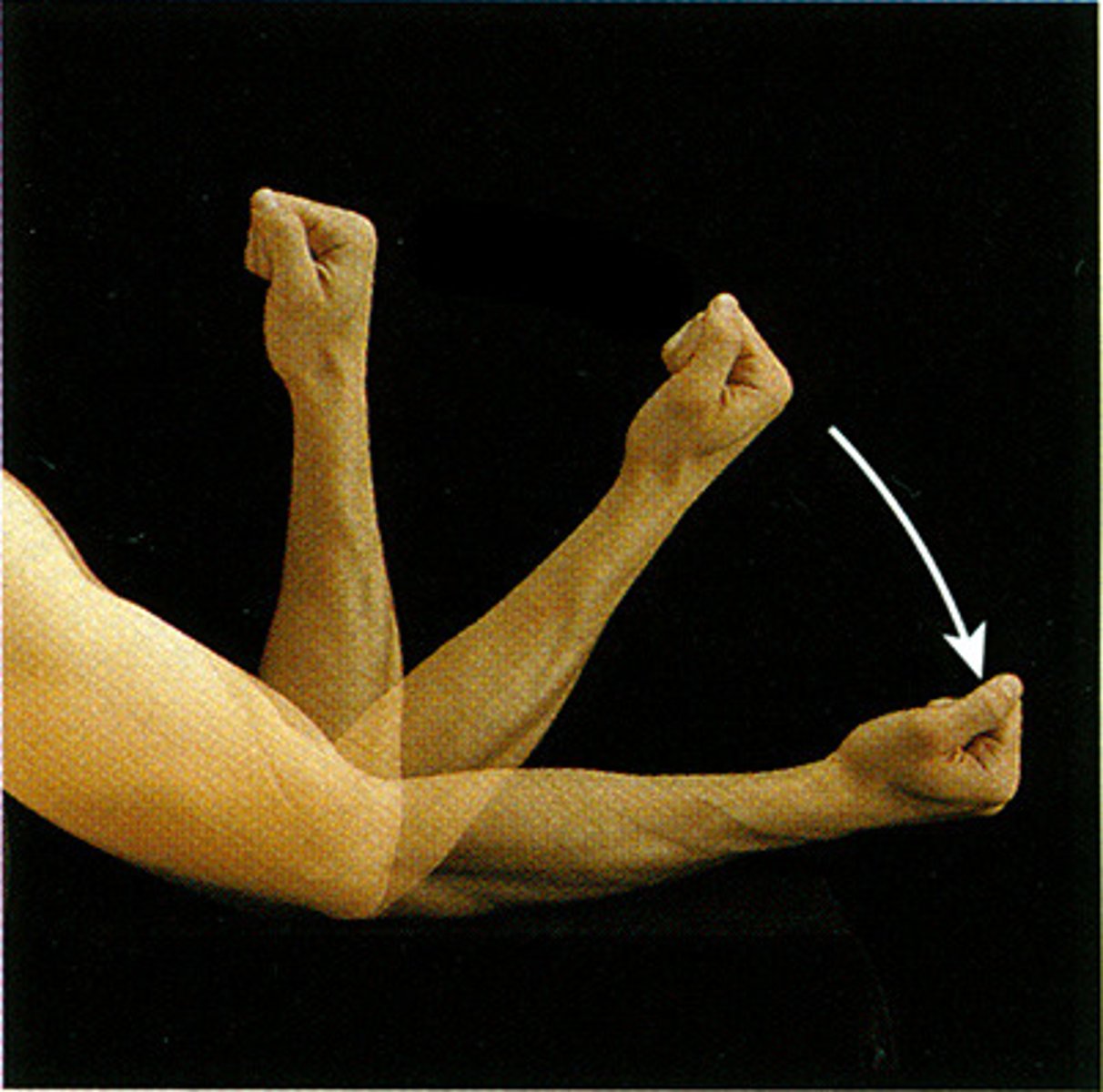
Extension
Joint angle increases

Agonist muscle
the muscle doing the movement
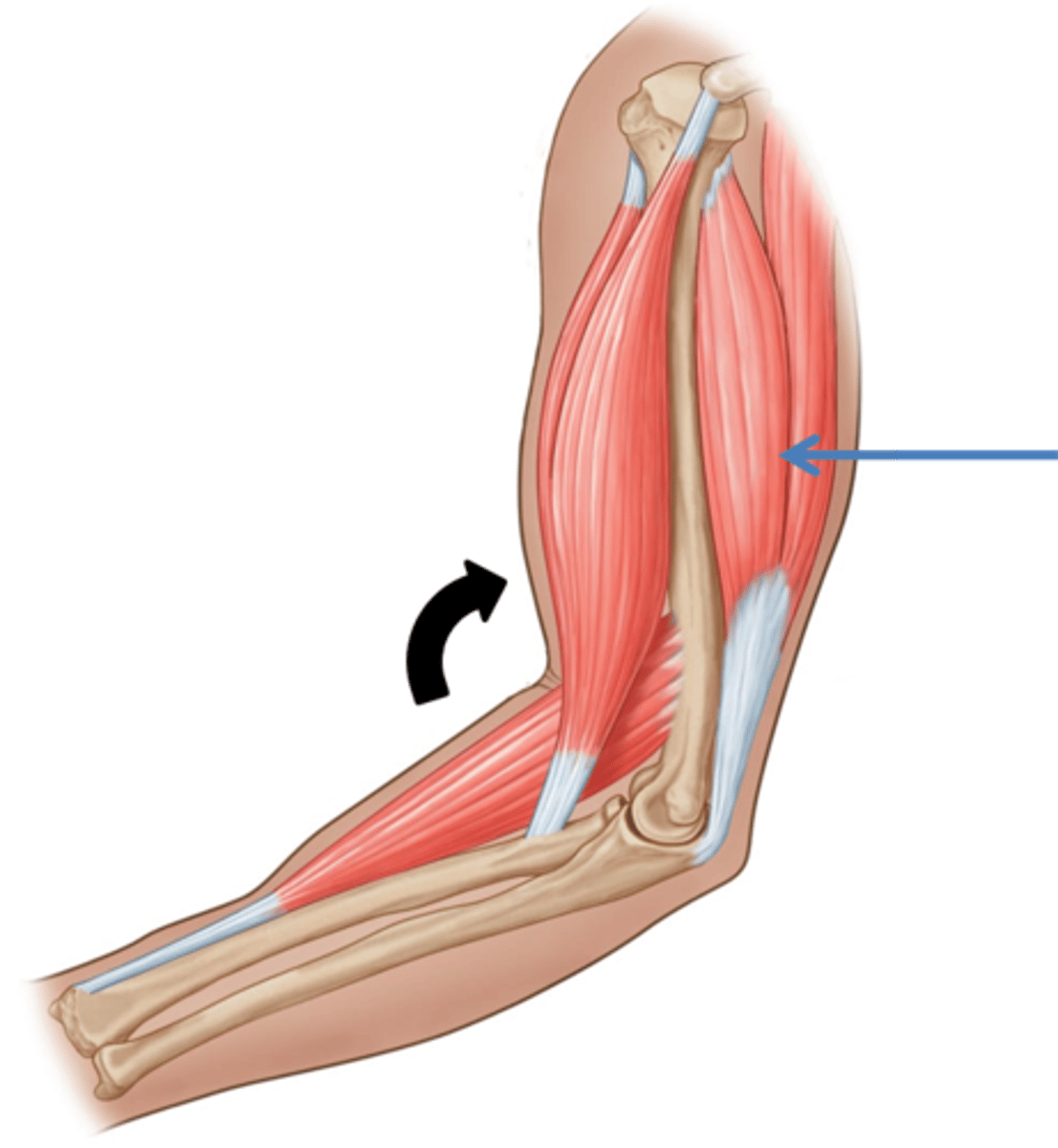
antagonist
The muscle responsible for the opposite movement
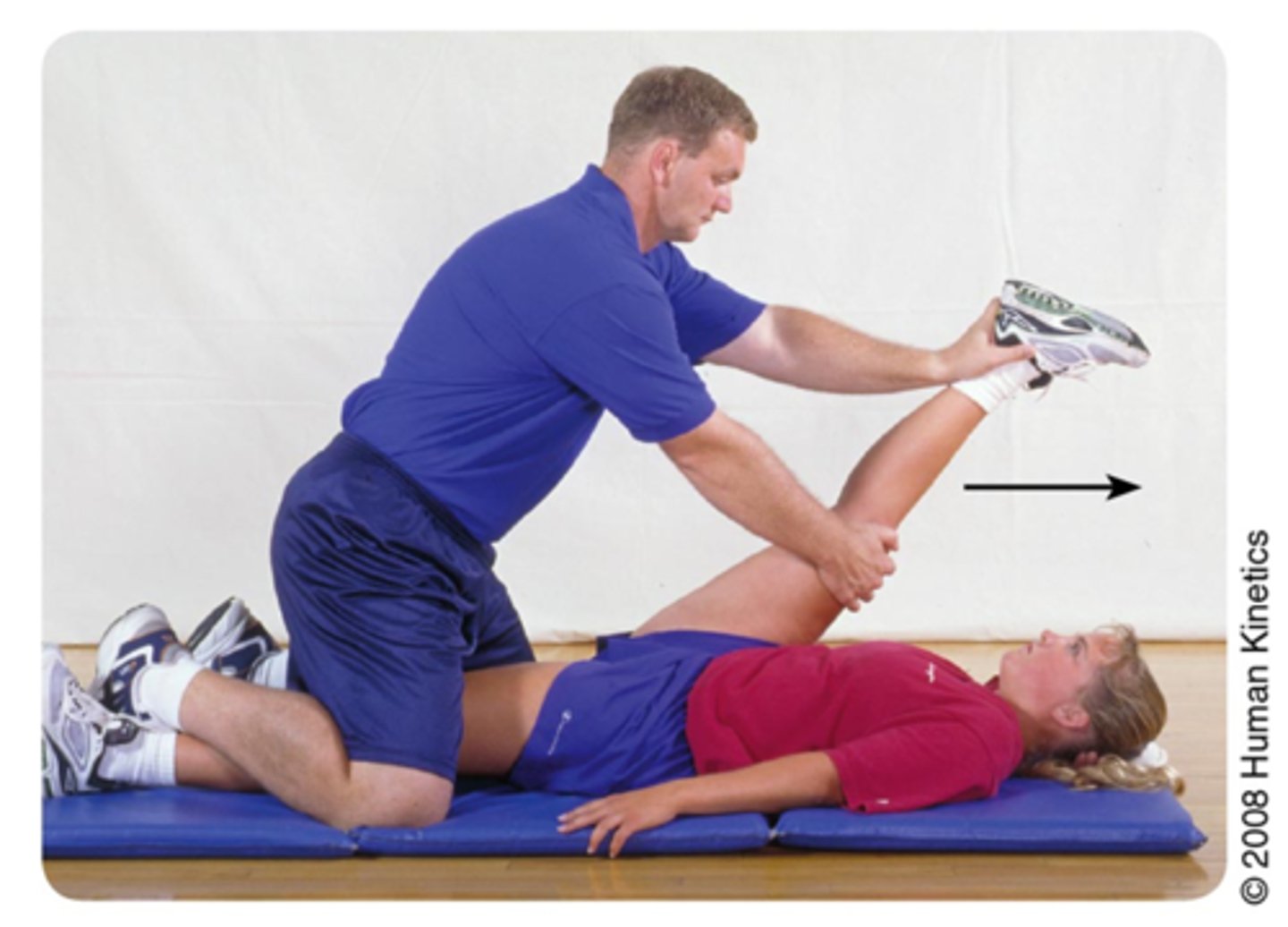
for the movement to occur, the antagonist has to ......
relax and stretch
precision movements are created by ...
A continues adjusted balance from the brain, b/w two apposing forces of the agonist, antagonist.
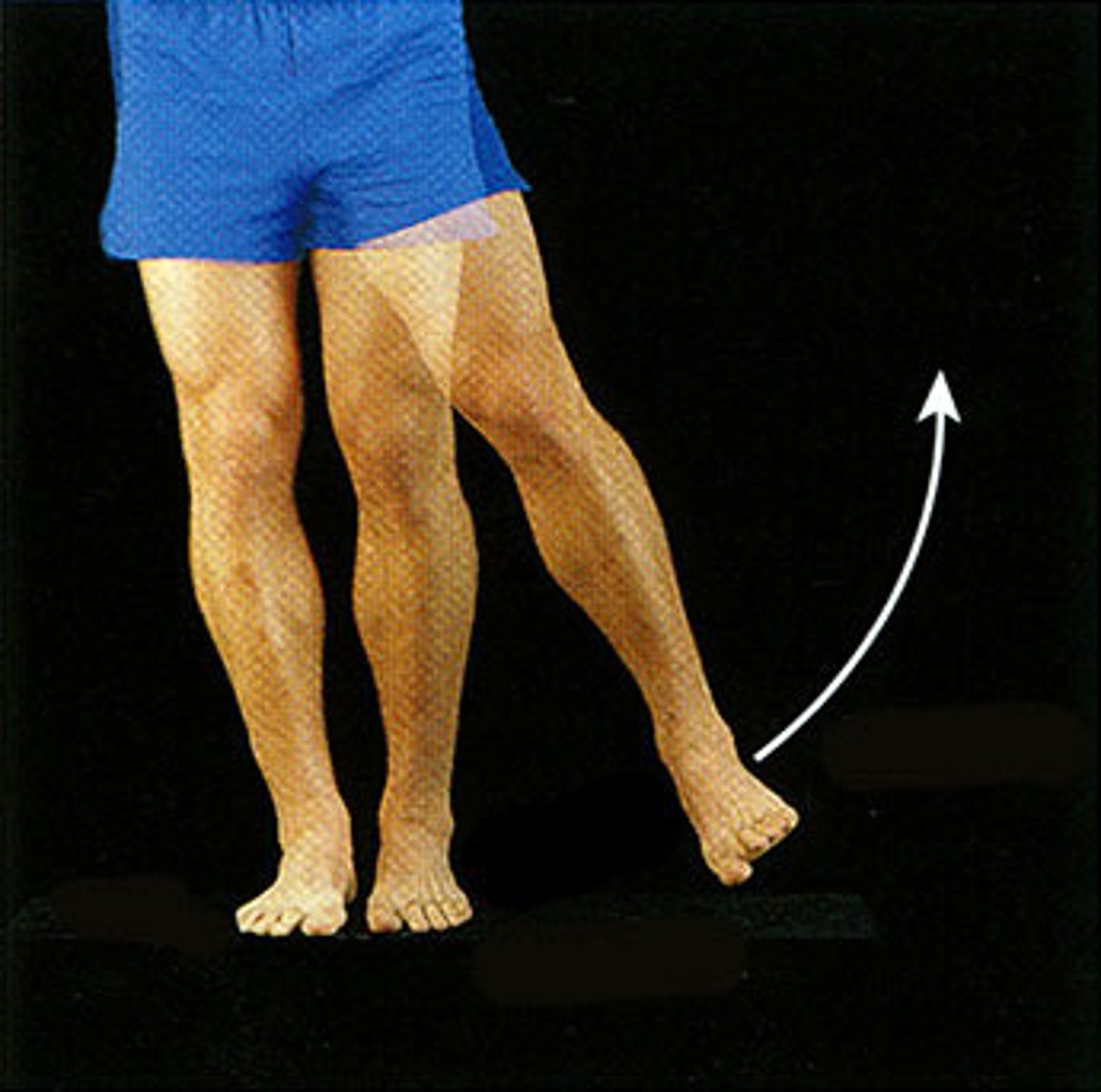
Movement away from the bodies midline
Abduction
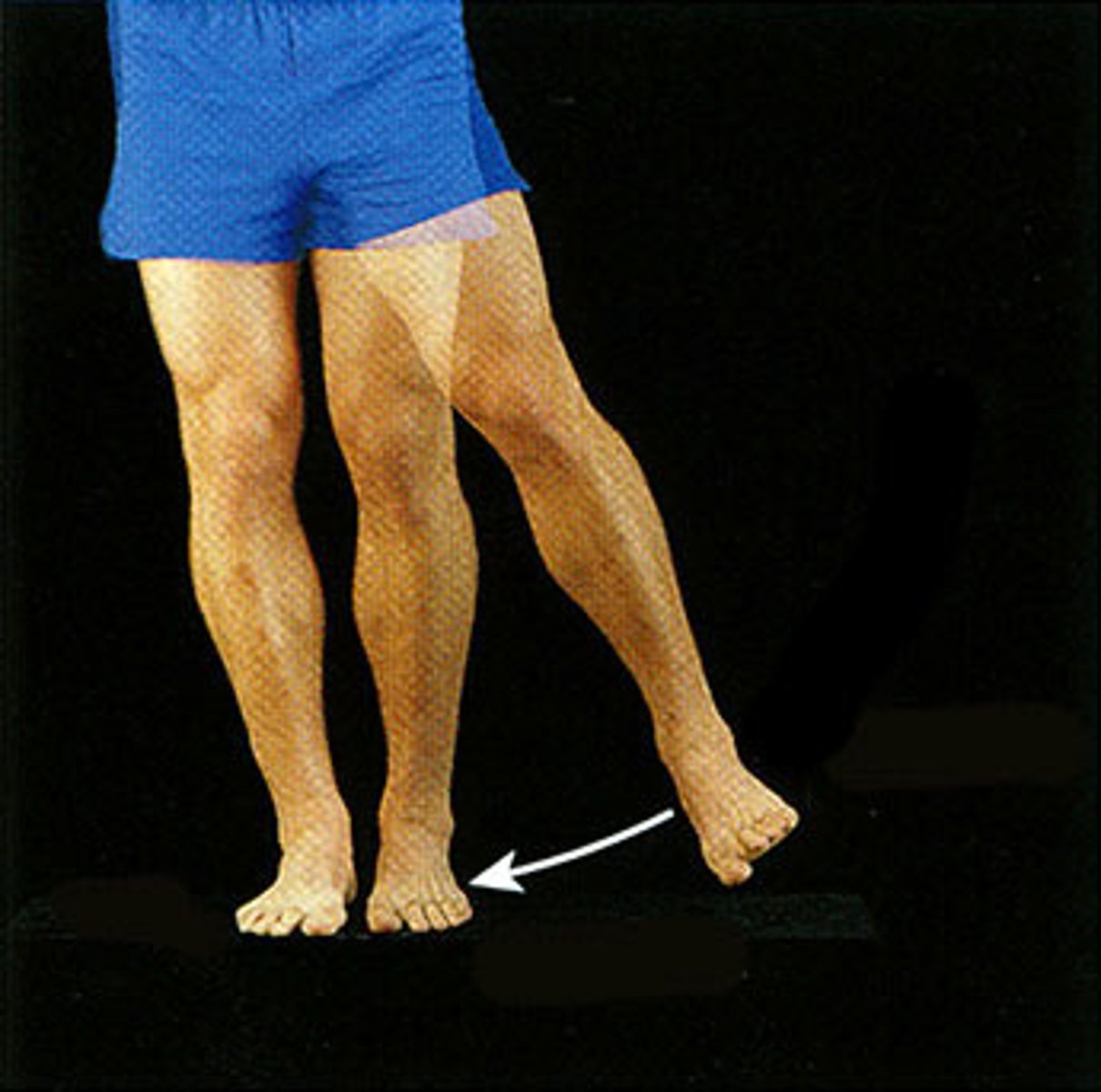
Movement towards the bodies midline
Adduction
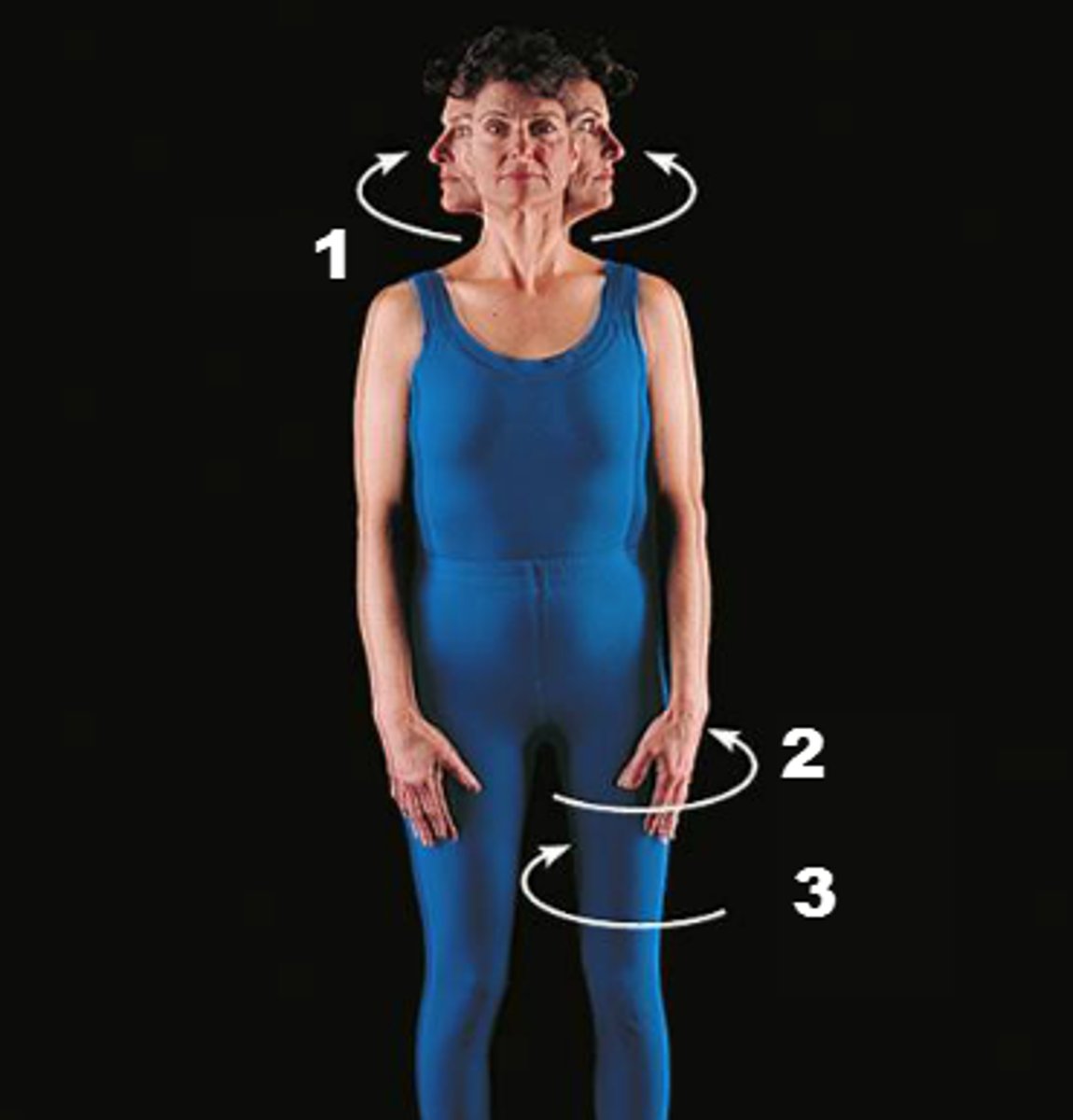
twisting movement of a joint
rotation
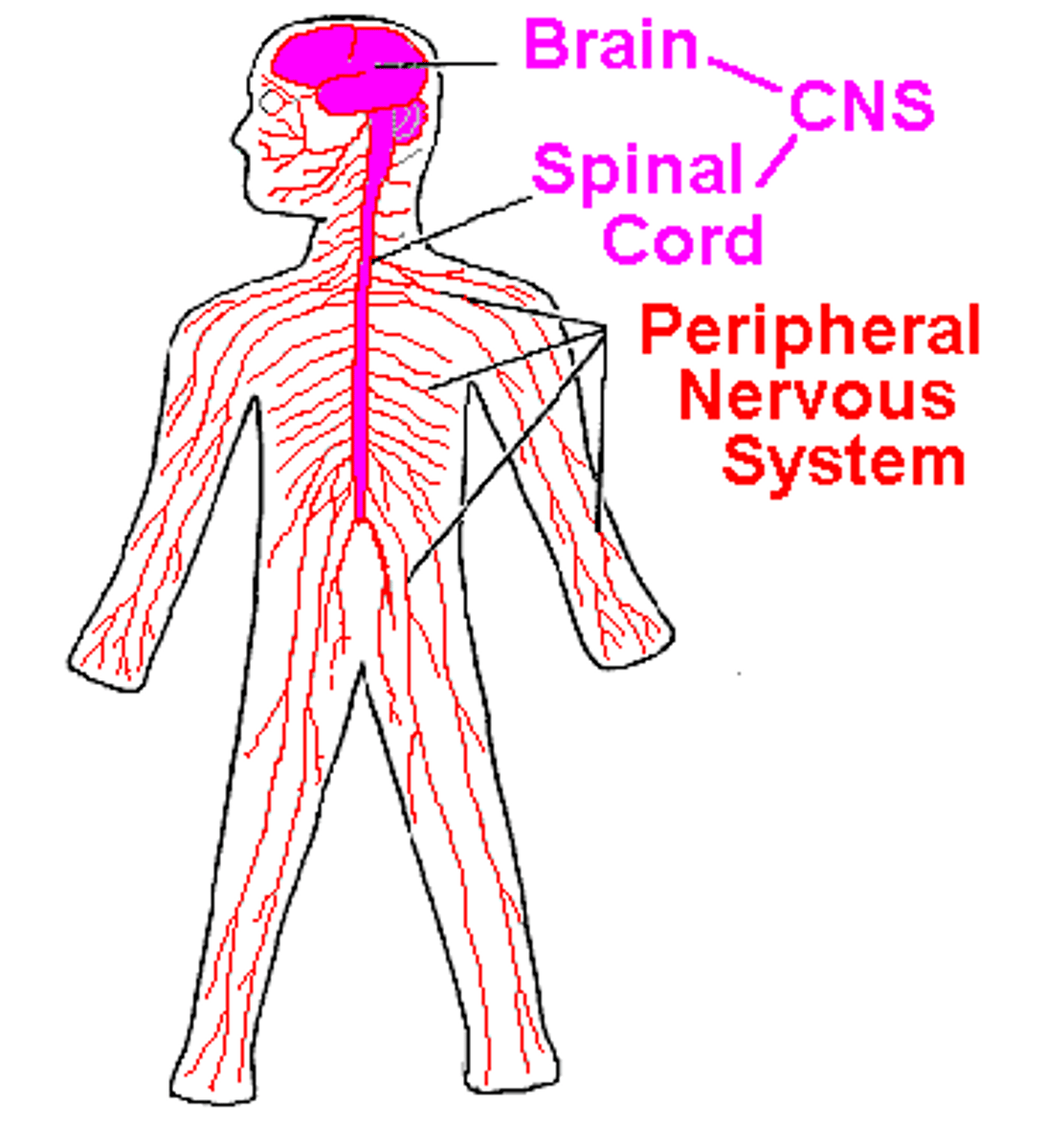
what monitors and controls the functions of the skeletal muscles
nervous system
Lung volume is roughly
9 liters of air
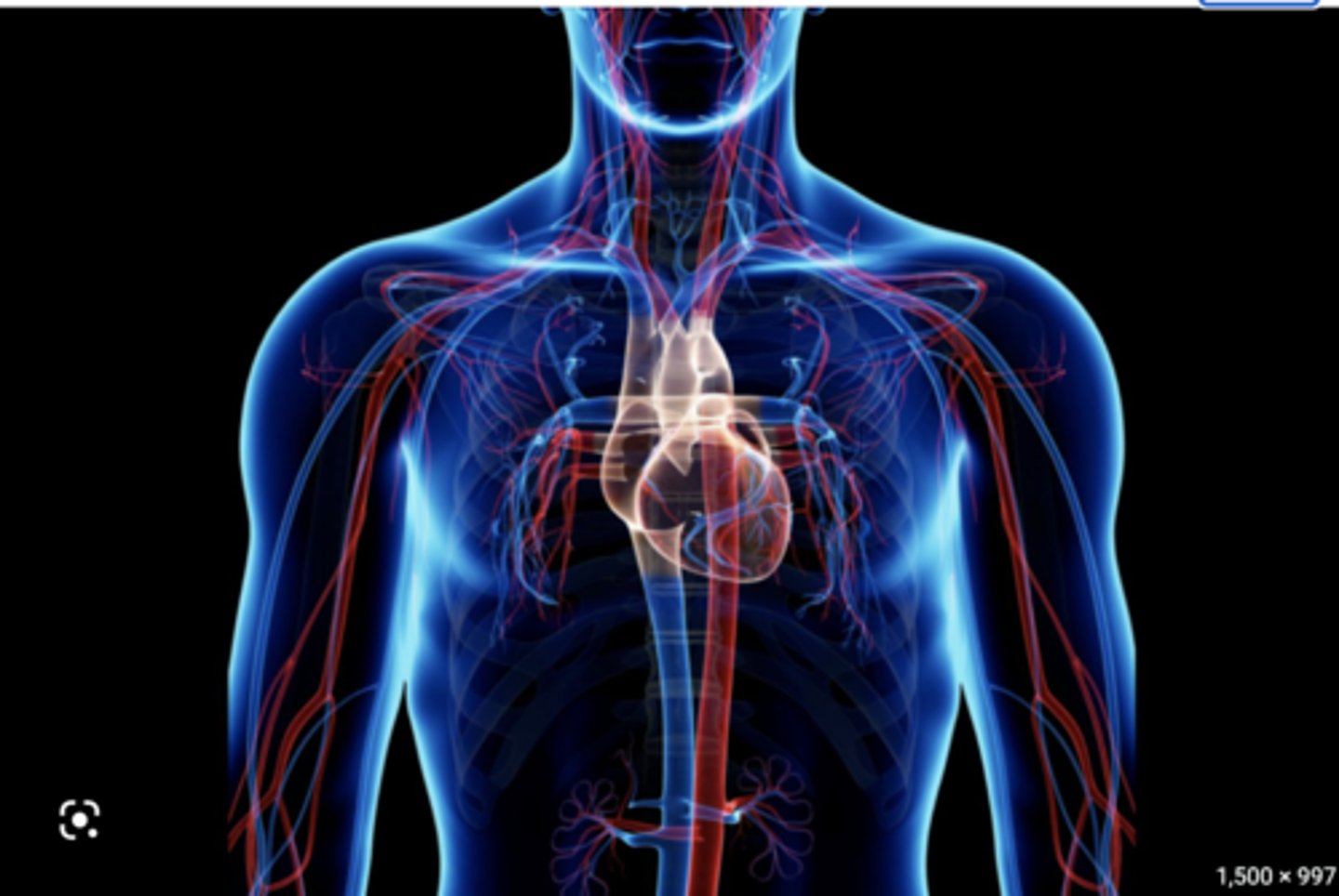
how does 02 get to the working muscles?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GVU_zANtroE&t=132s
Absorbed into the blood stream in the lungs and transported