Chapter 8
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 8 lecture notes for CHM - 151 (General Chemistry)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Chemical Bonds
Metallic
Ionic
Covalent.
Metallic Bonding
Free electrons hold metals atoms together.
Ionic Bonding
Electrostatic attraction between ions. Sometimes describe as the “transfer of electrons".
Describes: Na(s) + ½ Cl2 → NaCl(s); Ag + Cl^- → AgCl(s)
Covalent Bonding
Sharing of electrons. Attractions of electrons and nuclei (p+). Repulsions between electrons and repulsions between nuclei (p+).
Properties of Ionic Substance
Brittle
High melting points
Crystalline
Cleave along smooth line.
Lewis Structures (Meaning)
Lewis symbols contain a number of dots to represent the number of valence electrons.
Can be drawn to represent covalent bonding (none for ionic bonding).
All valence electrons are shown; a line is a single bond and represents the sharing of two electrons (also called a “bonding pair”)
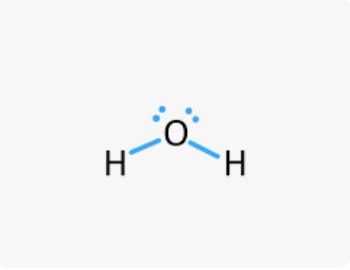
Octet Rule
Atoms share, lose, or gain electrons in order to have 8 valence electrons to become like noble gases.
Lattice Energy
Energy releases to make ionic compounds. Related to the strength of an ionic bond.
Larger ion size equals greater separation which equals…
smaller lattice energy, smaller attractive force.
Bigger charge equals greater attraction which equals…
greater attractive force and lattice energy.
Electronegativity
The ability of an atom to pull an electron towards itself.
Electronegativity ________ as you go left to right of a periodic table. Electronegativity ________ as you go down a periodic table.
increase; decrease.
Polarity of Bonds
Nonpolar covalent: 0 - 0.4
Polar Covalent: 0.5 - 1.9
Ionic: 2.0+
Polar
Electrons are unequally shared.
Nonpolar
Electrons are equally shared.
Dipole Moment
Shows which element pulls under (more electronegative).
Duet Rule
Lewis Structure (Steps)
Step 1: Draw skeleton structure “how are the atoms connected”. Usually the least electronegative atom are the center atom (not H).
Step 2: Count valence electrons.
Step 3: Add electrons so the total number equals step 2. Add electrons to the outside atoms first.
Step 4: Check total number of electrons and check octet/duet rule.
Double Bonds (=)
4 electrons shared, 2 pairs.
Triple Bonds (≡)
6 electrons shared, 3 pairs.
Have the highest bond enthalpy, hardest to break, strongest bonds, and shortest bonds.
Formal Charges (Meaning)
Pretends all electrons are equally shared.
All follow the octet rule and have the right amount of electrons. Formal charges will help pick which is best.
Note: Formal charges are in circles.
Formal Charges (Formula)
Formal Charge = (valence e-) - ½(bonding e-) - (all nonbonding e-)
Best Structure have the ______ formal charge. The ____ electronegative atom should have a _______ formal charge.
fewest; most; negative.
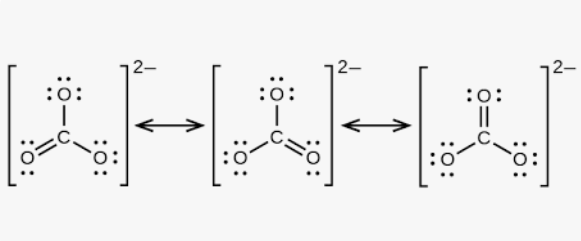
Resonance Structures
Needed when one Lewis Structures doesn’t accurately represent a molecule. Instead, the average of the structures best describes the molecule.
Resonance
Electrons are moved, same number of electrons, same atom arrangements.
Exceptions of Octet Rule
Odd number of electrons.
Fewer than eight electrons.
More than eight electrons.
Odd Number of Electrons
Second is better because the oxygen is more electronegative.
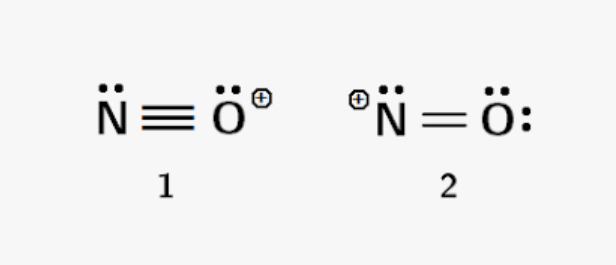
Fewer Than Eight Electrons
H and Be can have 2 valence electrons. B can have 6 valence electrons (use formal charges). F will not form more than one bond (no positive formal charges for F).
More Than Eight Electrons
Elements on row 3 and below can have more than eight electrons because they have access to d orbitals (use formal charges).
Bond Enthalpy
Energy needed to break a bond. Takes energy to break bond.