unit 4 chem
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/114
Last updated 3:19 PM on 2/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
1
New cards
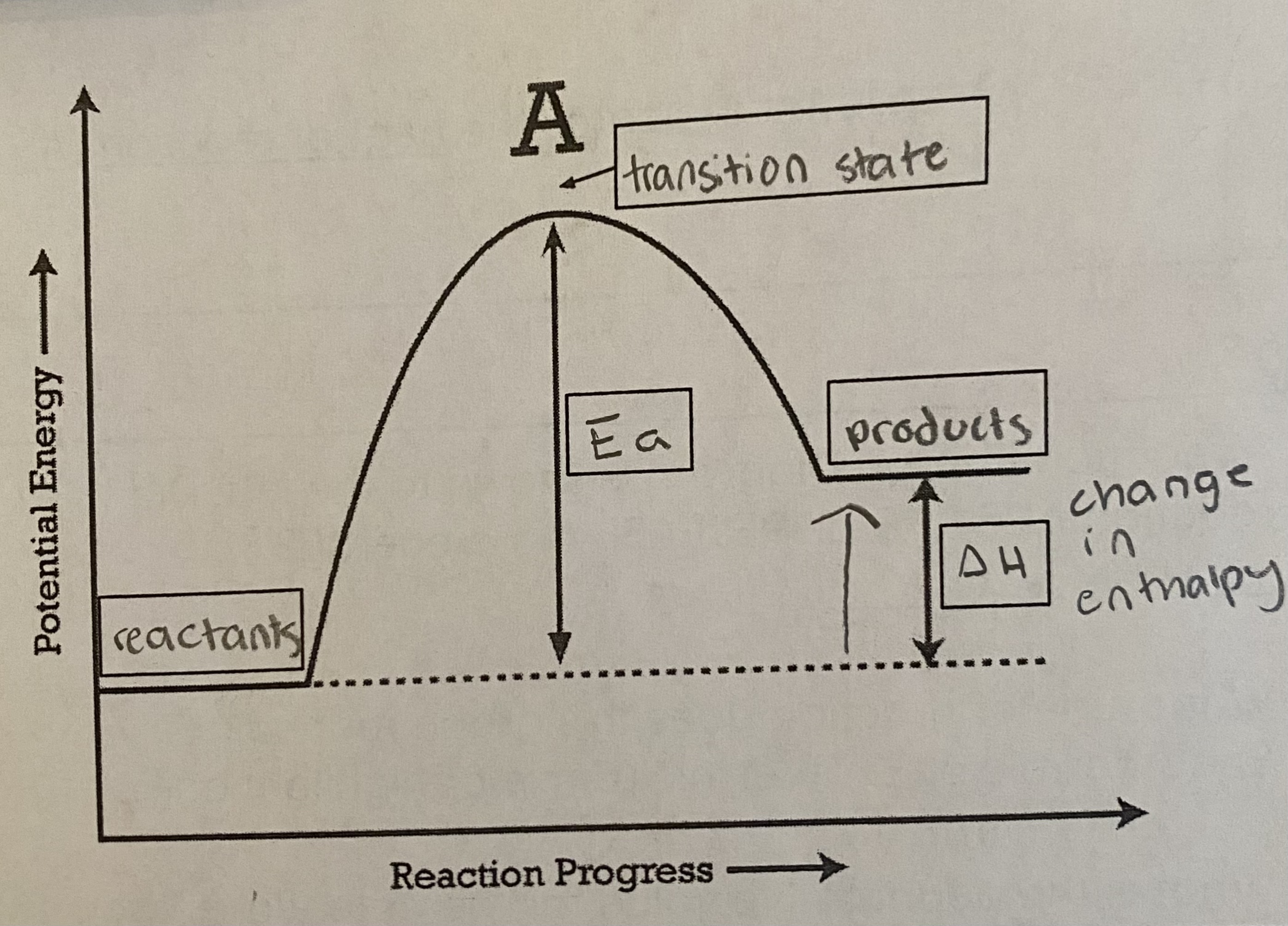
energy diagram
a graph showing the changes in potential energy during a reaction. It starts with the reactants on the left and proceeds to the products on the right
2
New cards
Ea
activation energy; the amount of energy that is required to start the reaction. the difference in potential energy between the reactants and the top of the ‘curve’.
3
New cards
ΔH
enthalpy; the difference in potential energy between the products and reactants
4
New cards
transition state
the high energy stage between the reactants and the products. rearranging of atoms has started, but not completed yet. also referred to as the activated complex.
5
New cards
endothermic
* gets __colder__
* __reactants__ have __less potential energy__ compared to products
* energy was __absorbed__ during this reaction (this is why the products have more energy)
* ΔH will be __positive__
* thermal → potential energy
* __reactants__ have __less potential energy__ compared to products
* energy was __absorbed__ during this reaction (this is why the products have more energy)
* ΔH will be __positive__
* thermal → potential energy
6
New cards
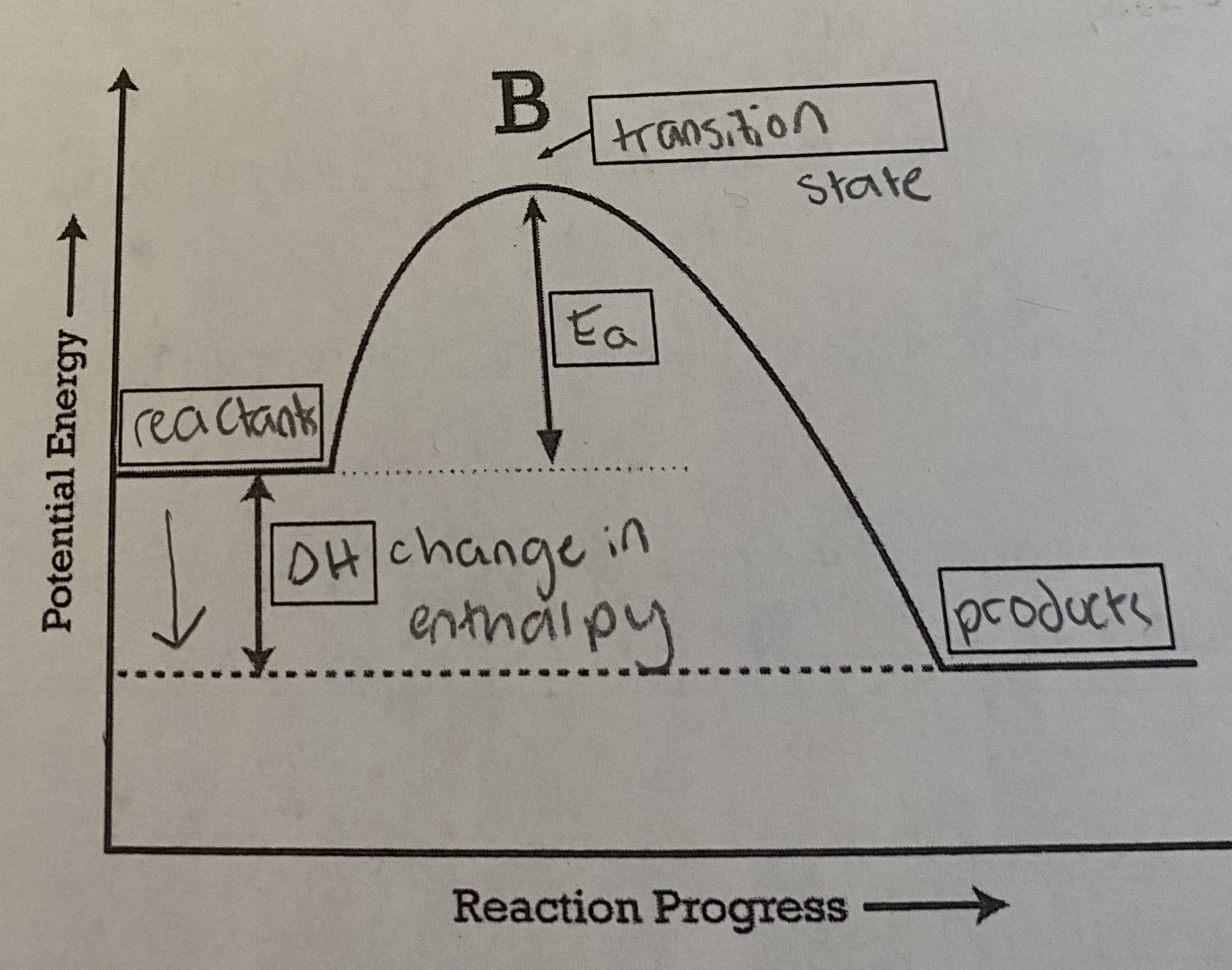
exothermic
* gets __warmer__
* __reactants__ have __more potential energy__ compared to products
* energy was __released__ during this reaction (this is why the products have more energy)
* ΔH will be __negative__
* potential → thermal energy
* __reactants__ have __more potential energy__ compared to products
* energy was __released__ during this reaction (this is why the products have more energy)
* ΔH will be __negative__
* potential → thermal energy
7
New cards
did this reaction absorb or release more energy?
absorb
8
New cards
what type of reaction does this graph represent?
endothermic
9
New cards
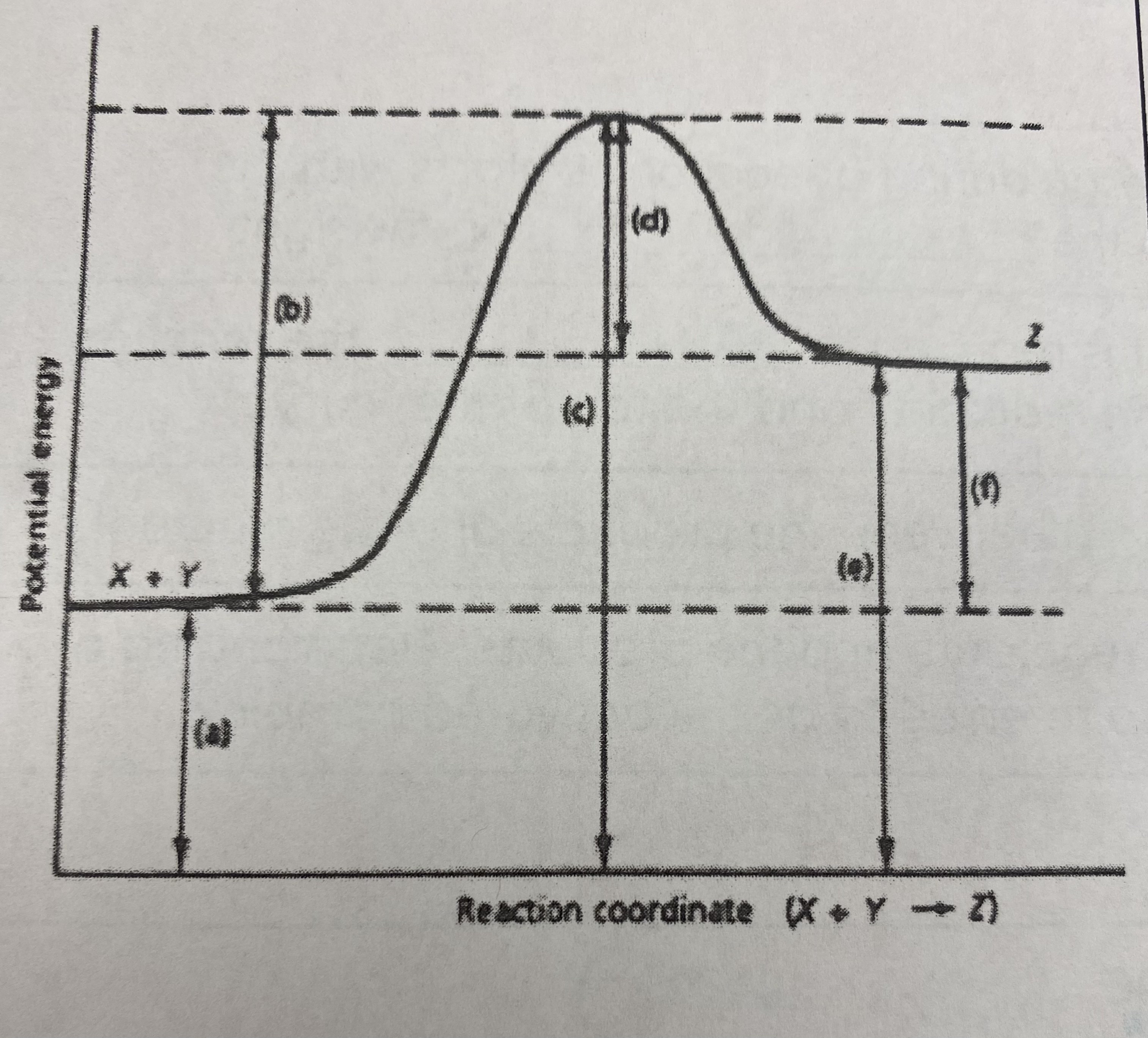
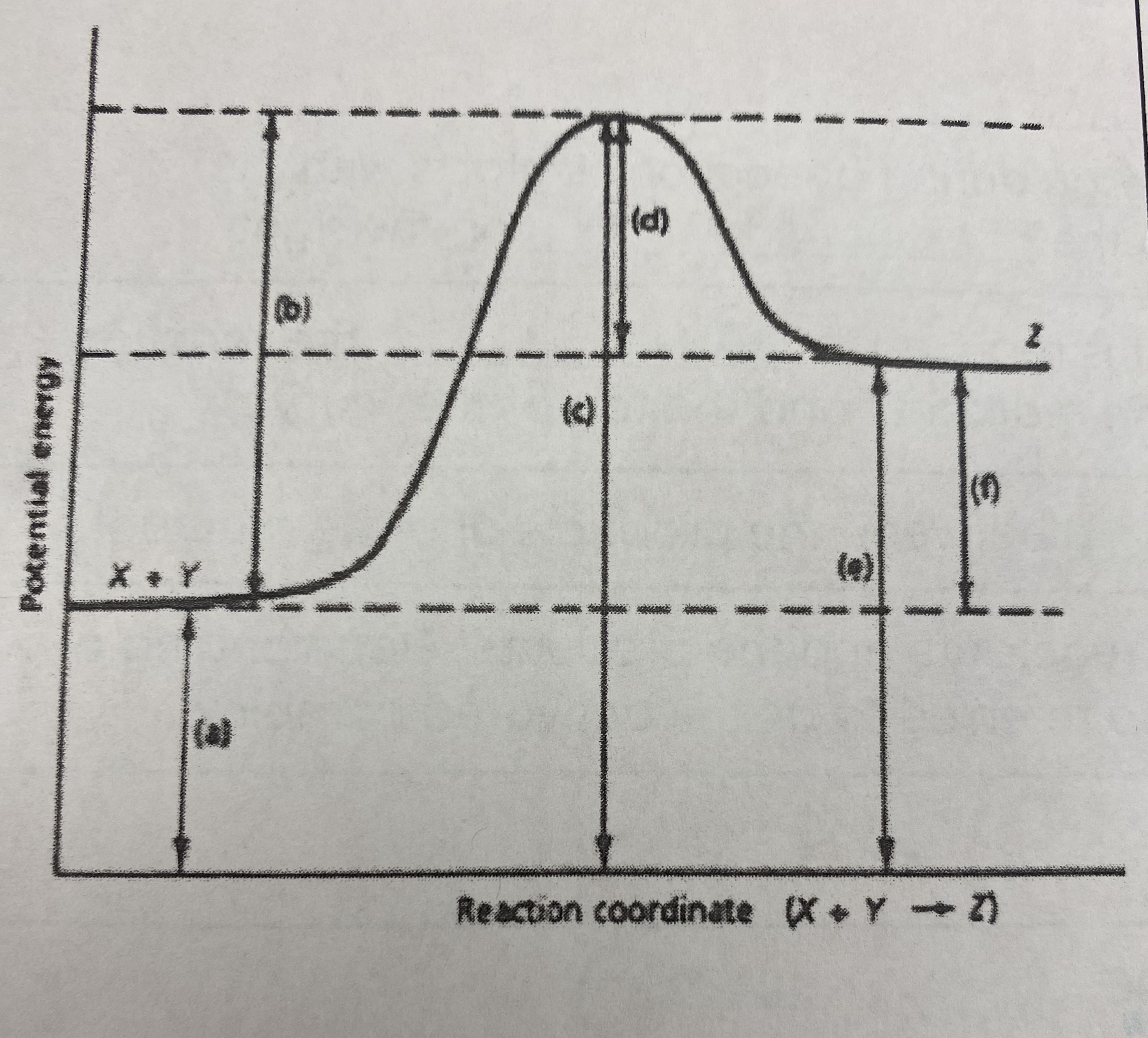
which of the letters a-f in the diagram represent the potential energy of the __products__?
E
10
New cards
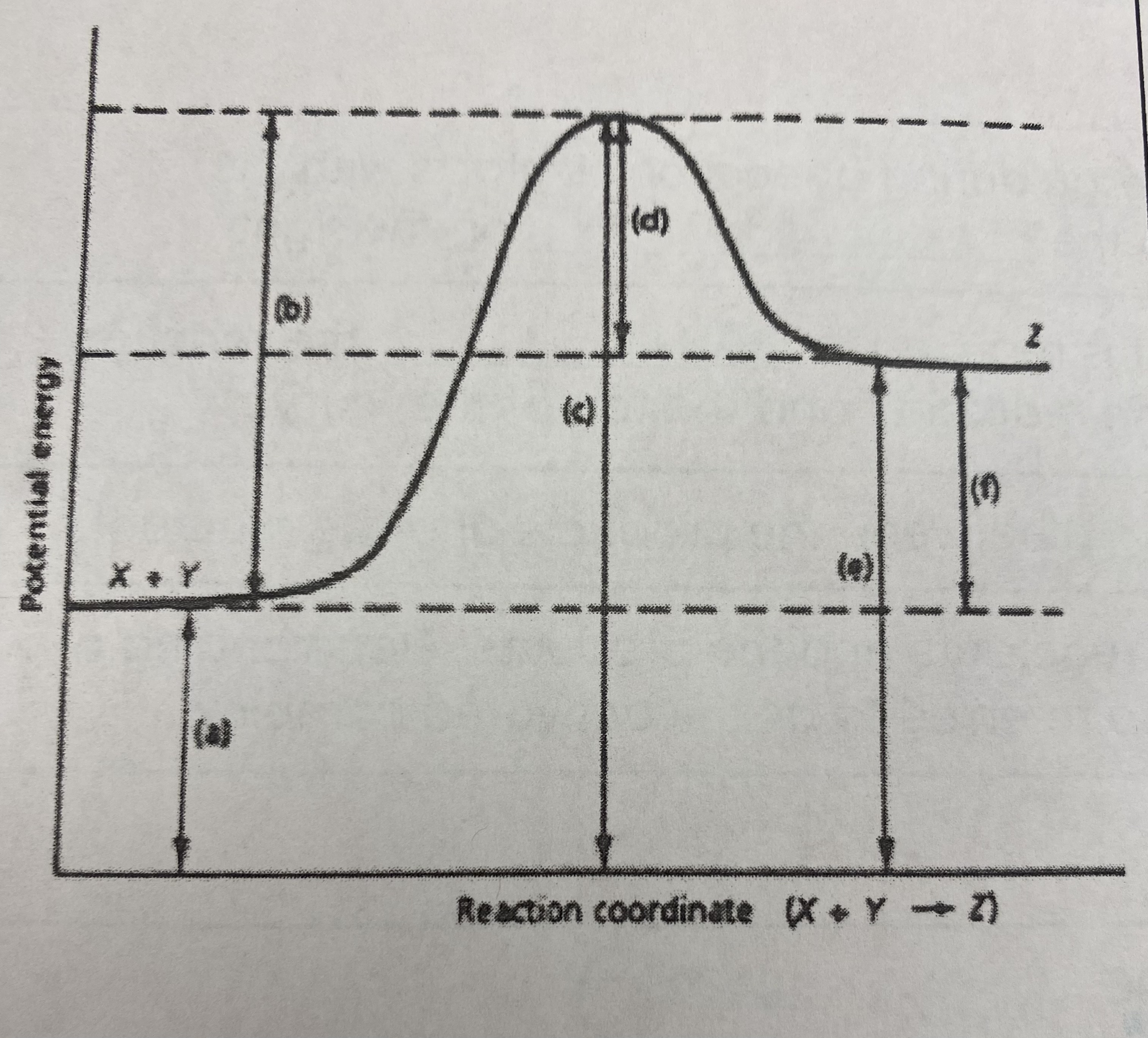
which of the letters indicate the potential energy of the __transitional state__?
C
11
New cards
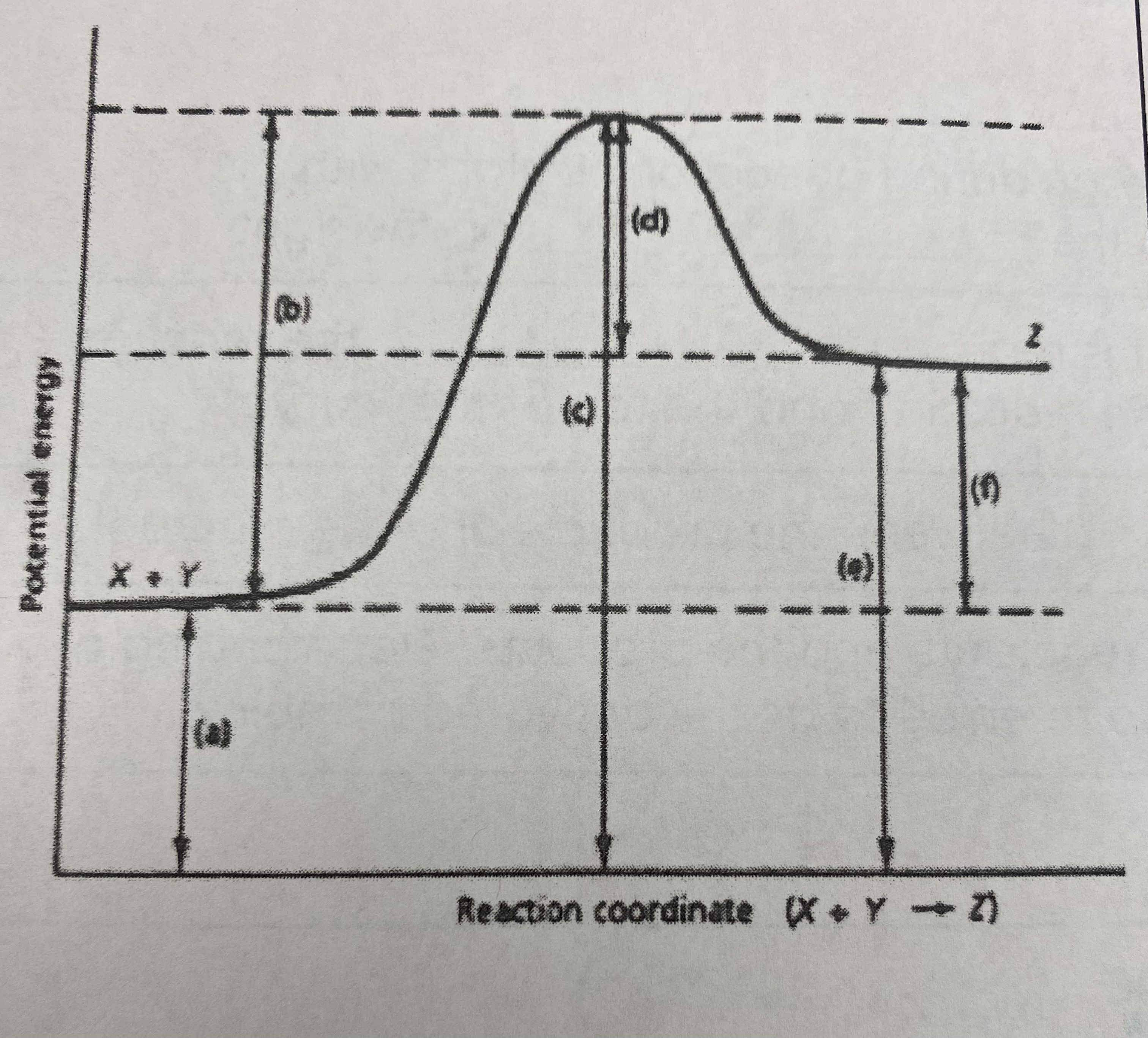
which letter indicates the potential energy of the __reactants__?
A
12
New cards
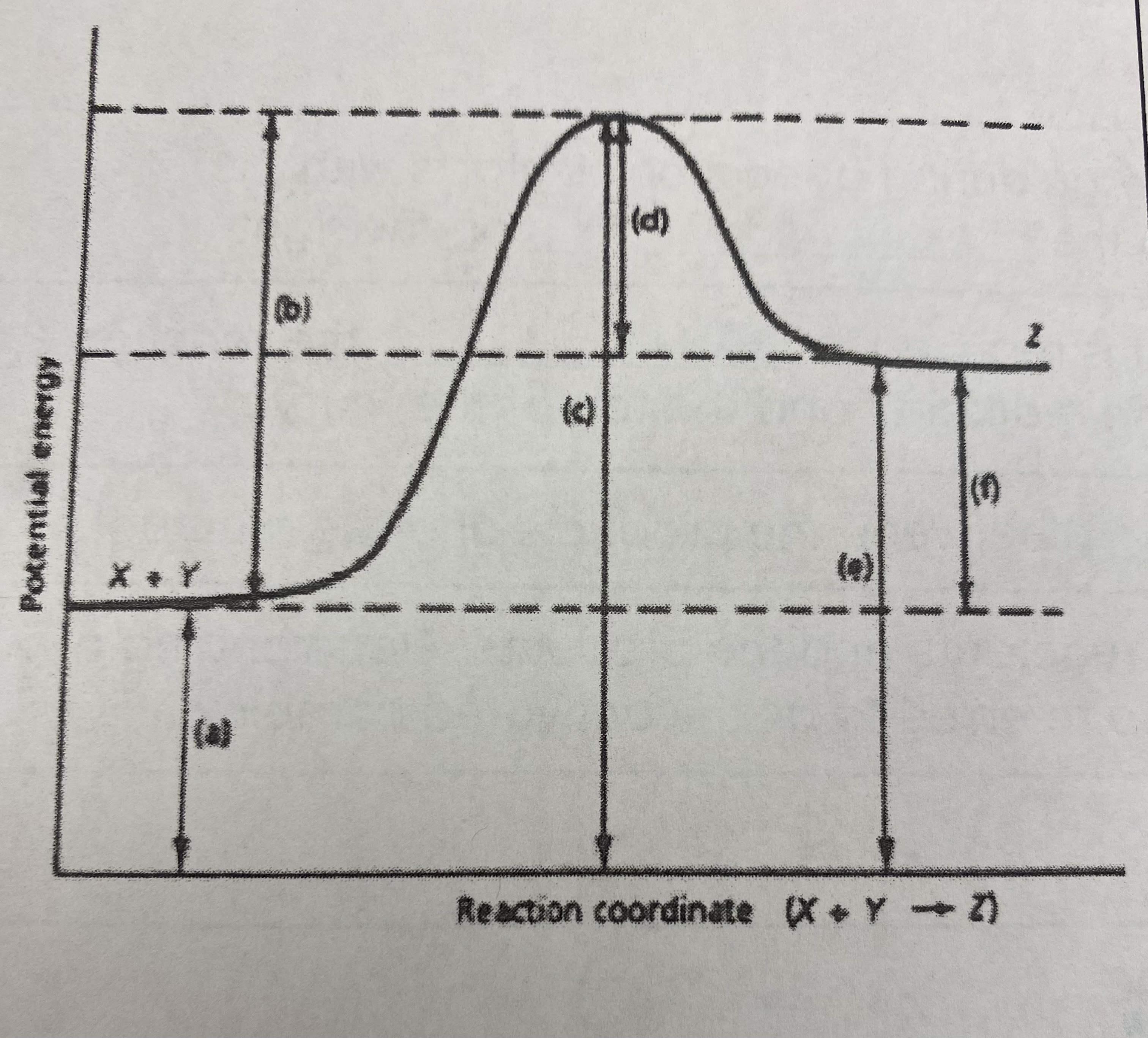
which letter indicates the __activation energy (Ea)__?
B
13
New cards
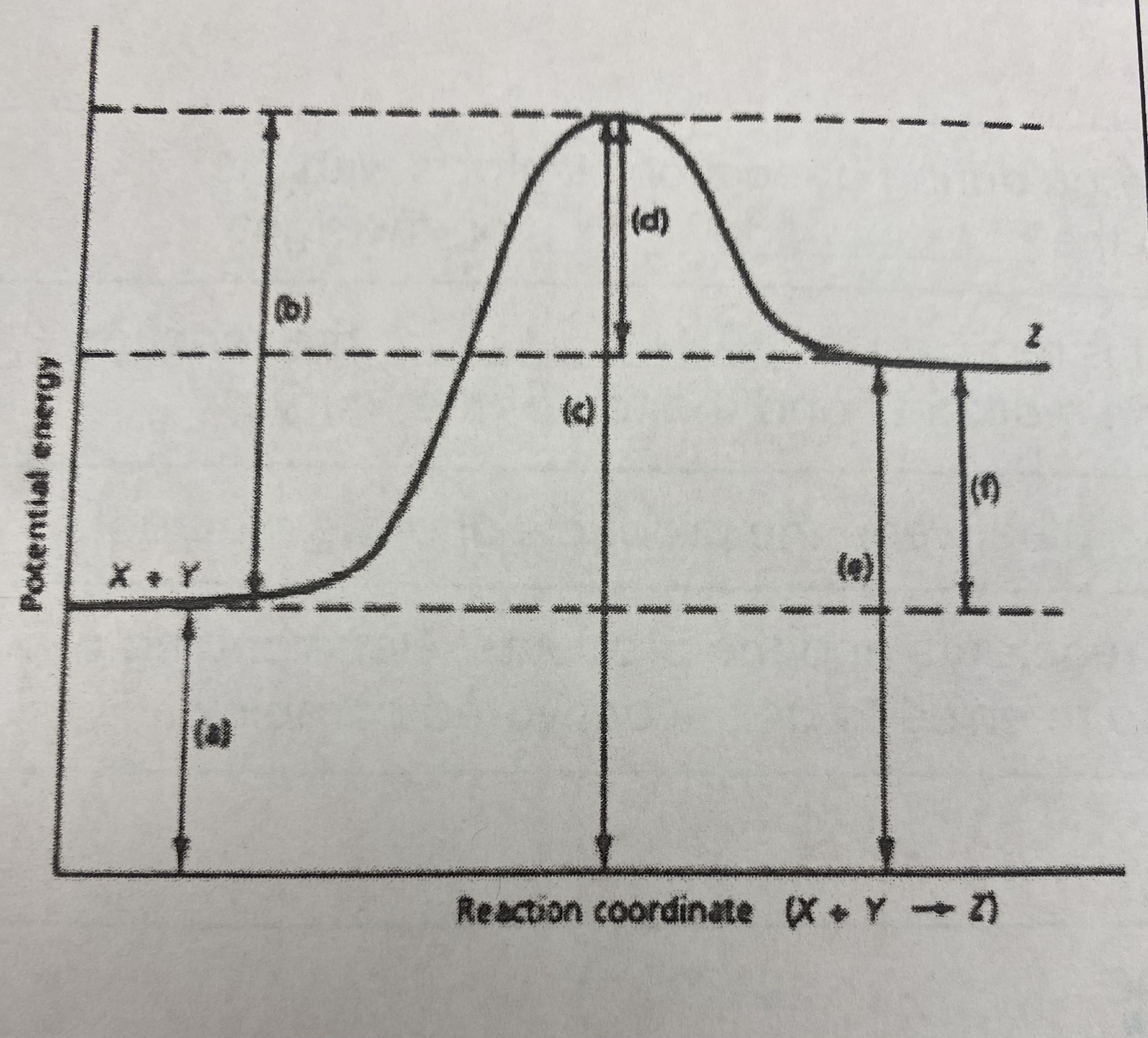
which letter indicates the __heat of reaction (Δ H)__?
F
14
New cards
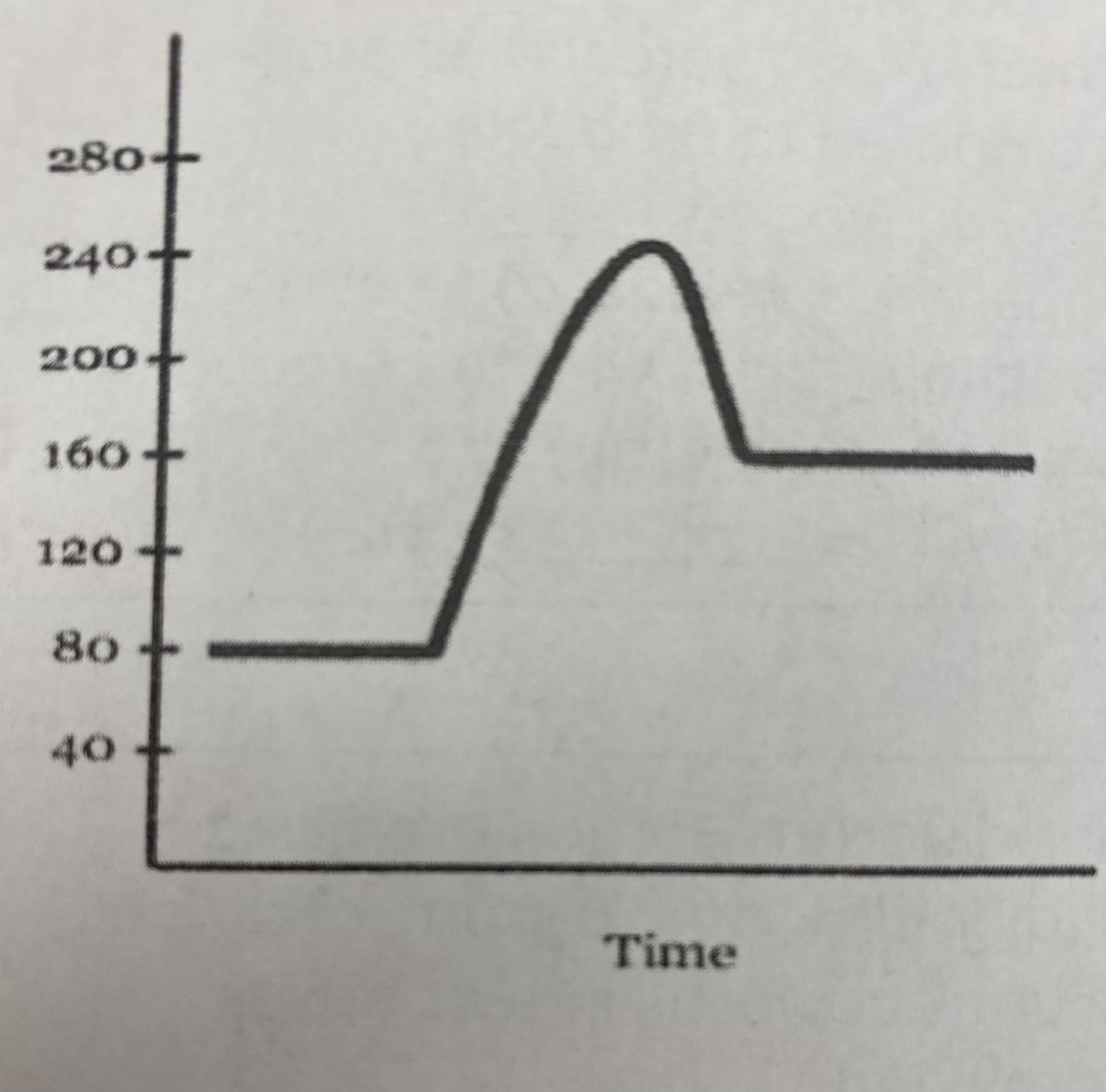
did this reaction absorb or release more energy?
absorb
15
New cards
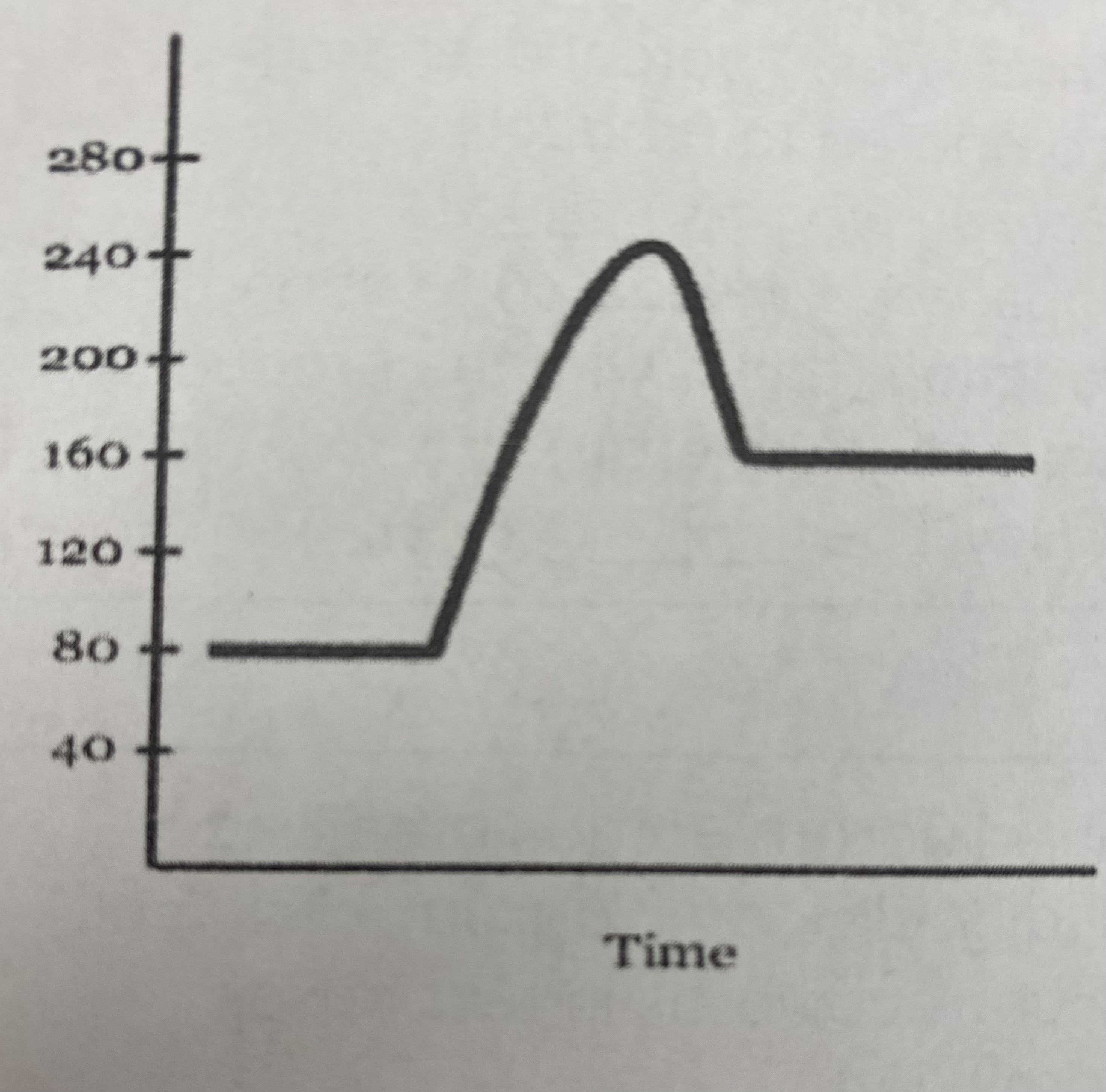
what type of reaction does this graph represent?
endothermic
16
New cards
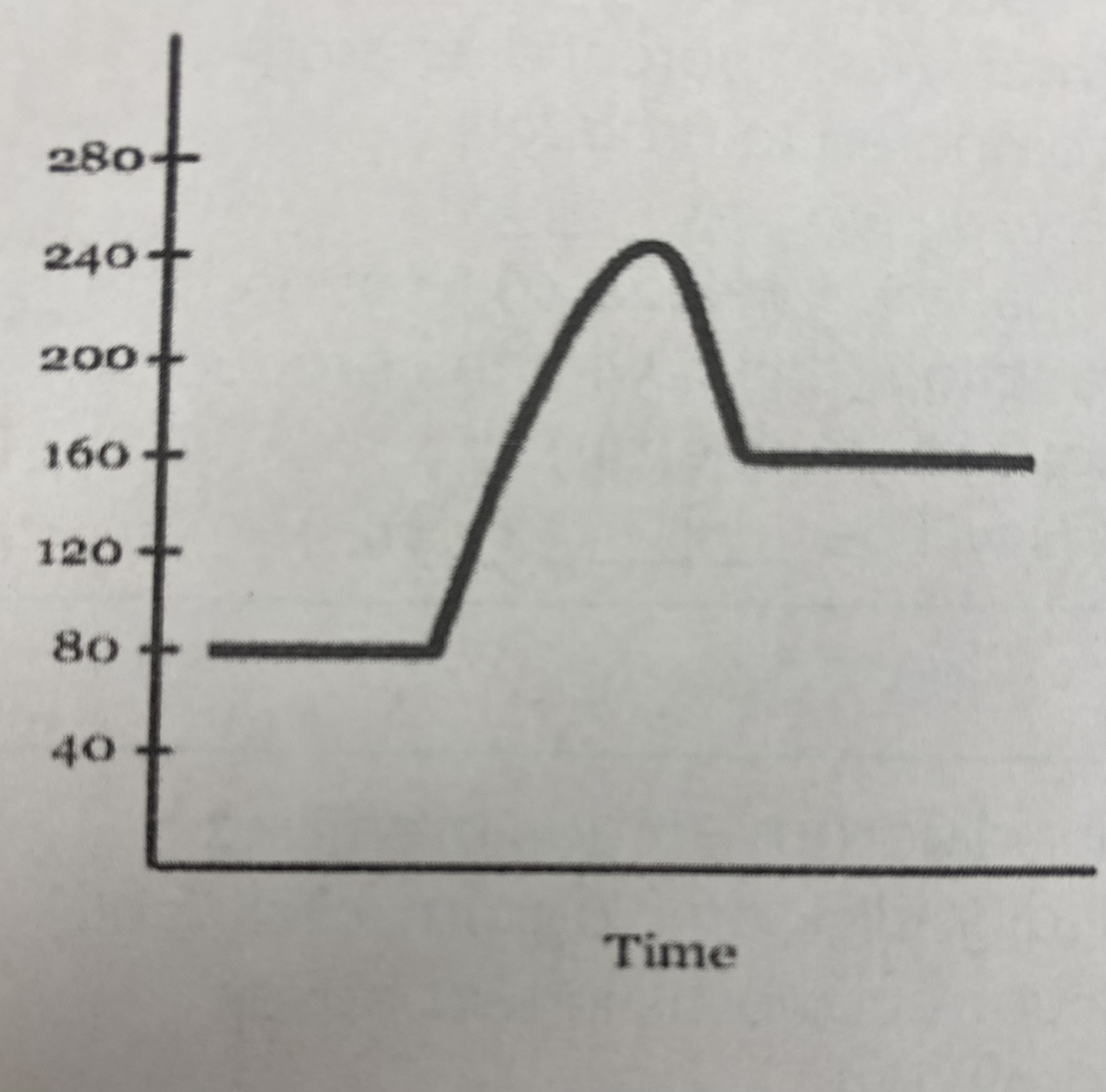
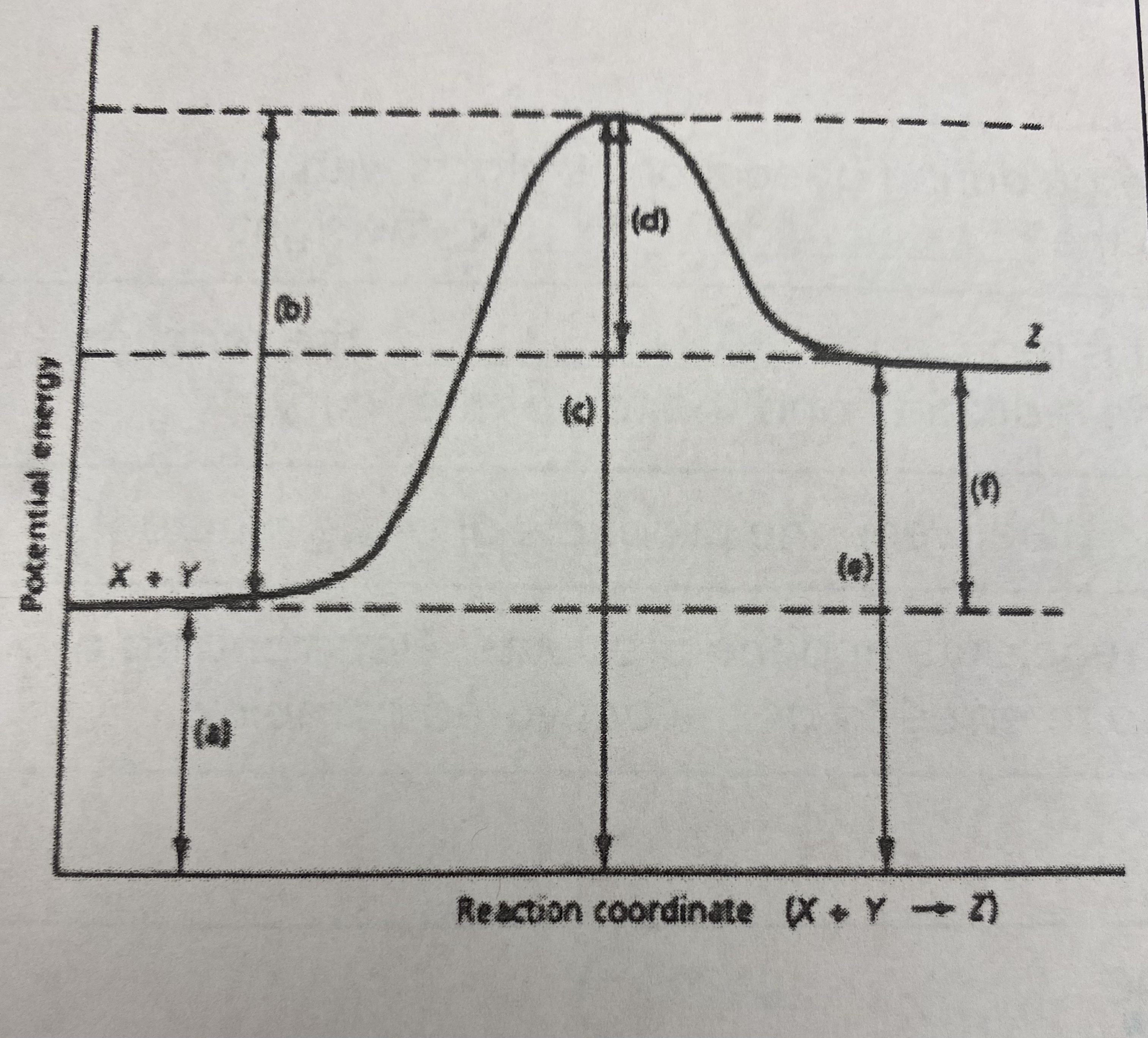
what is the quantitative value for the potential energy of the __reactants__?
80 kJ
17
New cards
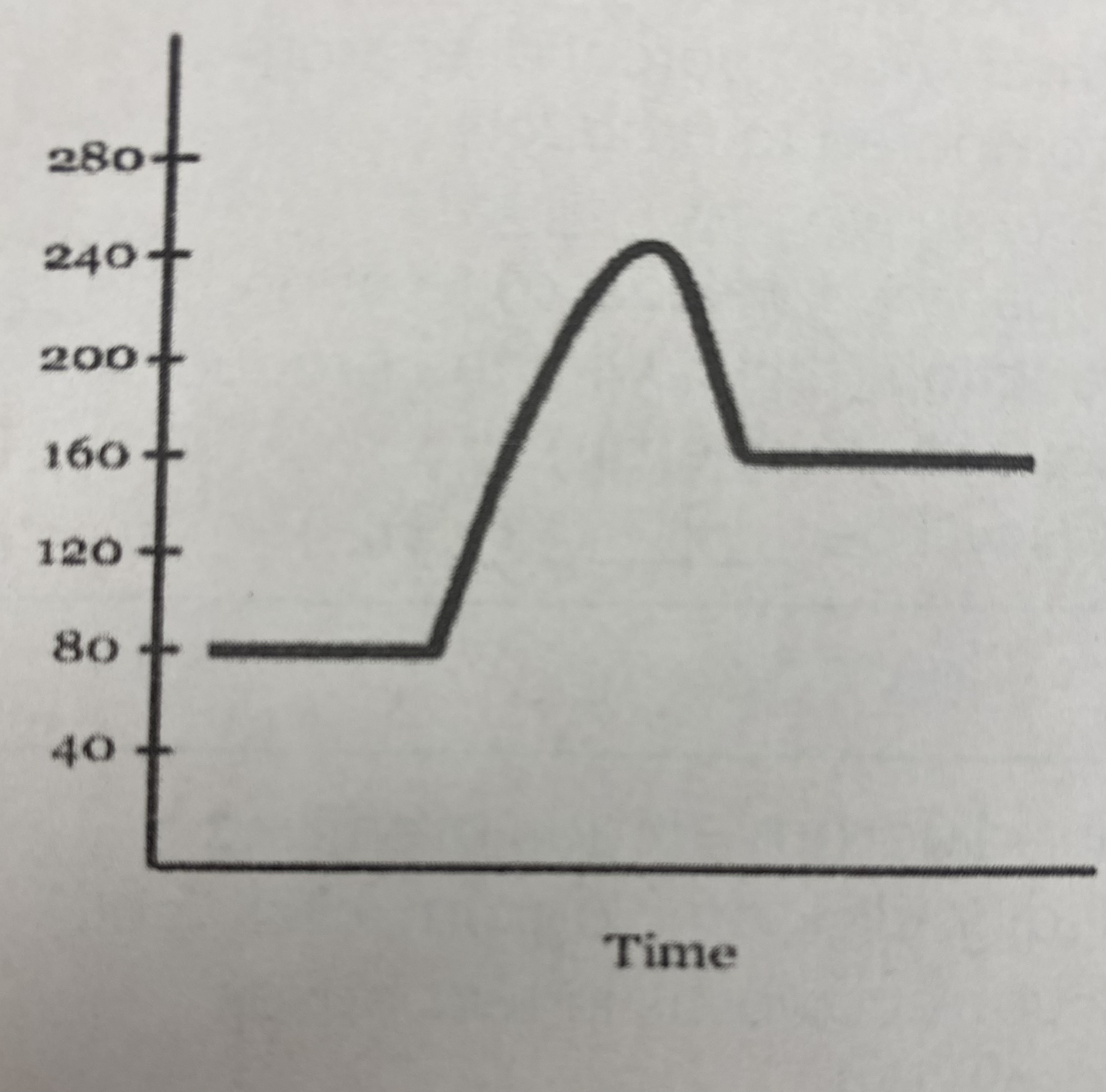
what is the quantitative value for the potential energy of the __products__?
160 kJ
18
New cards
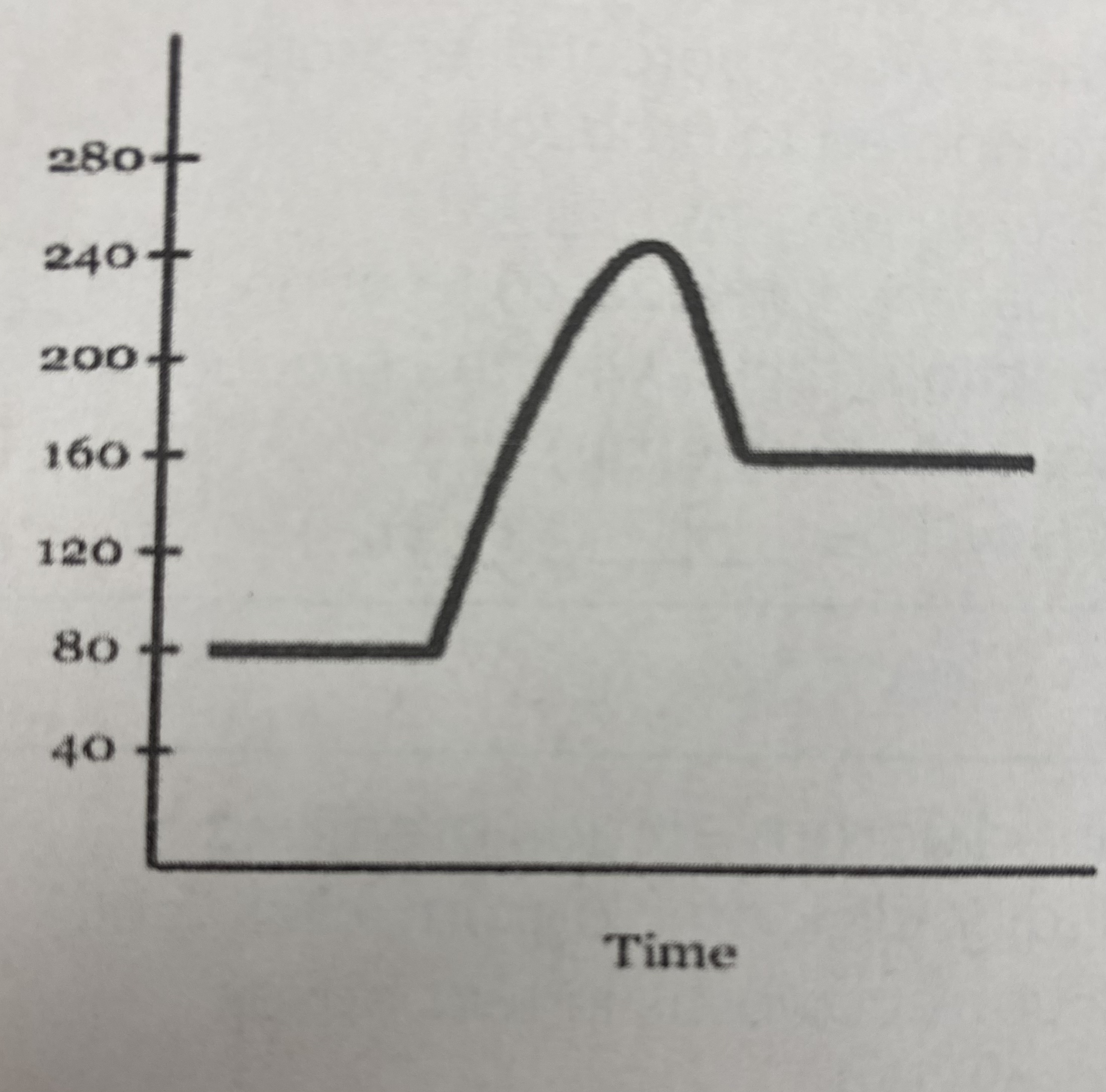
what is the numerical value for the __activation energy (Ea)__?
Ea = (240 kJ - 80 kJ) = **160 kJ**
19
New cards
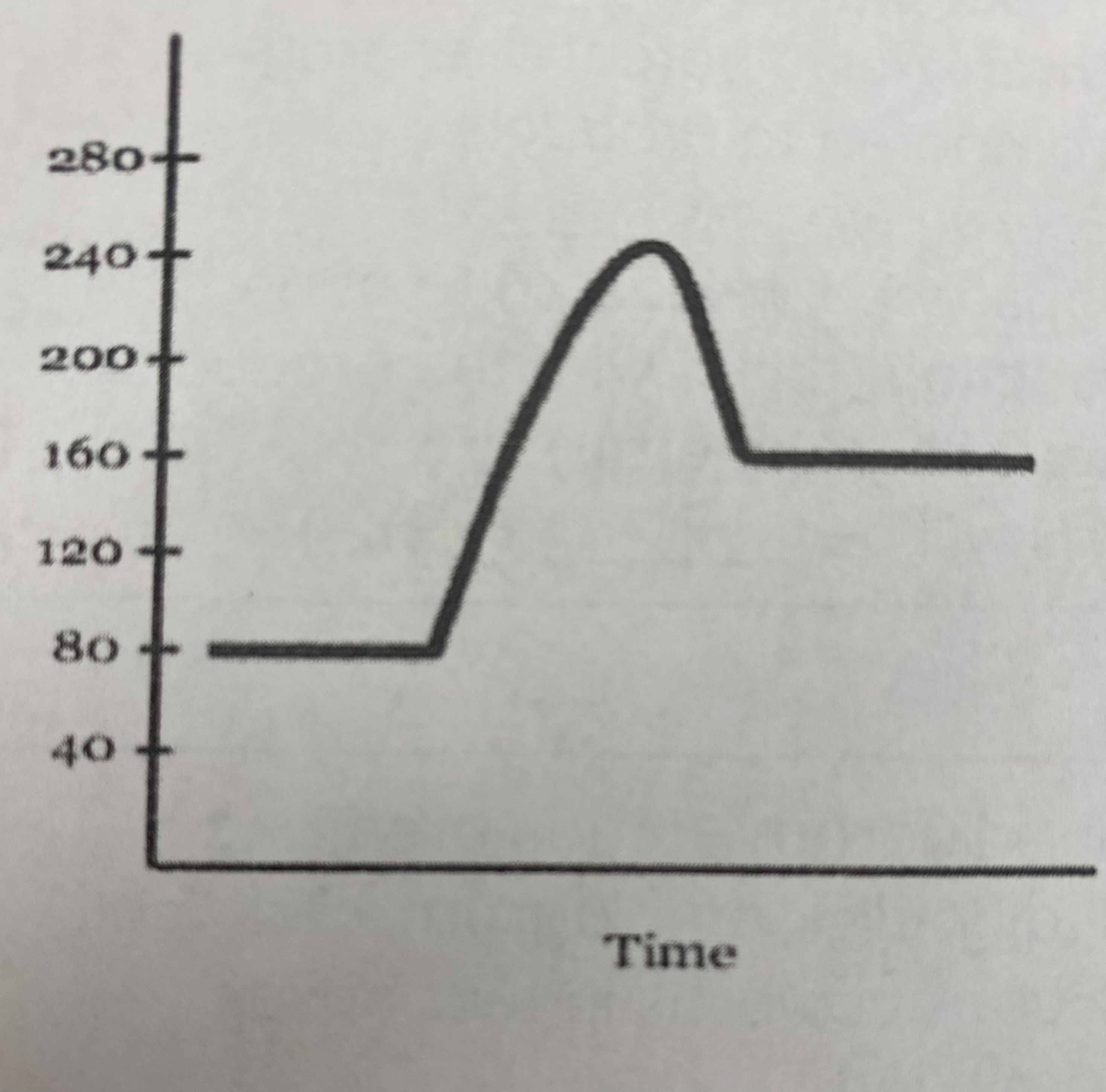
what is the numerical value for __heat of reaction (Δ H)__?
Δ H= 160 kJ - 80 kJ = **80 kJ**
20
New cards
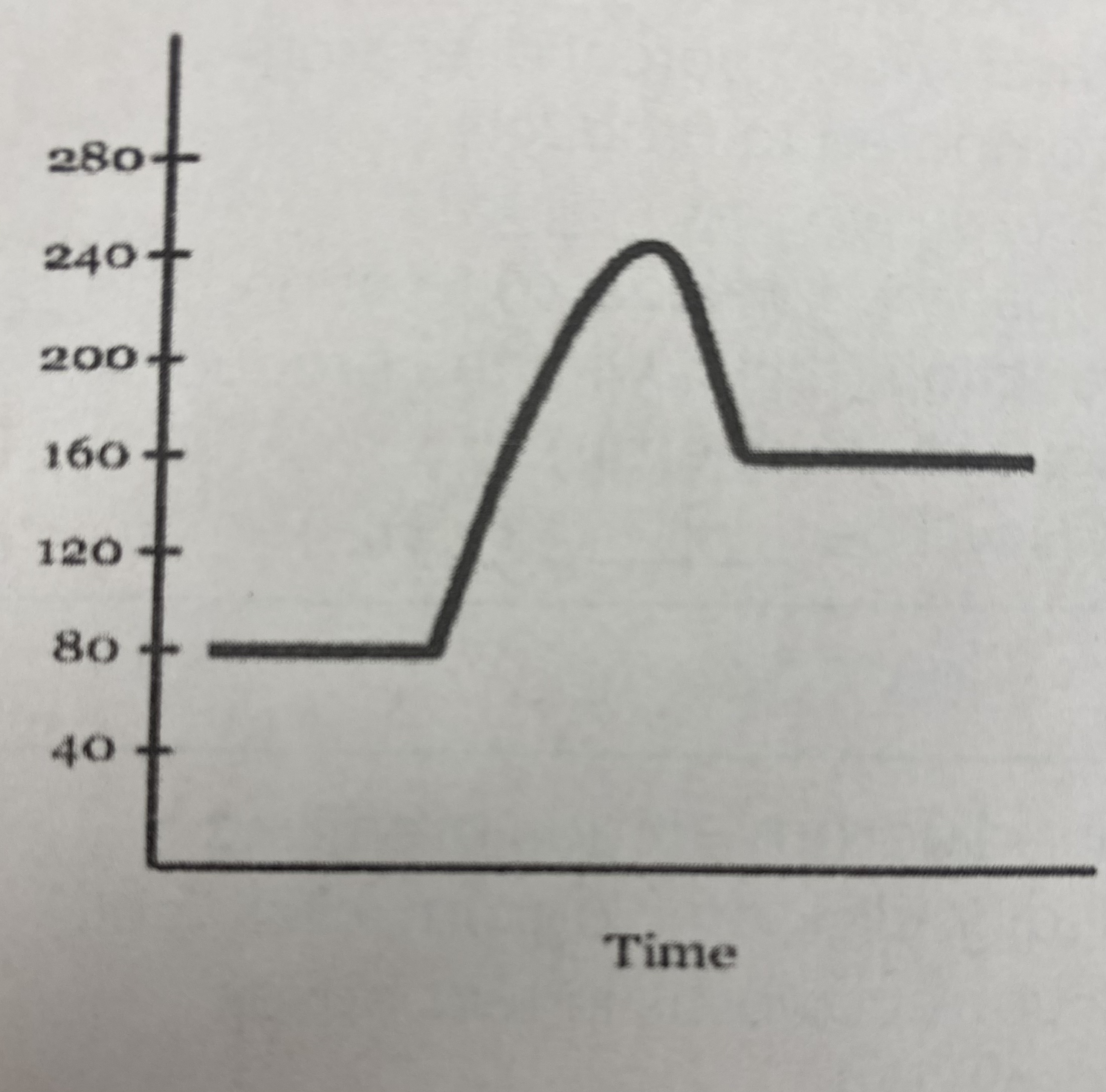
what is the potential energy of the __transitional state__?
240 kJ
21
New cards
compound
2 or more elements that are chemically combined (not just mixed)
22
New cards
metal + metal
metallic compound
23
New cards
metal + nonmetal
ionic compound
24
New cards
nonmetal + nonmetal
molecular compound
25
New cards
ion formation
each element has one particular ion it nearly always forms, when it bonds in an ionic compound (except for transition metals, which had multiple preferred ionic states).
26
New cards
in general, the ion an element will form can be predicted by the _____.
octet rule
27
New cards
octet rule
when an element forms an ion, it will do so in whatever way allows it to have a full outer shell (8 valence electrons) the easiest
28
New cards
ionic compound
consists of positive and negative ions that are held together in a crystal lattice
29
New cards
crystal lattice
a rigid geometric pattern
30
New cards
the forming of ionic compounds
* Generally, any compound containing a metal and a nonmetal is an ionic compound.
* The compound forms when the metal atom gives an electron to the nonmetal atom. T
* The metal atom becomes a positive ion (cation) and the nonmetal atom becomes a negative ion (anion).
* The compound forms when the metal atom gives an electron to the nonmetal atom. T
* The metal atom becomes a positive ion (cation) and the nonmetal atom becomes a negative ion (anion).
31
New cards
the net charge of an ionic compound should always be ____.
zero
32
New cards
chemical nomenclature
a set of rules that all chemists agree upon to allow us to consistently name compounds
33
New cards
steps to name ionic compounds
1. name the positive ion, then the negative ion
2. the name of the positive ion is the same as the name of the atom. Ex: Mg2+ is the “magnesium” ion
3. the name of the negative ion has the “ide” ending. Ex: Cl-1 is the “chloride” ion
4. if the positive ion is a transition metal, you must include the charge of the atom as a Roman numeral in parentheses. Ex: Cr+4 is the “chromium (IV)” ion
34
New cards
chemical formulas
tell how many of each atom (or ion) are in a compound. when writing chemical formulas, subscripts are used to note that the smallest whole number ratio of ions in a ionic compound. (the positive ion is always written first in the ionic compound.")
35
New cards
how to write formulas for ionic compounds
1. determine the charge of each ion
2. determine how many of each ion are in the compound. (cross the charges for a short cut)
3. write the positive ion, then the negative ion. don’t write their charges, but do use a subscript to tell how many there are
36
New cards
roman numerals
one: I
two: II
three: III
four: IV
five: V
six: VI
two: II
three: III
four: IV
five: V
six: VI
37
New cards
practice: when potassium and oxygen form a compound
* what ion does potassium form? symbol: K+ name: potassium
* what ion does oxygen form? symbol: O-2 name: oxide
* there are 2 potassium ions for every oxide ion
* name the compound: potassium oxide
* compound formula: K2O
* what ion does oxygen form? symbol: O-2 name: oxide
* there are 2 potassium ions for every oxide ion
* name the compound: potassium oxide
* compound formula: K2O
38
New cards
practice: when calcium and sulfur form a compound
* what ion does calcium form? symbol: Ca+2 name: calcium
* what ion does sulfur form? symbol: S-2 name: sulfide
* there is a calcium ion for every sulfide ion
* name the compound: calcium sulfide
* compound formula: CaS
* what ion does sulfur form? symbol: S-2 name: sulfide
* there is a calcium ion for every sulfide ion
* name the compound: calcium sulfide
* compound formula: CaS
39
New cards
polyatomic ions
groups of atoms that have bonded together and that have an overall charge. ex: SO4^-2 means that in one sulfur ion, there is one sulfur atom and 4 oxygen atoms and their overall charge is -2.
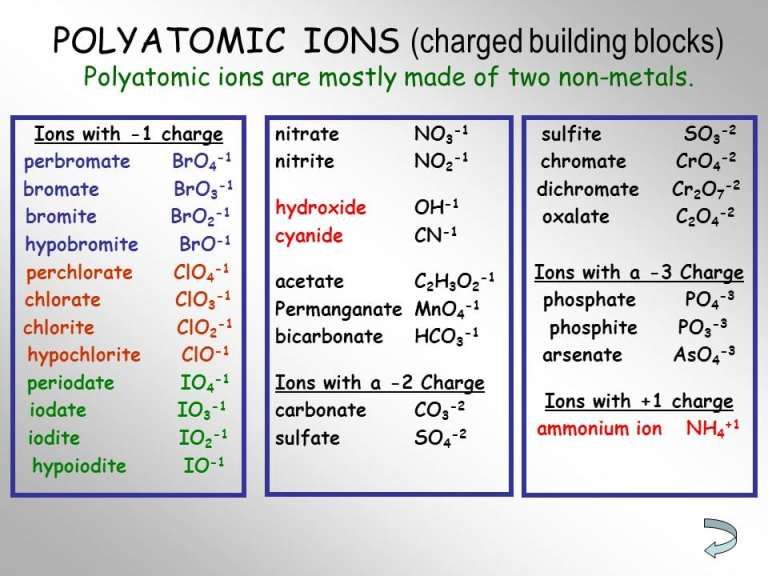
40
New cards
molecular compounds
* formed by __two nonmetals__
* composed of discrete molecules
* since nonmetals “need” to gain electrons to become more stable, they can share electrons to form molecular compounds
* called covalent bonding
* these compounds may exist as solids, liquids, or gases at room temp
* usually have lower melting points than ionic compounds
* composed of discrete molecules
* since nonmetals “need” to gain electrons to become more stable, they can share electrons to form molecular compounds
* called covalent bonding
* these compounds may exist as solids, liquids, or gases at room temp
* usually have lower melting points than ionic compounds
41
New cards
molecular compounds nomenclature
1. name each element
2. use a prefix to indicate the number of each atom there are in a molecule
3. for the first element, if there is only one atom in each molecule, don’t use “mono”
4. change the ending of the last element to “ide”
42
New cards
prefix of molecular compounds
1 : mono
2 : di
3: tri
4: tetra
5 : penta
6 : hexa
2 : di
3: tri
4: tetra
5 : penta
6 : hexa
43
New cards
SO3
sulfur trioxide
44
New cards
N2O5
dinitrogen pentoxide
45
New cards
when a metal and nonmetal bond, they form a ____
large crystal lattice
46
New cards
which one is a covalent compound?
Fe2O3
MgCl2
SeO
CaS
Fe2O3
MgCl2
SeO
CaS
SeO
47
New cards
when cesium and phosphorous bond, there are
3 times as many Cesiums ions as Phosphorous ions
48
New cards
what is the right name for BaCl2
Barium Chloride
49
New cards
what is the right formula for Selenium Diflouride
SeF2
50
New cards
endothermic reaction make their environment ___
colder
51
New cards
which bonds are stronger in endothermic reactions?
reactant bonds
52
New cards
what represents activation energy in a reaction?
reactants → transitional state
53
New cards
a reaction was calculated to have absorbed +200 kJ/mol and released -600 kJ/mol. this reaction is…
exothermic
54
New cards
stronger bonds require….
high activation energy
55
New cards
which is stronger: ionic or covalent bonds?
ionic
56
New cards
intermolecular forces
forces of attraction between molecules
57
New cards
intramolecular forces
hold atoms together in a molecule
58
New cards
hydrogen bonds
attractive forces in which a hydrogen covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom causes attractions to other molecules
59
New cards
ionic bond
A chemical bond resulting from the attraction between oppositely charged ions.
60
New cards
covalent bond
A chemical bond that involves sharing a pair of electrons between atoms in a molecule
61
New cards
polar bond
a covalent bond between atoms in which the electrons are shared unequally
62
New cards
polar molecule
a molecule in which one side of the molecule is slightly negative and the opposite side is slightly positive
63
New cards
nonpolar bond
a covalent bond in which electrons are shared equally
64
New cards
nonpolar molecule
a molecule that does not have oppositely charged ends
65
New cards
Melting
change from a solid to a liquid
66
New cards
Freezing
\n The change of state from a liquid to a solid
67
New cards
Condensing
The change of state from a gas to a liquid
68
New cards
Vaporizing
the change from a liquid to a gas
69
New cards
Sublimation
A change directly from the solid to the gaseous state without becoming liquid
70
New cards
Deposition
\n a change directly from a gas to a solid
71
New cards
weakest intermolecular force
london forces
72
New cards
strongest intermolecular force
hydrogen bond
73
New cards
intermolecular forces between ALL polar molecules
dipole dipole forces
74
New cards
London forces are strongest for __________________ molecules
nonpolar
75
New cards
hydrogen bonds can form when H is bonded to __________
nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine
76
New cards
Polar molecules will have ____________ boiling points than nonpolar molecules
higher
77
New cards
Nonpolar molecules will have __________ boiling points than polar molecules
lower
78
New cards
_________________ are the strongest of ALL forces
ionic bonds
79
New cards
Miscible
Describes two liquids that are soluble in each other
80
New cards
imiscible
liquids are not soluble in one another
81
New cards
lewis structure
simple models that show how atoms are connected in a molecule or polyatomic ion
\
* note: lewis structure do NOT show the shape of a molecule, just how atoms are connect
* each line represents 1 share pair of electrons
\
* note: lewis structure do NOT show the shape of a molecule, just how atoms are connect
* each line represents 1 share pair of electrons
82
New cards
ionic bonds are stronger when
there are higher charges and the smaller the atoms
83
New cards
covalent bonds are stronger when
more electrons are shared
84
New cards
covalent network compound
crystal lattice w/covalent bonds ex: diamond
85
New cards
intermolecular force
a force of attraction between two molecules. these forces must be overcome during phase changes
86
New cards
dipole-dipole forces
the attraction between the partial positive end of one polar molecule, and the partial negative end of a different molecule
* molecule MUST be polar to have this force
* stronger when molecules are more polar (more uneven sharing it a big difference in electronegativity)
* extra polar bonds: F-H, O-H and N-H
* molecule MUST be polar to have this force
* stronger when molecules are more polar (more uneven sharing it a big difference in electronegativity)
* extra polar bonds: F-H, O-H and N-H
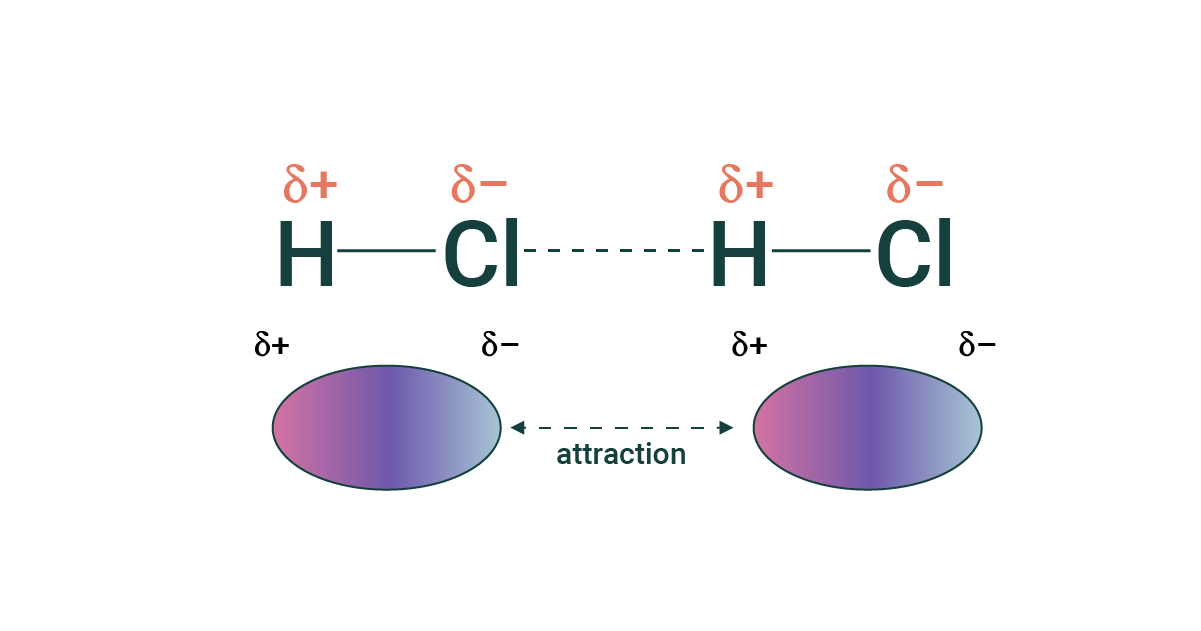
87
New cards
london dispersion forces
an attraction between TEMPORARY dipoles, that form because of the random motion of electrons within molecules
* stronger when there are more TOTAL electrons (more polarizable)
* stronger when there are more TOTAL electrons (more polarizable)
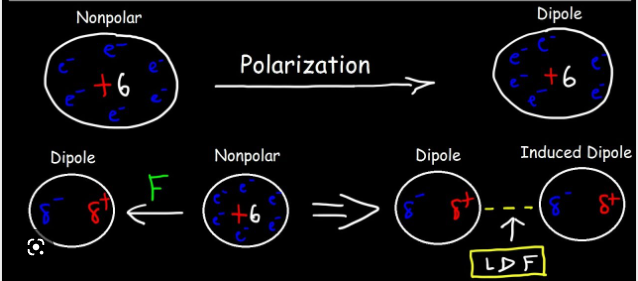
88
New cards
covalent networks are the _____ type of compound to seperate
hardest
89
New cards
if there is the same electronegative difference between molecules, check ____
size
90
New cards
what does not affect lattice energy?
polarity
91
New cards
what is an example of an intramolecular force?
H-Cl
92
New cards
what property describes a strong bond?
high boiling point
93
New cards
what is an example of a non polar covalent compound?
CO2
94
New cards
T/F : non polar covalent bonds are stronger than ion-ion bonds
false
95
New cards
T/F: hydrogen bonds are stronger than London dispersion forces
true
96
New cards
what is the correct order of bond strength from strongest to weakest: ion-dipole, dispersion forces, H-bond
H-bond, ion-dipole, dispersion forces
97
New cards
what is a London dispersion force?
interaction between non polar molecules
98
New cards
what is an ion-dipole force?
interaction between an ion and polar molecule
99
New cards
what is an ion-ion force?
interaction between a cation and anion
100
New cards
what is hydrogen bonding?
interaction between polar molecules