Biology Honors - Midterm Exam
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/165
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:58 AM on 1/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
166 Terms
1
New cards
biological hierarchy/levels of organization
atom → molecule → organelle → cell → tissue → organ → organ system → organism → population → community → ecosystem → biosphere
2
New cards
characteristics of life
* has cells
* genetic material
* can reproduce
* regulate internal environment/homeostasis
* obtain and use energy
* grow and develop
* respond to stimuli
* adapt and evolve
* genetic material
* can reproduce
* regulate internal environment/homeostasis
* obtain and use energy
* grow and develop
* respond to stimuli
* adapt and evolve
3
New cards
CHNOPS
Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur
4
New cards
Cell
The basic unit of structure and function in living things
5
New cards
prokaryotic cell
simple, unicellular organisms that don't have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles.
6
New cards
Prokaryote (example)
bacteria
7
New cards
Eukarytoic Cells
There are nuclei (a nucleus in each) in these cells. Larger cells, have membrane-bound organelles, appeared later in fossil record, more advance, more complex.
8
New cards
Eukaryote (Example)
plants, animals, fungi
9
New cards
cell membrane
thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell
10
New cards
Nucleus (cell)
A part of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
11
New cards
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
12
New cards
Organelle
A tiny cell structure that carries out a specific function within the cell
13
New cards
Ribosome
Cytoplasmic organelles at which proteins are synthesized.
14
New cards
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
15
New cards
Mitochondria
\-Power-house of the cell
\-organelles specialized for synthesizing ATP (Energy)
\-organelles specialized for synthesizing ATP (Energy)
16
New cards
cell wall
\-A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell
\-Composed of cellulose
\-Composed of cellulose
17
New cards
phosopholipid bilayer
composition of cell membrane, two layers of phospholipids arranged tail-to-tail
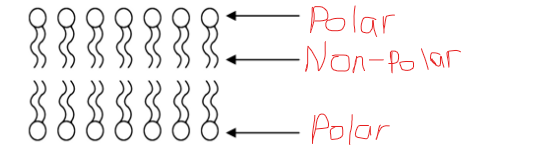
18
New cards
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
19
New cards
Hydrophilic
Attracted to water
20
New cards
Semi-permeable
characteristic of a cell membrane which allows some molecules to pass through but not others
21
New cards
Scientific Method
A logical, systematic approach to the solution of a scientific problem
22
New cards
Hypothesis
\-A testable prediction, often supported by research.
\-An educated guess
\-An educated guess
23
New cards
dependent variable
The outcome factor; the data collected in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
24
New cards
independent variable
The experimental factor that is manipulated; the variable whose effect is being studied.
25
New cards
control group
In an experiment, the group that is not exposed to the treatment; contrasts with the experimental group and serves as a comparison for evaluating the effect of the treatment.
26
New cards
Constants
Conditions that stay the same in the experiment
27
New cards
Biosphere
part of Earth in which life exists including land, water, and air or atmosphere
28
New cards
Ecosystem
A community of living organisms and their abiotic environment
29
New cards
Organism
An individual living thing
30
New cards
Population
A group of individuals that belong to the same species and live in the same area
31
New cards
Community
All the different populations that live together in an area
32
New cards
qualitative data
Information describing color, odor, shape, or some other physical characteristic
33
New cards
Quantitative data
numerical data
34
New cards
organ system
group of organs that work together to perform a specific function
35
New cards
Tissue
A group of similar cells that perform the same function.
36
New cards
Atoms
smallest unit of matter
37
New cards
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
38
New cards
nucleic acids (Function)
stores and transmits genetic information
39
New cards
nucleic acid (Monomer)
nucleotide
40
New cards
nucleotide (Image)
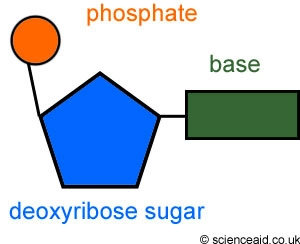
41
New cards
nucleic Acid (Examples)
DNA and RNA
42
New cards
Protein (Function)
builds and repairs muscle, body movement, defend against germs or viruses, speeds up chemical reactions
43
New cards
Protein (Monomer)
amino acids
44
New cards
Amino Acid (Image)
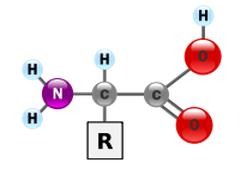
45
New cards
Lipids (Function)
\-long term energy storage stored as fat
\-makes up cell membranes
\-makes up cell membranes
46
New cards
Saturated Fat (Description)
\-A lipid made from fatty acids that have no double bonds between carbon atoms.
\-Solid at room temperature
\-Solid at room temperature
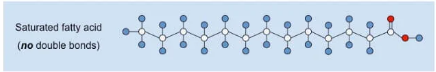
47
New cards
Saturated Fat (Examples)
Butter, animal fats, shortening (crisco)
48
New cards
Unsaturated Fat (Description)
\-A lipid made from fatty acids that have at least one double bond between carbon atoms.
\-Liquid at room temperature
\-Liquid at room temperature
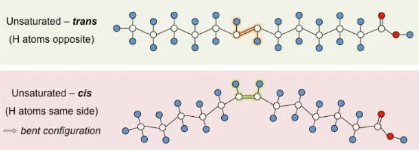
49
New cards
Unsaturated Fat (Examples)
olive oil, vegetable oil, fish oil, coconut oil, etc.
50
New cards
Lipid (Image)
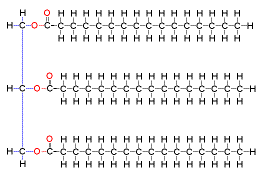
51
New cards
Carbohydrate (Function)
short term energy storage, main source of energy, makes up the cell wall of plants
52
New cards
Carbohydrate (Examples)
sugars, starches, glycogen, and cellulose
53
New cards
Carbohydrate (Monomer)
monosaccharide (glucose)
54
New cards
Glucose (Image)
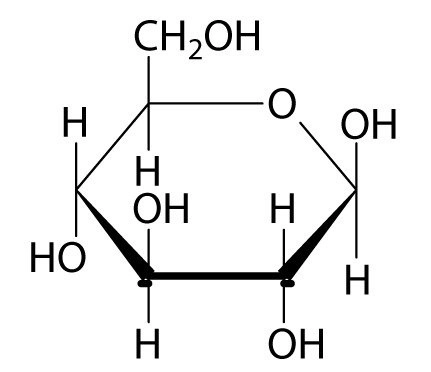
55
New cards
Polysaccharide (Image)
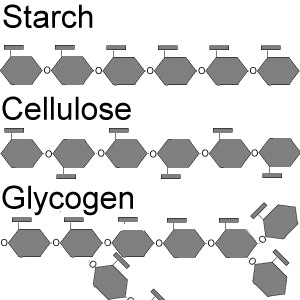
56
New cards
Starch (Function)
short-term energy storage in plants
57
New cards
Glycogen (Function)
short-term energy storage in animals
58
New cards
Cellulose (Function)
component of plant cell walls
59
New cards
Monomer
a molecule that can be bonded to other identical molecules to form a polymer.
60
New cards
Polymer
molecules composed of many monomers; makes up macromolecules
61
New cards
dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction in which two molecules are bonded together with the removal of a water molecule.
62
New cards
Hydrolysis
Breaking down complex molecules by the chemical addition of water
63
New cards
Homeostasis (Definition)
the balance and maintenance of constant internal conditions
64
New cards
positive feedback loop
Feedback loop that causes a system to change further in the same direction.
65
New cards
negative feedback loop
A feedback loop in which a system responds to a change by returning to its original state, or by decreasing the rate at which the change is occurring.
66
New cards
Stimulus
any event or situation that evokes a response
67
New cards
response
An action or change in behavior that occurs as a result of a stimulus.
68
New cards
Effector
An organ (a gland or muscle) that becomes active in response to nerve impulses from the brain.
69
New cards
set point
the "normal" range that an environmental parameter is to be controlled. (Body temp, blood sugar levels)
70
New cards
cell theory
\-idea that all living things are composed of cells
\
\
71
New cards
-new cells are produced from existing cells
72
New cards
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane
73
New cards
Diffusion (Passive Transport)
\-Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
\-Requires NO ENERGY!
\-Requires NO ENERGY!
74
New cards
concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
75
New cards
Vacuole
A sac inside a cell that acts as a storage area and supports structure
76
New cards
Lysosome
A small, round cell structure containing enzymes
77
New cards
Which evolved first - prokaryotes or eukaryotes?
prokaryotes
78
New cards
prokaryotes have no
no nucleus, no membrane bound organelles
79
New cards
Carb Elements
CHO
80
New cards
Lipid Elements
CHO
81
New cards
Protein Elements
CHON (S)
82
New cards
Nucleic Acid Elements
CHONP
83
New cards
peptide bond
Bonds that connect amino acids.
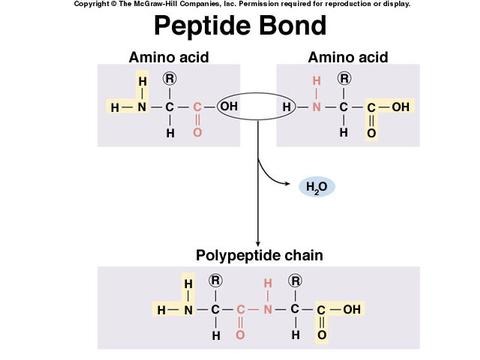
84
New cards
polypeptide bond
long chain of amino acids
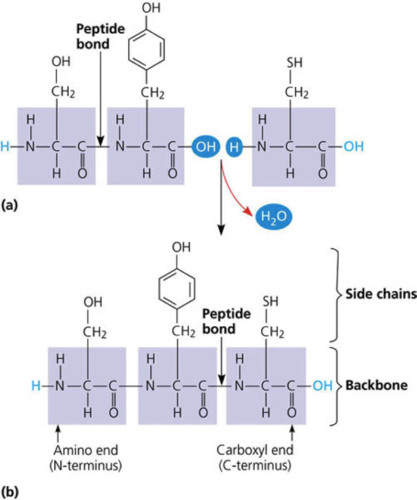
85
New cards
Structure determines
function
86
New cards
enzyme
protein catalyst that speeds up the rate of specific biological reactions
87
New cards
denatured protein
when a protein loses its shape and its function
88
New cards
Osmosis helps homeostasis by...
regulating water in the body
89
New cards
kinetic energy
the energy an object has due to its motion
90
New cards
potential energy
energy that is stored and held in readiness
91
New cards
chemical energy
Energy stored in chemical bonds
92
New cards
atp
adenosine triphosphate
93
New cards
atp cycle
ADP forms when ATP loses a phosphate group, then ATP forms as ADP gains a phosphate group.
94
New cards
what is the purpose of cellular respiration
makes ATP for cells to use
95
New cards
How are breathing and cellular respiration related?
the inhaled oxygen goes into your bloodstream and is used in cellular respiration, and co2 is exhaled as a waste product
96
New cards
aerobic
Process that requires oxygen
97
New cards
anaerobic
Process that does not require oxygen
98
New cards
cellular respiration equation
C6 H12 06 + 6O2 \---\> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
99
New cards
why do we need atp
ATP is the energy needed for our cells to do work
100
New cards
Where does glycolysis occur?
cytoplasm