Water Resources Midterm
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
Competing interests in water management
Domestic use
Agriculture
Hydropower generation
Recreational use
Ecosystems
International boundaries
Esthetic and spiritual interests
Constituents of well being
Security
Basic material for life
Health
Good social relations
Four key issues in water disputes
Quantity
Quality
Timing
Space
Why have international basins increased over time?
Changing political borders, improved mapping technology, refined data collection methods
What are the cooperative management mechanisms?
Providing forums for joint negotiation
Considering different perspectives
Building trust through collaboration
Making cooperative decisions even if there is no consensus
Global water issues (examples)
Climate change
Transboundary water stress
Urbanization
Local water issues (examples)
Boil water advisories
Seasonal shortages
Flash floods
Groundwater depletion
Considerations for small-scale design
Simplicity and ease of maintenance
Use of locally available materials
Flexibility and modularity
Cultural compatibility
Community involvement in design
Wastewater treatment plant community considerations
Noise
Odor and air quality
Traffic and road access
Visual impact and aesthetics
Stormwater management system community considerations
Flood risk and property protection
Green space and recreation
Public safety and visibility
Maintenance and stewardship
Clean Water Act of 1972
Gave the EPA authority to set effluent standards; “swimmable and fishable”
Point source
a source of potential pollution that is discharged to a lake, river, or stream from a defined point, such as the end of a pipe or channel
National Pollutant Discharge Elimination System (NPDES)
Enforcement arm of the EPA Clean Water Act; the discharge of pollutants into US water requires an NPDES permit
Non-point source
A source of potential pollution that enters a lake, river, or stream indirectly (ex. snowmelt, rainfall)
Total maximum daily load (TMDL)
Establishes the maximum amount of a pollutant allowed in a waterbody and serves as the starting point or planning tool for restoring water quality
TMDL State Actions
Identify waters that are impaired or in danger of becoming impaired
Calculate and allocate pollutant reduction level necessary to meet approved water quality standards
Most common TMDL impairments
Bacteria
DO
Mercury
Nutrients
Sediment
Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA)
Focuses on protecting public drinking water supplies; sets national health-based standards
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA)
Govern the management of hazardous and solid waste; regulates landfills, incinerators, and underground storage tanks
Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act (CERCLA)
Addresses the cleanup of hazardous waste sites and holds polluters financially responsible
Tragedy of the commons
Situation where individuals, acting in their own self-interest, overuse and deplete a shared resource; leads to market inefficiency due to overconsumption and depletion
Consumer surplus
The difference between what consumers are willing to pay and what they actually pay; area above price level and below demand curve
Producer surplus
The difference between what the price producers receive and the minimum they would accept; area below price level and above the supply curve
Efficient market
When consumer and producer surplus and maximized
Type of water laws in the east
Riparian doctrine
Type of water laws in the west
Appropriation (prior use) doctrine
Riparian doctrine
Water allocation based on property ownership along the water source’s path
Prior appropriation doctrine
“First in time, first in right"
Water rights are granted based on priority of beneficial use and/or permit holding
Statutory water right doctrine
State owns all water and can manage to balance needs
Water resources/rights in the U.K.
Riparian doctrine; if water amounts cannot satisfy needs, allotments are generally fixed in proportion to frontage on the water source
Water resources/rights in Australia
Cap and trade system; shares of water are assigned by the government, but branches can redistribute/trade amounts between eachother
Water rights in Wisconsin
Hybrid (restatement of torts rule)
Water resources/rights in UAE
Water rights are centralized, and access is determined by government regulation; heavy reliance on desalination and treated wastewater
Amount of groundwater used
69.8 billion gallons/day
How much of water is consumed for irrigation?
81%
Most common groundwater doctrines
Rule of capture
Correlative rights
Reasonable Use Rule
Prior Appropriation
Prior appropriation
first in time, first in right
Reasonable Use rule
extraction allowed unless it harms others
Correlative rights
allocation based on land area over aquifer
Rule of capture
unlimited extraction
EPA
regulates underground injection and drinking water safety under the Safe Drinking Water Act
USGS
monitors groundwater levels and trends
USACE and Reclamation
Support aquifer recharge and infrastructure
Why does it matter when rivers reach the ocean?
Deltas are biologically rich
Fisheries are important economically and culturally
How have changes to ecosystems provided substantial benefits?
Food production has more than doubled since 1960
Food production per capita has grown
Food prices have fallen
Market contributions of agriculture
Accounts for a large amount of the world’s labor force
Accounts for 24% of GDP in developing countries
Market contribution of ecosystem-service industries
Food production
Timber industry
Marine fisheries
Marine aquaculture
Recreational hunting and fishing
Nonlinear changes in ecosystems
Accelerating, abrupt, and potentially irreversible changes to ecosystems
ex. Newfoundland fisheries collapse in 1992, Iceland’s deforestation
Traditional economist capital
Produced means of production; where produced implies “produced by humans”
Ecological economist capital
Means of production provided by nature
Ecosystems are the combined interactions of what?
biological/living components and physical/non-living components
ecosystem services
services provided by the natural environment which benefit people
Types of ecosystem services
Provisioning services, regulating services, supporting services, cultural services
Provisioning services
food, fresh water, fuel, fiber (direct)
Regulating services
climate regulation, flood regulation, water filtration (indirect)
supporting services
nutrient cycling, soil formation (indirect)
cultural services
aesthetic, spiritual, educational, recreational (existence)
single payment compound amount
A = amount of money accrued after t years
P = principal amount
r = rate of interest as a decimal
t = number of years
n = number of time the interest in compounded per year
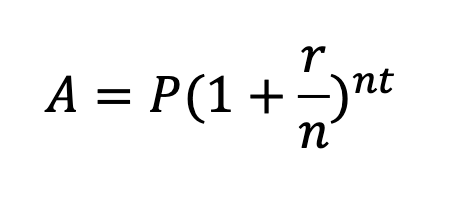
Future worth of level annuity
FW = future worth
A = annual amount
i = interest rate as a decimal
n = number of years
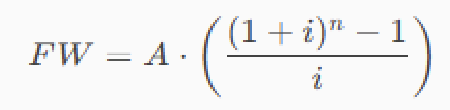
What factors influence consumption/production levels and sustainability in ecosystems?
population change, change in economic activity, sociopolitical factors, cultural factors, technological change
Approaches to ecosystem services valuation
Market-based, replacement-cost, avoided cost, travel cost, hedonic pricing, contingent valuation, choice experiments
Market based valuation method
Used to approximate the value of environmental goods that are bought and sold on a market
Replacement cost method
The amount of money that it would take to replace an ecosystem service with human made equipment
Avoided cost method
The amount of money from potential damages or expenditures that would occur if you lost an ecosystem service
Travel cost method
The value of recreational benefits generated by ecosystems; assumes that the value of the site or its recreational services is reflected in how much people are willing to pay to get there
Hedonic pricing method
Quantifies value of ecosystem services by analyzing house prices and potential effects of the environment
contingent valuation method
Surveys people’s willingness to pay for ecosystem components
Choice experiments
Survey to discover individual preferences for changes in an environmental good or service; allows for broader choices and comparisons of issues
What are the key purposes of ecosystem valuation?
To recognize and quantify the benefits ecosystems provide
To support informed decision making
To help compare natural systems to built infrastructure in terms of cost-effectiveness and sustainability
Areas to integrate valuation methods
Policy development and regulation
Cost-benefit analysis
Environmental impact assessments
Public investment and budgeting
Net present value
Financial method used to evaluate the profitability of an investment by calculating the difference between the present value of expected cash inflows and outflows over a specific time period; time value of money
Rt = Net cash flow in year t
i = discount rate (reflects the time value of money and opportunity cost)
t = time period (year cash flow)
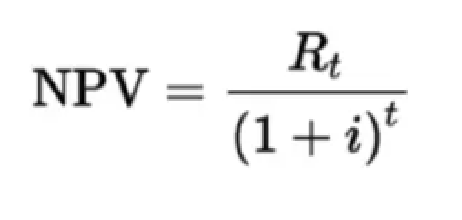
Environmental impact assessment (EIA)
Formal processes used to evaluate the potential environmental consequences of proposed projects before they are approved; National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA)
Millenium Ecosystem Assessment (MA) Scenarios
These examples design future scenarios caused by water resources conditions:
Order from strength
Technogarden
Adapting Mosaic
Global orchestration
Order from strength
A fragmented world focused on security and regional interests
Weak environmental governance and slower development
Adapting mosiac
Regional, community-based ecosystem management
Mixed success in sustainability across regions
Technogarden
A globally connected world using technology to solve ecological problems
Ecosystem services maintained through innovation
Global orchestration
Strong international cooperation and equity-focused policies
Rapid economic development with coordinated ecosystem protection