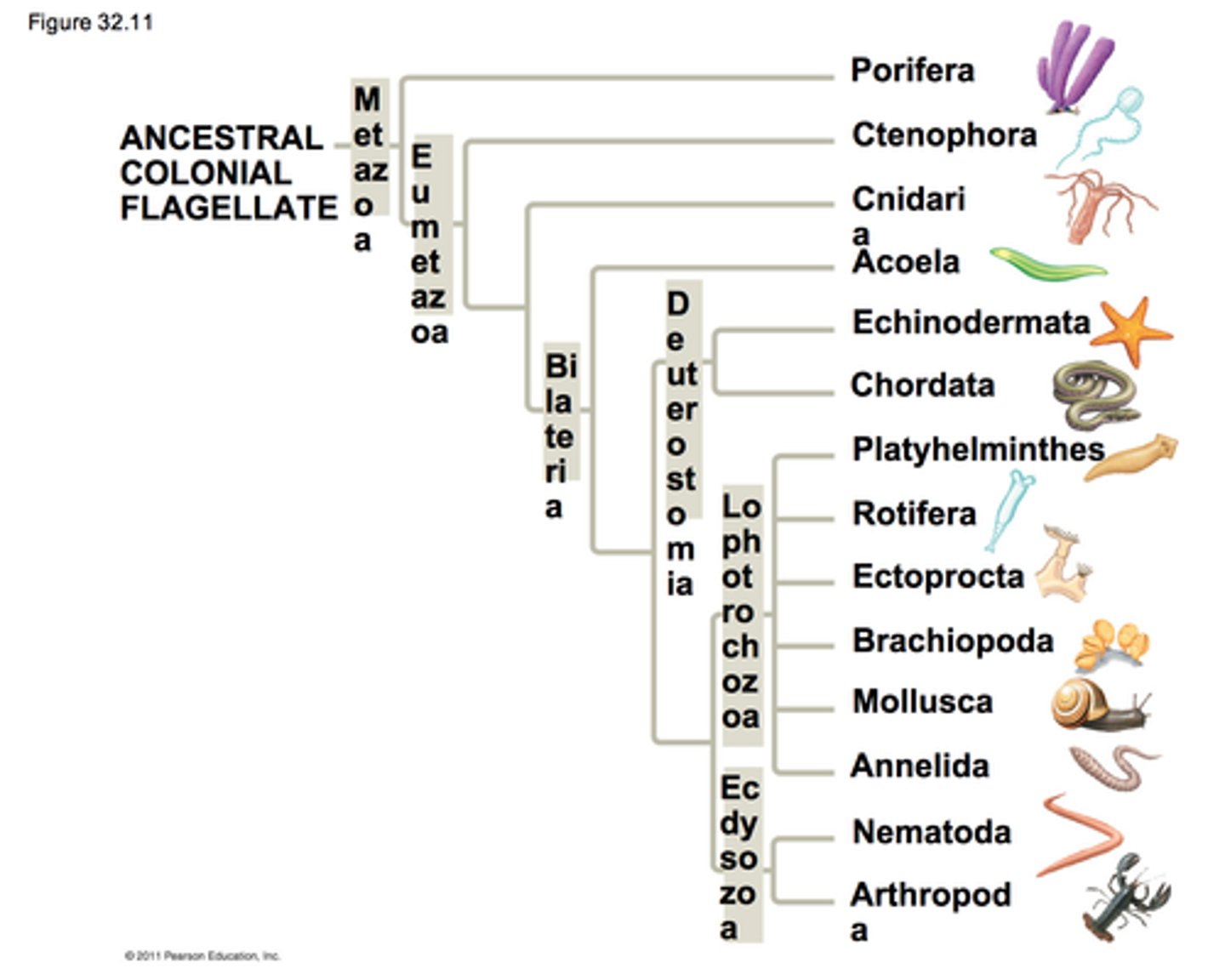
Chapter 33 - Animal Form, Function, and Evolutionary History
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
what stage (haploid or diploid) is the life cycle of animals dominated by?
diploid
what process are haploid gametes made by in animals vs plants and fungi
animals: meiosis
plants and fungi: mitosis
binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in single-celled organisms by which one cell divides into two cells of the same size
(bacteria and archaea)
budding
A form of asexual reproduction of yeast in which a new cell grows out of the body of a parent.
fragmentation
A means of asexual reproduction whereby a single parent breaks into parts that regenerate into whole new individuals.
(some molds, algae, worms, sea stars and corals)
Parthenogenesis
Asexual reproduction in which females produce offspring from unfertilized eggs.
(lots of invertebrates and a few special vertebrates)
external fertilization
The process by which the female lays eggs and the male fertilizes them once they are outside of the female
Higher chance of failure
how do organisms offset fail rate of external fertilization
1. need lots of gametes
2. need to get sperm close to eggs
internal fertilization
Process in which eggs are fertilized inside the female's body
radial symmetry
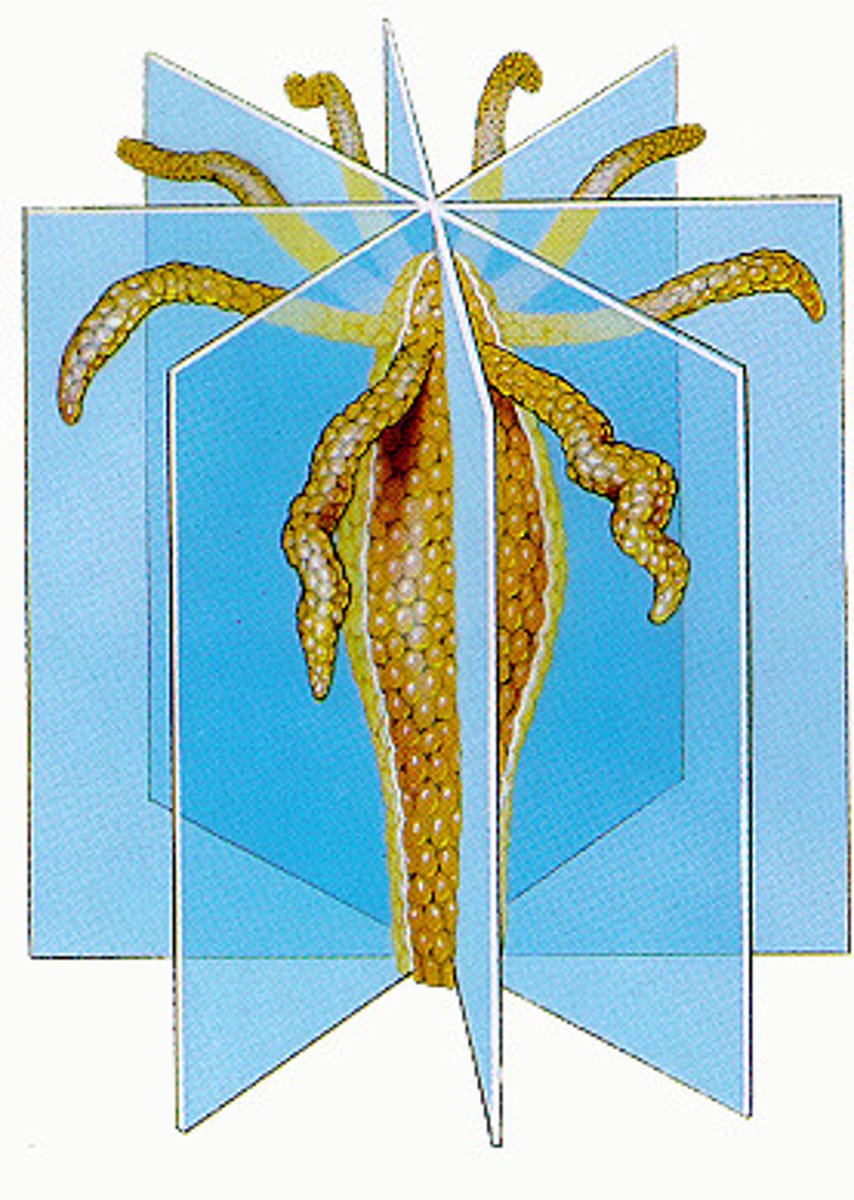
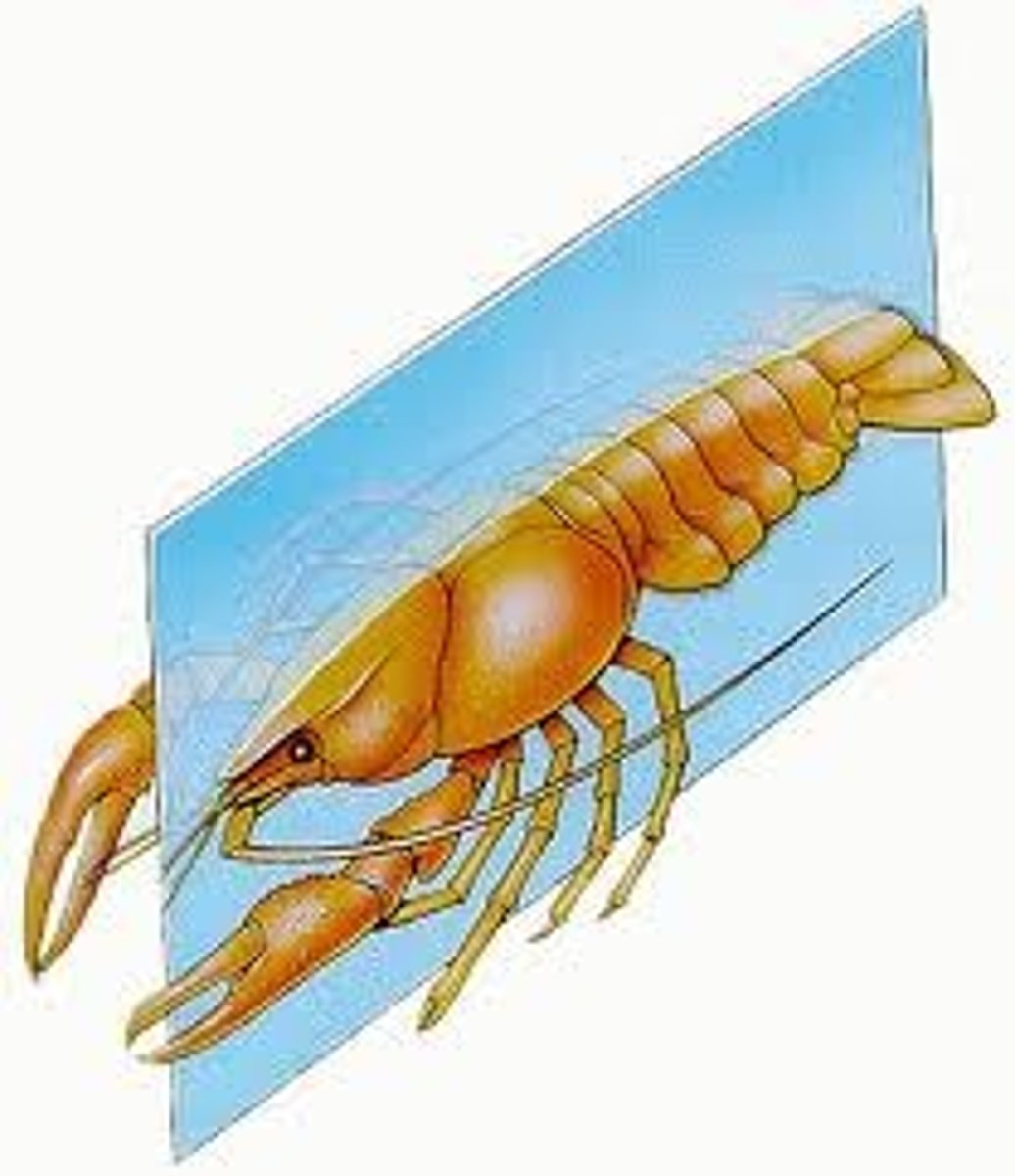
bilateral symmetry
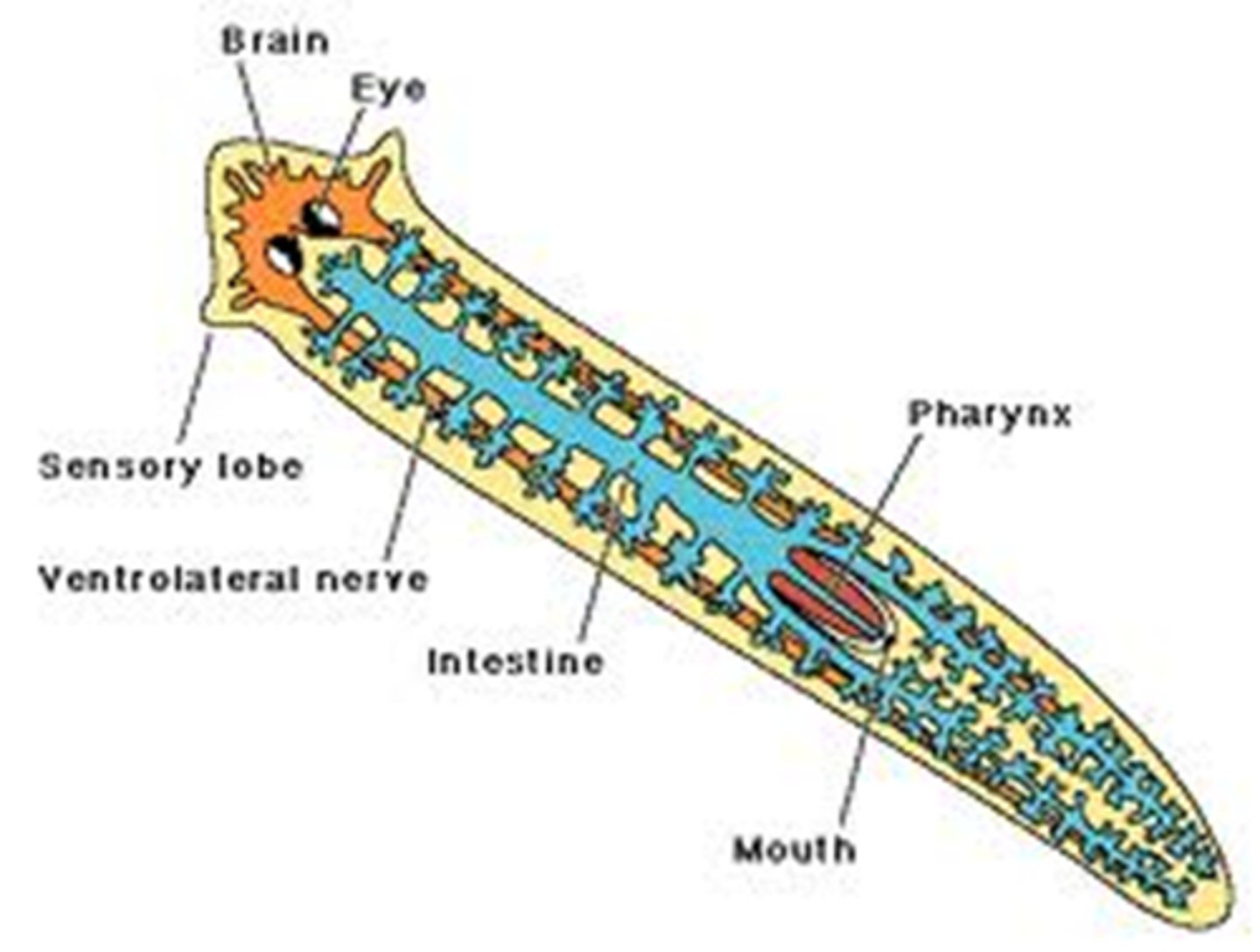
cephalization
the concentration of nerve tissue and sensory organs at the anterior end of an organism
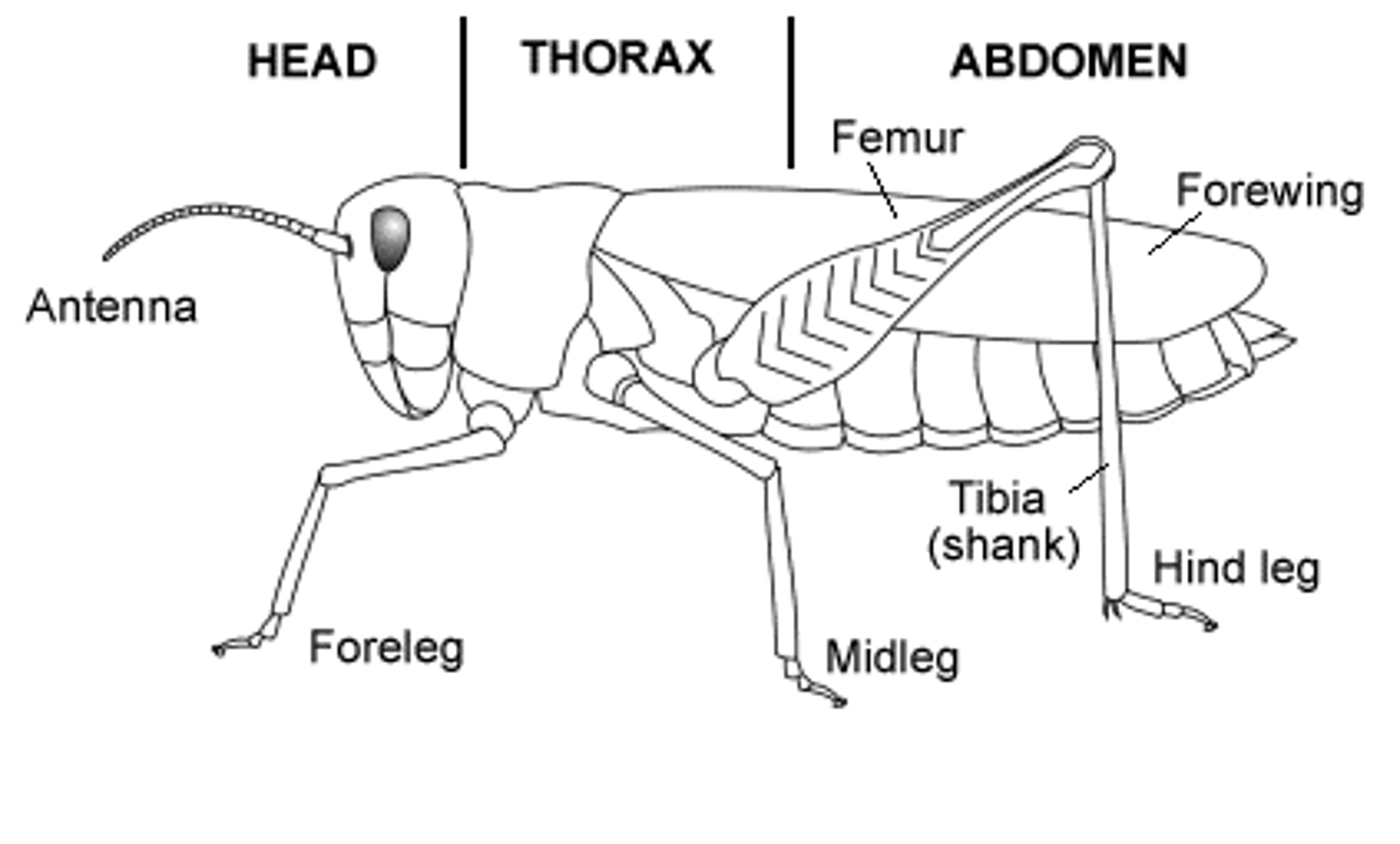
segmentation
the division of the body of an organism into a series of similar parts
bilaterians
Member of a clade of animals with bilateral symmetry and three germ layers.
Diploblastic vs. Triploblastic
Diploblasts have only two germ layers (jellyfish), while triploblasts have all three (most animals)
layers of a triploblastic organism
ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
deuterostomes vs protostomes
deuterostome: blastopore becomes anus
protostome: blastopore becomes mouth
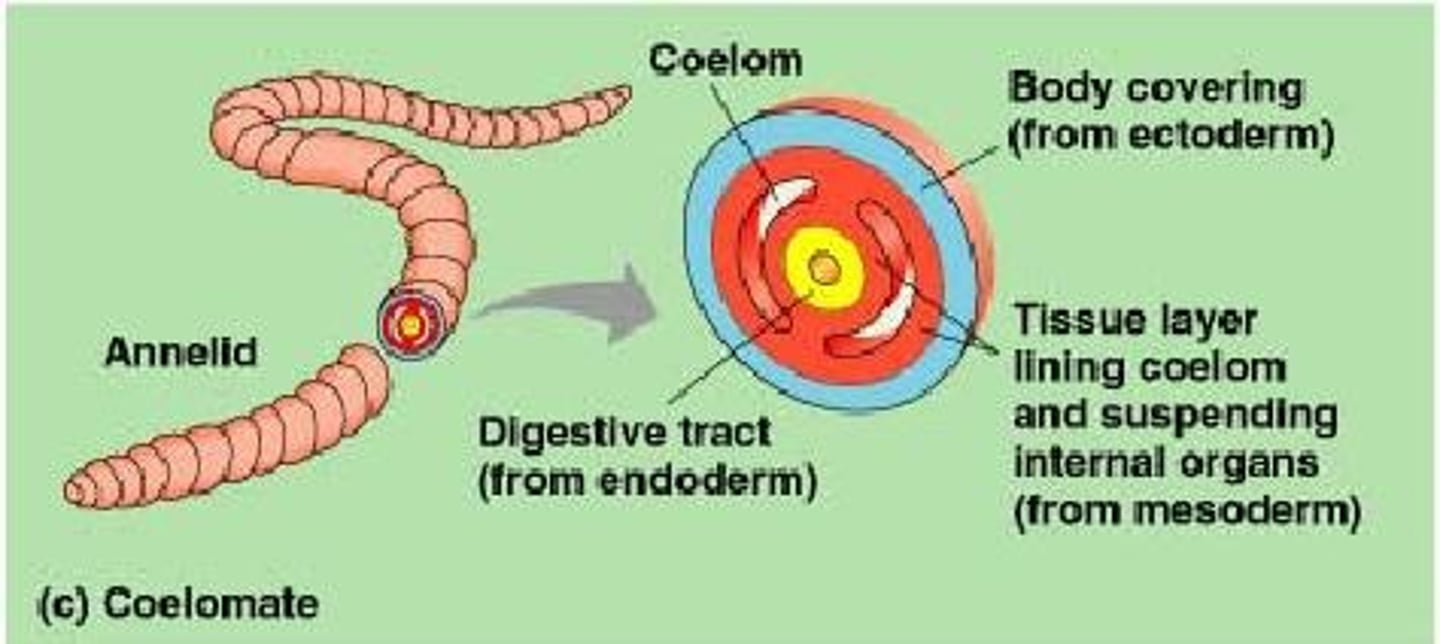
coelom
A fluid-filled body cavity which cushions the internal organs against hard blows to the body and enables the body to turn without twisting these organs.
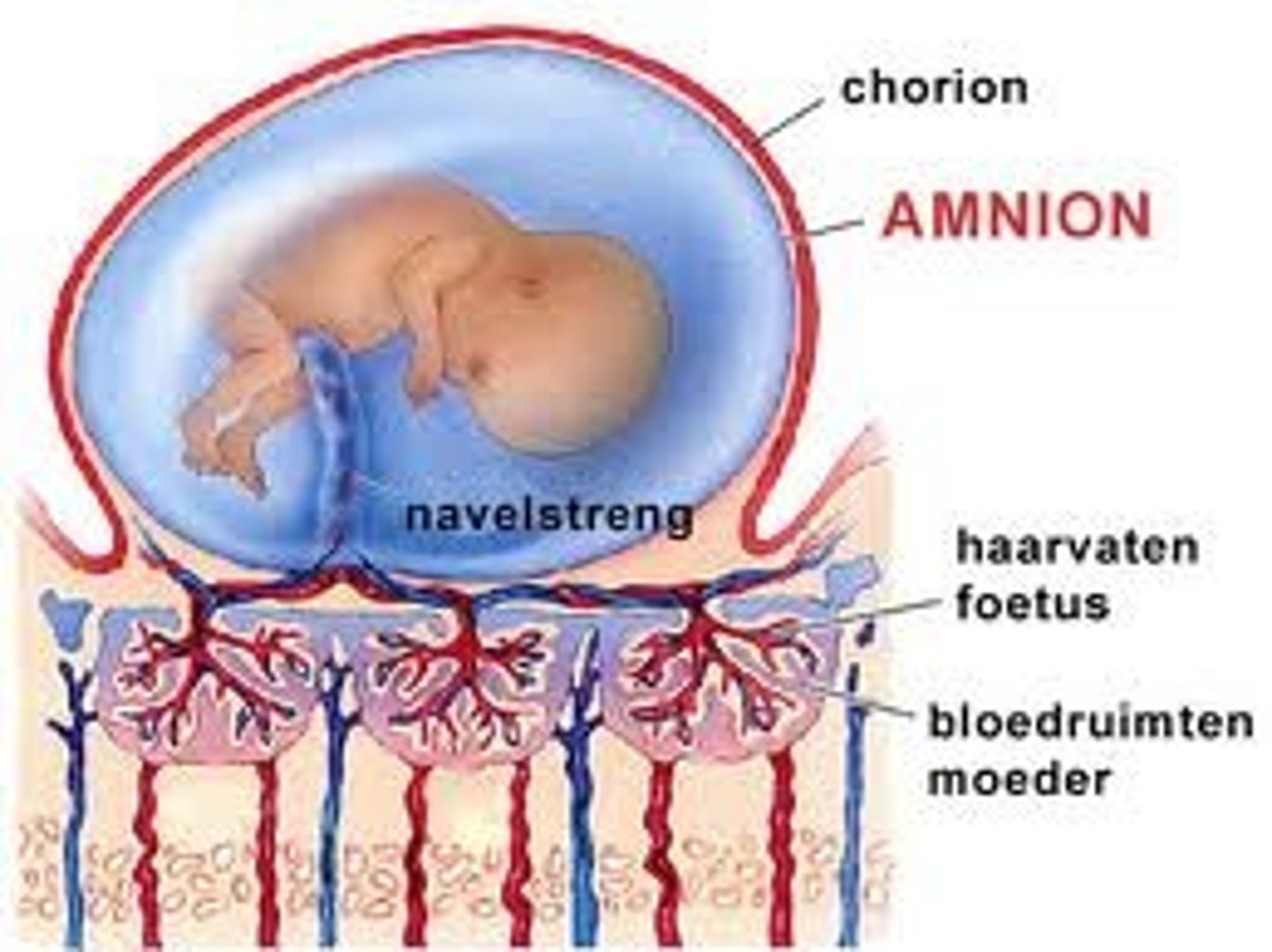
amnion
more freedom from water for reproduction
a membrane surrounding a fluid-filled cavity that allows the embryo to develop in a watery environment
later developmental stages of bilaterians
- larva (in some), a free-living stage different in form from adult
- Juvenile
- Adult
what changes at a cellular level during animal development
- cell form
- cell to cell interactions
- cell position (unique to animal development)
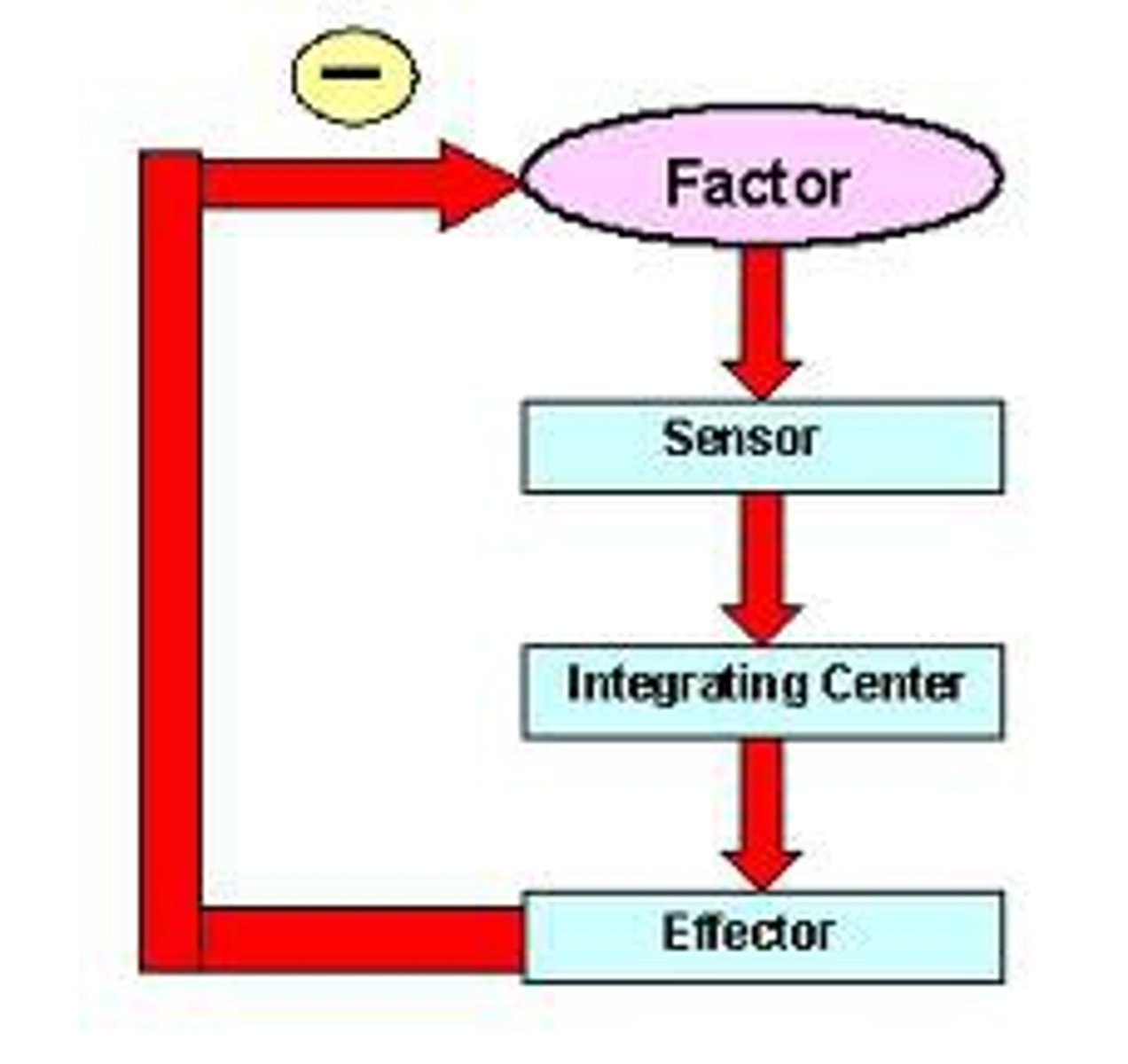
negative feedback loop
cambrian explosion
The body plans characteristic of most bilaterian phyla took shape in this transition period
relatively short time with a huge accumulation of new characters - lots of new stuff appearing in a short time is not normal, hence, "transition
brachiopod fossils
Majority of 'shells' would be from brachiopods, not a modern mollusk as we see today - clams, snails, etc.
However, at the end of the Permian (252 mya) mass extinctions had wiped out most genera living in oceans