TOPIC 4: Equilibrium Price and Quantity & Elasticity of Demand and Supply
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Output or Product/Goods Markets
Equilibrium Price and Quantity
In markets where goods and services are being sold, also known as __________, firms are the producers of outputs, while households buy them
Input or Factor Markets
Equilibrium Price and Quantity
In markets where the factors of production (like labor or capital) are sold, also called __________, households sell resources to firms
1) Buyer
2) Seller
Equilibrium Price and Quantity
We shall assume that in these two markets (Input/Factor and Output/Product/Goods Markets, neither the 1)__________ nor the 2)__________ can influence the market price.
Market Equilibrium
Equilibrium Price and Quantity
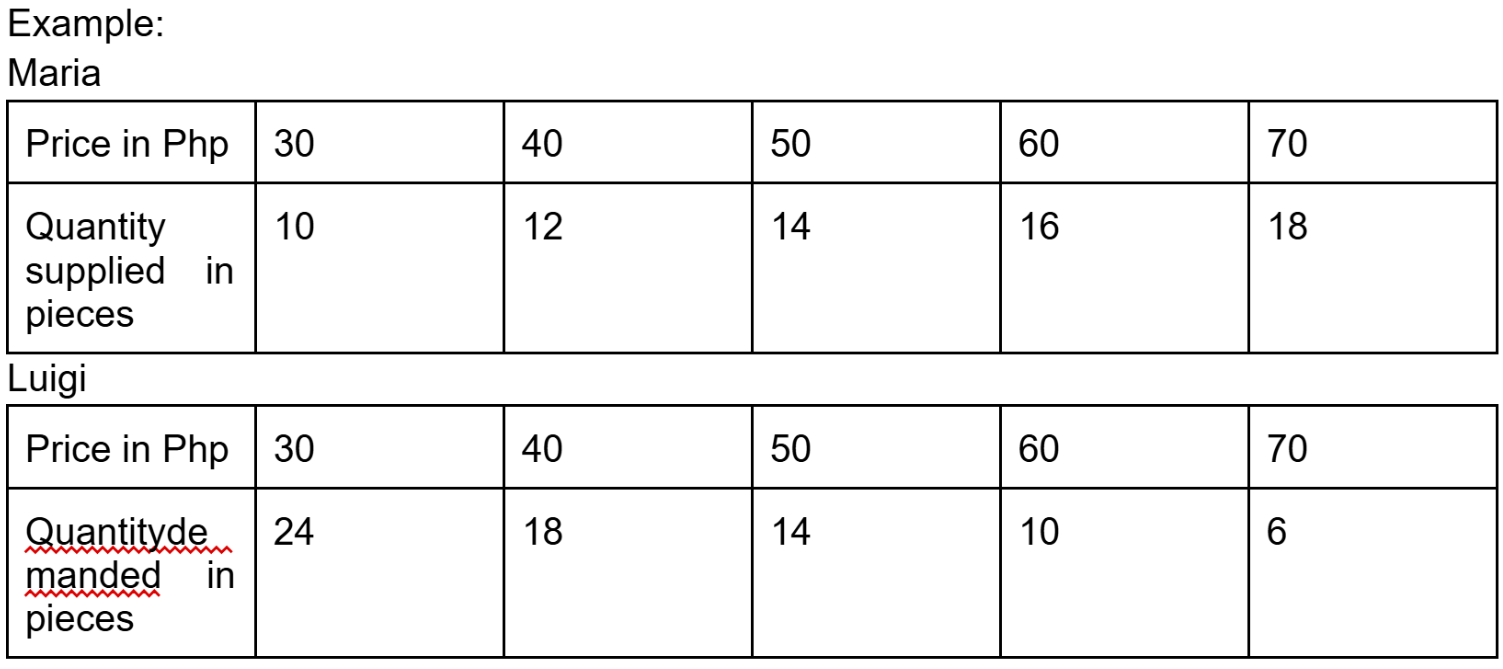
By inspection, we can see that the quantity supplied by Maria is equal to the quantity demanded by Luigi when the price is at Php 50.00. This means that both of them agree to buy and sell 14 pieces of cupcakes at a price of Php 50.00. This implies that this price-quantity combination is the most likely market outcome in this case.
We call this situation the _________.
Market Equilibrium
Equilibrium Price and Quantity
_________ is achieved when both buyers and sellers in the market agree to buy and sell a resource at a particular price.
Equal
Equilibrium Price and Quantity - Market Equilibrium
At the equilibrium price, the amount that buyers want to buy is _________ to the amount that sellers want to sell.
No reason for prices to change as long as other things remain unchanged
Equilibrium Price and Quantity - Market Equilibrium
We call this situation an equilibrium because when the forces of demand and supply are in balance, there is _________.
1) Buy and sell a quantity of a resource
2) Particular price
Equilibrium Price and Quantity - Summary
In summary, market equilibrium is the condition when both buyers and sellers in the market agree to 1]_________ (known as the Equilibrium Quantity or Q*) at a 2]_________ (known as the Equilibrium Price or P*).
Balanced
Equilibrium Price and Quantity - Summary
When the forces of demand and supply are _________, there is no reason for prices to change as long as other things remain unchanged.
Intersection of the Supply and Demand Curves
Equilibrium Price and Quantity - Summary
Graphically, the market equilibrium is represented by the _________.
Elasticity
Elasticity of Demand and Supply
What is the measure of the responsiveness of one variable to changes in another?
Price Elasticity
Elasticity of Demand and Supply
What type of Elasticity does the variable Ep refer to?
Income Elasticity
Elasticity of Demand and Supply
What type of Elasticity does the variable Ey refer to?
Cross Elasticity
Elasticity of Demand and Supply
What type of Elasticity does the variable Exy refer to?
Price
Elasticity of Demand and Supply
Price elasticity of demand is the responsiveness of a product’s _________ to changes in quantity demanded.
Inversely Related
Elasticity of Demand and Supply
The value of elasticity is negative because the price and quantity demanded are _________.
Absolute Terms
Elasticity of Demand and Supply
Elasticity is talked about in __________.