Structure of Skeletal Muscle & Sliding Filament Model
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
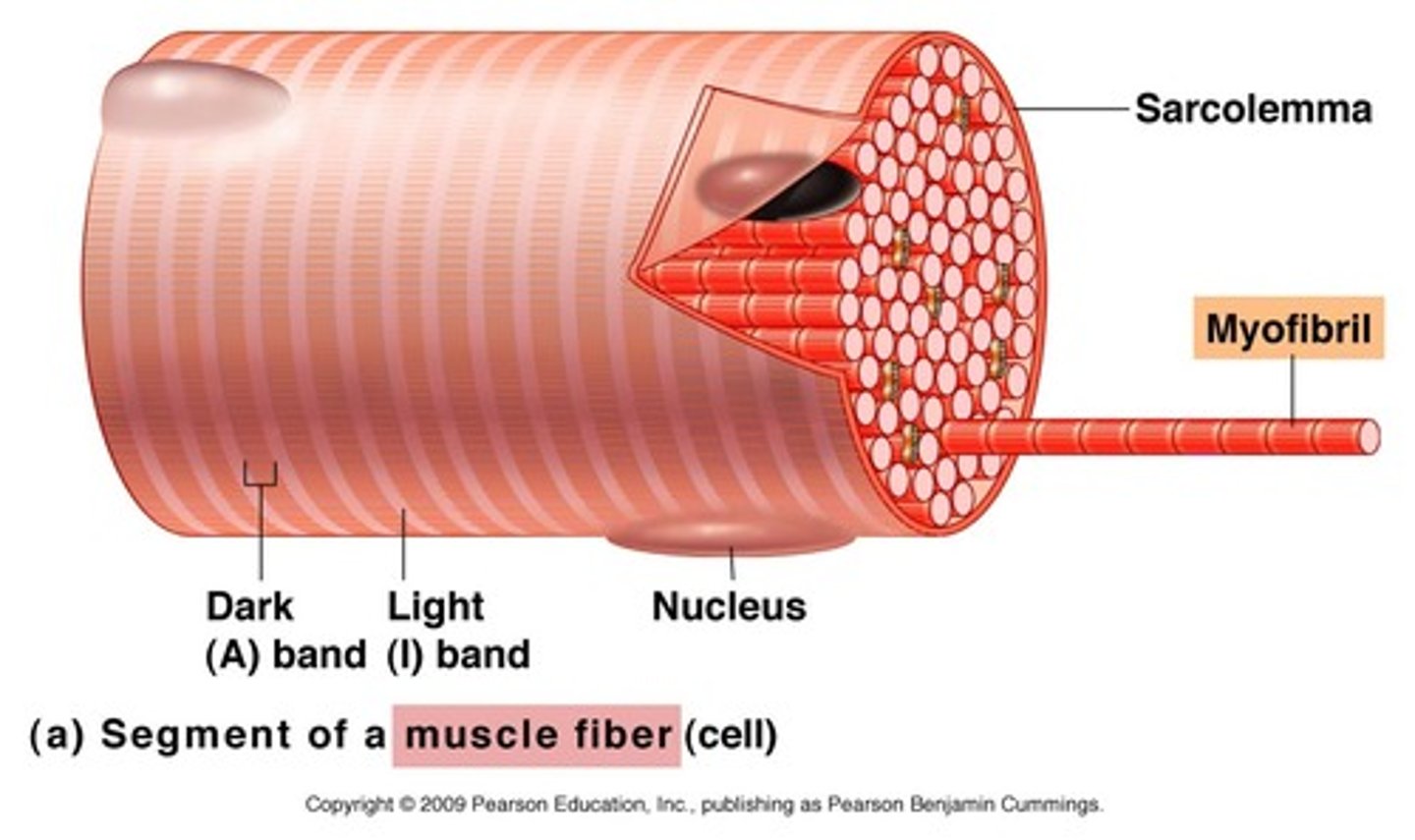
Sarcolemma
Plasma membrane of muscle fibres
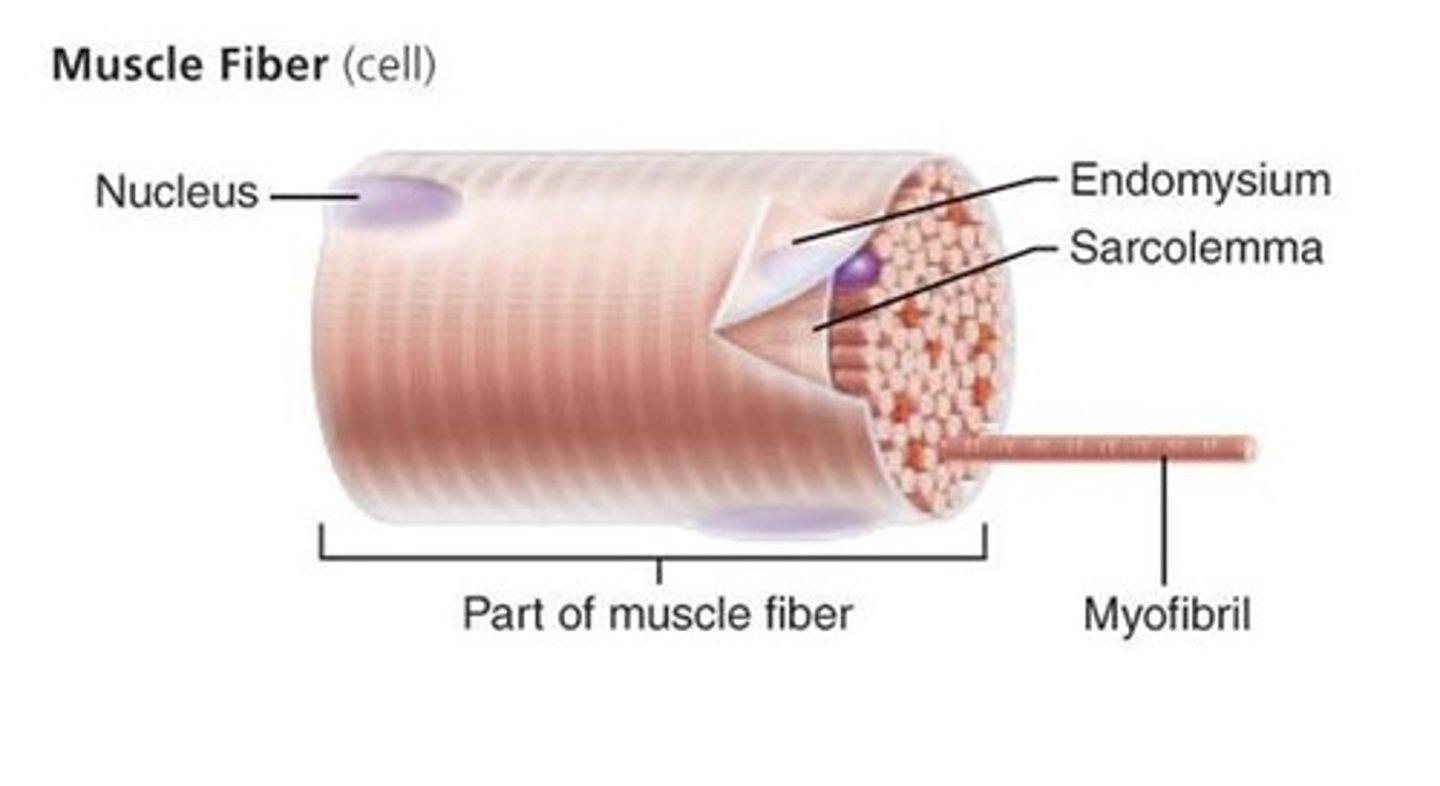
Sarcoplasm
Cytoplasm within a muscle fibre
T-tubules
Parts of the sarcolemma fold inwards to help spread electrical impulses throughout the sarcoplasm.
It ensures the whole fibre receives the impulse to contract at the same time.
What do muscle fibres have a lot of?
Mitochondria to provide ATP that is needed for muscle contraction.
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
A modified version of the endoplasmic reticulum.
Extends throughout the muscle fibre and contains calcium ions required for muscle contraction
What does each muscle fibre contain?
Myofibrils
Myofibrils
Long, cylindrical organelles made of protein and specialised for contraction.
Lined up in parallel to provide maximum force when they all contract together.
What makes up myofibrils?
Actin
Myosin
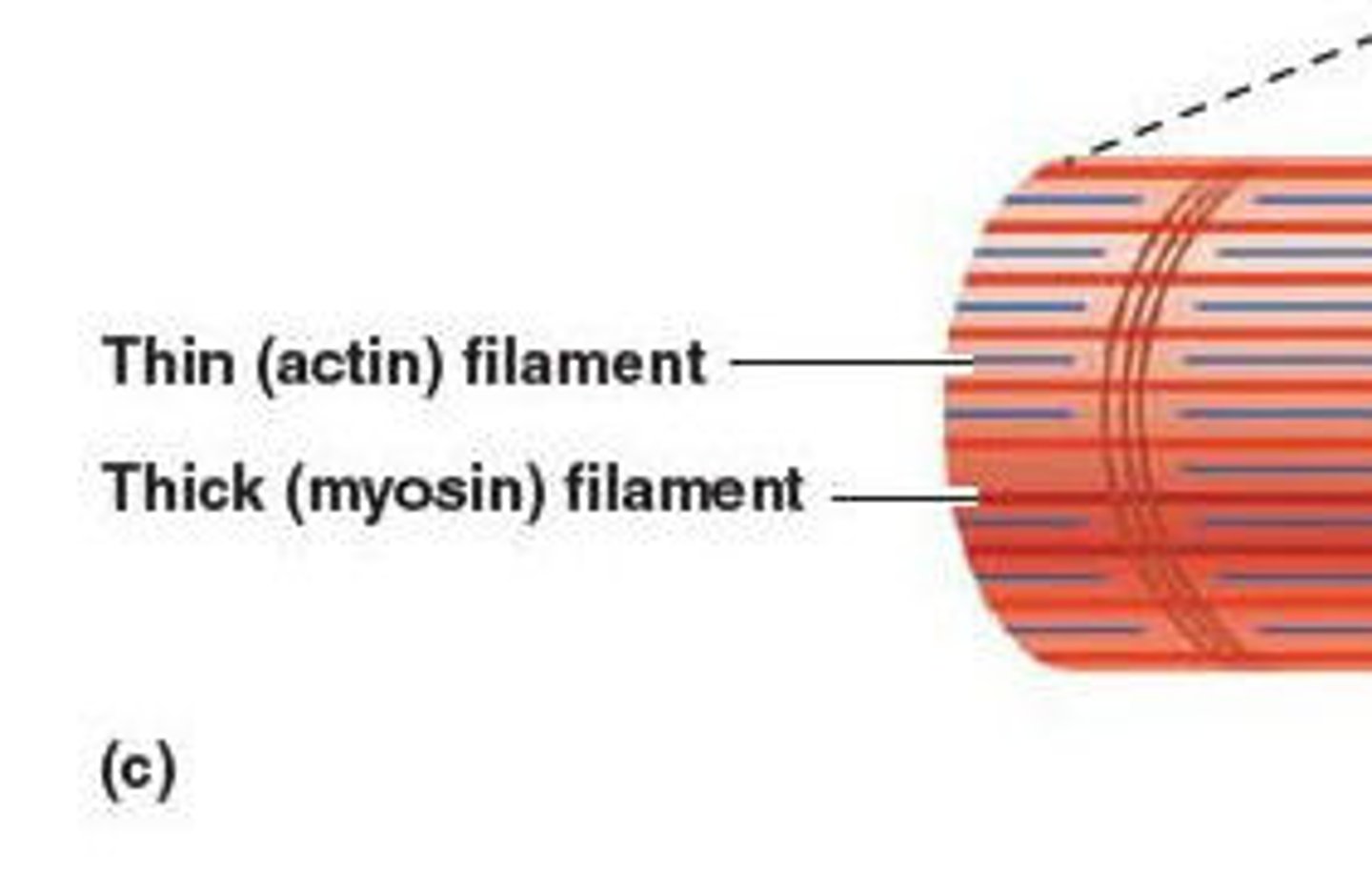
Actin
Thinner filament
Consists of 2 strands twisted around each other
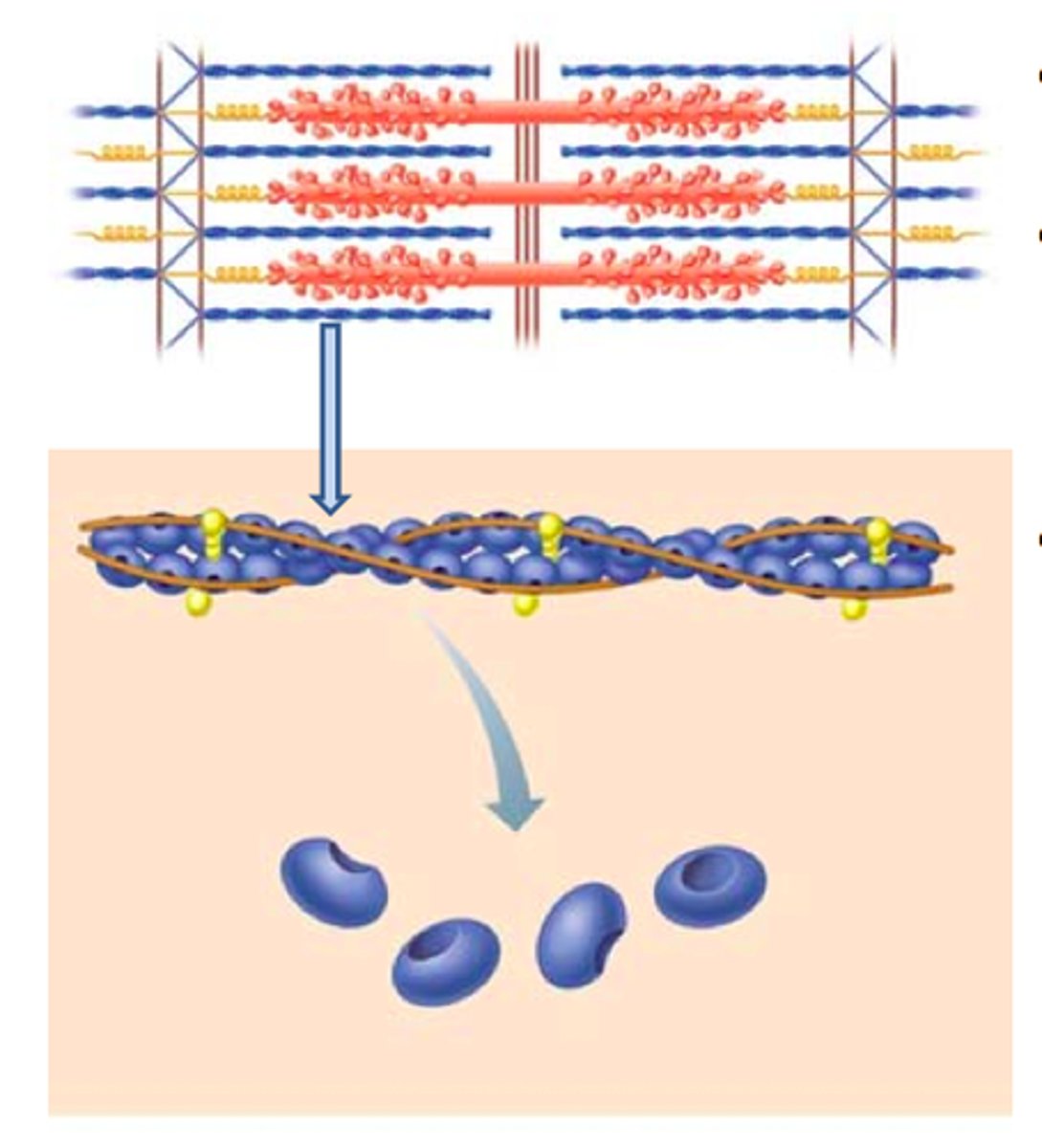
Myosin
Thicker filament
Consists of long rod shaped fibres with bulbous heads that project to one side
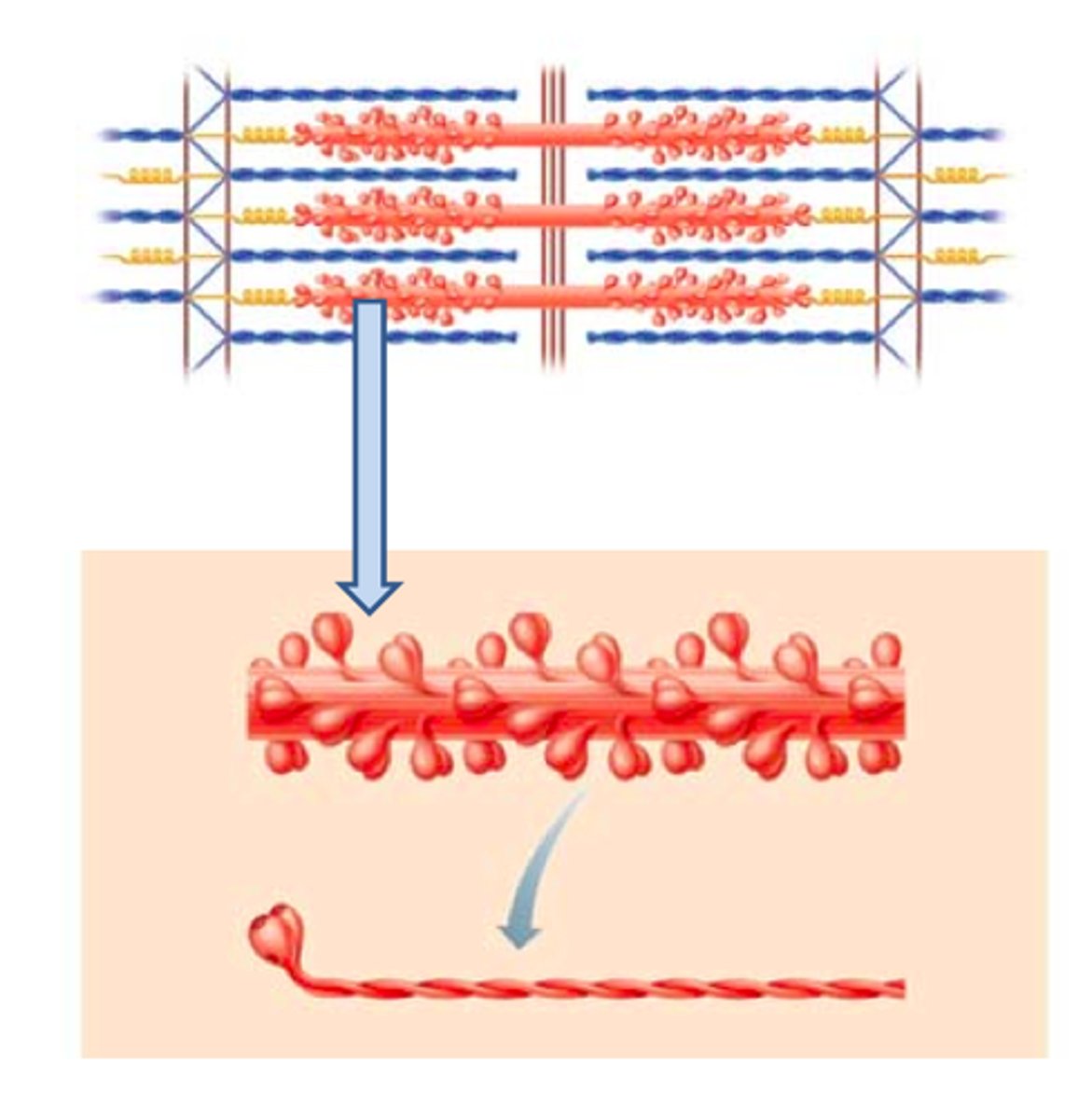
Why do myofibrils have a striped appearance?
They have alternating light bands and dark bands
Light bands
These areas appear light as they are the region where the actin and myosin filaments do not overlap
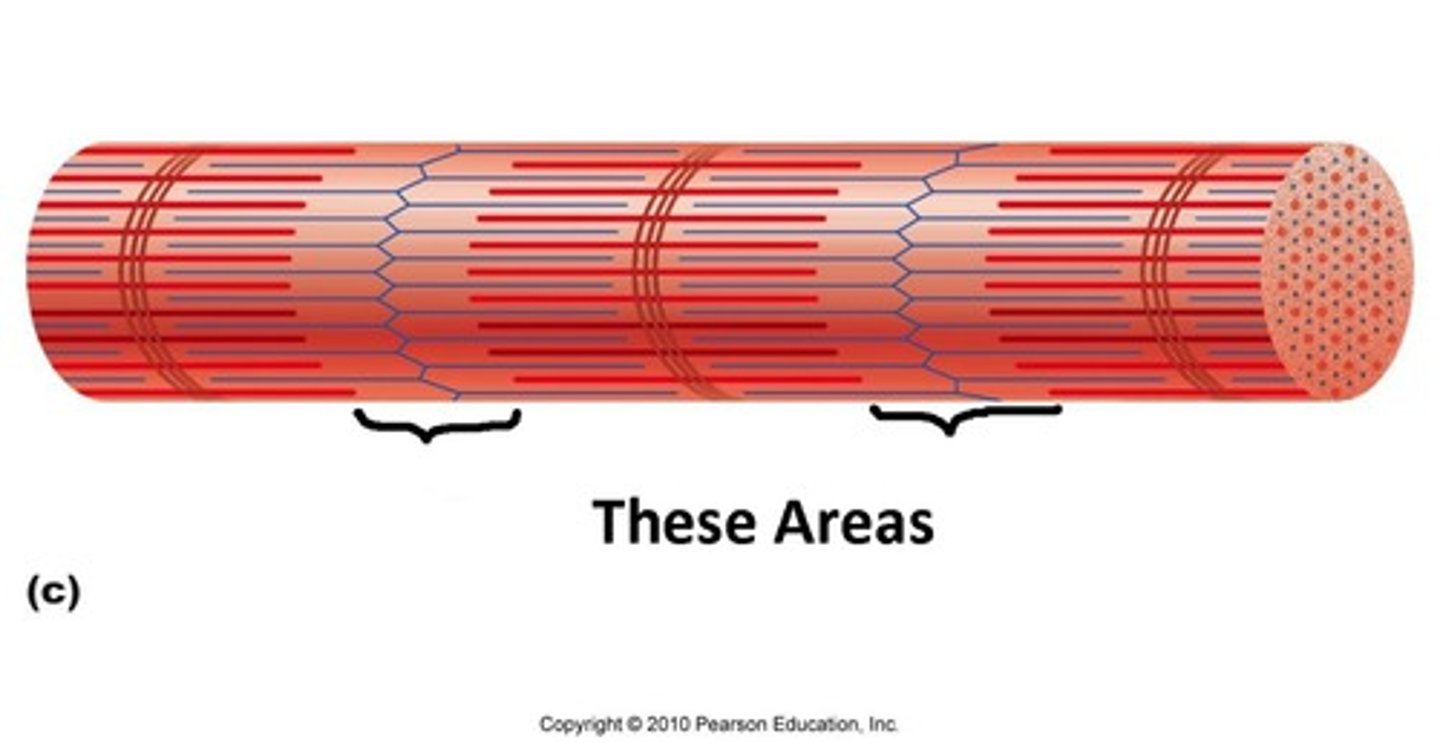
What are light bands also known as?
I-bands
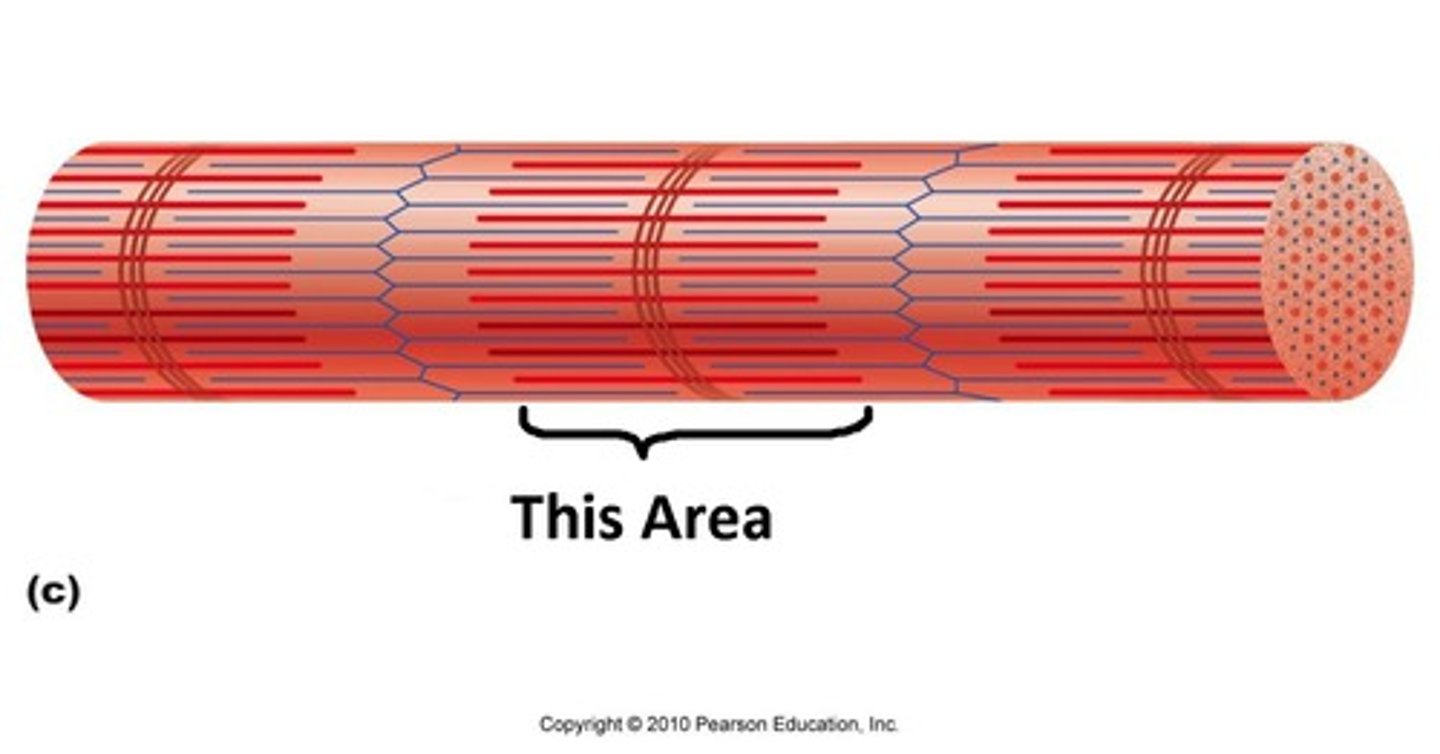
Dark bands
These areas appear dark because of the presence of thick myosin filaments.
The edges are particularly dark as myosin is overlapped with actin
Z-line
The line at the centre of each light band
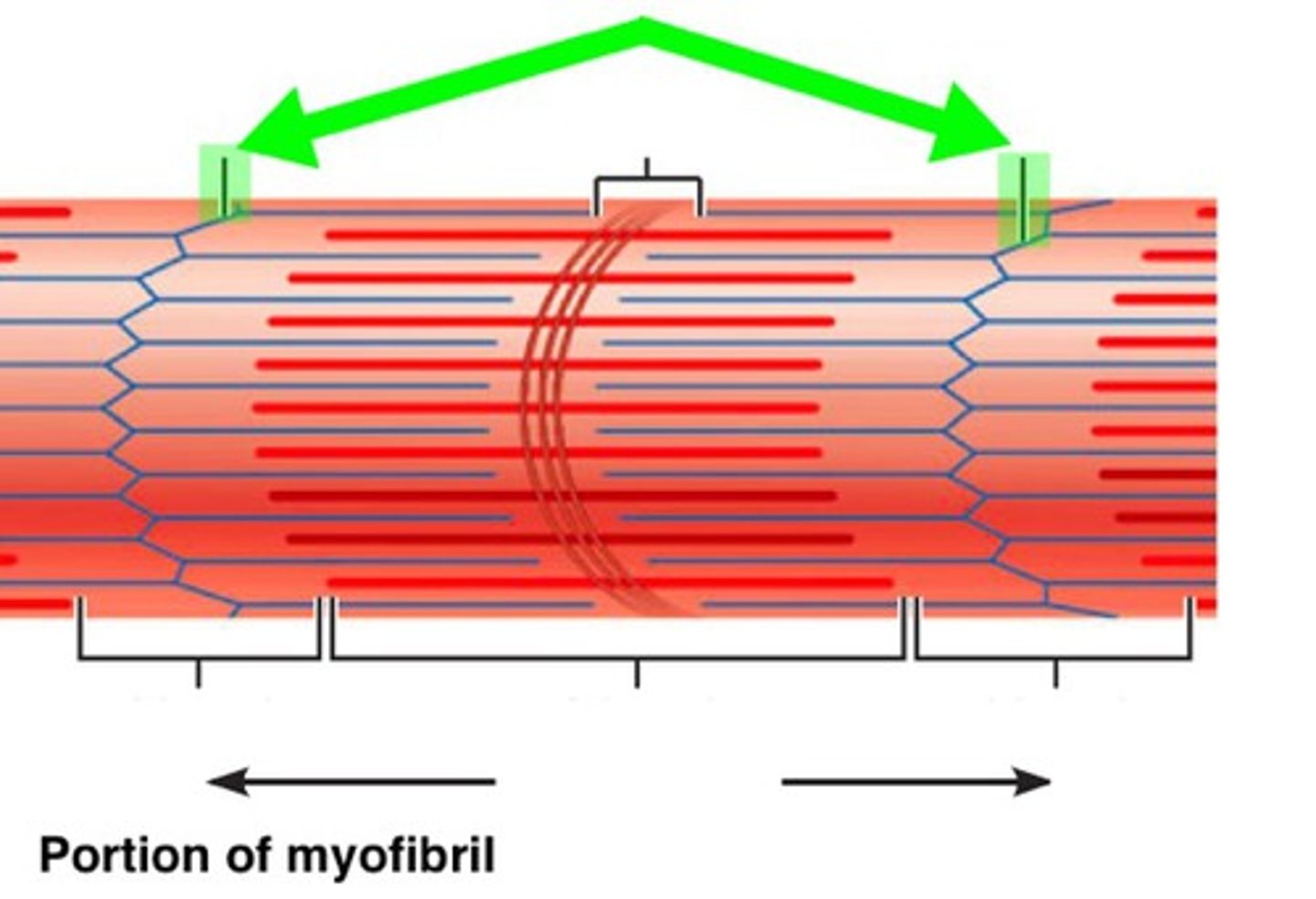
What's the distance between adjacent Z-lines called?
Sarcomere
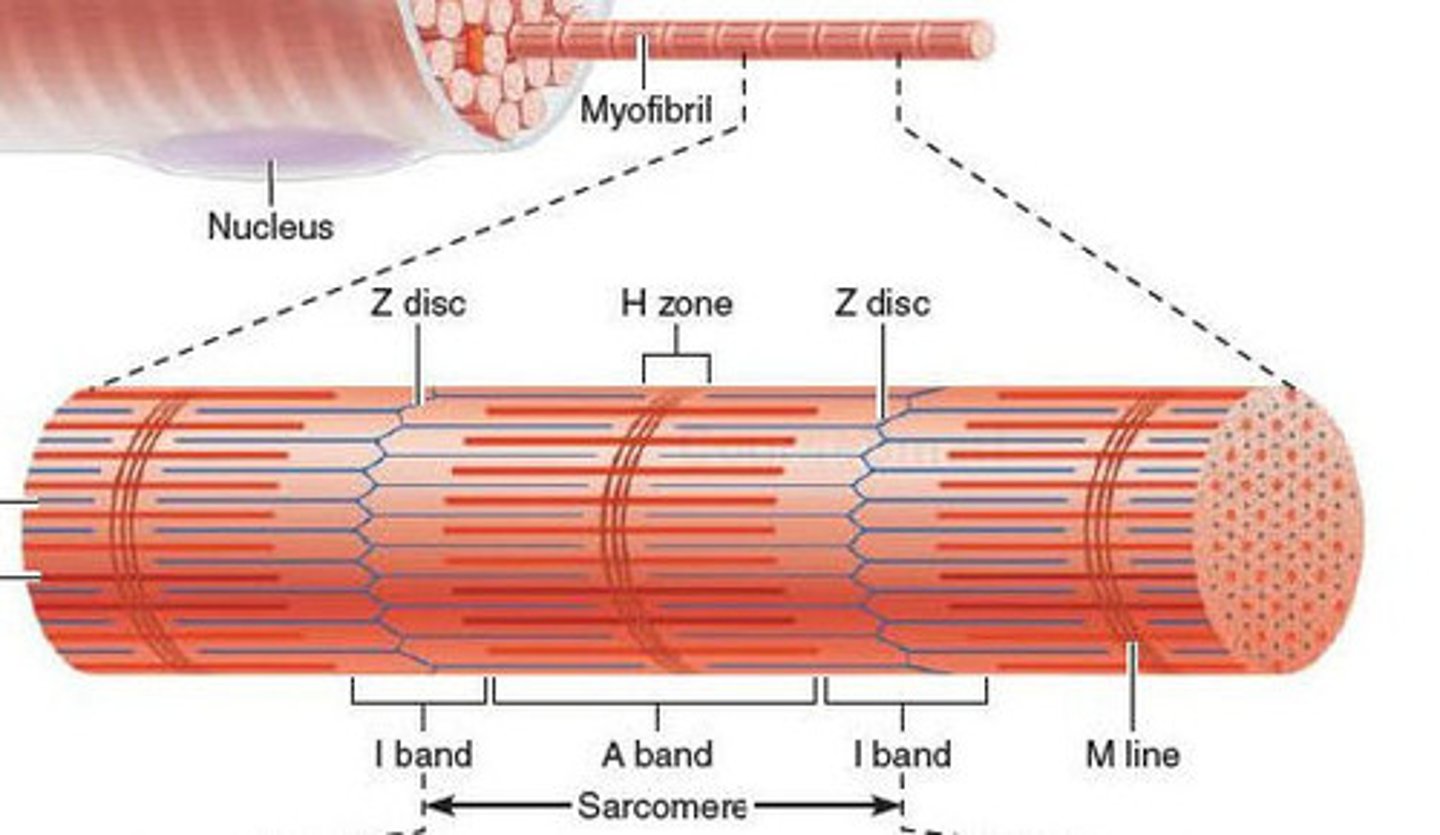
H-zone
This is a lighter coloured region found in the centre of each dark band. O
nly myosin filaments are present at this point.
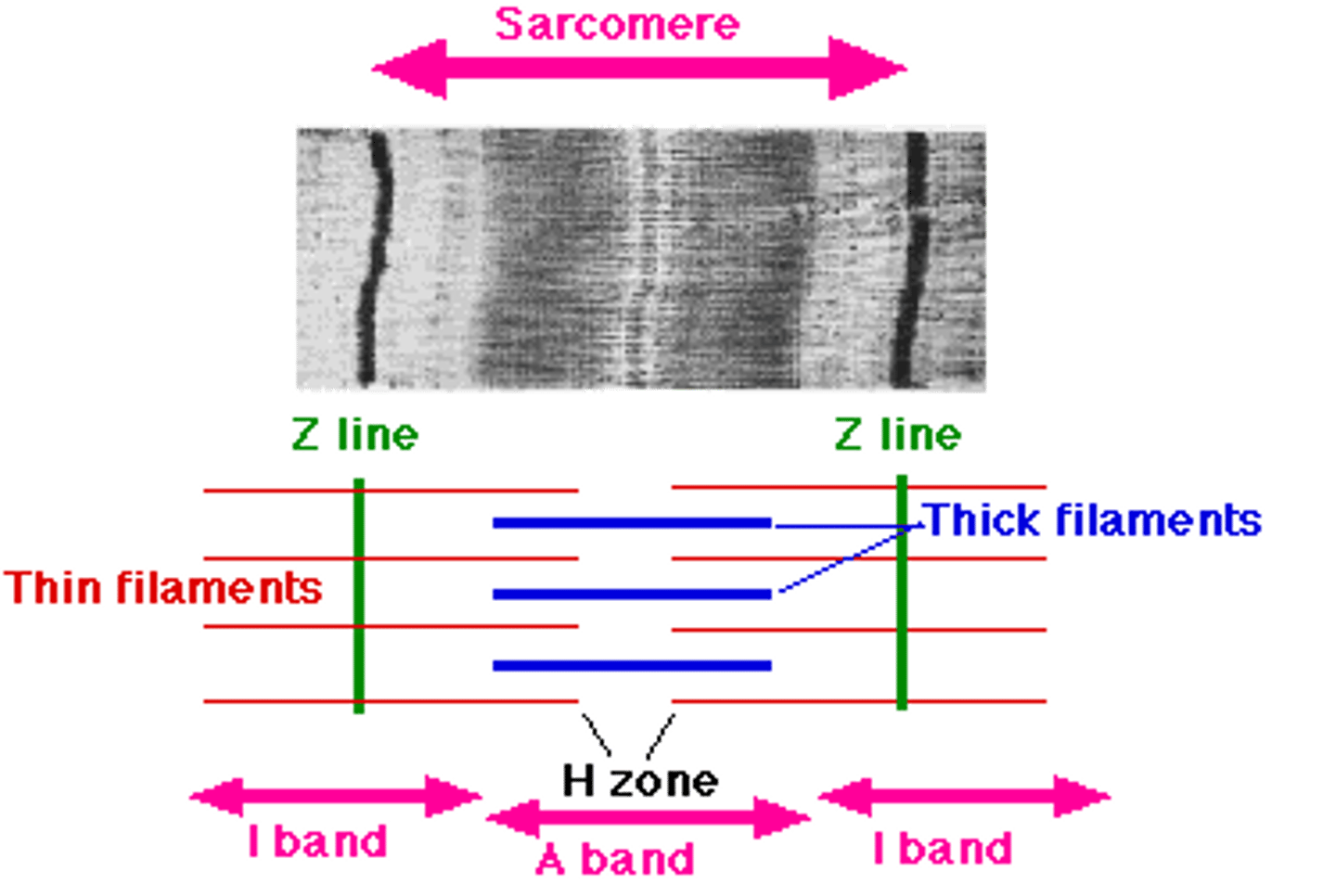
When muscle contracts, what happens to the H-zone?
The H-zone decreases
Drawing a labelled diagram of a sarcomere
- Draw 2 Z-lines
- Ensure heads are present on myosin filaments
- Connect actin filaments to the Z-line
- Label the light and dark bands
- Show the position of the H-zone
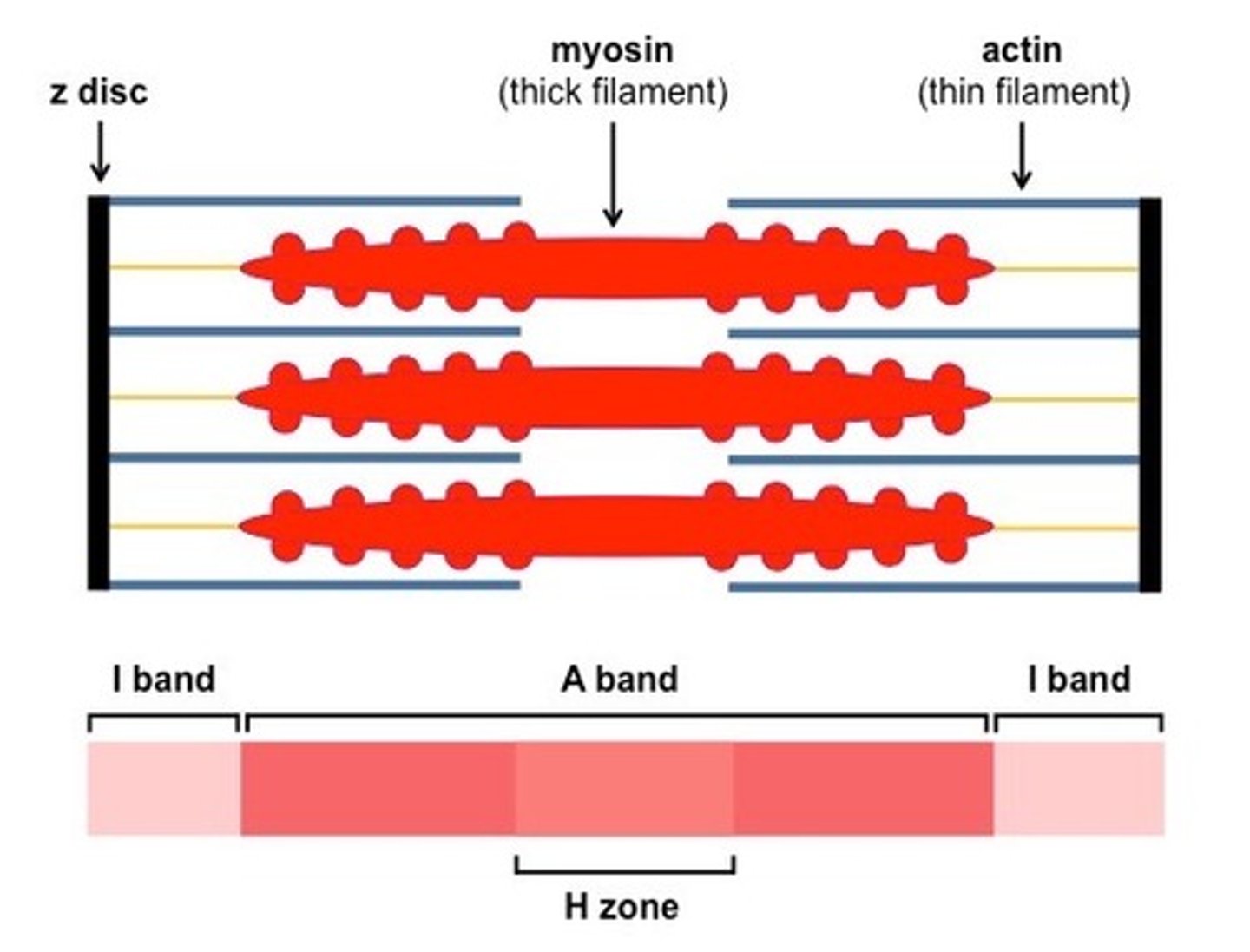
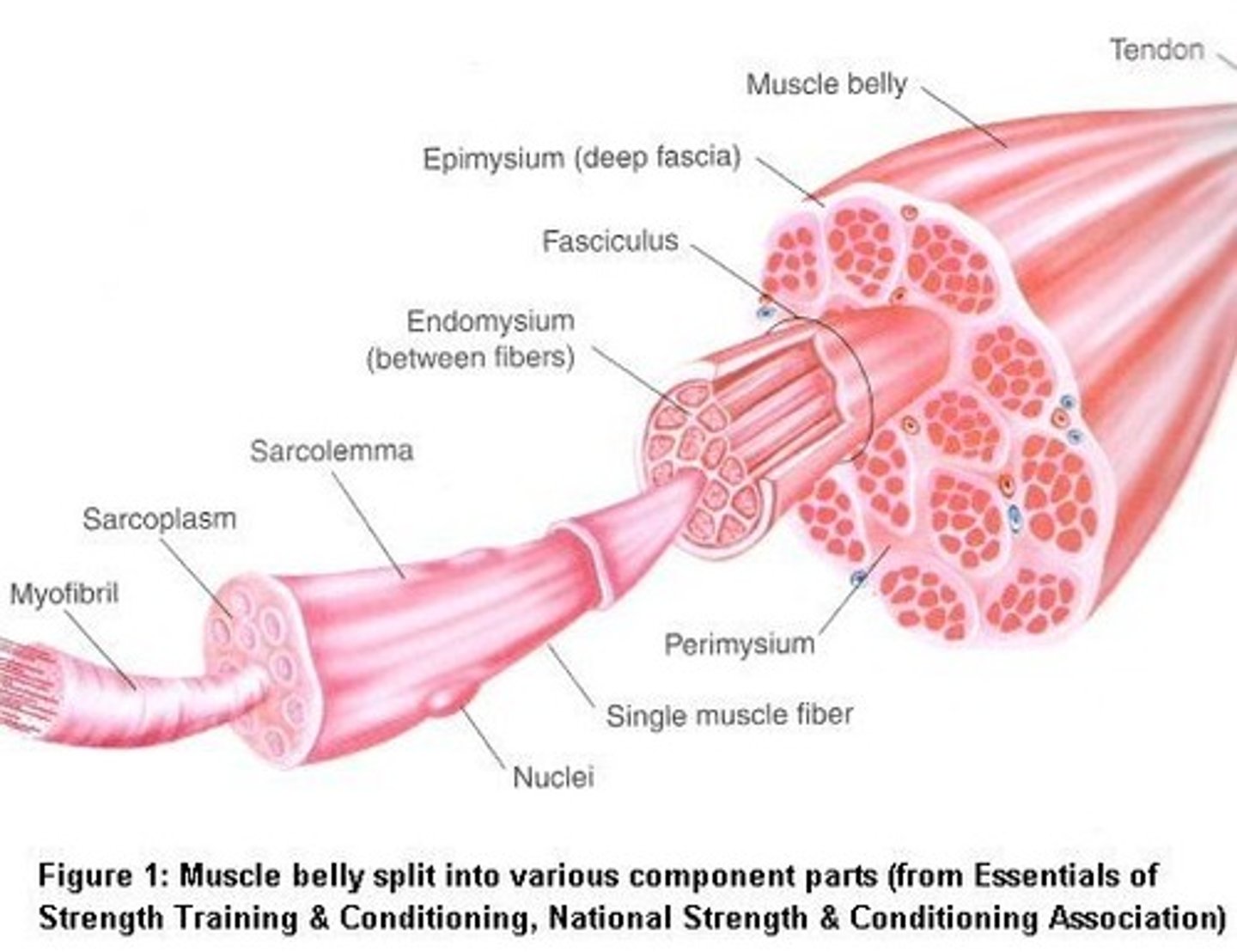
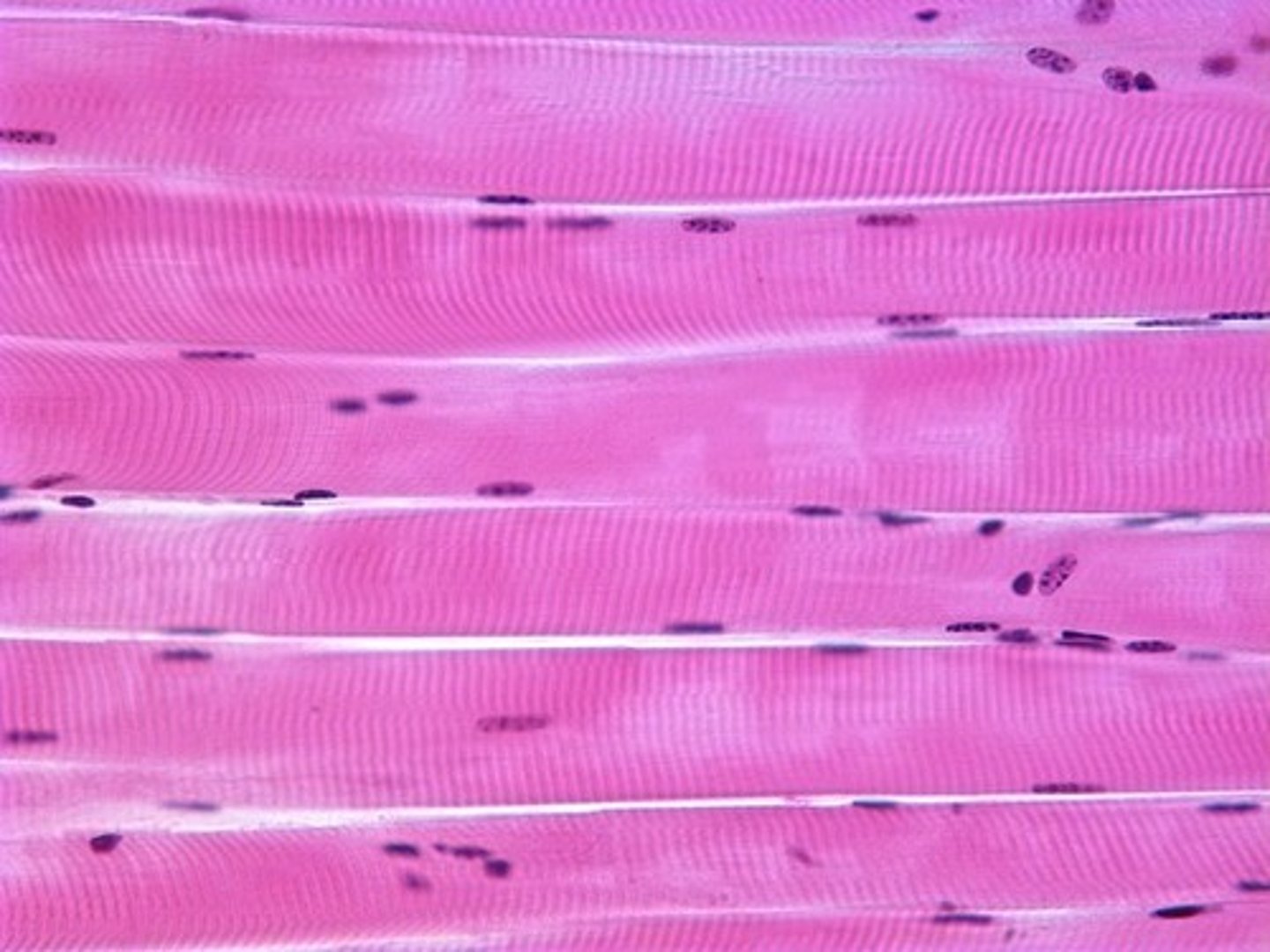
Histology
- Individual muscle fibres, which are long, thin, multinucleated that are striated
- The highly structured arrangement of sarcomeres which appear as dark (A-bands) and light (I-bands)
- Streaks of connective and adipose tissue
- Capillaries running in between the fibres
During contraction, what happens?
The myosin filaments pull the actin filaments inwards towards the centre of the sarcomere.
What happens to the structure of the myofibril during contraction?
- Light band becomes narrower
- Z lines move closer together, shortening the sarcomere
- H zone becomes narrower
- Dark band remains the same width
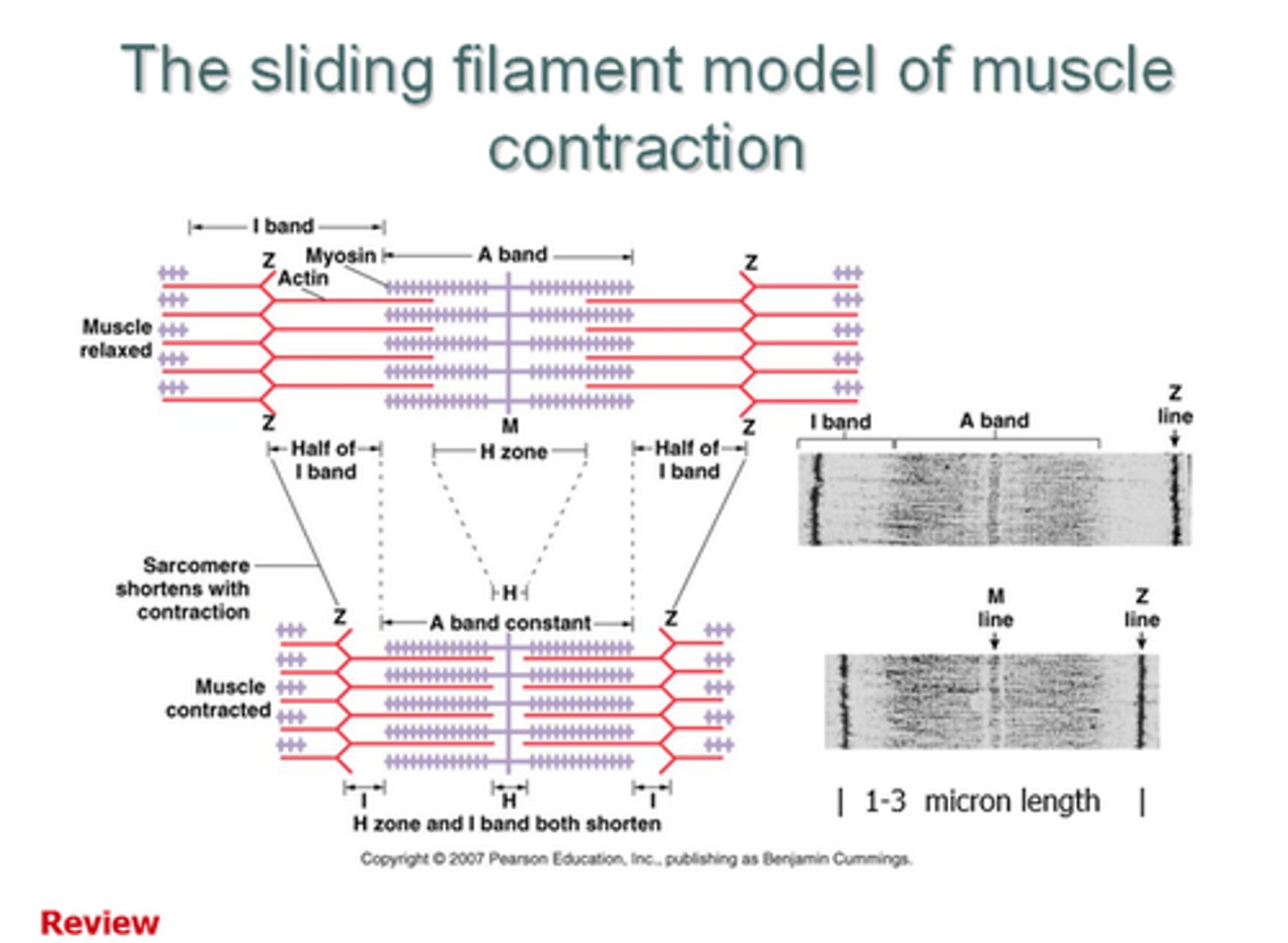
What does the simultaneous contraction of sarcomeres mean for the myofibrils and muscle fibres?
It makes the myofibrils and muscle fibres contract too.
When sarcomeres return to their original length...
...the muscle relaxes