psych chapter 4 and 9
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Developmental psychologist study?
changes in people from conceivement to death
what ways do we develop?
physically, cognitively, socioemotionally
what are the development stages?
prenatal, neonatal, infancy, childhood, adolescence, middle adulthood, late adulthood/elderly
when is prenatal period
in the womb
what are teratogens?
anything mom does that can cause birth defects (alcohol, drugs)
toxoplasmosis
type of blood poisoning
ex: can’t change cat litter bc bacteria is sniffed and effects baby, eating raw fish and meat
APGAR test?
test on newborns to asses overall health, 7 or above is good and 10 is max
neonatal period
newborns are good for nothing, tests newborn reflexes
perceptual development of a newborn
newborn vision is bad, hearing is good, visual preference (likes looking at faces)
infancy socioemotional development
1st year of life is very important, needs secure attachment to caretaker
what is the experiment on 1 year olds and their mom leaving them and coming back called?
strange situation (aimsworth and bowlby)
secure attachment
children who show some distress when their caregiver leaves but are able to compose themselves quickly when the caregiver returns
insecure attachments
avoidant and resistant attachment
avoidant attachment
when an infant or child does not consistently receive the care and attention that they need to develop a healthy relationship with their parent or caregiver
resistant attachment
extremely distressed by the separations and cannot be soothed at reunions, essentially displaying much distress and angry resistance to interactions with the caregiver
development theories by who? (cognitive development)
Jean Piaget (Swiss psychologist)
Schemes
mental models of people, places, events. as we age we change our schemes
how do schemes change
assimilation: including new info to your existing scheme
ex: you learn what traits a dog has, furry, 4 legs, barks
accommodation: describes how we later adjust our schemas
ex: thinks a cat is a dog bc furry and 4 legs but meows so parents tells kid that it is a cat
4 stages of development (SPCF)
sensorimotor stage, preoperational, concrete operational, formal operational
sensorimotor stage
age: birth-2yrs
motor skills
object permanence, realizing things exist without seeing it
preoperational stage
age: 2-7
limitations = egocentric, animism, centration
egocentric (can’t understand other perspectives)
animism (thinks everything has a life to it)
centration (can only focus on one/center part of a problem)
conservation not developed (cannot tell diff between volume)
straightforward thinking, no reversibility
concrete operational stage
age: 7-12
beginning adult logic
decentration
reversibility
formal operational stage
age: 12+
logic, abstract reasoning
creativity, hypothetical reasoning
erik eriksons psychosocial theory
8 stages, birth to death, developmental crises
what re the 8 stages of erik eriksons psychosocial theory?
Trust vs. Mistrust (0-1)
Autonomy vs. Shame & Doubt (1-2)
Initiative vs. Guilt (2 - 6)
Industry vs. Inferiority (6 - 12)
Identity vs. rule diffusion (12 - 20)
Intimacy vs. Isolation (20 - 40)
generativity vs. Stagnation (40 - 60)
Integrity vs. Despair (60 +)
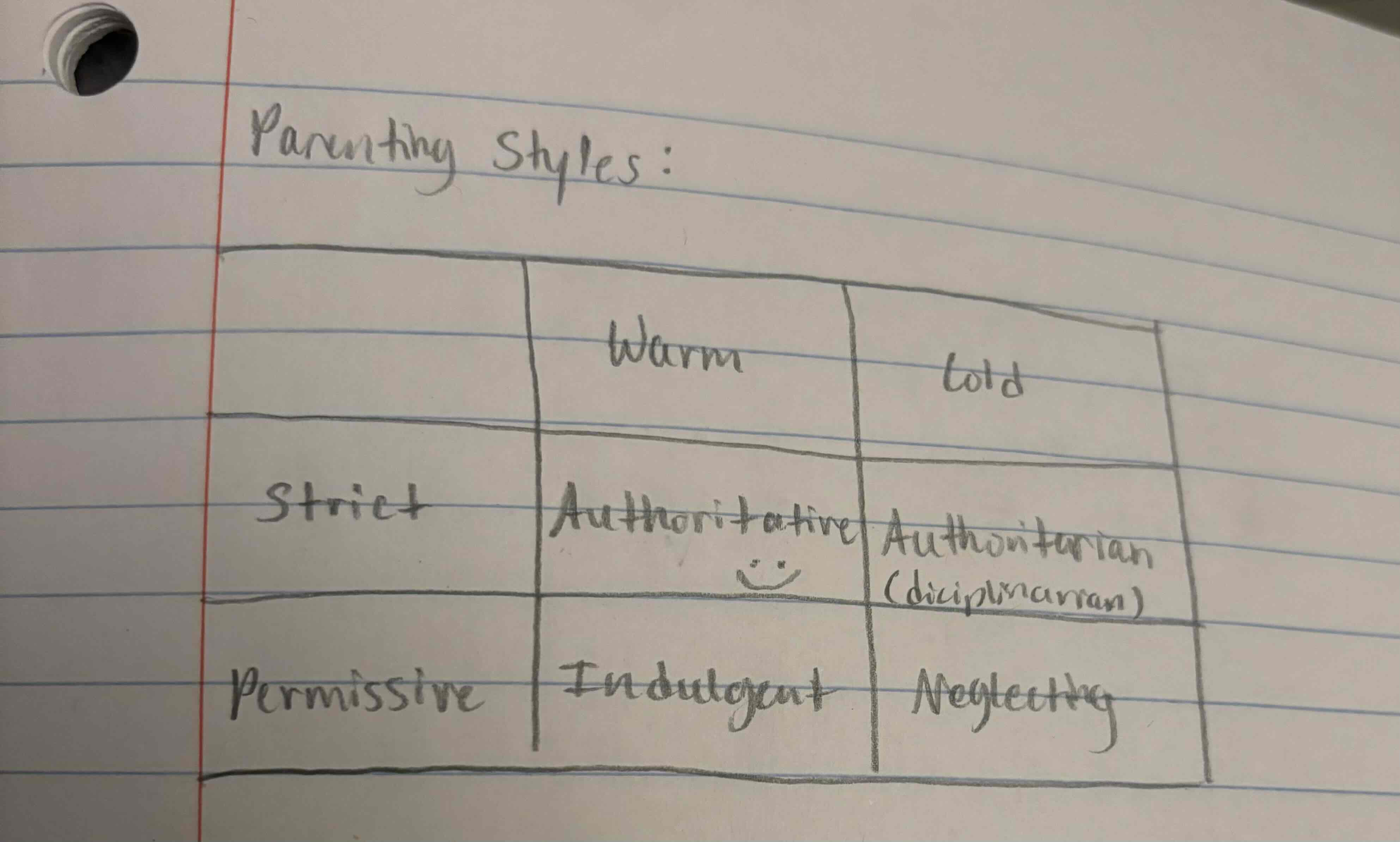
parenting styles
authoritative = good parenting
authoritarian = dictarian
indulgent and neglecting
strict vs permissive
sensation
deals with senses activating
perception
piecing senses all together in the brain
sensation neurons?
sends data to brian to put tgt
cornea
like plastic covering to protect the eye
iris
color part, regulates light in and out
pupil
hole in eye that changes size to let light into the eye, bright light, small pupil, dark, big pupil
lens
help you see by putting things into focus
cataract
cloudy lenses
floaters
dead cells in fluid
photoreceptors in eye?
rods, cones
rods
back of retina
black and whites
low light/darkness
cones
cones work well in light
in fovea (most sensitive part)
depth perception
3d takes 2 eyes
monocular depth cues
interposition
if one item blocks other it is closer
linear perspective
parallel lines are wider the closer it is and less wide further away (a road)
relative size
how much space does somebody take up
closer guy is bigger than smaller guy far way but we know that they are about the same size
texture gradient
closer details, farther away we can’t see it
atmospheric perspective
clear close up, foggy far away
shadow/shading
circle to sphere
motion parallax
things close move faster than things far away (on train looking at trees and mountains)
perceptual constancies
size constancy, when things move closer/farther, know it’s abt same size
shape constancy, shape remain same, from diff angles
color constancy, color same in diff light (gold vs blue dress)
context guide our perceptions
hearing
measured in hertz, freq
freq is faster higherpitched
decibels is volume
the ear parts
outer ear
middle ear
inner ear
cochlea
bottom up processing
In bottom-up processing, we allow the stimulus itself to shape our perception, without any preconceived ideas
top down processing
In top-down processing, we use our background knowledge and expectations to interpret what we see.
backward masking
chemical senses
smell olfaction and taste gustation
where are taste receptors?
papillae on tongue
5 basic tastes
salty
sour
bitter
sweet
umami
flavor = ?
flavor = taste + smell