Eukaryotic Cell Anatomy
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
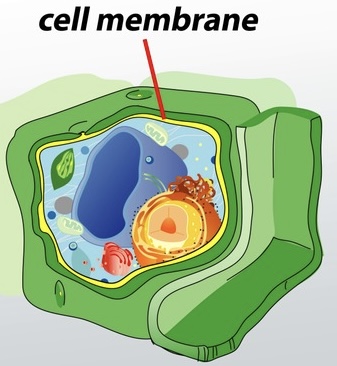
Plasma membrane
Double layer of lipids (mainly phospholipids and cholesterol) with embedded proteins; some proteins span the membrane while others are on one side; outer surface may have attached sugar groups; functions as a selective barrier, controls transport, maintains electrical potential, and enables cell signaling and recognition
Cytoplasm
Region between the nuclear and plasma membranes containing cytosol, inclusions (stored nutrients, pigments, secretory products), and organelles; site of most cellular metabolic activity
Centrioles
Paired cylindrical structures made of nine triplets of microtubules; organize the spindle and asters during mitosis and form the bases of cilia and flagella
Cilia
Short cell-surface projections made of nine pairs of microtubules surrounding a central pair; move substances across the cell surface in a coordinated manner
Flagella
Long cell-surface projections similar to cilia; in humans found only on sperm cells; function in cell movement
Tonoplast
Specialized membrane surrounding the central vacuole in plant cells; regulates movement of ions, nutrients, and wastes into and out of the vacuole and helps maintain turgor pressure and cellular homeostasis
Plasmodesmata
Microscopic cytoplasmic channels that pass through plant cell walls; connect adjacent cells and allow direct transport of water, ions, small molecules, and signaling substances for cell-to-cell communication
Golgi apparatus
Stack of flattened membrane sacs near the nucleus; modifies, packages, and sorts proteins for secretion, lysosomes, or membrane insertion
Intermediate filaments
Protein fibers of varying composition; provide mechanical strength, stabilize cell structure, and help anchor chromatin to the nuclear membrane
Lysosomes
Membrane-bound sacs containing digestive enzymes (hydrolases); responsible for intracellular digestion and recycling
Microfilaments
Thin actin filaments; involved in muscle contraction, cell movement, and maintaining cell shape
Microtubules
Hollow tubes made of tubulin; maintain cell shape, assist in movement, and form structures such as centrioles and spindle fibers
Mitochondria
Double-membraned organelles with folded inner membranes (cristae) and circular DNA; site of ATP production and involved in signaling, cell death, and differentiation
Peroxisomes
Membrane-bound sacs containing oxidase enzymes; detoxify harmful substances and break down hydrogen peroxide using catalase
Ribosomes
Small particles made of rRNA and proteins; free in cytoplasm or attached to rough ER; sites of protein synthesis
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Membranous network studded with ribosomes; modifies proteins, attaches sugar groups, packages proteins into vesicles, and synthesizes phospholipids and cholesterol
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Membranous sacs and tubules without ribosomes; site of lipid and steroid synthesis, lipid metabolism, and drug detoxification
Vesicles
Small membrane-bound structures including transport vesicles, lysosomes, and peroxisomes; involved in transport and metabolism
Nucleus
Largest organelle surrounded by a nuclear envelope; contains nucleoplasm, nucleoli, and chromatin; control center that stores genetic information and directs protein synthesis
Chromatin
Thread-like material made of DNA and histone proteins; contains genes
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane with pores; separates nucleus from cytoplasm, regulates molecular transport, and anchors chromatin
Nucleoli
Dense, non-membrane-bound regions inside the nucleus; sites of ribosome subunit production
Central vacuole (plant cells)
Large membrane-bound compartment; stores ions, wastes, pigments, and protective compounds
Chloroplasts (plant cells)
Membrane-bound organelles containing thylakoids arranged in grana and surrounded by stroma; site of photosynthesis