BIO 202: Chapter 9 Urinary System
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
urinary system
plays critical role in maintaining homeostasis and carries out most functions by the kidneys
functions of the urinary system
filter blood to remove metabolic wastes
regulate fluid, electrolyte, and acid base balance
assists liver in detoxifying certain compounds
produce glucose during starvation
produce the hormone erythropoietin
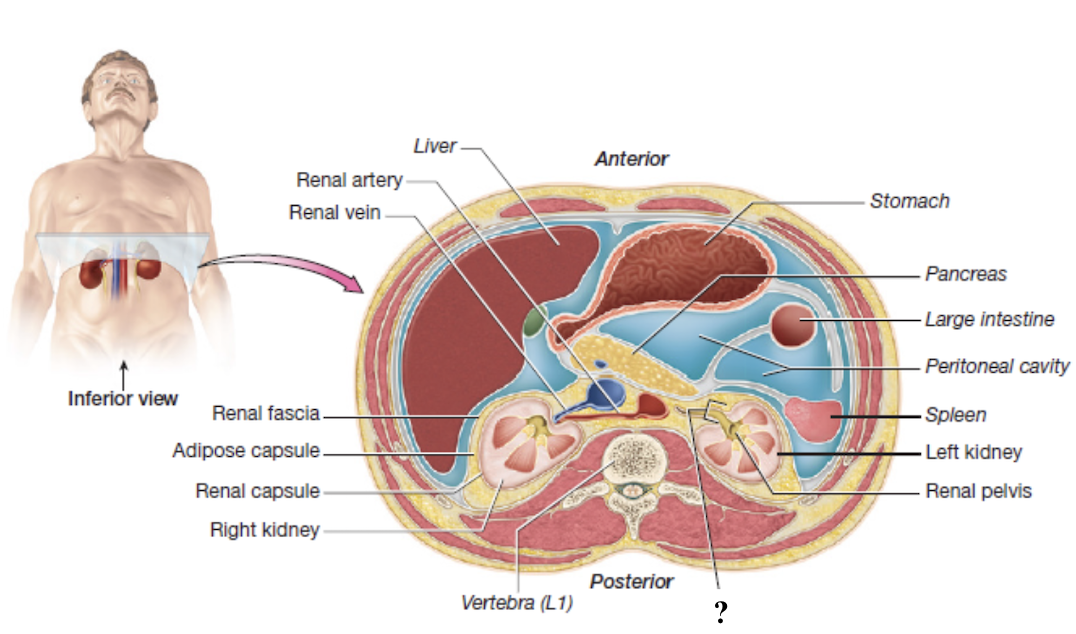
kidneys
paired, retroperitoneal, and encased by external connective tissue layers
renal fascia
superficial layer of dense irregular collagenous connective tissue
anchors the kidneys to the posterior abdominal wall and the peritoneum
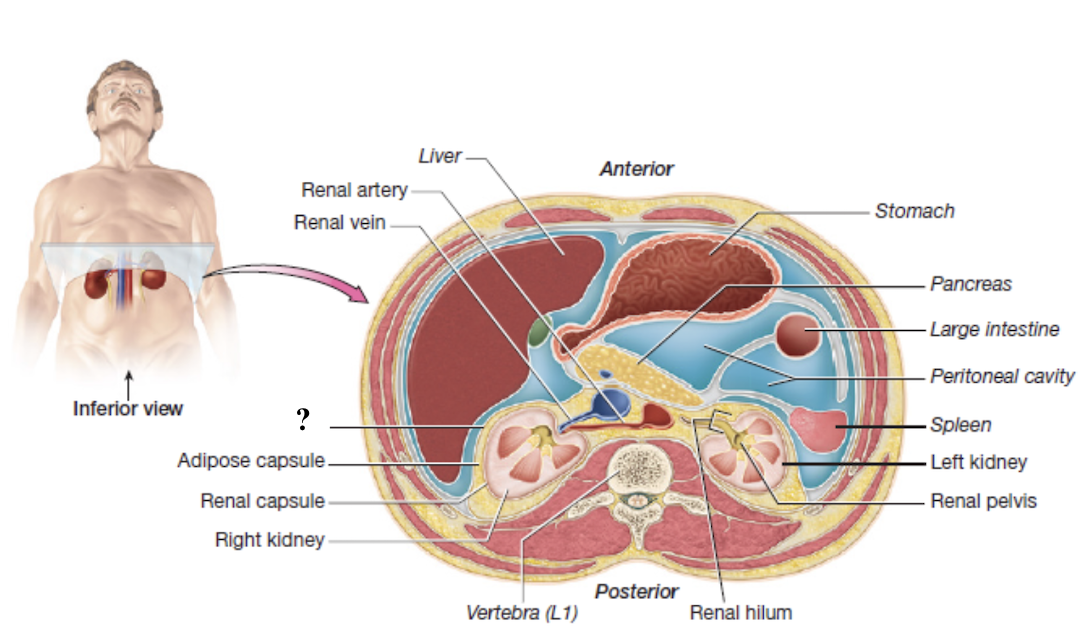
adipose capsule
thick layer of adipose tissue
cushions and holds the kidneys in place
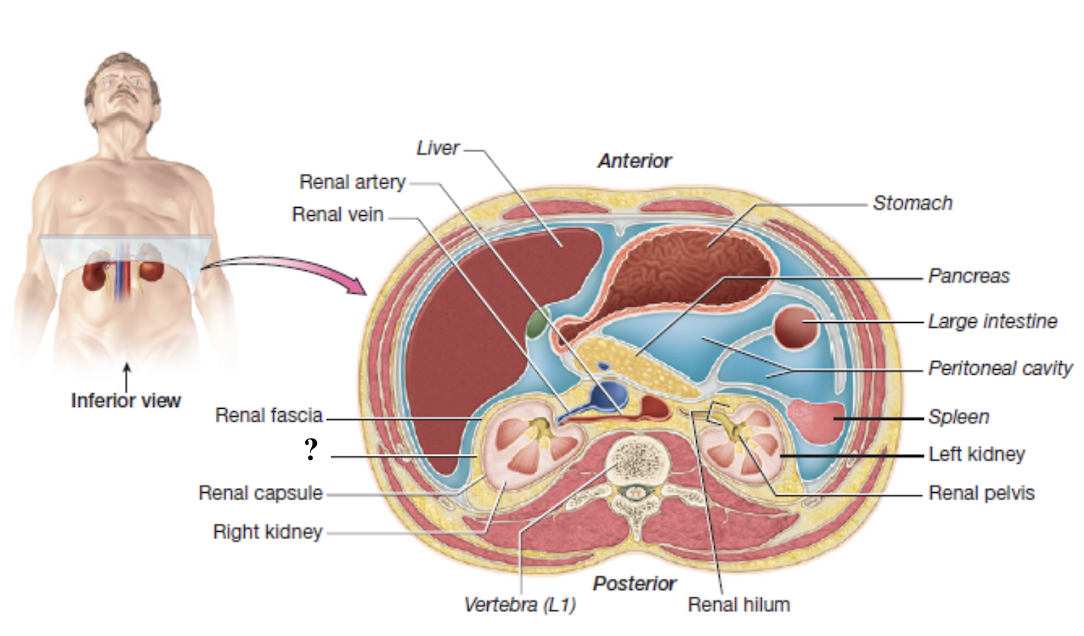
renal capsule
thin, tough layer of dense irregular collagenous connective tissue
encases each kidney like plastic wrap
renal hilum
medial indentation where blood vessels and the ureter enter and exit the each kidney
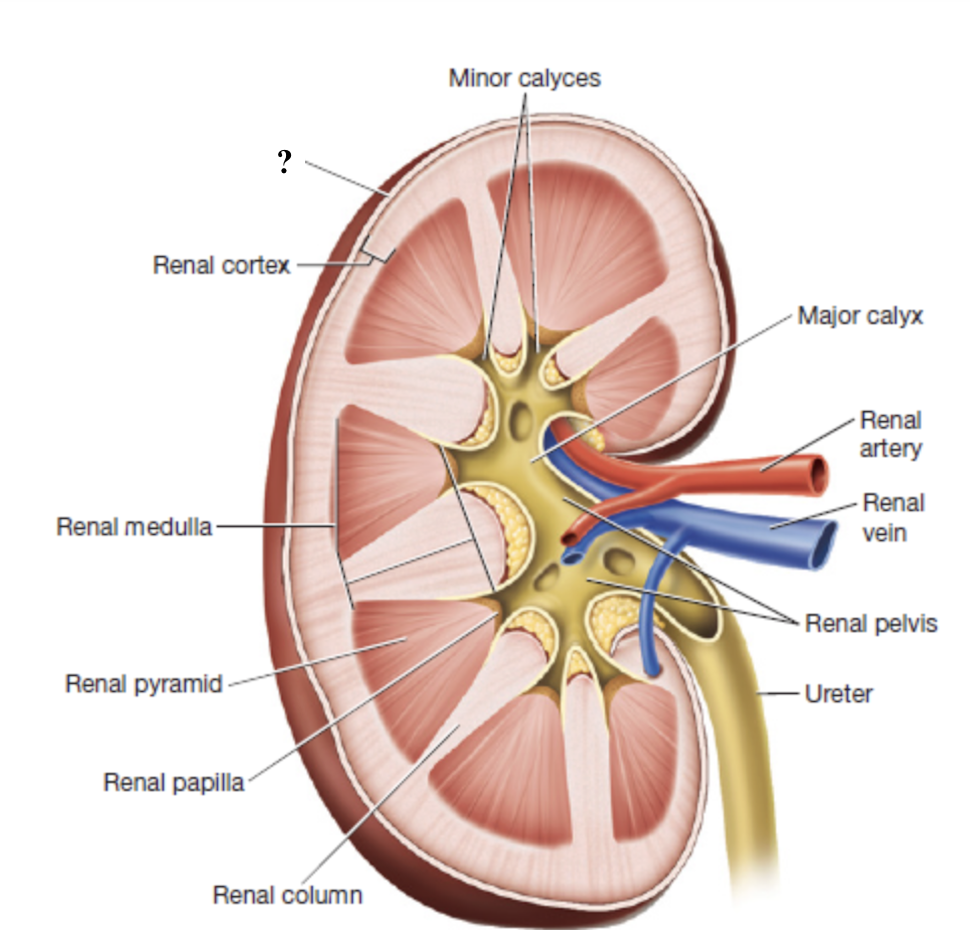
renal cortex
outermost region of the kidney
dark brown due to high density of blood vessels
contains most nephron structures that perform blood filtration
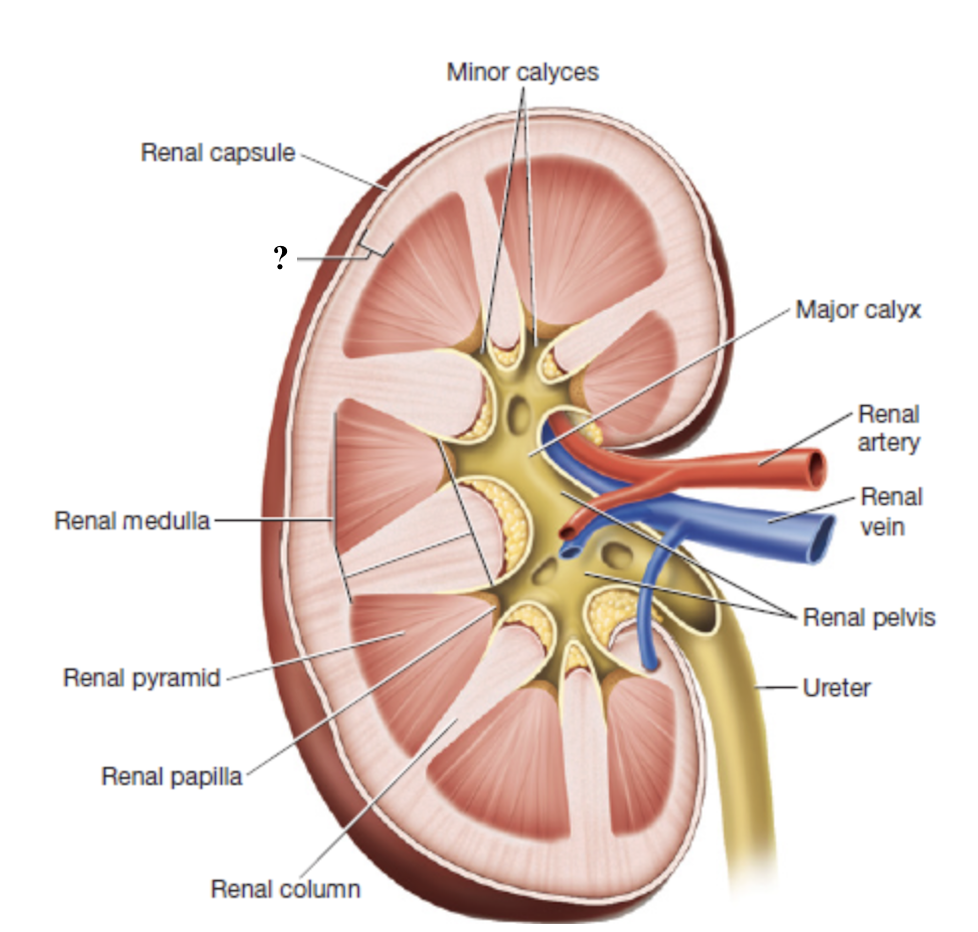
renal medulla
middle region of the kidney
composed of triangular renal pyramids
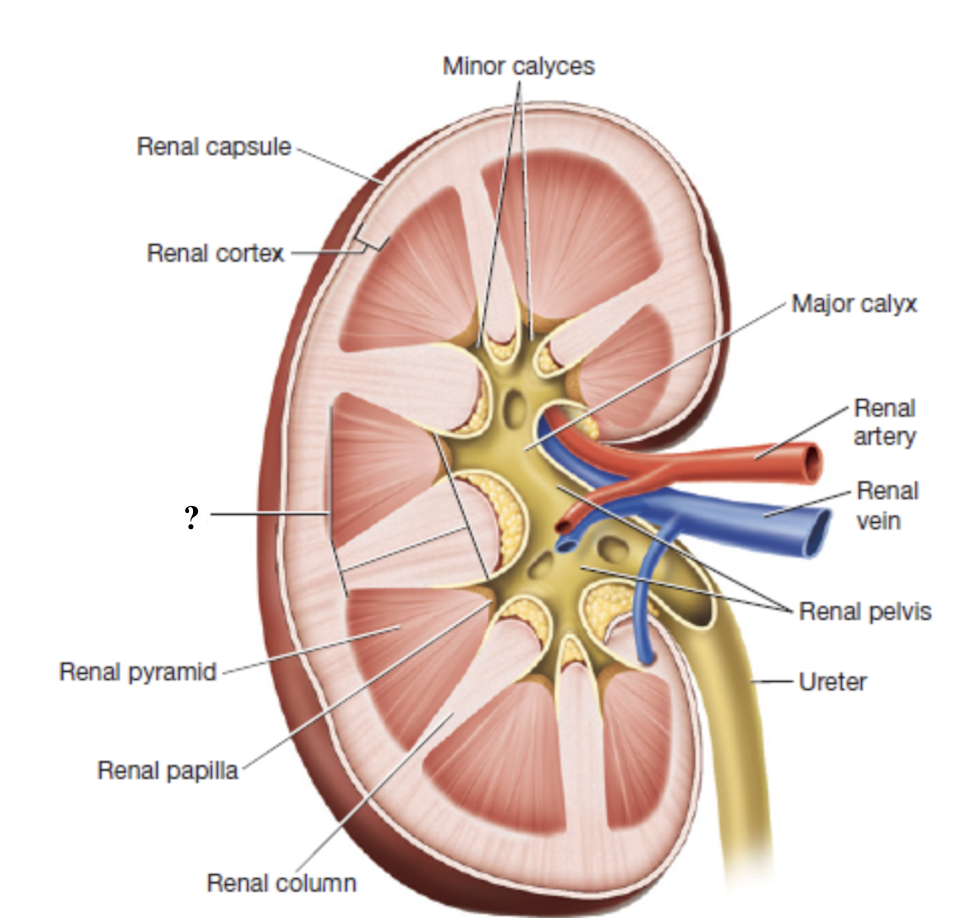
renal pyramids
contain looping nephron tubules and associated drainage structures which give them a striped/striated appearance
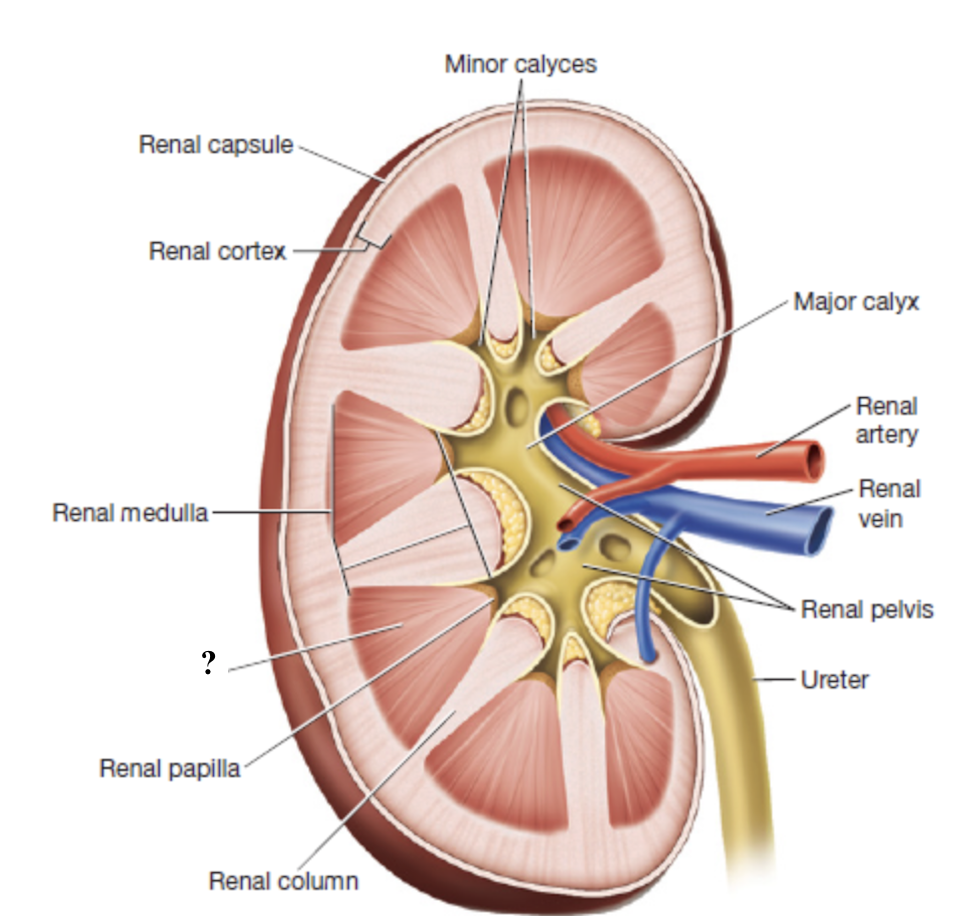
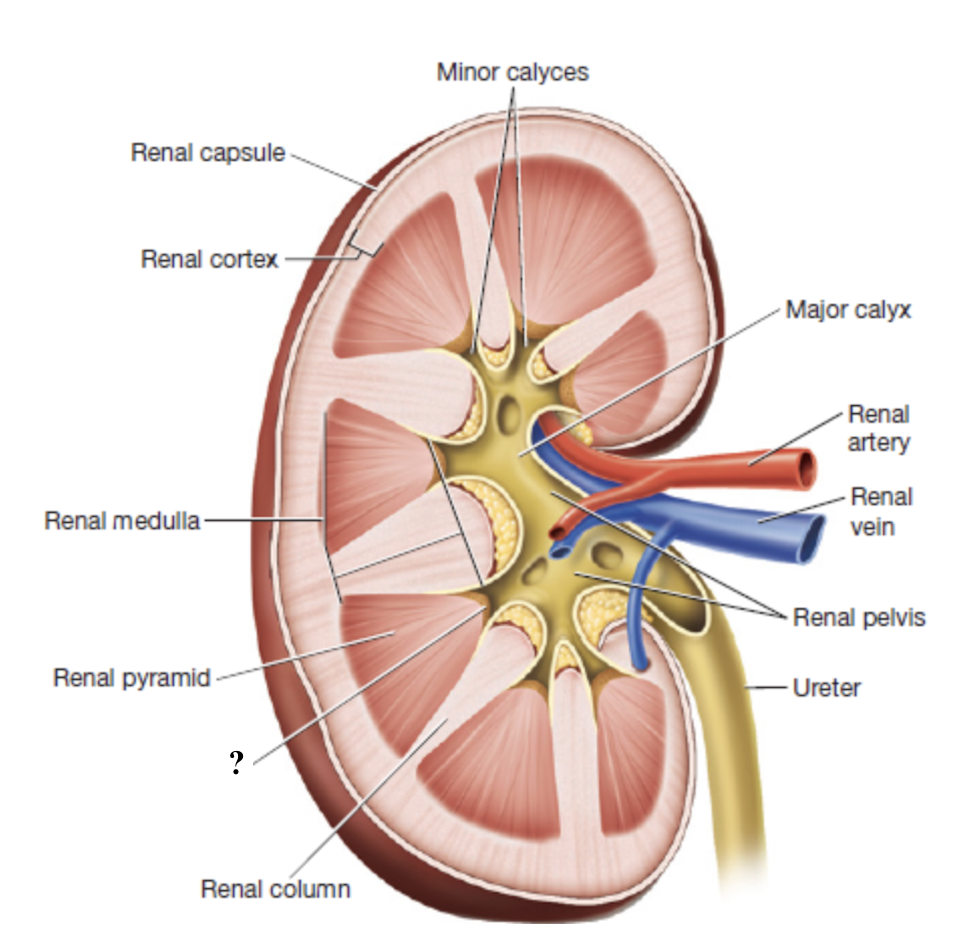
renal columns
inward extensions of the cortex that separate renal pyramids and contain blood vessels
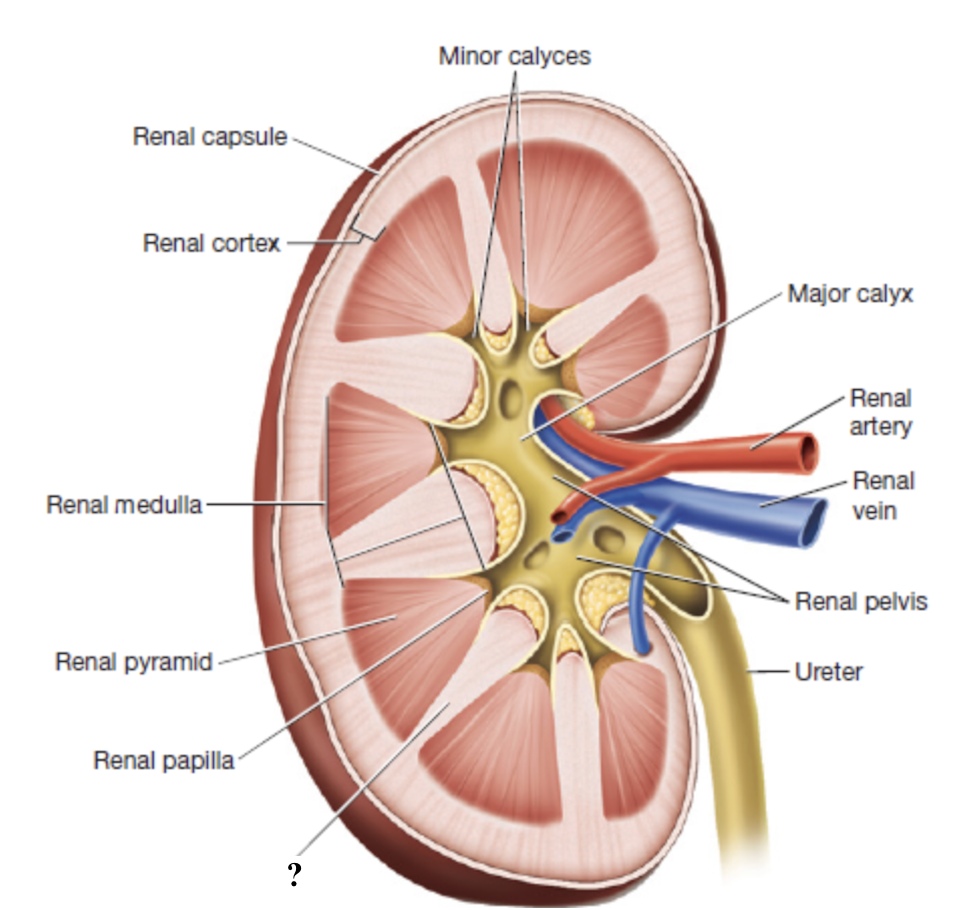
renal papilla
tip or apex of each renal pyramid
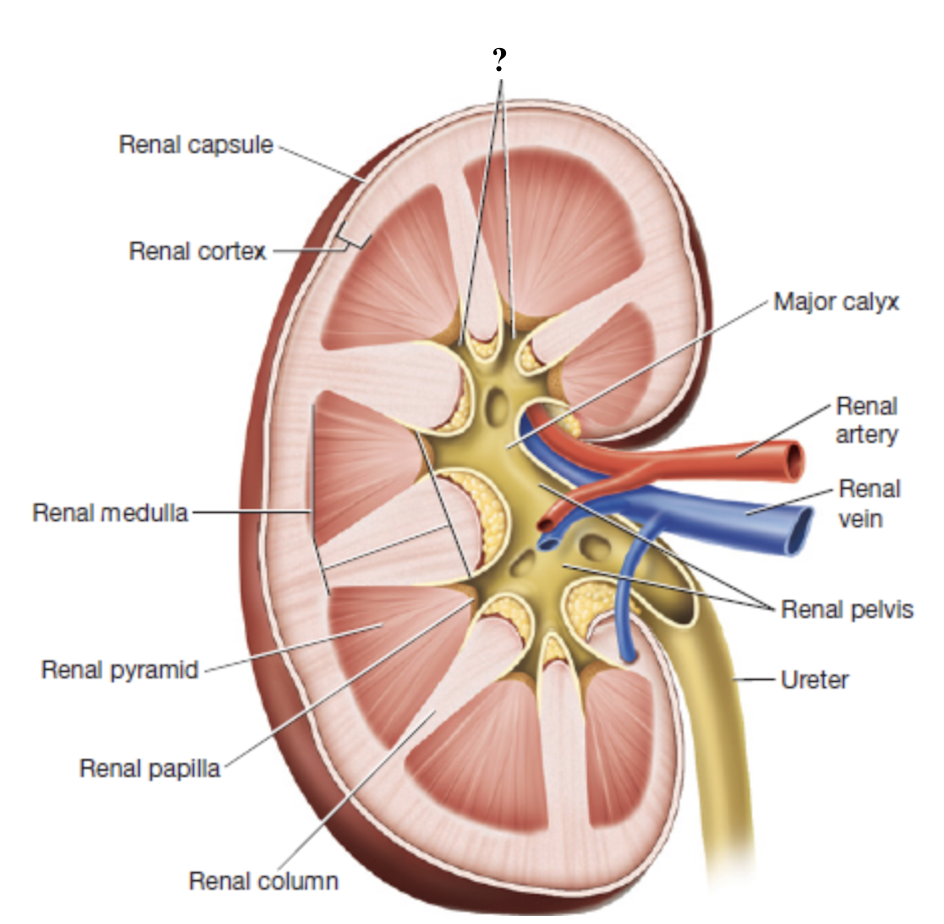
minor calyces
urine from each renal papilla drains into this small space
merge into major calyces which drain the rest of the renal pelvis
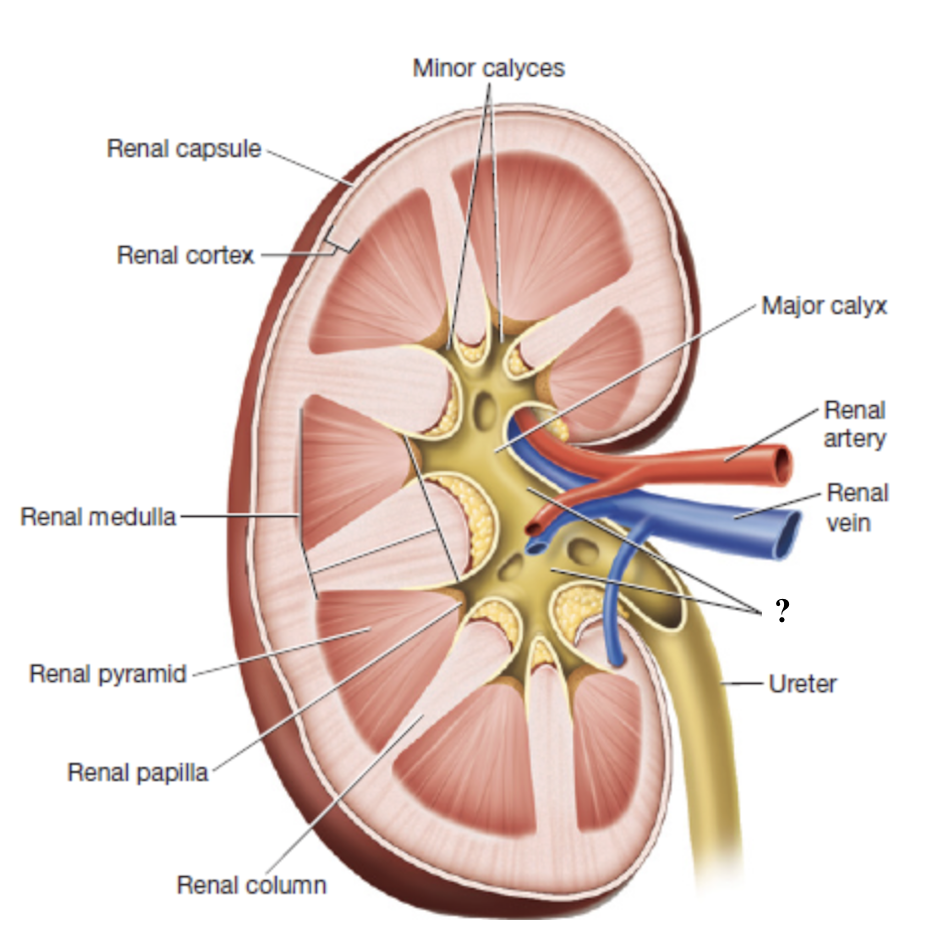
renal pelvis
innermost region of the kidneys that acts as a basin for urine collection
major calyces drain here
exits through the renal hilum and narrows to form the ureter
renal calculi
aka kidney stones, hard mineral deposits that form in the kidneys when urine becomes too concentrated
cause severe pain, blood in urine, and difficulty urinating
best prevented by staying hydrated
renal arteries
enter through the renal hilum
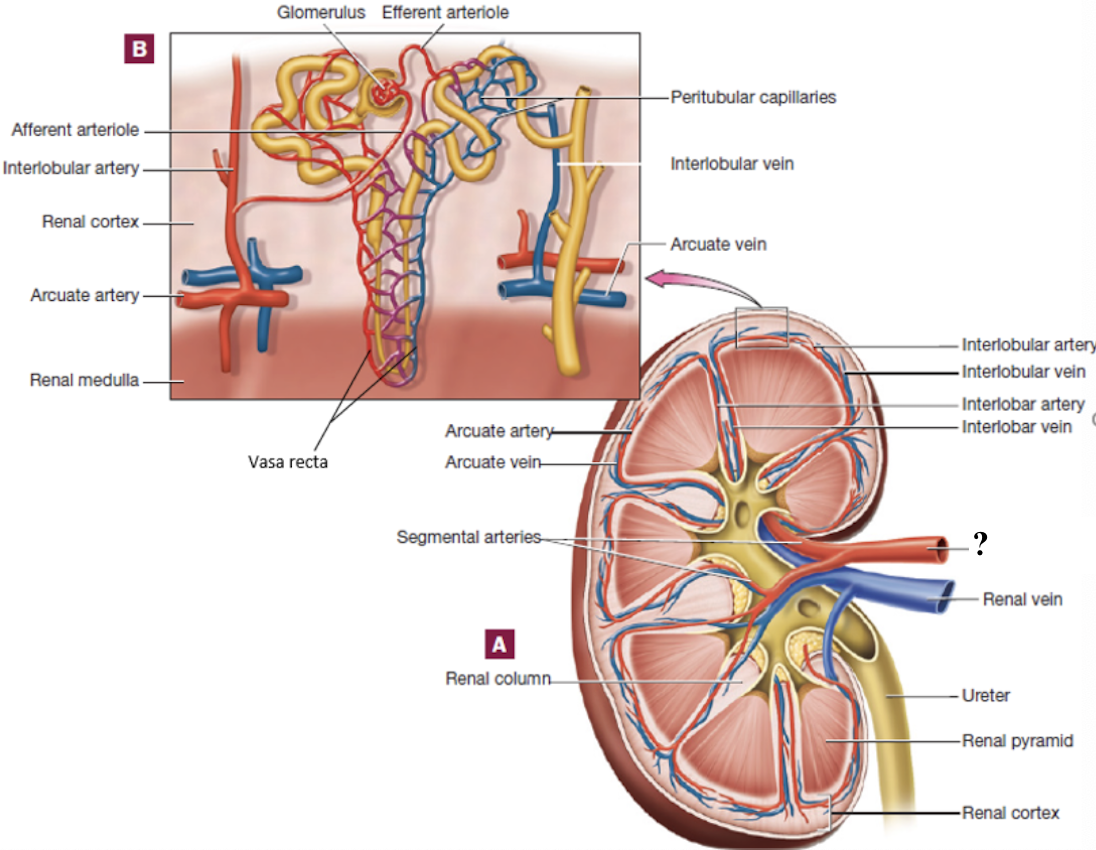
segmental arteries
located in the region of the renal pelvis
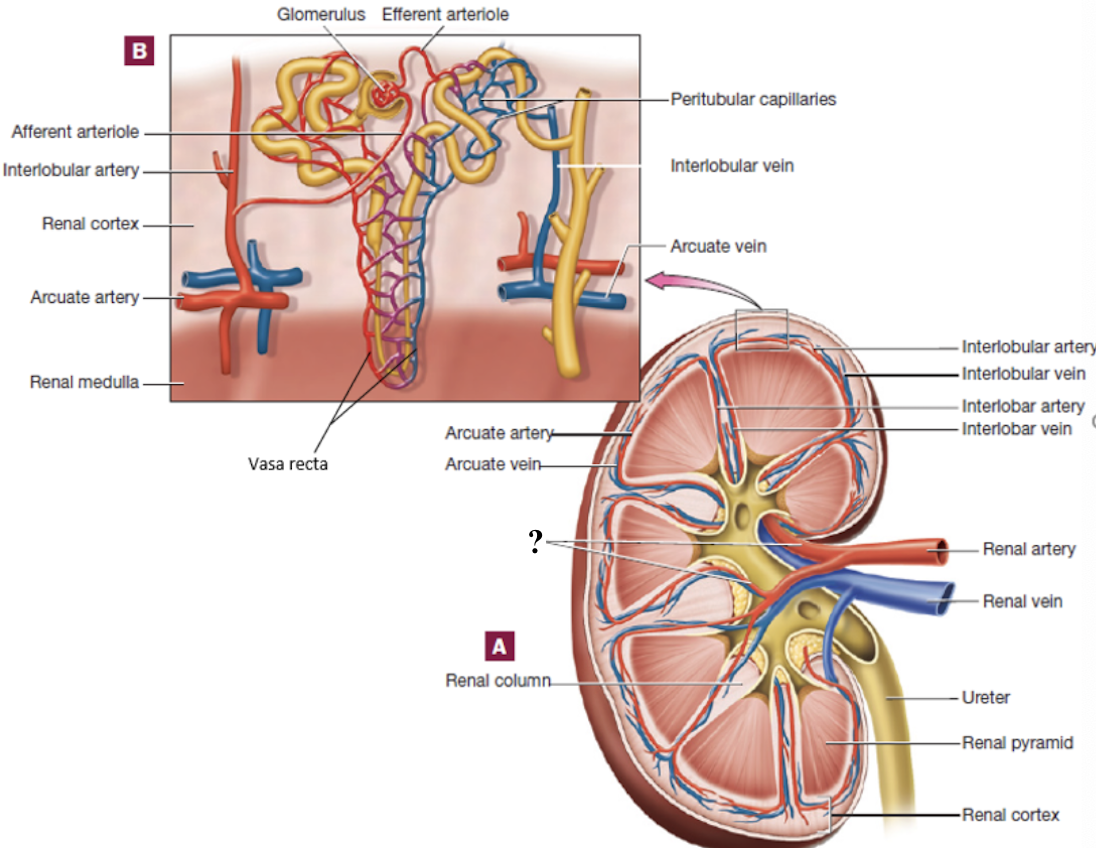
interlobar arteries
positioned between the renal pyramids
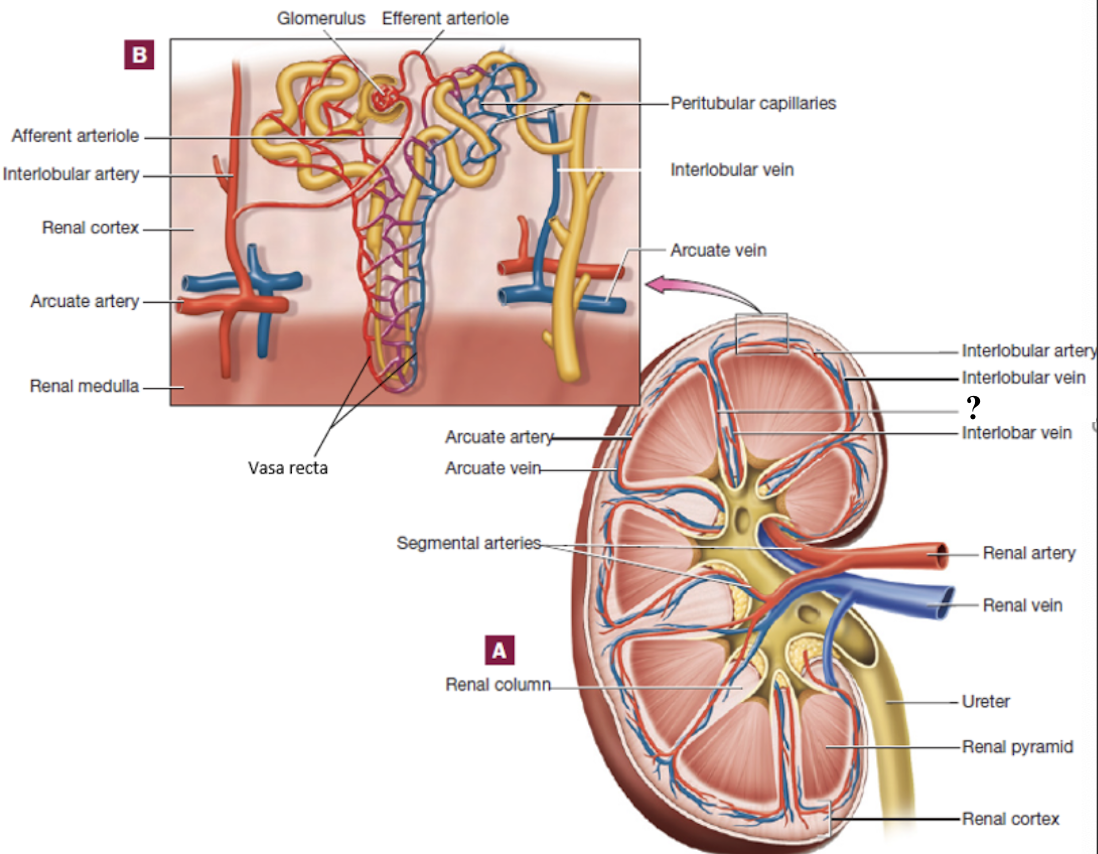
arcuate arteries
curve around the base (top) of the renal pyramids
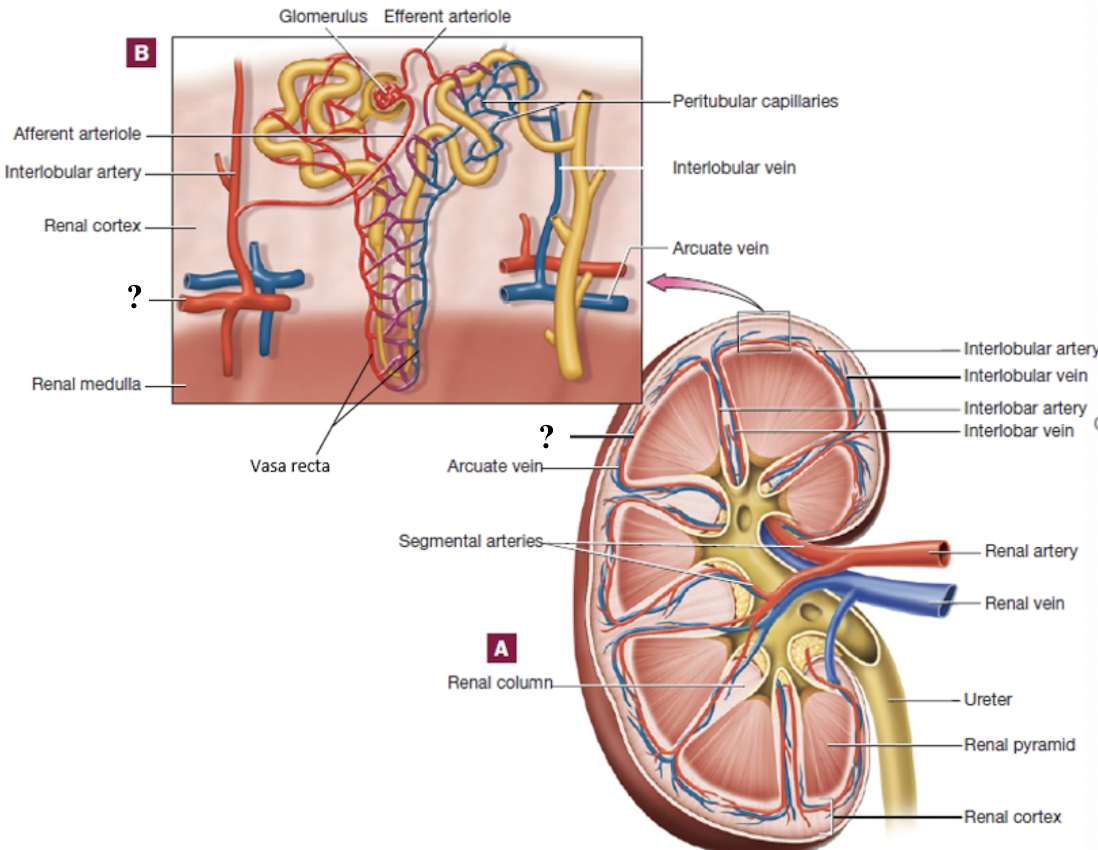
interlobular arteries
radiate outward in the renal cortex
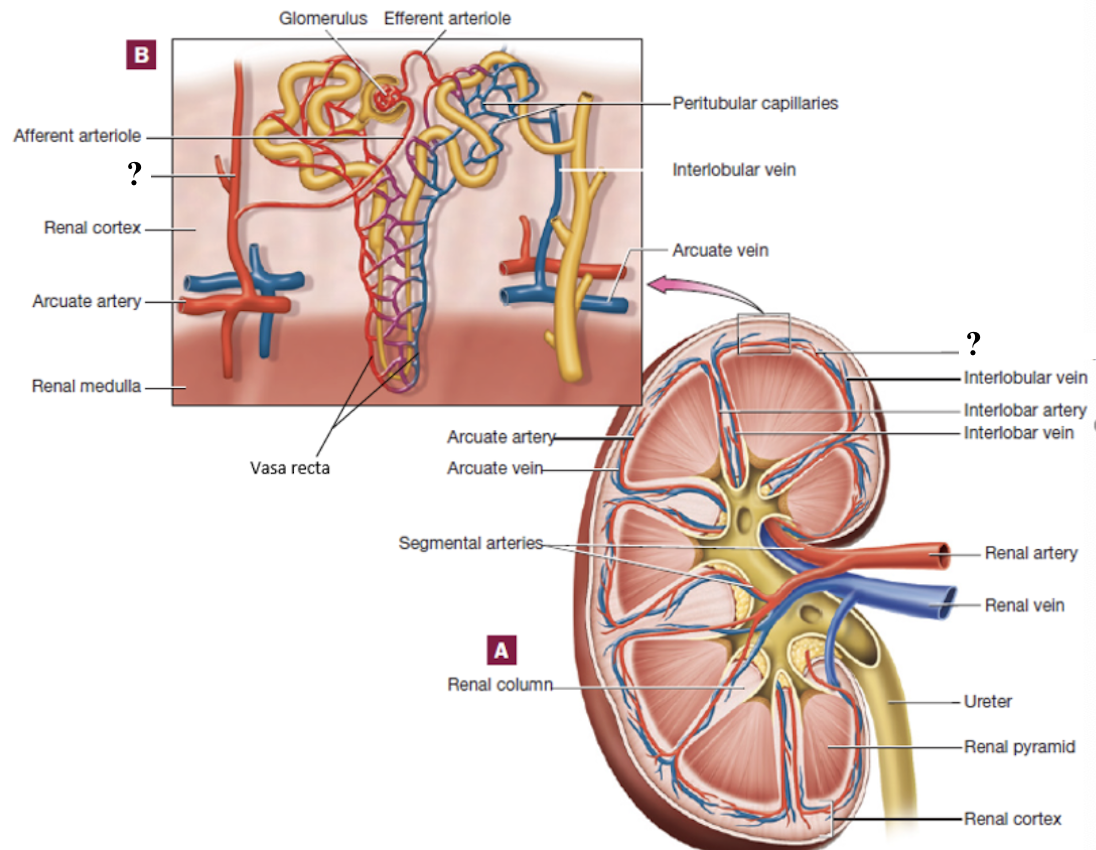
afferent arterioles
branch from interlobular arteries, each supply a glomerulus
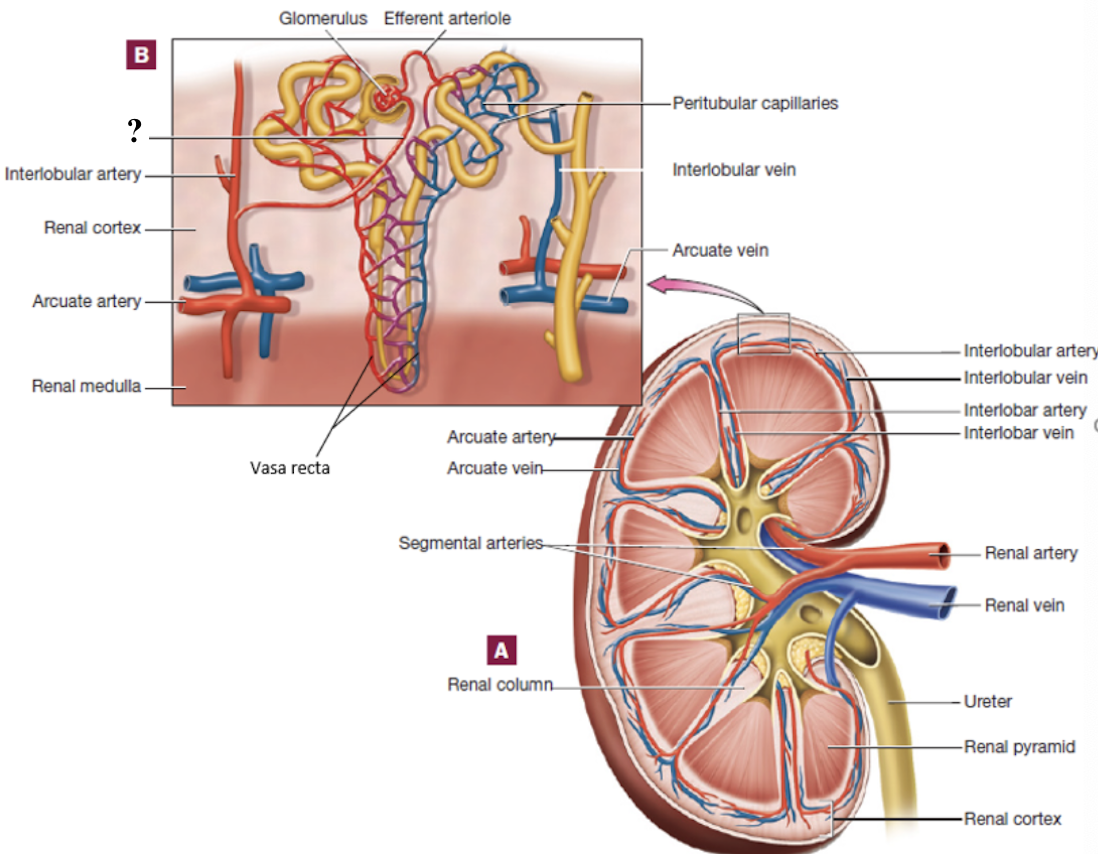
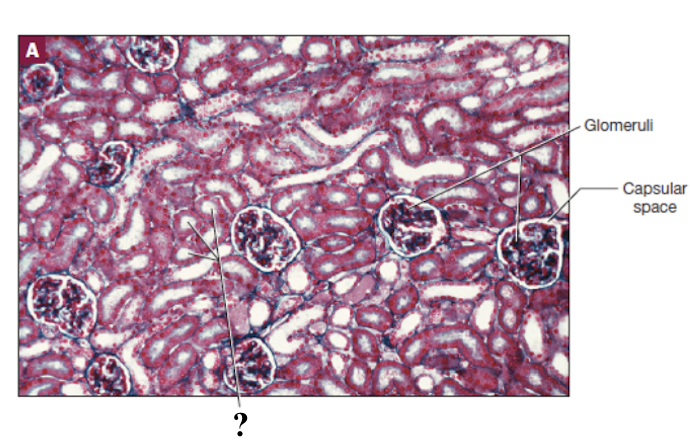
glomerulus
ball of fenestrated capillaries where blood is filtered
allow rapid passage of water and small solutes
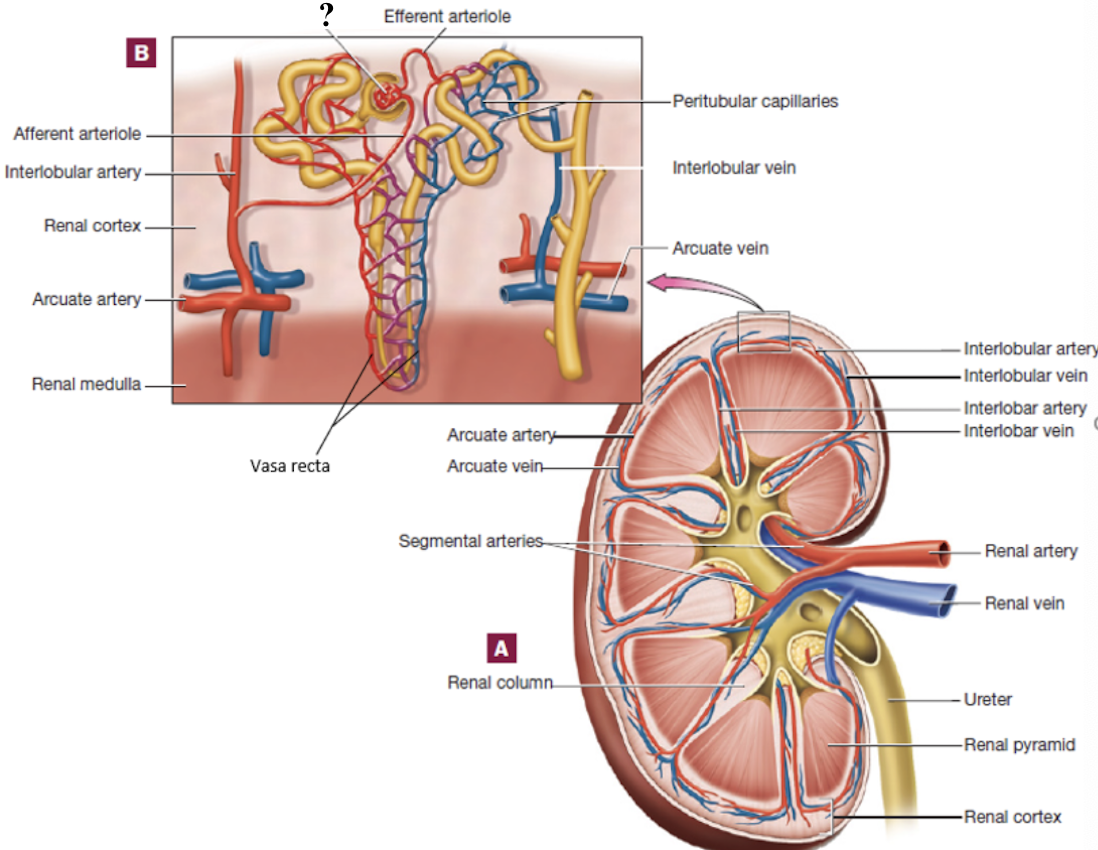
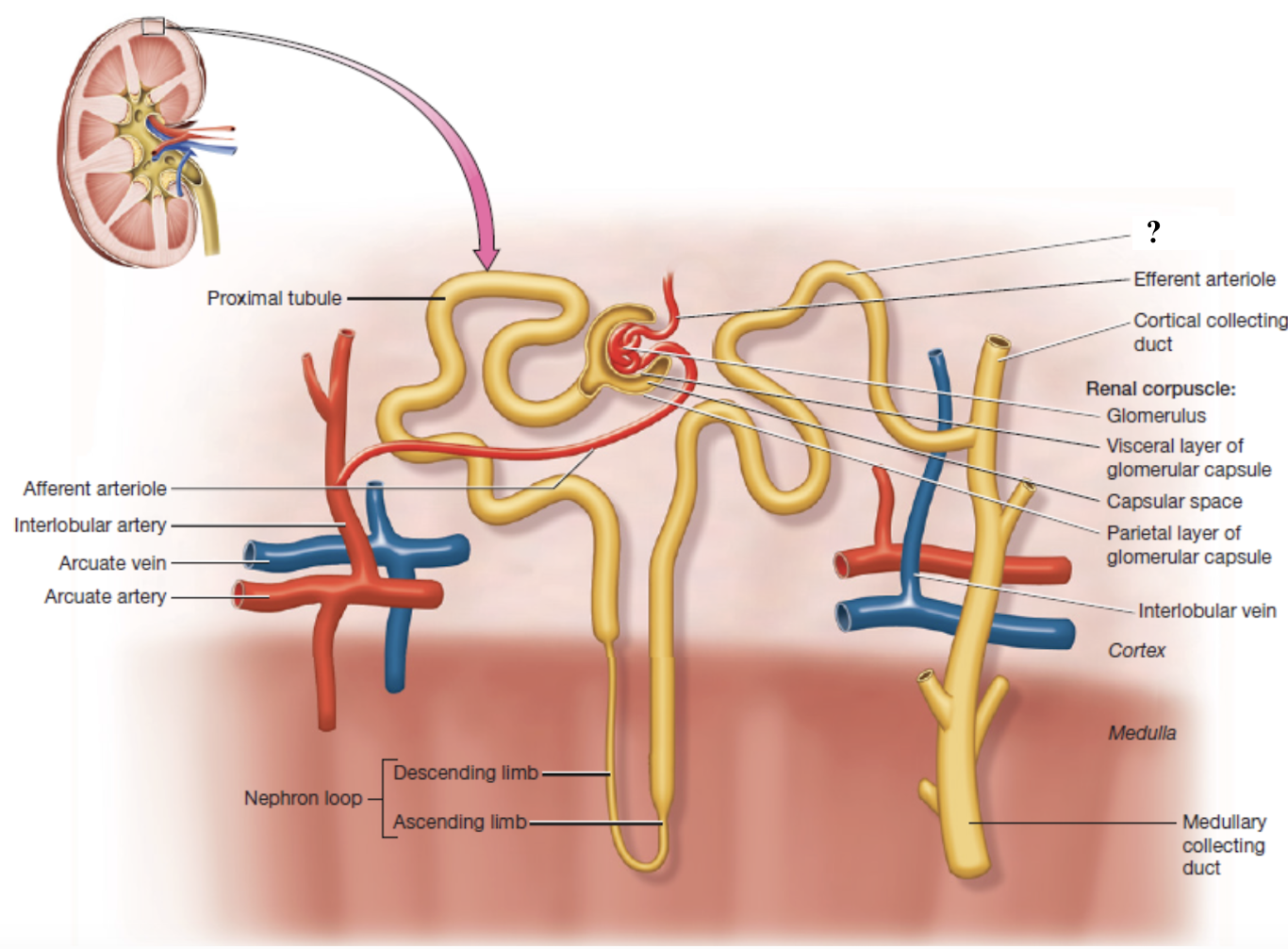
efferent arterioles
drain the glomerulus and have two options of pathways that it can follow
peritubular capillaries
vasa recta
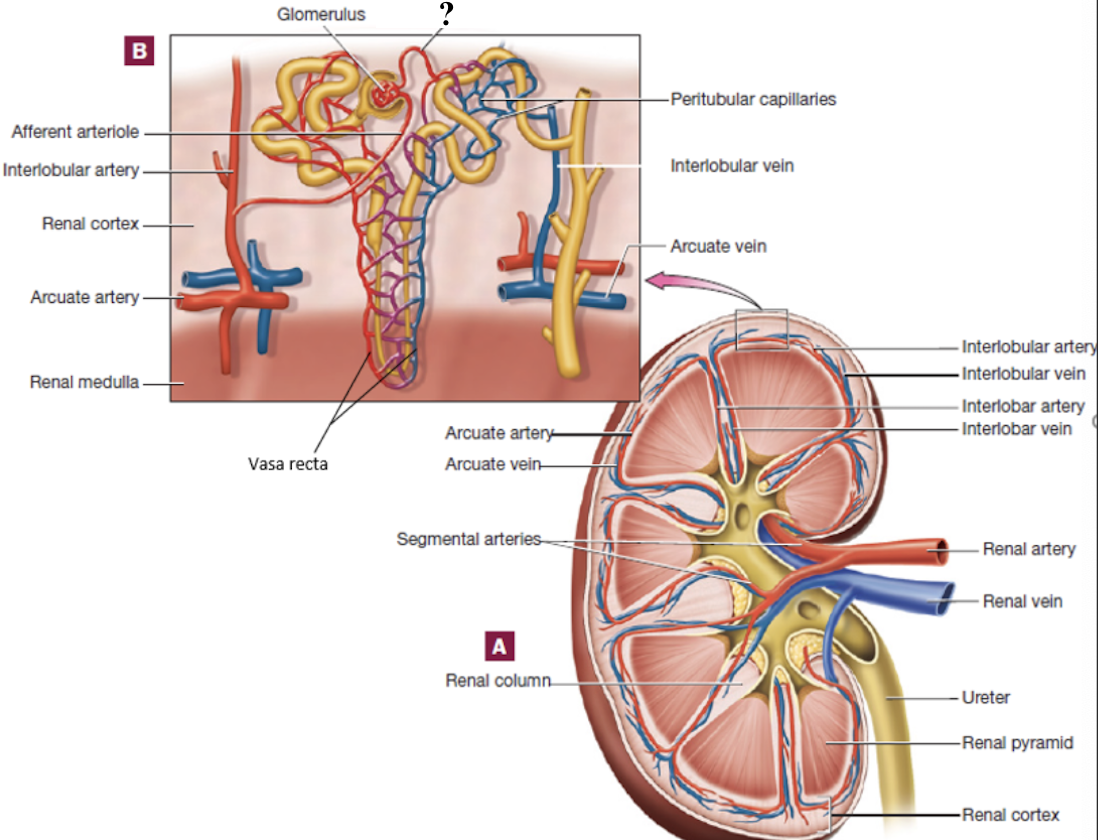
peritubular capillaries
capillary bed surrounding cortical nephron tubules
provide tubules with oxygen and nutrients
reabsorb substances from the tubules back into the blood
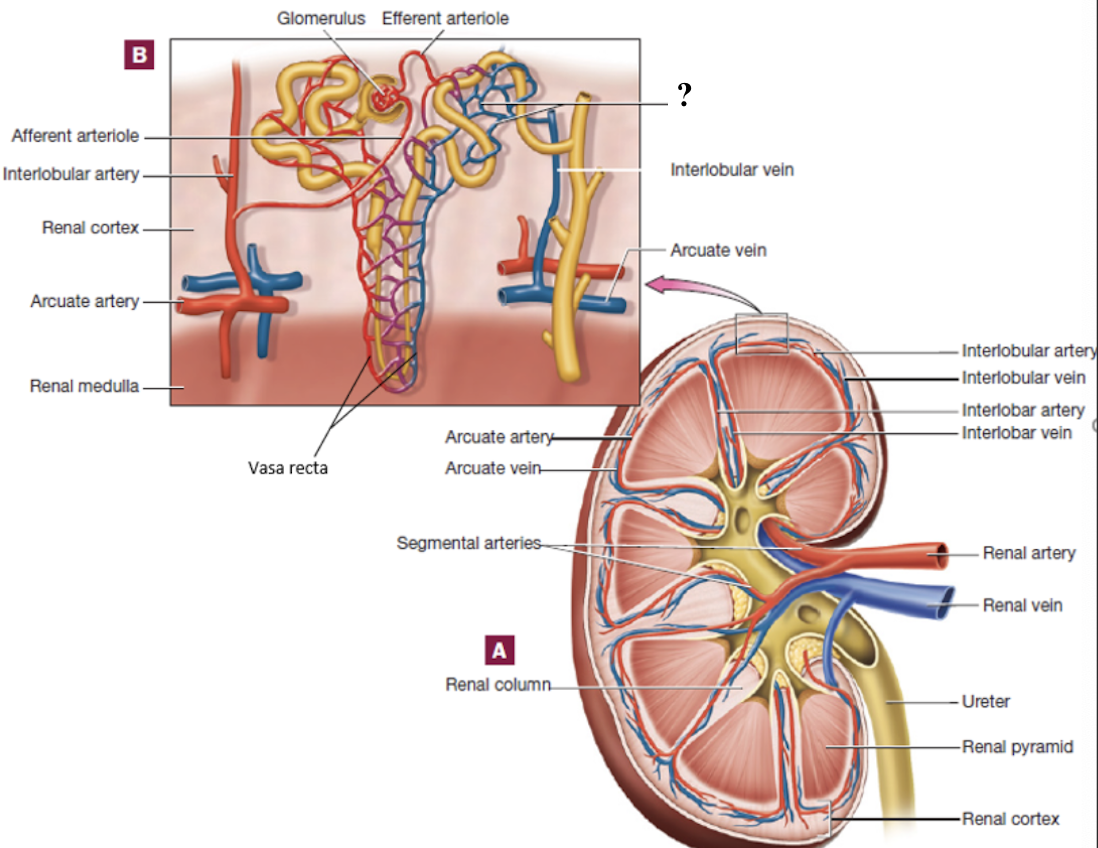
vasa recta
long, straight capillaries that run parallel to nephron loops of juxtamedullary nephrons in the medulla
keep the medulla’s salt and water balance to make concentrated urine
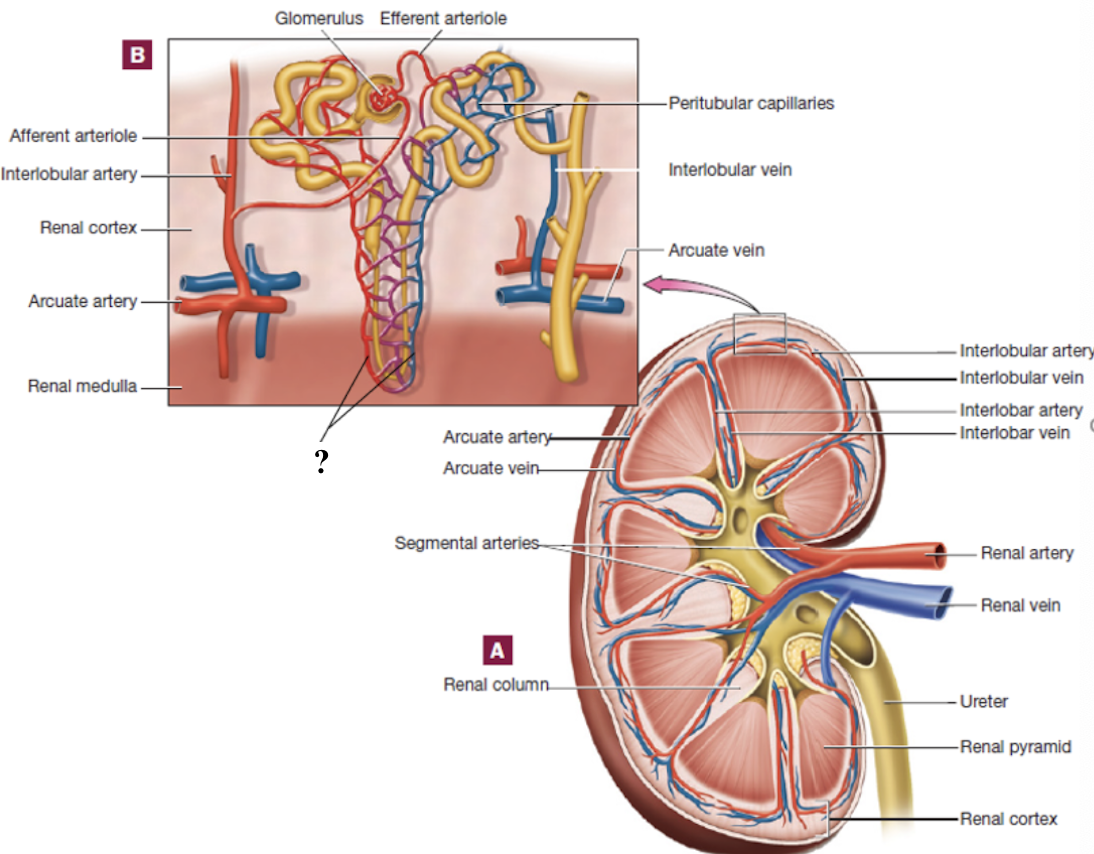
interlobular veins
drain blood from the peritubular capillaries and vasa recta in the cortex
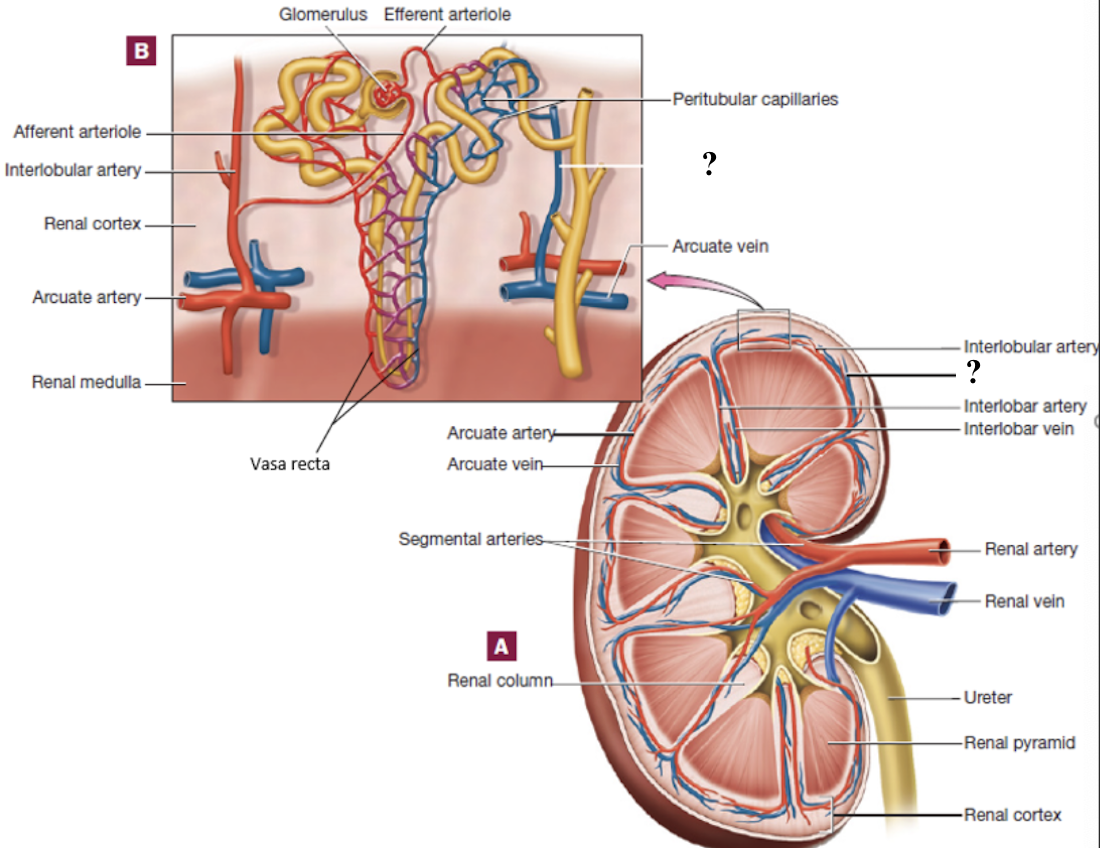
arcuate veins
follow the curve around the base of the pyramids
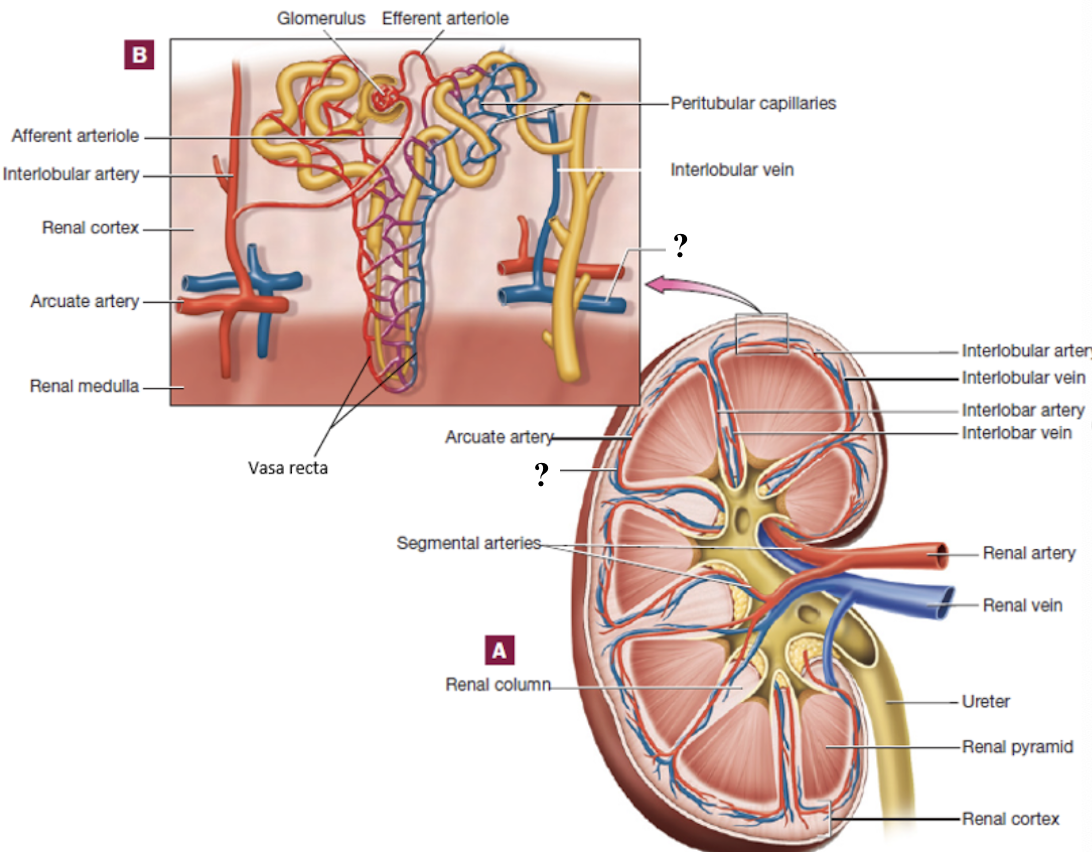
interlobar veins
pass between the medullary pyramids
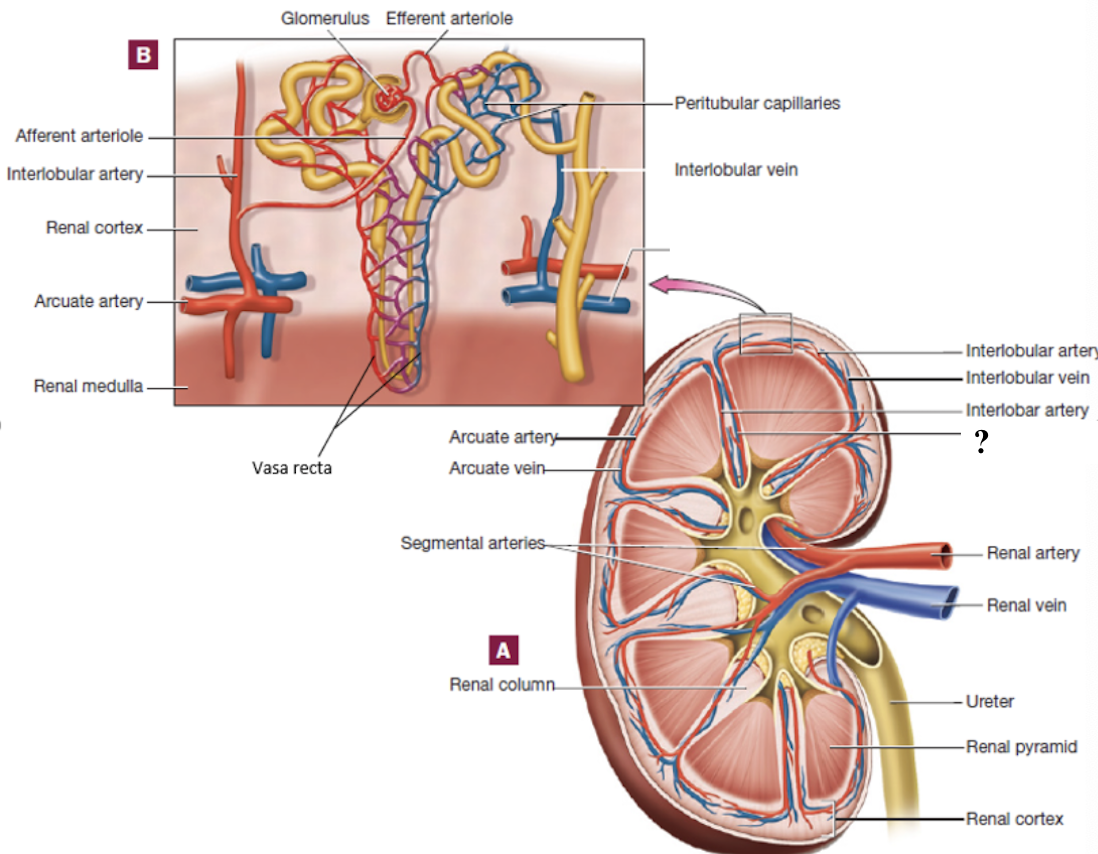
renal vein
drains into the inferior vena cava
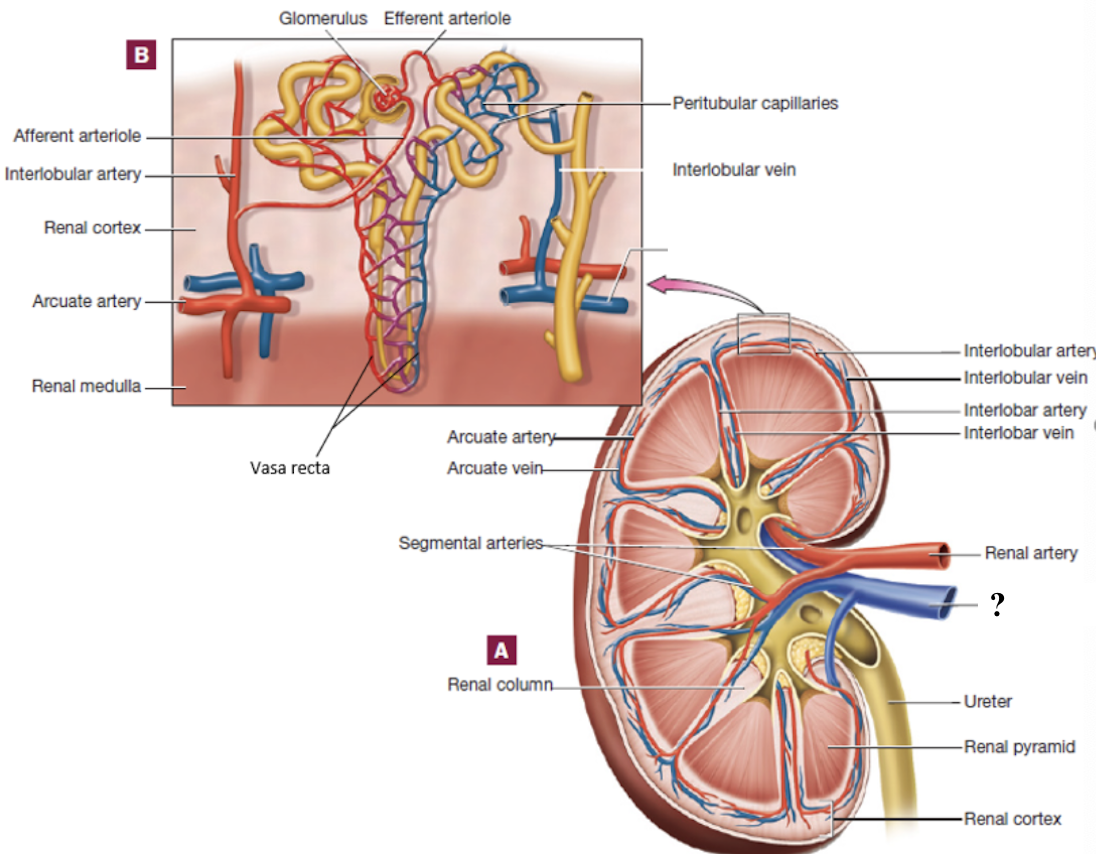
abdominal aorta → renal arteries → segmental arteries → interlobar arteries → arcuate arteries → interlobular arteries → afferent arterioles → glomerulus → efferent arterioles → peritubular capillaries or vasa recta → interlobular veins → arcuate veins → interlobar veins → renal vein → inferior vena cava
renal blood flow
true
true or false: the kidneys have segmental arteries but NO segmental veins because each segmental artery is an end artery that supplies a distinct renal segment with little to no overlap
filtration
process at the glomerulus in which blood pressure forces water and small solutes into the Bowman’s capsule while keeping large proteins and cells in the blood
reabsorption
process in the tubules in which needed substances move back into the blood
recovery of substances from filtrate after filtration
secretion
process in which wastes and excess ions are added from the blood into the filtrate for removal
diffusion
process in which passive movement of molecules from high to low concentration throughout the nephron and capillaries
filtrate
fluid that gets pushed out of the blood in the glomerulus of the kidney and collected in the nephron
contains water, ions, glucose, amino acids, and wastes
nephron
microscopic functional units of filtration and urine formation in the kidneys
two parts: renal corpuscle and renal tubule
renal corpuscle
composed of the glomerulus and glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule
site of filtration
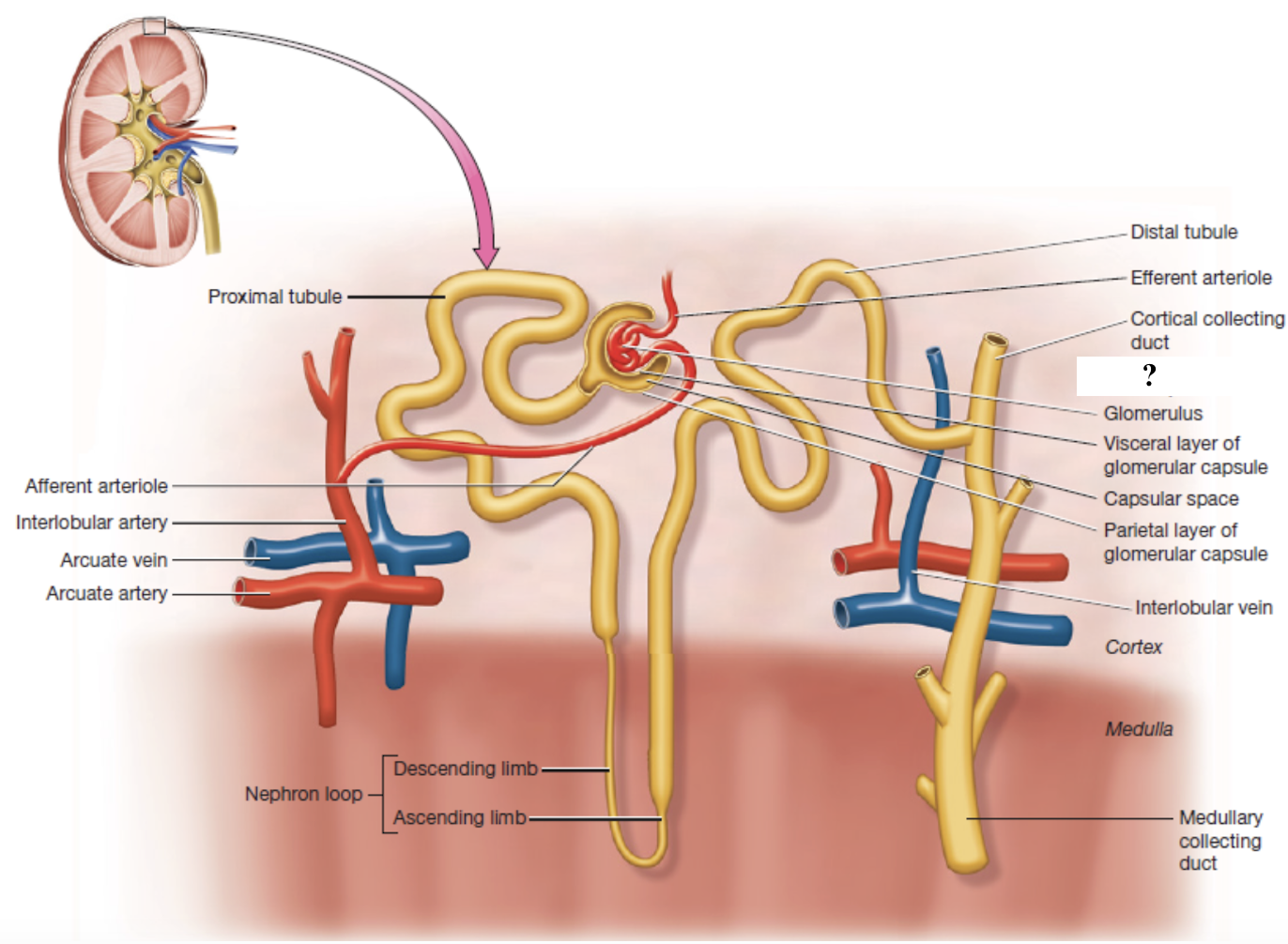
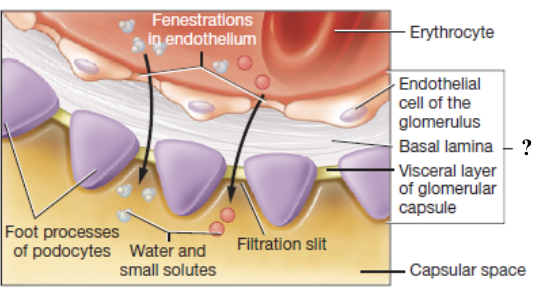
glomerular (Bowman’s) capsule
surrounds the glomerulus with two layers
parietal layer: simple squamous epithelium outer wall
visceral layer: podocytes with interlocking foot processes that form filtration slits
capsular space
space between the parietal and visceral layers of the glomerular capsule where filtrate collects before entering the renal tubule
filtration membrane
made of glomerular endothelial cells, podocytes, and their shared basal lamina
blocks large substances while allowing water, electrolytes, glucose, amino acids, and nitrogenous waste to pass
renal tubule
lined with thin layer of simple epithelium ideal for reabsorption and has three main segments where filtrate passes through and is modified into urine
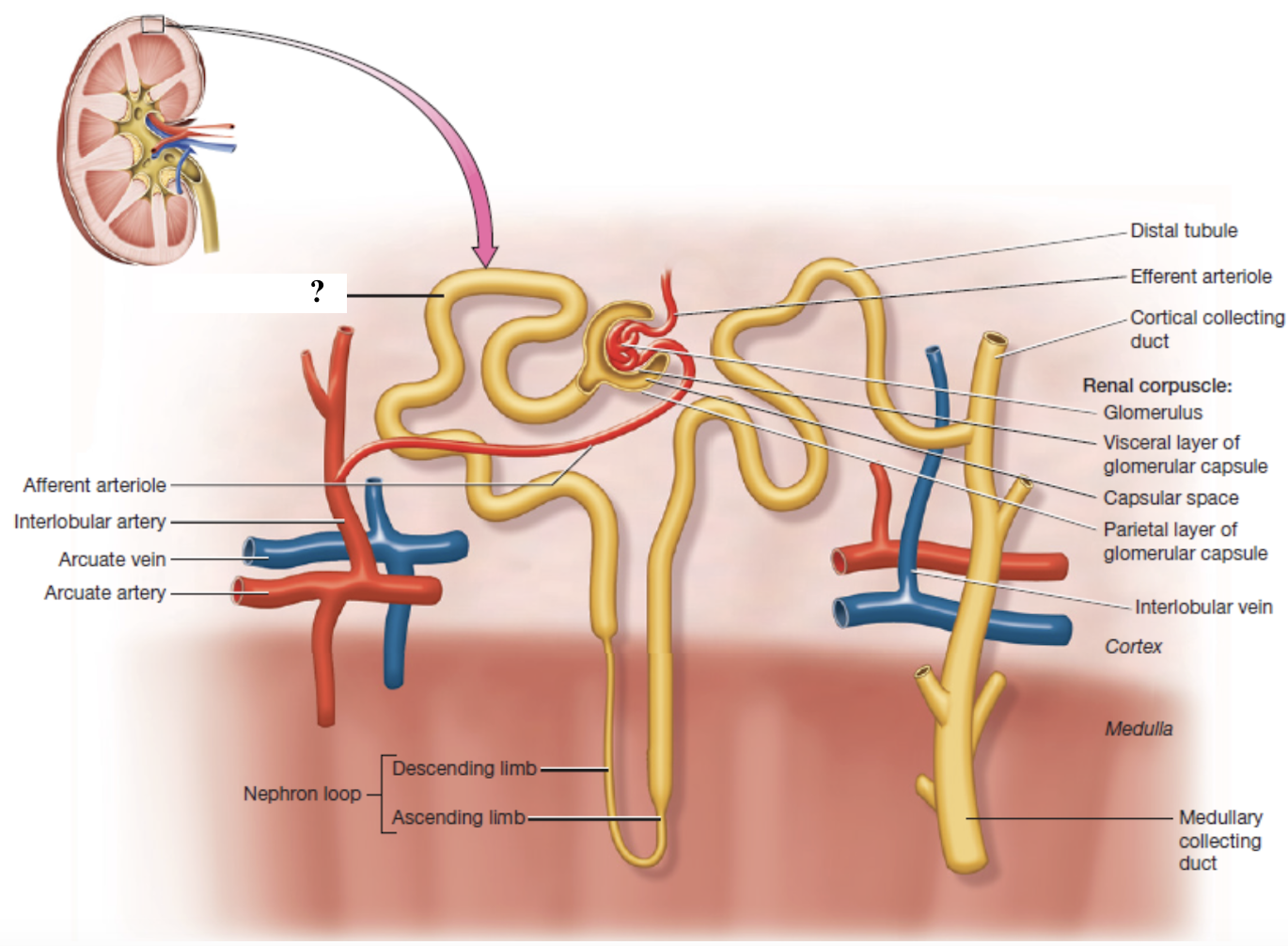
proximal convoluted tubule
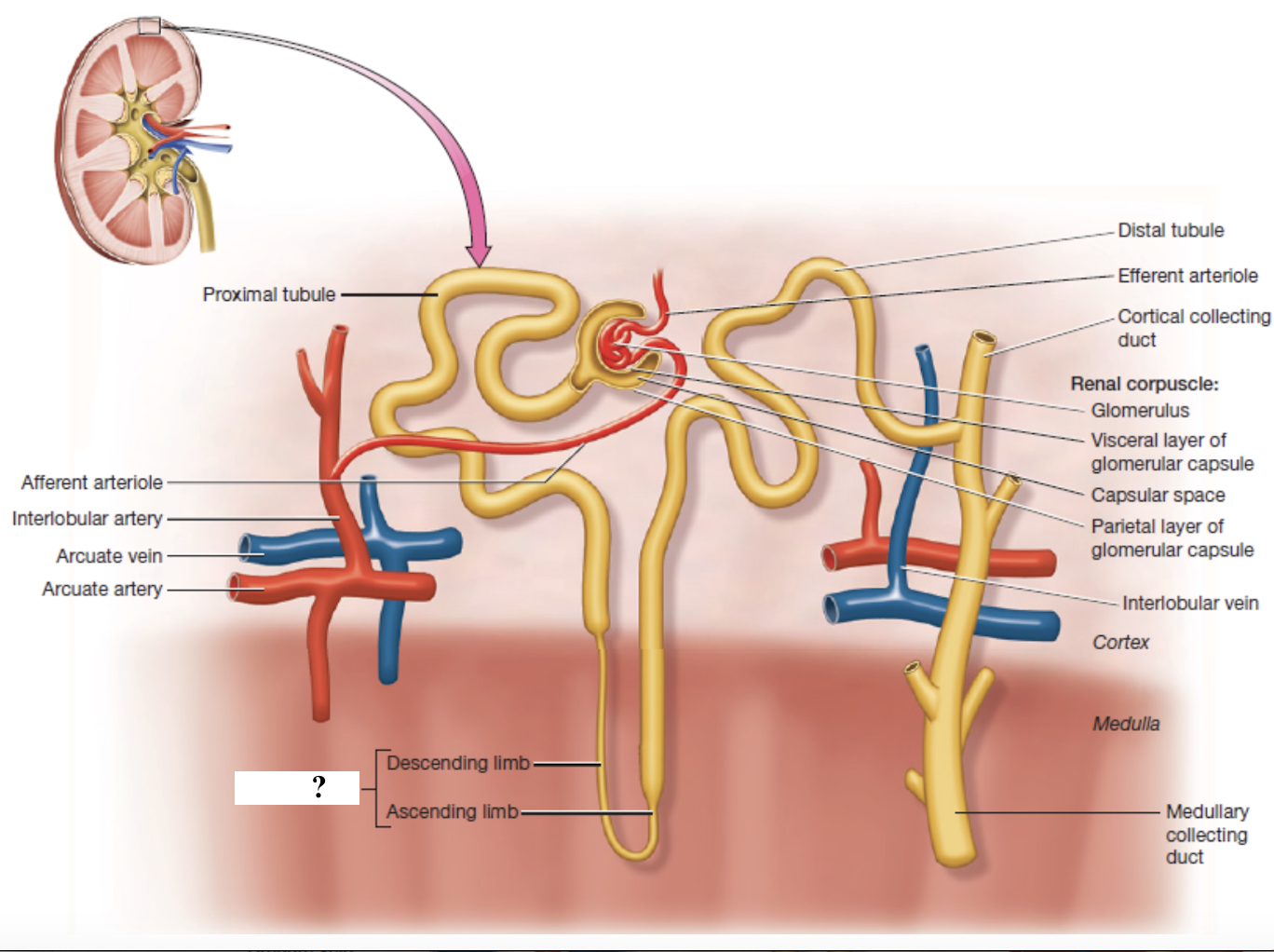
nephron loop
distal convoluted tubule
proximal convoluted tubule
has dense covering of microvilli that increase surface area
reabsorbs about 65-70% of filtrate volume
reabsorbs water, glucose, amino acids, sodium, potassium, chloride, calcium, magnesium, bicarbonate, and vitamins
secretes hydrogen ions, drugs, and toxins
nephron loop
descending limb: lined with simple squamous epithelium and reabsorbs water
ascending limb: lined with simple cuboidal epithelium and reabsorbs sodium, potassium, and chloride
distal convoluted tubule
has few microvilli which reflects its reduced role in reabsorption
fine-tunes reabsorption of sodium, calcium, and chloride under hormonal control
secretes potassium, hydrogen ions, and drugs
collecting duct
regulated by antidiuretic hormone for water reabsorption
reabsorbs urea to maintain medullary concentration gradient
adjusts urine concentration based on hydration
NOT part of the nephron
cortical collecting ducts
collecting ducts in the renal cortex
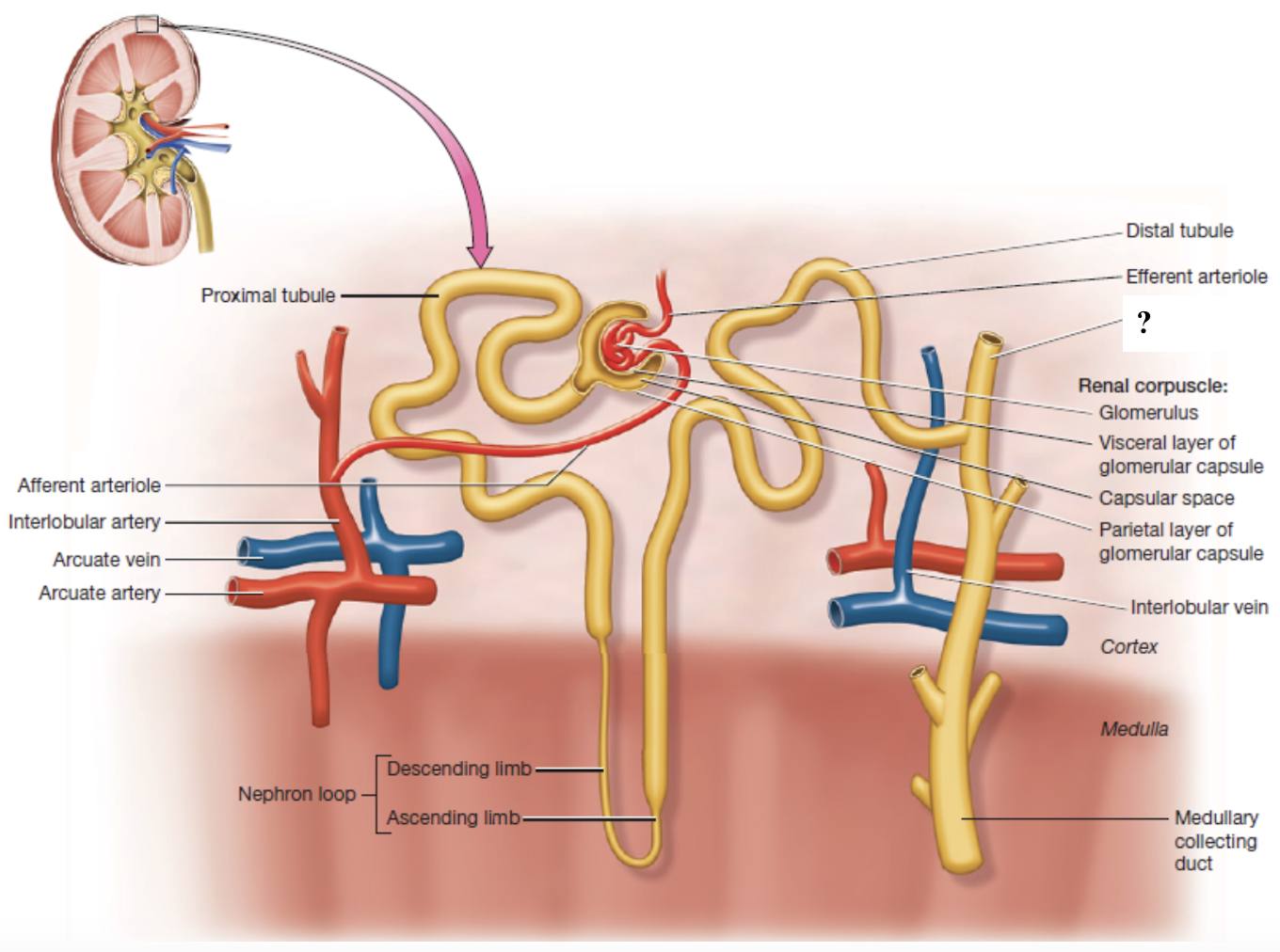
medullary collecting ducts
collecting ducts in the renal medulla
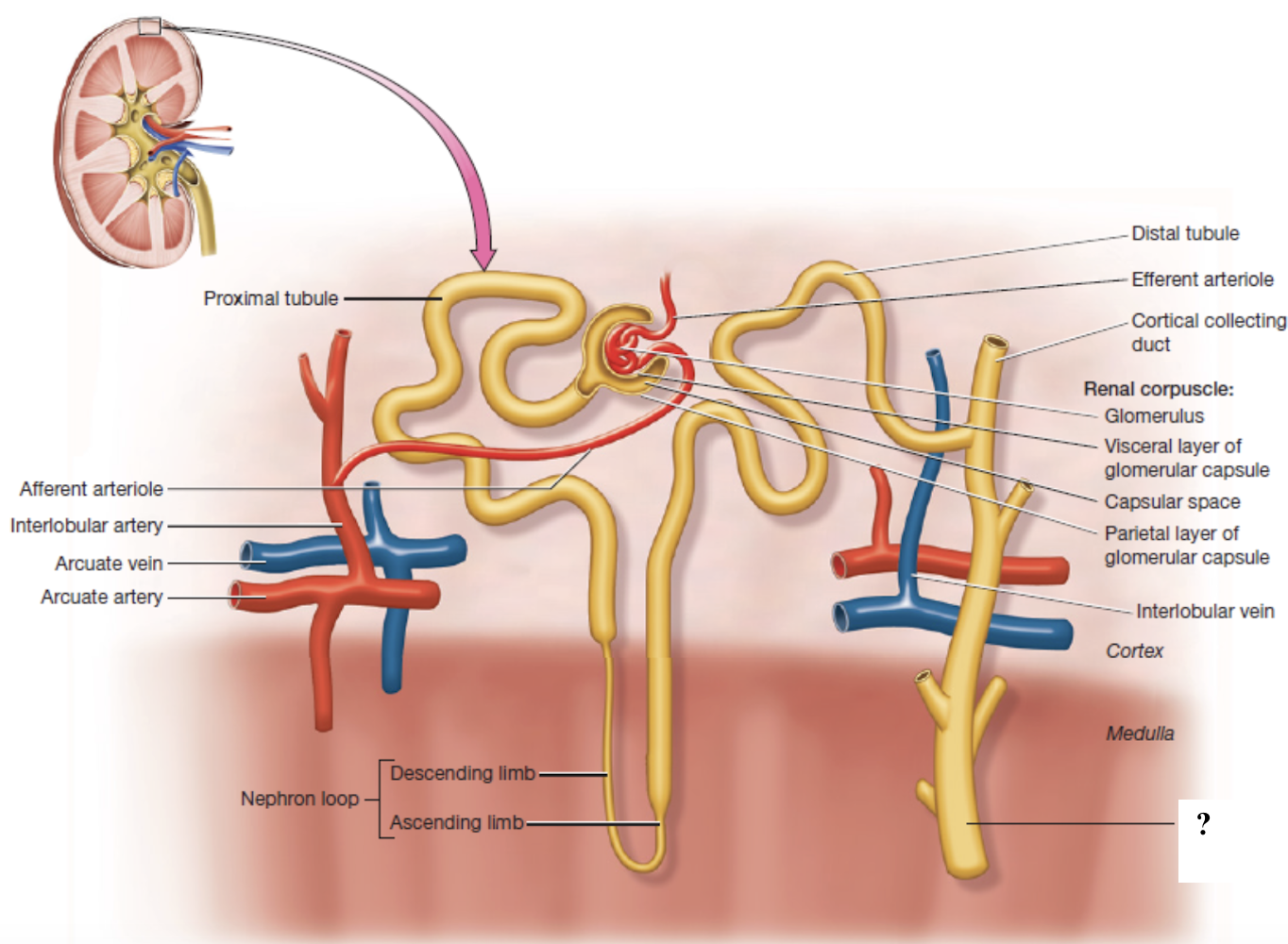
papillary ducts
collecting ducts near the renal papilla that empty into minor calyces
formed by medullary collecting ducts
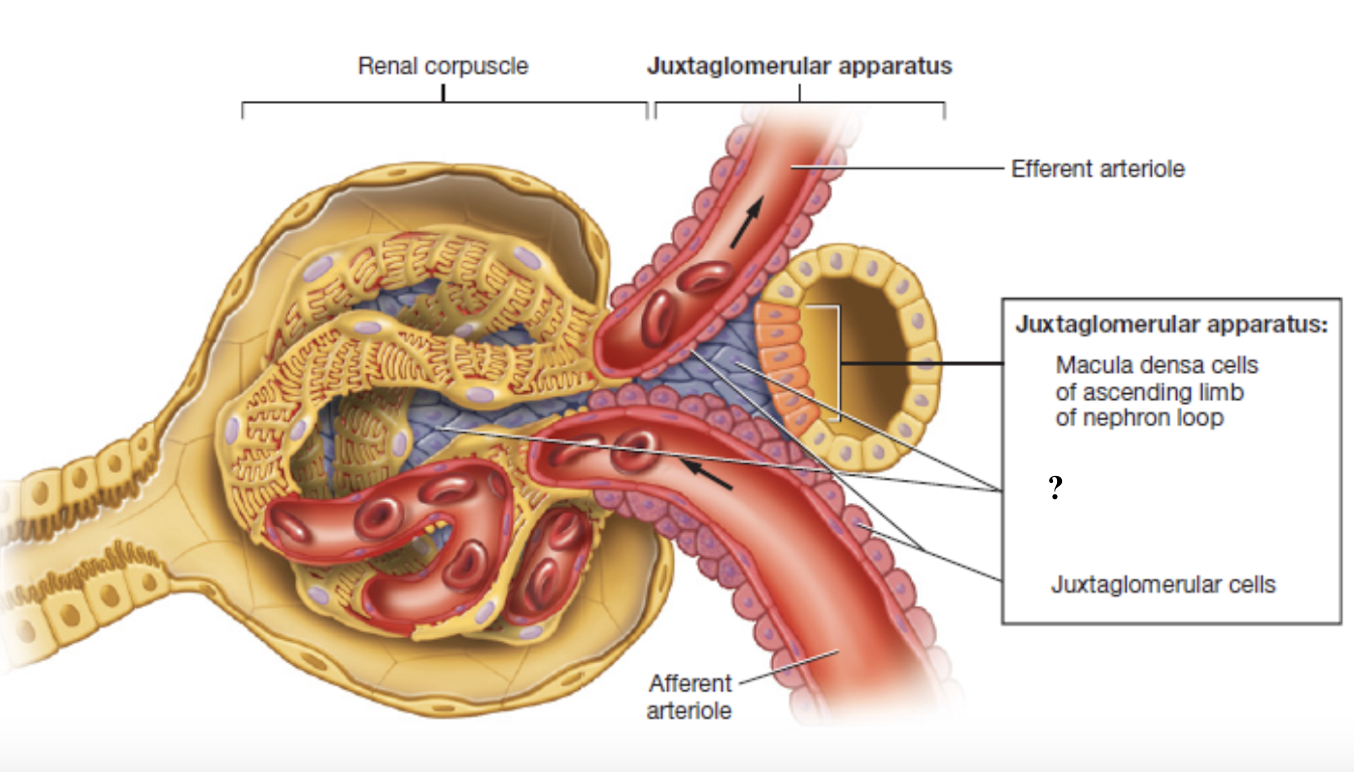
juxtaglomerular apparatus
controls the flow of filtrate through the nephron and blood pressure within the glomerulus
made up of three cell types: macula densa cells, juxtaglomerular cells, mesangial cells
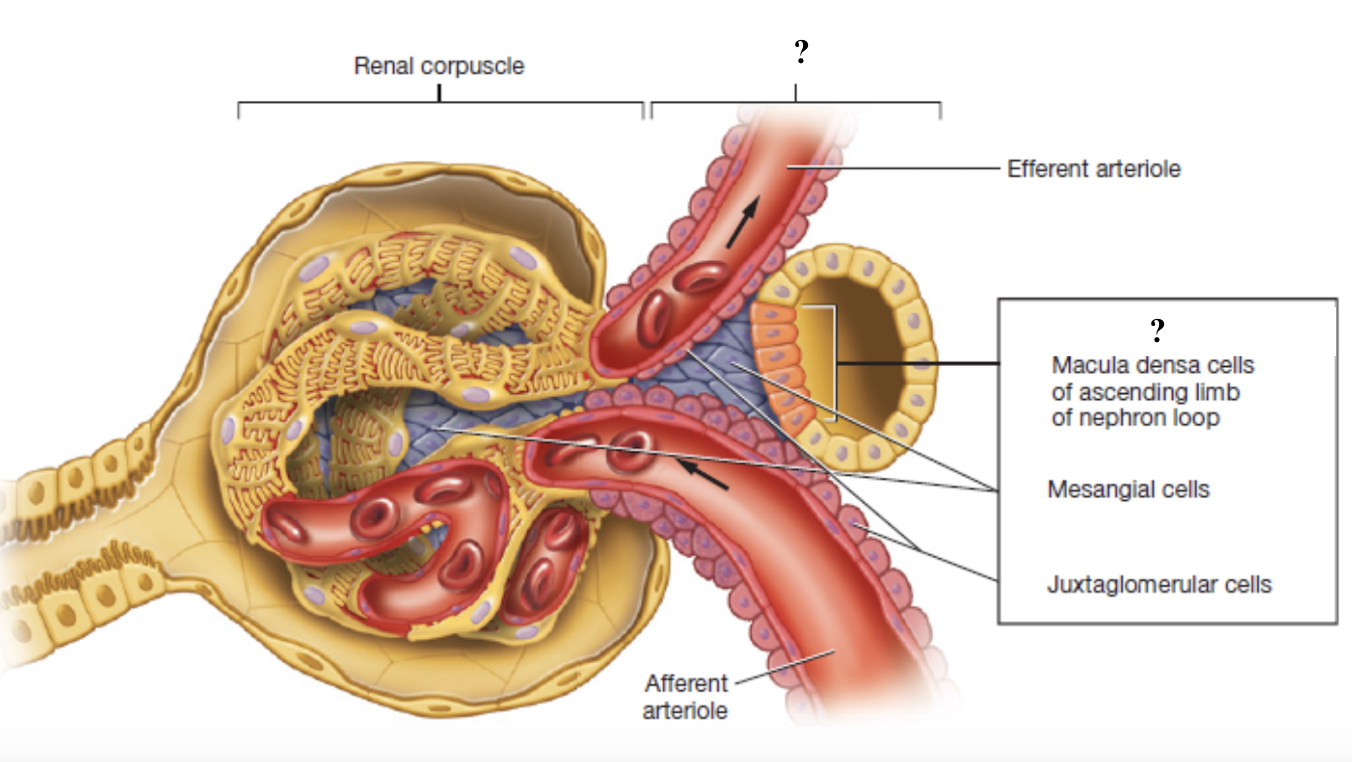
macula densa cells
tightly packed sensory cells located where the ascending limb of the nephron loop meets the distal convoluted tubule
monitor concentration of sodium chloride (NaCl) in the filtrate
act as chemical sensors that signal when salt levels are too high or low
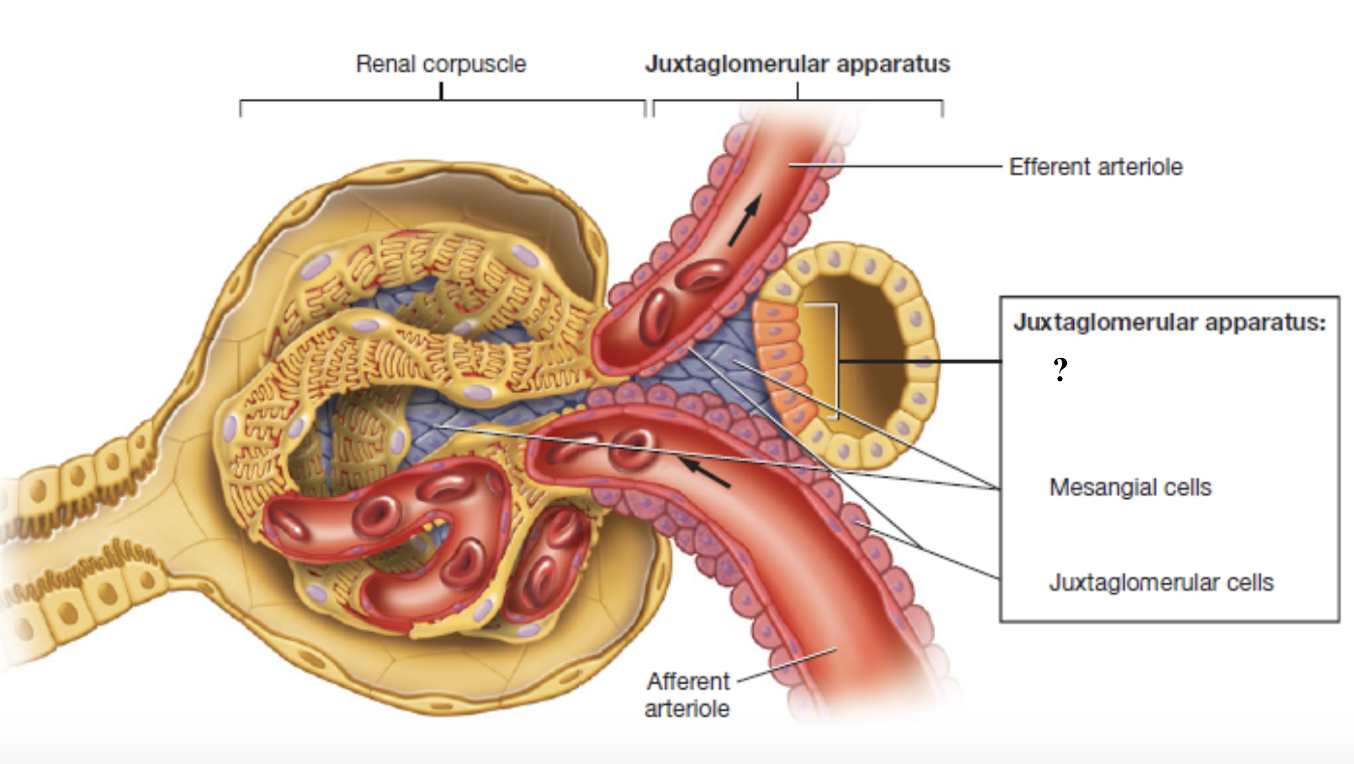
juxtaglomerular cells
specialized smooth muscles cells found on the afferent arteriole
store and secrete the enzyme renin which starts chain reaction to increase blood pressure and maintain filtration
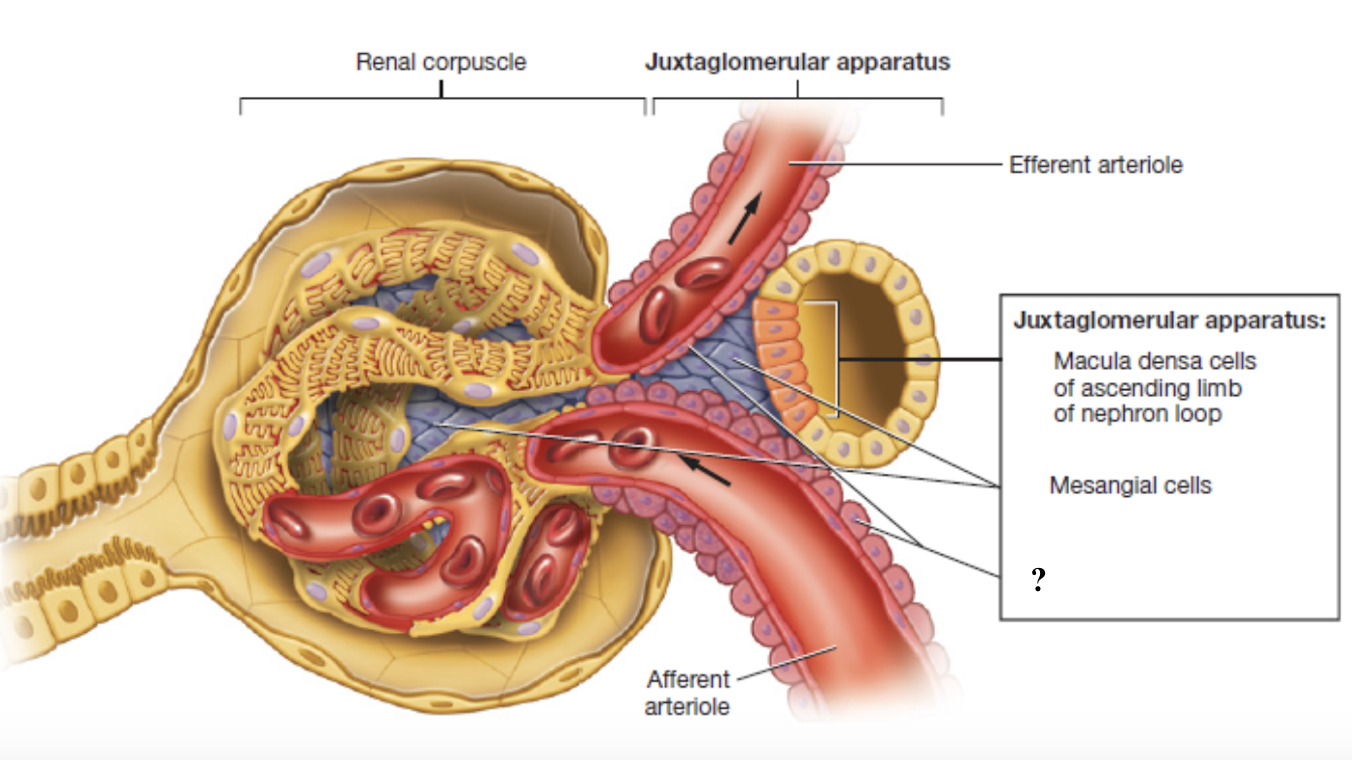
mesangial cells
cells located within the glomerulus and between the afferent and effferent arterioles
give structural support and contract or relax to change surface area available for filtration
indirectly affect the glomerular filtration rate
glomerular filtration rate
volume of filtrate produced by the kidneys each minute
regulated by the juxtaglomerular apparatus
urine
fluid containing water, salts, and metabolic waste products
completes its transformation once it leaves the papillary ducts and enters the minor calyces
urinary tract
made up of several organs of the urinary system
ureters, urinary bladder, urethra
ureters
tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder
lined with transitional epithelium for stretch and smooth muscle for peristalsis
connect to posteroinferior wall of urinary bladder at ureteral orifices
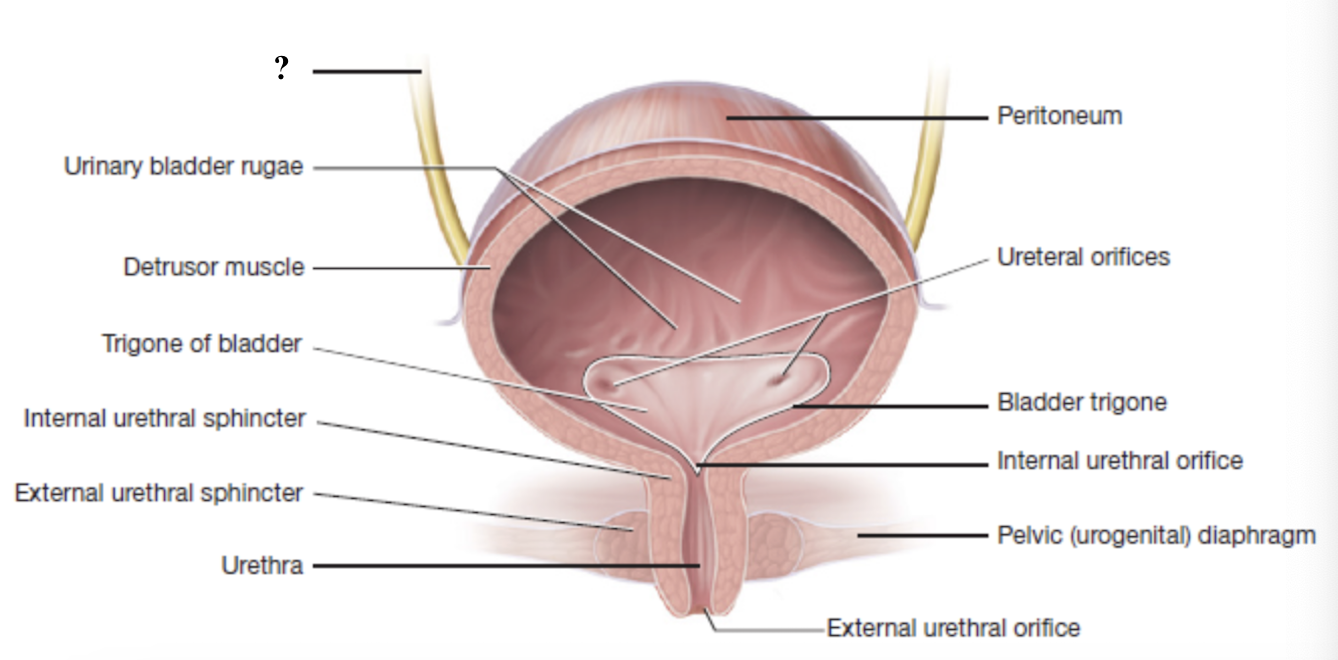
ureteral orifices
openings in the posteroinferior wall of the urinary bladder where each ureter connects
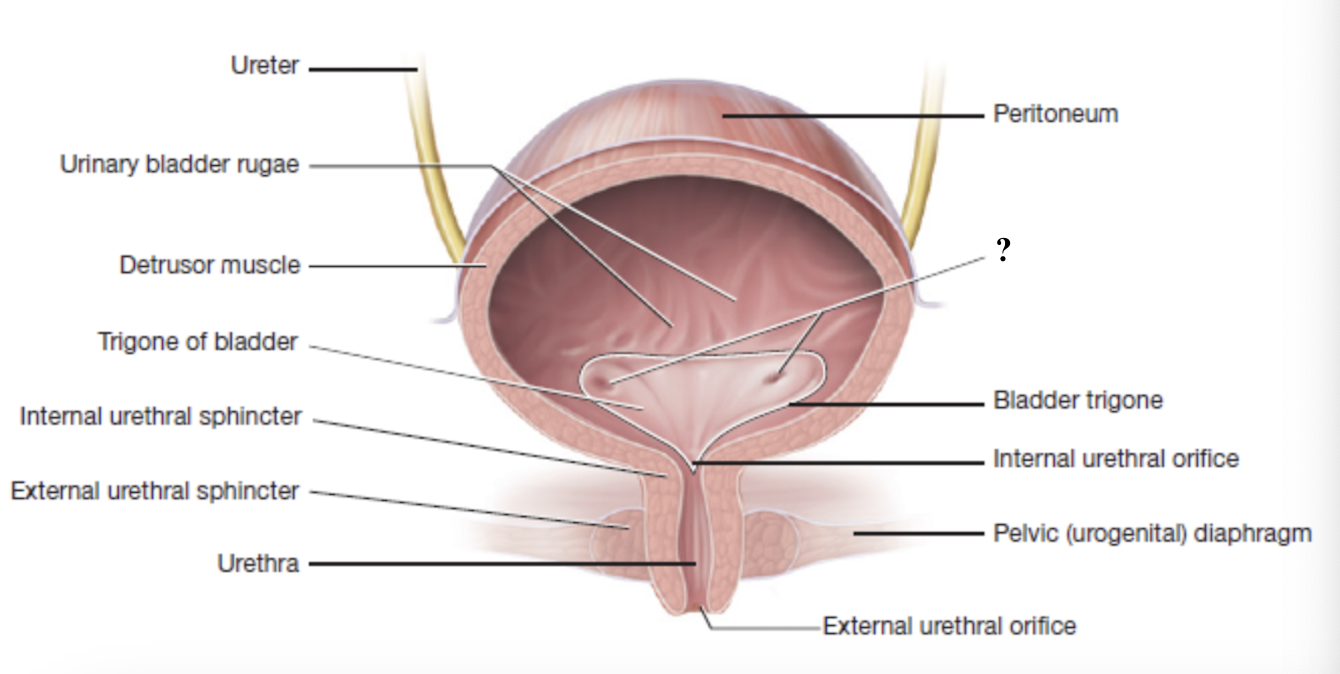
urinary bladder
muscular, hollow organ that stores urine until it is ready to be expelled
lined with transitional epithelium for stretch
contains detrusor muscle and urinary bladder rugae
detrusor muscle
smooth muscle in the urinary bladder that contracts during urination
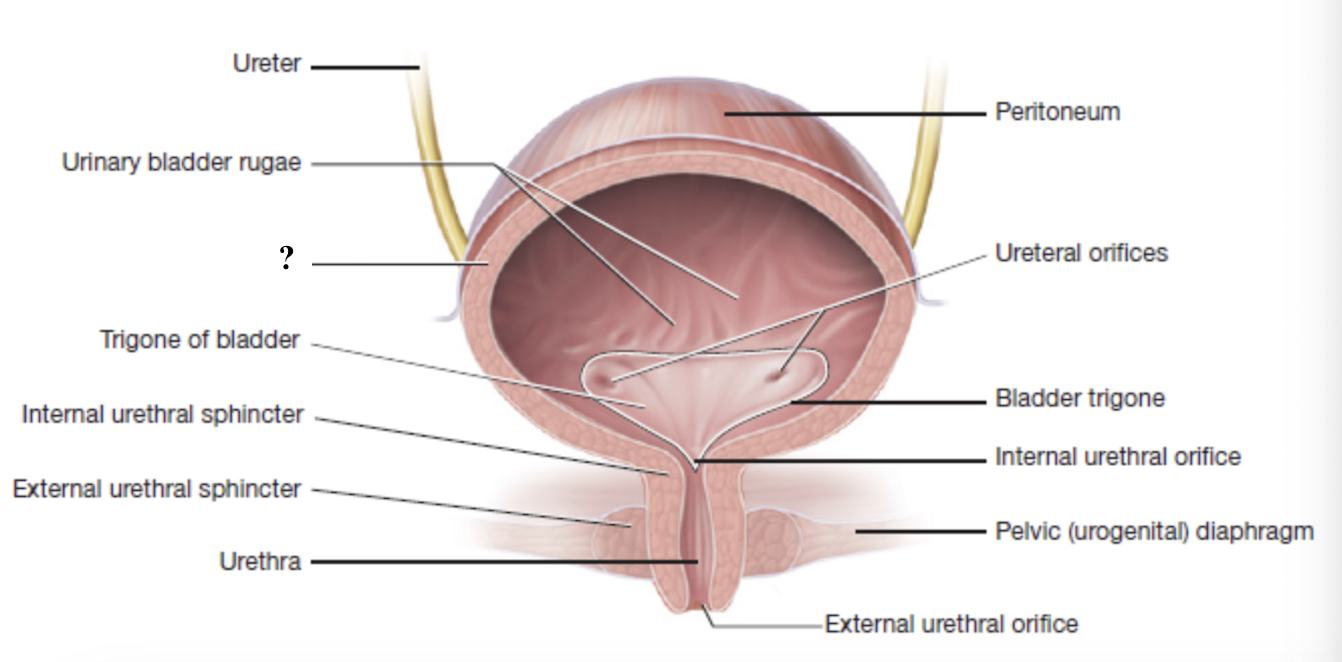
urinary bladder rugae
inner wall folds of the urinary bladder that flatten out as the bladder fills
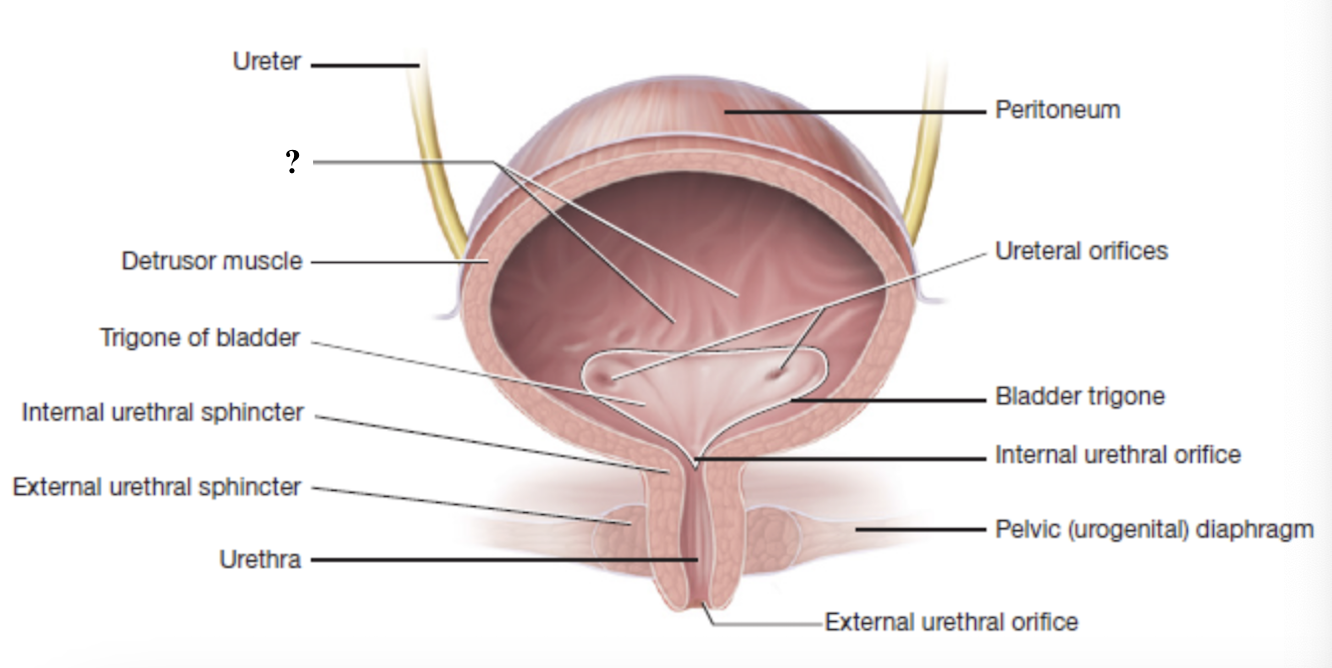
trigone
smooth, triangular shaped region at the base of the bladder
has three openings for the two ureters and one urethra
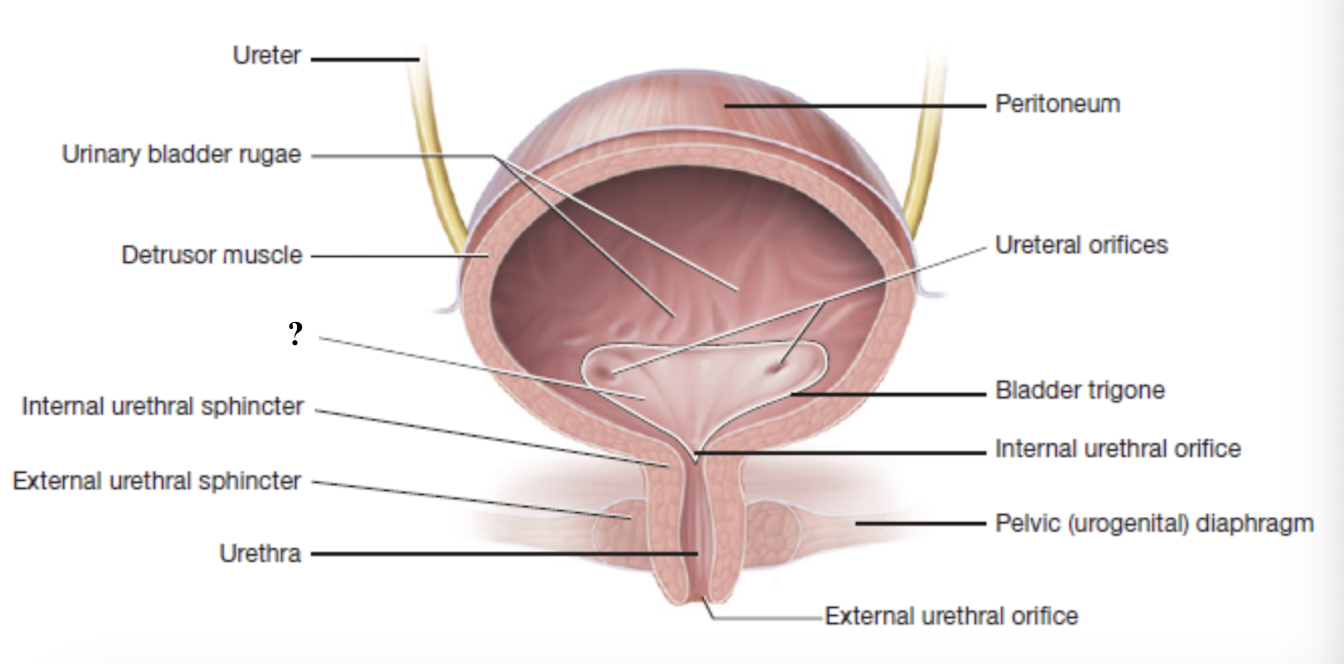
internal urethral orifice
opening at the bottom of the trigone that marks the start of the urethra and the point where urine leaves the bladder
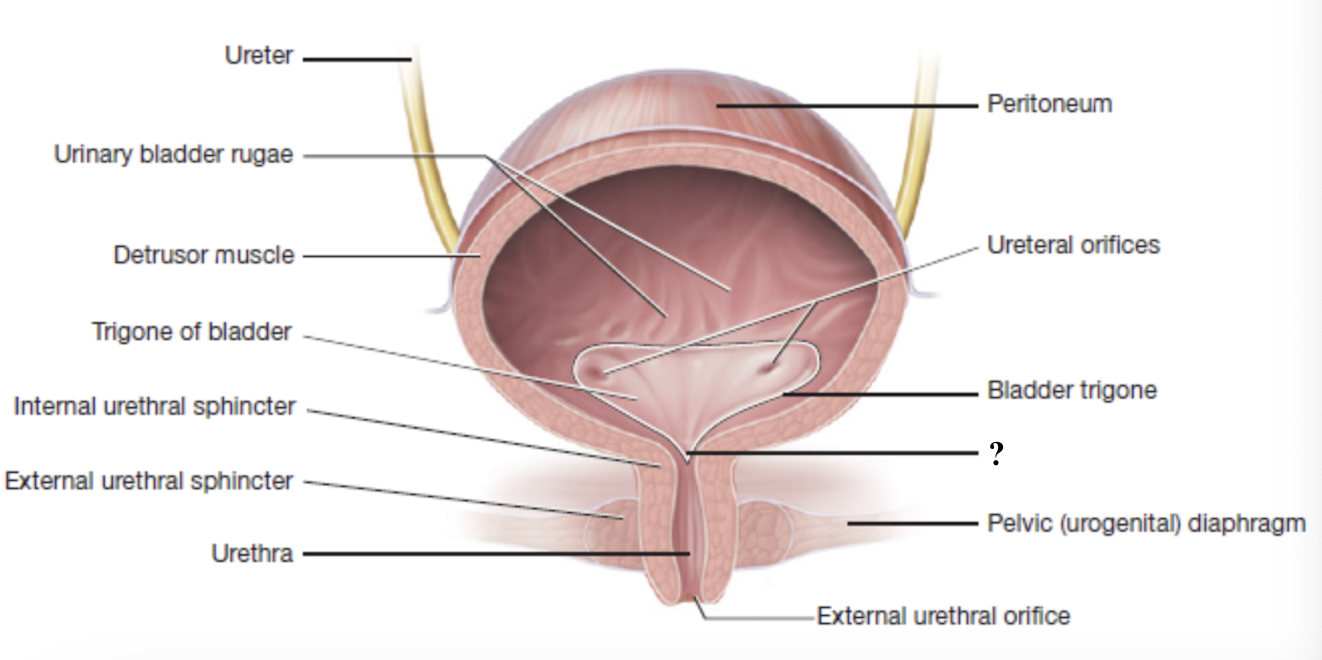
urethra
final tube through which urine leaves the body
surrounded by two sphincters
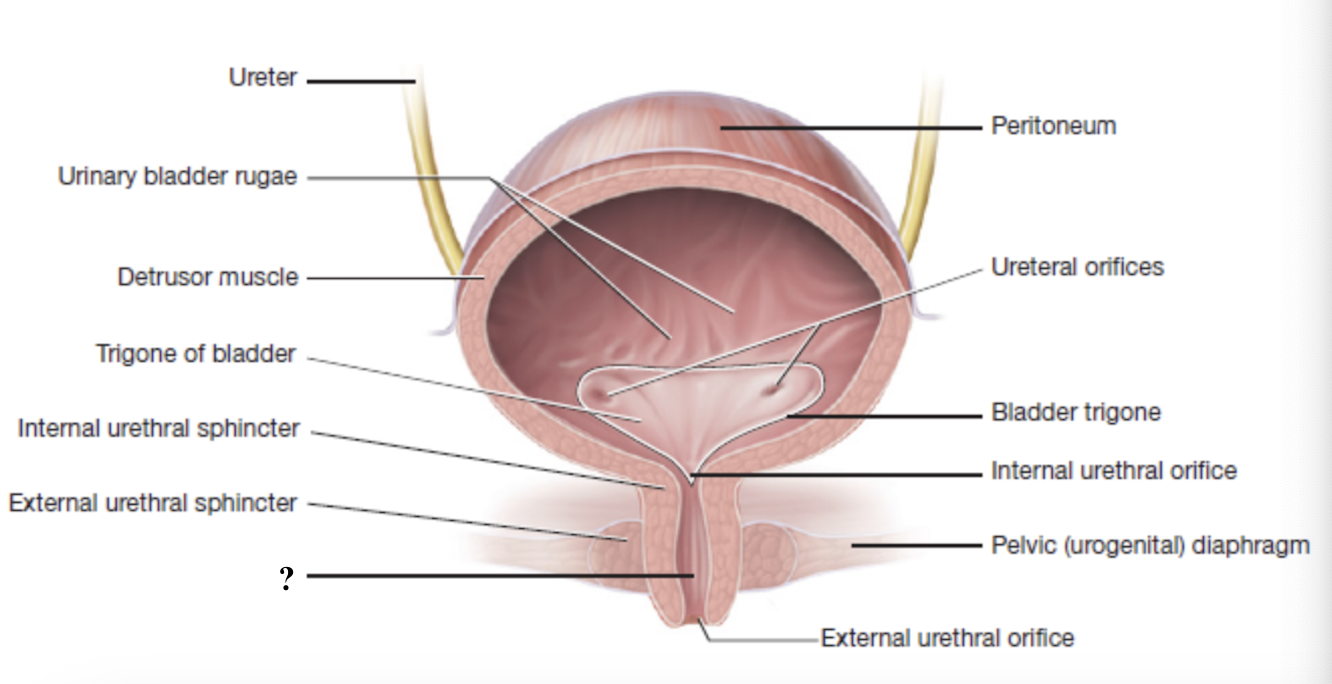
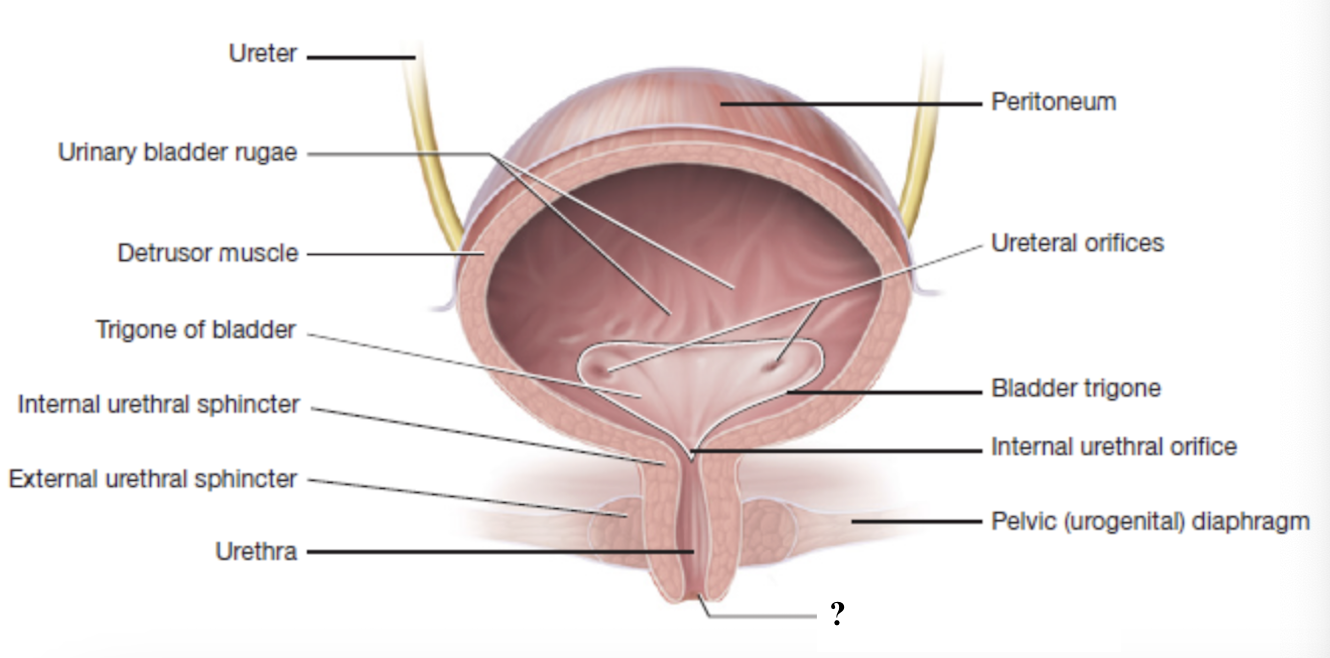
internal urethral sphincter
involuntary control, made of smooth muscle
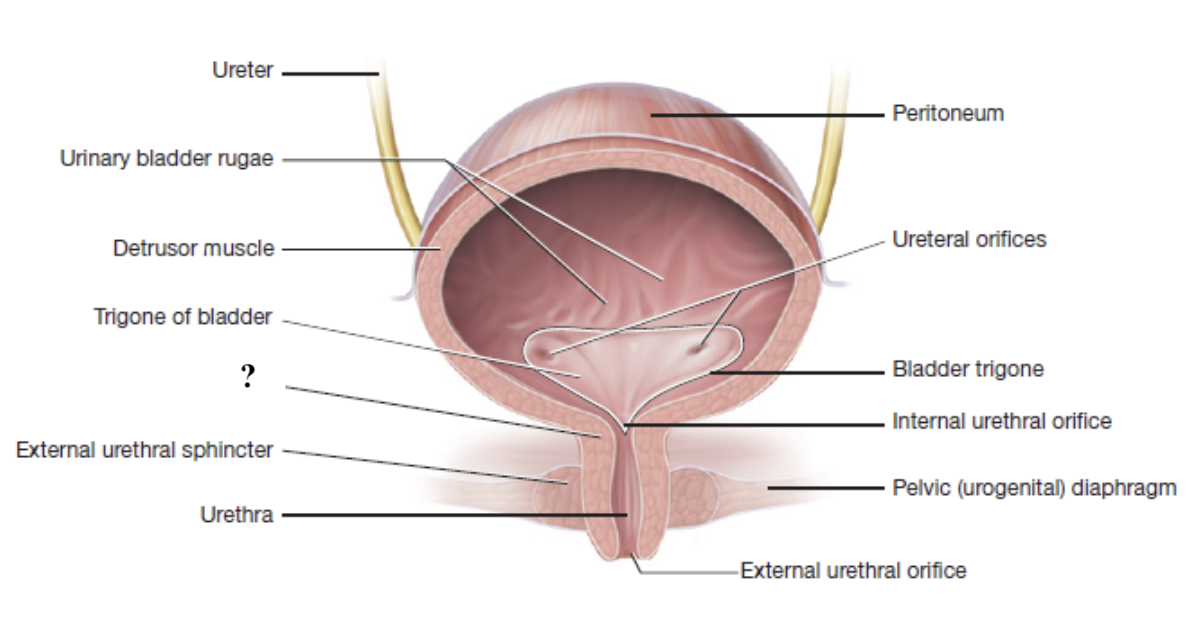
external urethral sphincter
voluntary control, made of skeletal muscle
part of the levator ani muscle group (pelvis urogenital diaphragm)
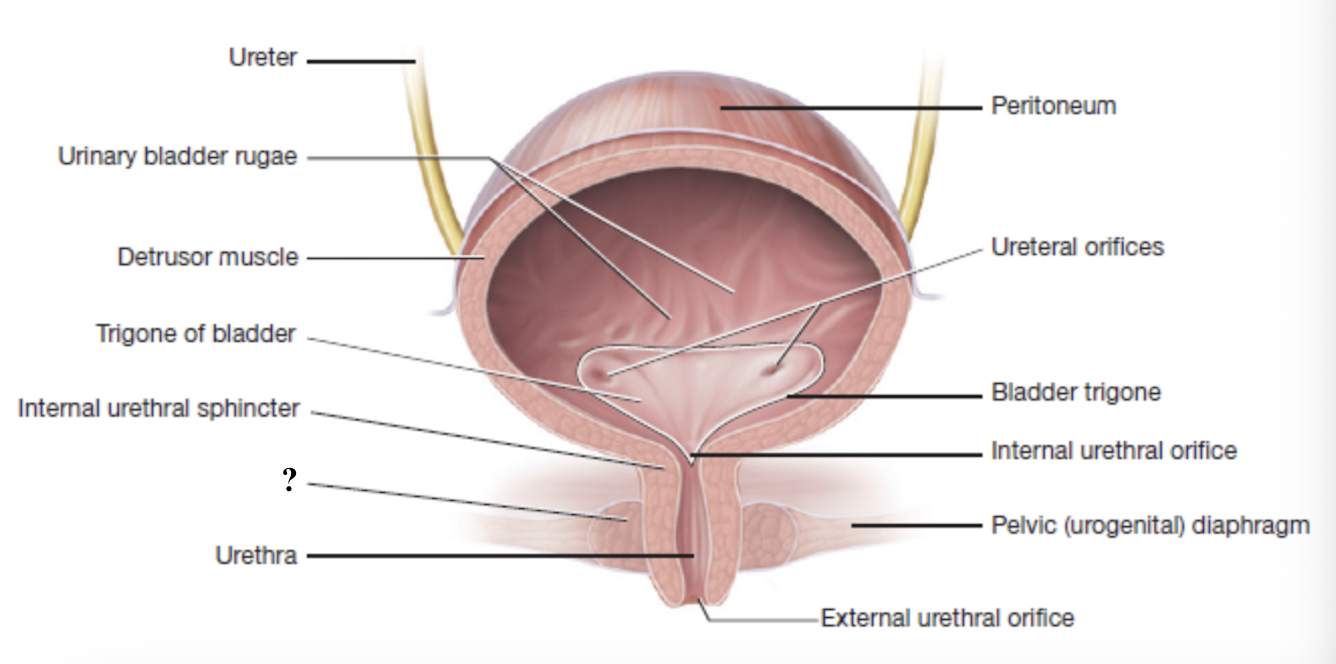
external urethral orifice
urine passes through this during micturition/urination when both sphincters relax
filtrate forms in nephron → renal tubule → collecting duct → papillary ducts → minor calyces → major calyces → renal pelvis → ureters → ureteral orifices → urinary bladder → trigone → internal urethral orifice → internal urethral sphincter → external urethral sphincter → urethra → external urethral orifice → urine exits body
path of urine flow
female urethra
short at about 4 cm
more prone to urinary tract infections
male urethra
much longer at about 20 cm
divided into three regions
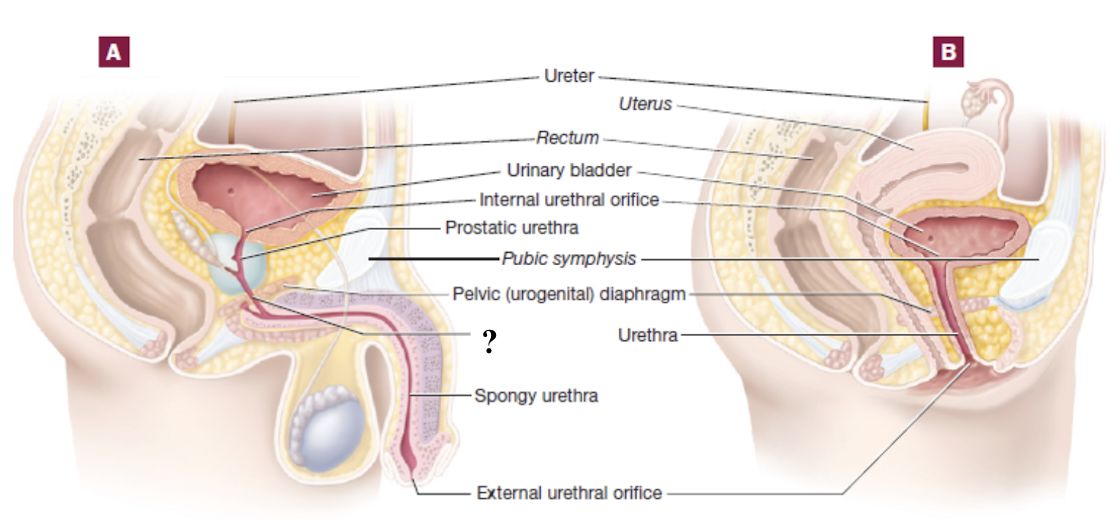
prostatic urethra
part of male urethra that passes through the prostate gland
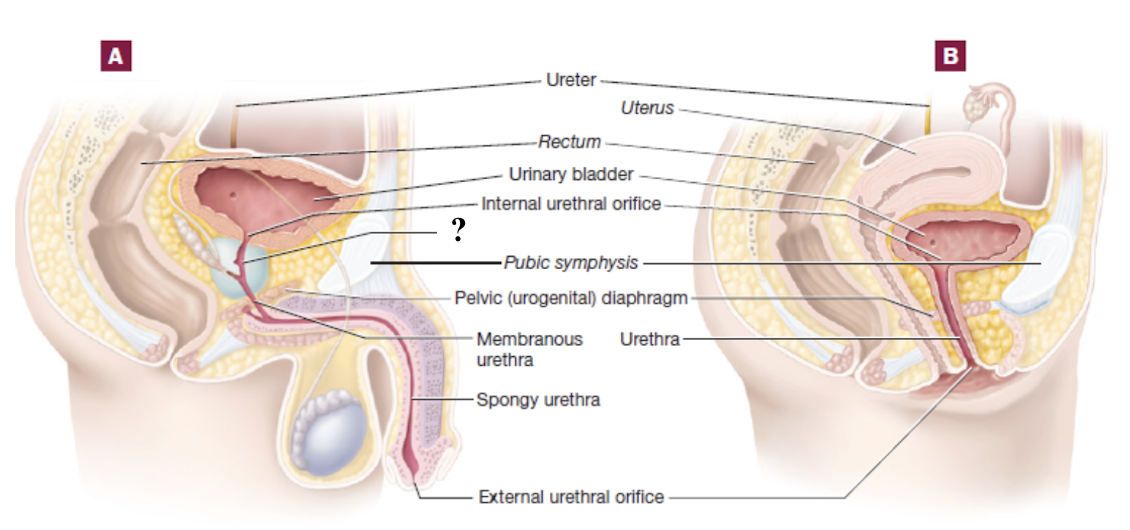
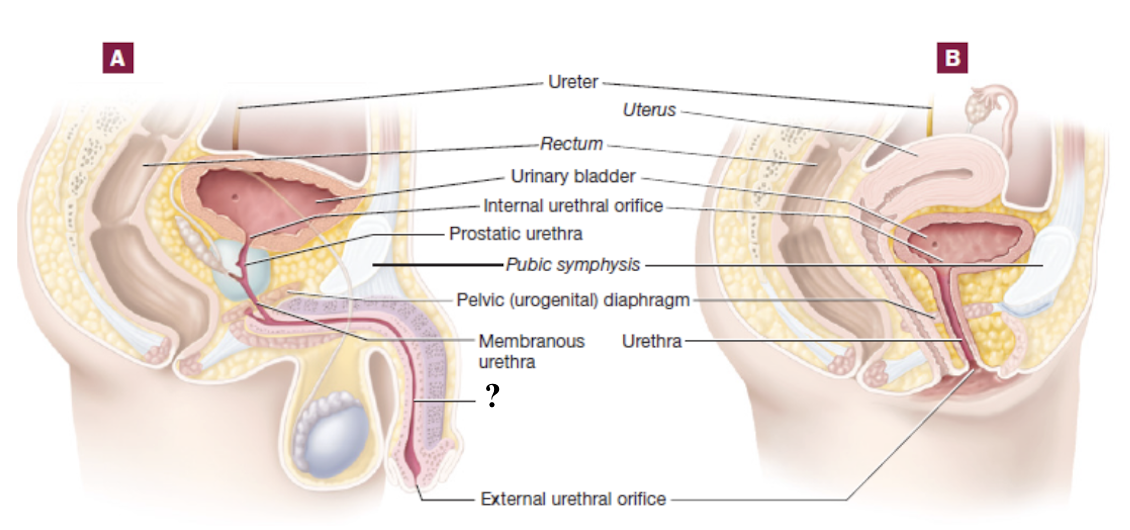
membranous urethra
short segment of male urethra that passes through the pelvic diaphragm
spongy or penile urethra
part of male urethra that passes through the penis within erectile tissue
urinalysis
quick and noninvasive laboratory examination of urine properties
physical: color, clarity, and odor
chemical: pH, protein, glucose, ketones, or blood
microscopic: cells, crystals, bacteria, or casts
urochrome
pigment that gives urine its normal, pale yellow color
dialysis
treatment that takes over the kidney’s role of cleaning the blood when the kidneys can no longer do so effectively
removes waste products, excess fluids, and toxins
helps keep electrolytes in balance
hemodialysis
type of dialysis in which blood is pumped through a machine with a special filter (dialyzer) and then returned to the body
peritoneal dialysis
type of dialysis in which cleansing fluid is placed in the abdominal cavity and the peritoneum acts as a natural filter before the fluid is drained
high creatinine in blood
above 5-10 mg/dL
kidney function decline causes creatinine to build up in blood as kidneys cannot filter it into urine
high blood urea nitrogen
poor filtration as kidneys cannot remove urea nitrogen through urine
proteinuria
protein in urine which may be due to kidney damage
hematuria
blood in urine which may be due to kidney disease, infection, or injury
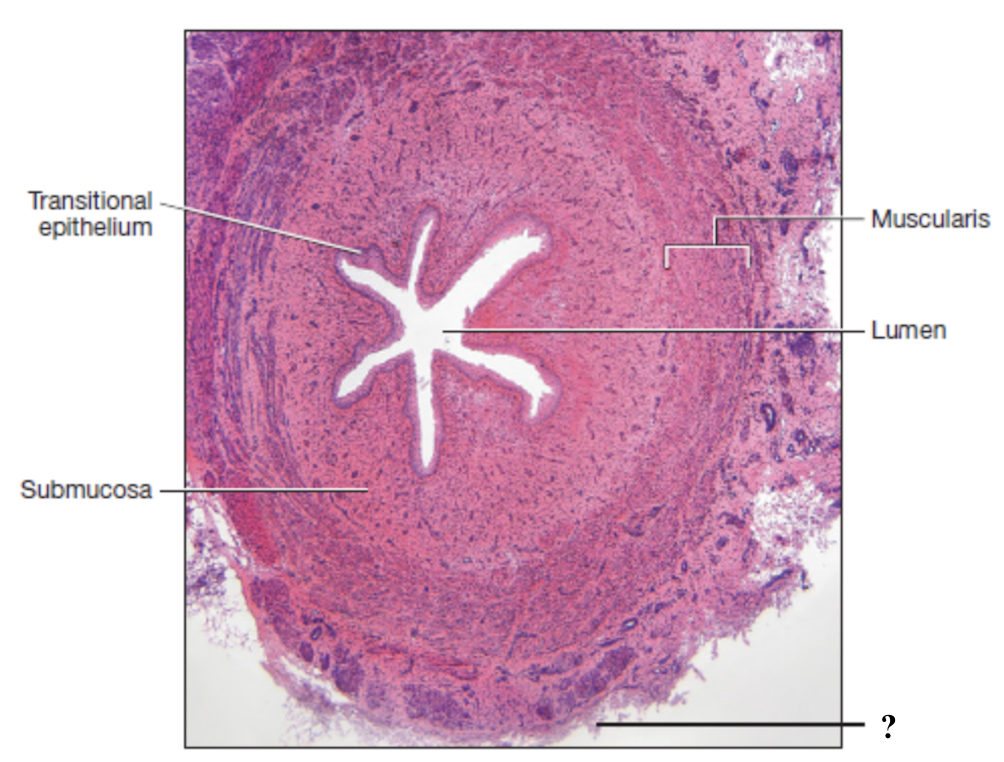
mucosa of ureter
innermost layer consisting of transitional epithelium (stratified) and thin layer of loose connective tissue
apical cells: dome shaped or flat and can stretch or flatten to allow expansion of the urinary bladder
basal cells: cuboidal and provide support for upper layers
submucosa of ureter
middle layer made of loose connective tissue
contains many glands that secrete mucus to act as a protective barrier
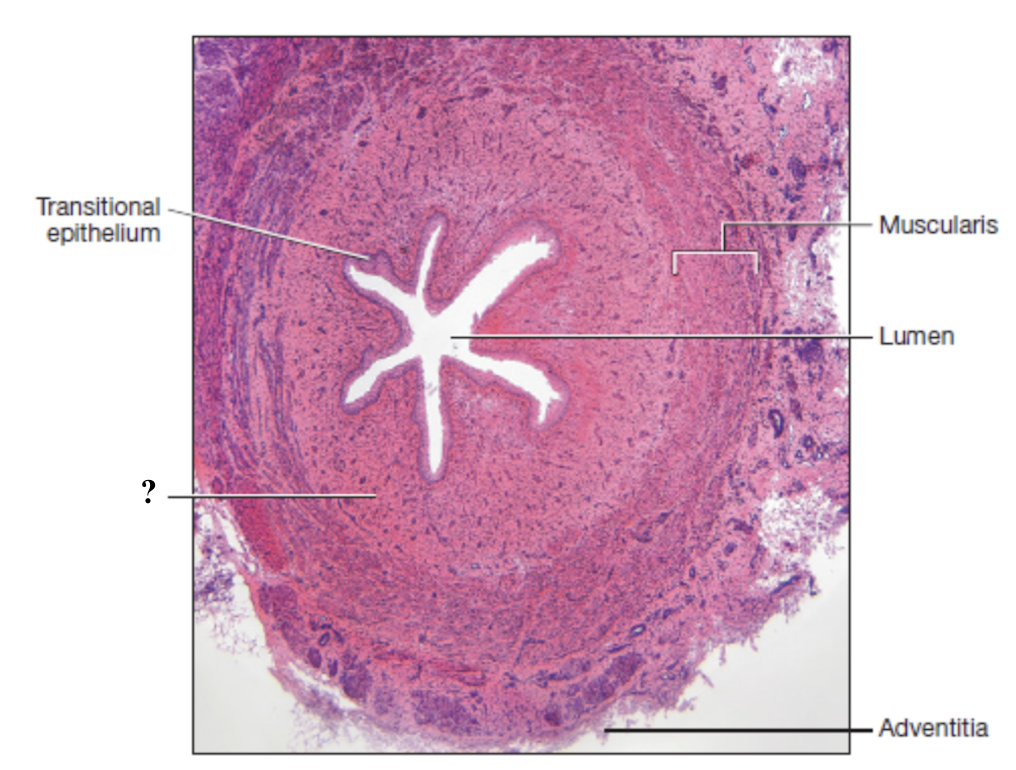
muscularis of ureter
layer of smooth muscle that contracts to propel urine through the urinary tract by peristalsis
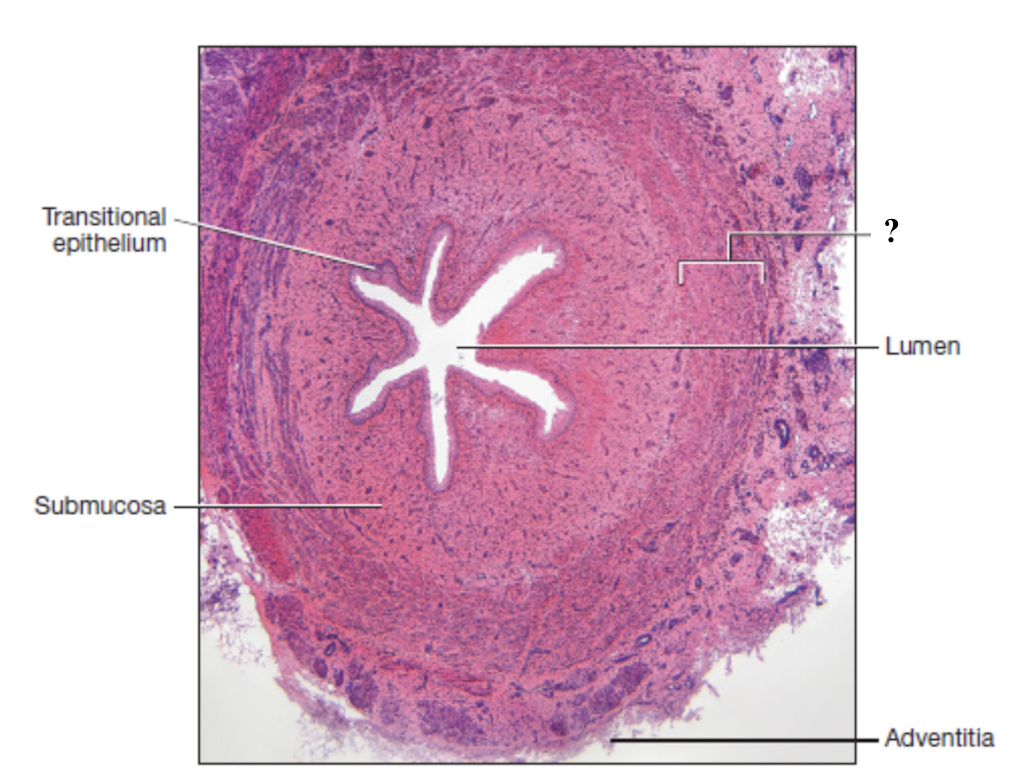
adventitia of ureter
outermost layer composed of dense irregular collagenous connective tissue
anchors the ureters and bladder in place