GI - Pathology
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
what is the purpose/role of gastric mucosa?
Protection from auto-digestion by stomach acid
• Mucus secreted by foveolar cells
• Bicarbonate secreted by epithelial cells
• Epithelium with tight junctions
• Blood flow removes acid
• Prostaglandins
concurrent symptoms in acute gastritis may indicate what?
"acute erosive hemorrhagic gastritis"
causes of chronic gastritis:
Autoimmune gastritis
H. Pylori gastritis
(MOST COMMON)
• Radiation
• Reflux• Trauma
• Systemic diseases
what is the most common pattern of gastritis?
H. pylori
what gastritis is associated with gastric adenocarcinoma and lymphomas?
H. pylori
- unrelated to pernicious anemia, antibodies or achlorhydria
Antibodies to parietal cells and/or decrease in intrinsic factor leads to pernicious anemia(megaloblastic, macrocytic anemia) in minority of patients is seen in what pathology?
autoimmune gastritis
what consequence of chronic gastritis presents a predisposition to adenocarcinoma?
intestinal metaplasia
what intestinal metaplasias can arise from chronic gastritis?
❖ Goblet cells (similar to small intestine) replace normal gastric epithelium
❖ Mucous cells (similar to pyloric antrum)
❖ Predisposition to adenocarcinoma
what is often associated with H. pylori, NSAIDs, or cigarettes?
peptic ulceration
what is Produced by imbalance between gastroduodenal mucosal defense mechanisms and damaging forces (e.g., gastric acid and pepsin)?
peptic ulceration
Damage by gastric secretions breaks down mucosa is known as...
peptic ulceration
the gross morphology of what is usually several cms, sharply defined (punched out) ulcers?
peptic ulcers
the histopathology of what presents as fibrous scar with granulation tissue, inflammation, and necrotic slough?
peptic ulcers
symptoms of gastric adenocarcinoma:
❖ Dyspepsia
❖ Dysphagia
❖ Nausea
- Weight loss- Anorexia- Altered bowel habits- Hemorrhage- Anemia
❖ H. pylori and EBV
❖ Partial gastrectomy (but not directly associated with peptic ulcers)
these show an increased incidence of what other pathologies
gastric malignancies
what gastric malignancy has a site most commonly in the distal stomach along the lesser curvature of the antrum and is rare in fundus?
adenocarcinoma
❖ Increasing in cardia, likely related to Barrett esophagus and GERD
rates of adenocarcinoma are increasing in the cardia likely related to what?
Barrett esophagus and GERD
Sheets of discohesive cells with vacuoles of mucindisplacing nuclei to one side (signet-ring cell) describes which type of histopathology seen in gastric carcinoma?
the diffuse type
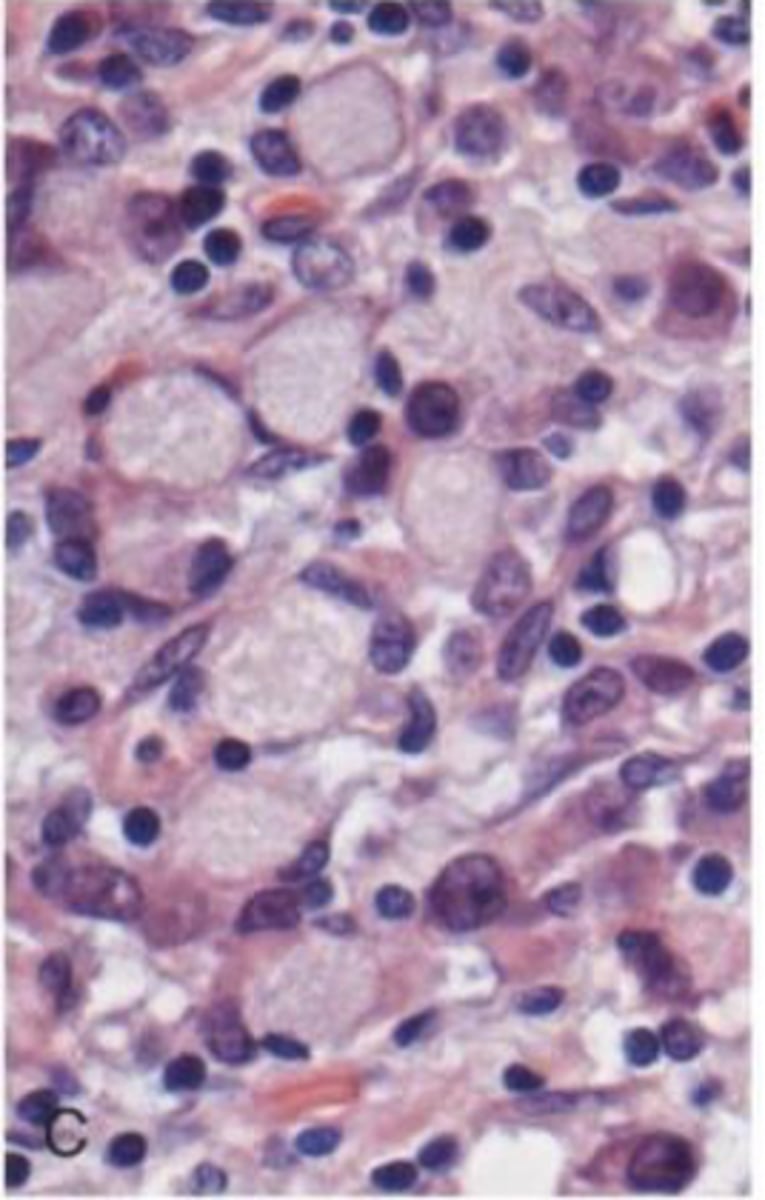
what is the predilection of the intestinal type histopathology in gastric carcinoma?
2:1 in favor of men
mean age of the intestinal type histopathology?
55
the intestinal type histopathology seen in gastric carcinoma is more common in which countries?
Japan,South America, Eastern Europe
what is the overall prognosis of gastric carcinoma?
Overall 5 year survival 28%
what percentage of gastric carcinomas are adenocarcinomas?
90%
between intestinal and diffuse infiltrative growth patterns seen in gastric carcinomas, which is more common
intestinal
what is the most common growth pattern in gastric carcinomas?
intestinal
between the intestinal and diffuse types of gastric carcinoma, which has incidence that varies with geography?
intestinal type
overall survival rate for gastric carcinoma is
less than 30 percent in 5 years
the most common cause of childhood diarrhea-related deaths worldwide is
infectious enterocolitis
what is the most common bacterial enteric pathogen?
Campylobacter jejuni
what are the 2 bacteria that are seen in infectious enterocolitis?
Clostridium difficile
Campylobacter jejuni
Enterotoxin causes superficial, gray mucosal exudate and fibrinous necrosis describes what?
Pseudomembranous colitis (C. diff overgrowth)
what is associated with an overgrowth of C. diff
Pseudomembranous colitis
symptoms of Pseudomembranous colitis?
Fever, toxicity, abdominal pain and diarrhea
what is the Most common parasitic infection in humans?
Giardia lamblia
the most common malabsorption syndrome?
Celiac disease
common causes of malabsorption syndromes
❖ Crohn disease
❖ Celiac disease
❖ Pancreatic insufficiency
Celiac sprue or gluten-sensitive enteropathy is seen in...
celiac disease
Small intestinal villi atrophy is seem in...
celiac disease
celiac disease is _______ and _______ mediated
genetic and immune mediated
Familial linkage with HLA-DQ2, HLA- DQ8 describes the genetic-mediated aspect of what disease?
celiac disease
Immune response to gliadin, a glycoprotein component of wheat, barley, and rye describes the immune-mediated aspect of what disease?
celiac disease
Loss of villous architecture and crypts is a histopathological finding in what disease?
celiac disease
treatment for celiac disease
gluten-free diet
what disease is most common in terminal ileum, but may involve any part of GI tract?
Crohn's disease
Transmural inflammation is seen in...
Crohn's disease
T or F: Crohn's disease present as a discontinuous pattern
TRUE
❖Cobblestone pattern and fissured ulcers
❖Stricture formation
❖Regional nodes enlarged
❖Discontinuous lesions
the above are features of what pathology?
established Crohn's disease
❖ Aphthous-like ulcers
❖ Linear ulcers with hyperplastic margins
❖ Cobblestone appearance of mucosa due to hyperplasia with fissuring
❖ Epulis fissuratum-like polypoid tags on vestibular and retromolar mucosa
❖ Lip swelling
the above are oral lesions seen in what pathology?
Crohn's disease
❖ Transmural inflammation with submucosal edema
❖ Ulcers extend deep into the bowel and form fissures
❖ Noncaseating granulomas
the above describe histopathology of what disease?
Crohn's disease
Chronic inflammation of rectal mucosa that may involve the entire colon (pancolitis) in a continuous pattern is what pathology?
ulcerative colitis
T or F: you expect to see transmural inflammation, skip lesions, or granulomas in ulcerative colitis
FALSE you will not see any of these signs
Pancolitis of 8-10 or more years increases cancer risk
the above is a complication of what?
local complication of ulcerative colitis
what percentage of ulcerative colitis includes chronic, quiescent colitis with infrequent episodes of relapse?
80%
Multiple GI hamartomatous polyps and perioral and/or oral pigmentation are characteristics of what?
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
what is the lifetime risk of cancer in someone with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome?
40%
• Testicular, gastric, small intestine, colon, pancreas, lung, ovary, uterus
what is the biggest risk factor for malignant transformation in adenomas of the colon?
size
T or F: Precursors of colorectal adenocarcinomas are a risk for malignant transformation
TRUE
what pathology more often shows invasion than tubular pattern which is likely a feature of size more than architecture
villous benign tumor of the colon
Poorly differentiated, highly aggressive, mucin-producing adenocarcinomas
these are characteristics that are common amongst what group of pathologies?
malignancies of the colon
what is the second most common cause of neoplastic death (15%) in USA?
malignancies of the colon
what is the most common pattern seen in malignancies of the colon?
sporadic colon cancer
childhood onset of multiple colorectal adenomas; hundreds by age 30-40, is characteristic of what pathology?
familial adenomatous polyposis
what disease presents with nearly 100% risk of adenocarcinoma, often multiple?
familial adenomatous polyposis
• Often by age 35, nearly 100% by 50
• Onset 20-30 years before sporadic cases
what are the two inherited polyposis syndromes?
❖ Turcot syndrome
❖ Gardner syndrome
of the two inherited polyposis syndromes, which presents with the following symptoms?
❖ Adenomas in colon, rectum, and small intestine
❖ High risk of carcinomas
❖ Osteomas of bone
❖ Soft tissue tumors
❖ Supernumerary teeth
Gardner syndrome
what determines the clinical patterns of malignancies of the colon?
morphology of the malignancy
what malignancy has peak incidence in people older than 60?
malignancies of the colon
obstruction, blood loss, or fatigue and anemia are the main clinical features of what group of pathologies?
malignancies of the colon
in the case of malignancies of the colon, why might there be no obstruction despite the existence of a large tumor?
feces are more fluid in the right (ascending) colon
between left and right malignancies of the colon, which is often diagnosed earlier?
left
❖ Feces more solid so obstructions are noticed earlier
this is in contrast to right colon cancers where feces is more liquid
do right or left cancers go longer undetected?
right
which group of cancers has overall, the best 5 year survival rate of internal malignancies in the USA?
malignancies of the colon
❖ 5 year survival = 65%
❖ 90% if localized; 13% if metastatic
diverticulosis is caused by.....
abnormal gut motility
❖ Abnormally high intraluminal pressure in colon (often sigmoid) caused by contractility of muscularis propria
❖ Herniation occurs at site of blood vessel supply to colon, between tenia coli
the above are characteristic of what pathology?
diverticulosis
most important complication of diverticulosis?
perforation of the colon wall
Acute inflammation of muscularis propria is characteristic of what pathology?
acute appendicitis
what is frequently associated with HPV infection?
SCCA
Most primary tumors of the peritoneum are...
mesotheliomas associated with asbestos exposure