AP Psychology: Unit 3 - Conditioning
1/47
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
behavioral perspective
explains behavior through conditioning
classical conditioning
form of conditioning where a NS elicits a response after being associated with a stimulus that already elicits that response
aquisition
the moment when a response is established based on conditioning
associative learning
learning that certain events occur together
unconditioned stimulus
something that has a natural response and can be used to create certain behaviors through classical conditioning
unconditioned response
the unlearned, naturally occurring response to the unconditioned stimulus
conditioned stimulus
formerly NS that comes to produce a conditioned response after being associated with an US
conditioned response
learned responses acquired through classical conditioning
extinction
gradual weakening of a CR that results in the behavior decreasing or disappearing
spontaneous recovery
the reappearance of a CR that has been extinguished
stimulus discrimination
the ability to distinguish between one stimulus and similar stimuli
stimulus generalization
occurs when an individual responds to stimuli similar to the original CS
higher-order conditioning
when a NS becomes linked to a CS
counterconditioning
technique developed by psychologists that is intended to change how we perceive certain stimuli
taste aversion
learned association between the taste of a certain food and illness, such that the food is considered to be the cause of the illness
one-trial conditioning
theory that learning takes place in a single pairing of a response and stimulus and is not strengthened over time by repeated exposure to stimulus
biological predaredness
idea that people and animals are inherently inclined to form associations between certain stimuli and responses
habituation
process of becoming desensitized to a repeated or continuous stimulus, resulting in a decreased response over time
operant conditioning
method of learning that uses rewards and punishment to modify behavior
reinforcement
process that increases the likelihood of a behavior being repeated in the future
punishment
consequence reducing the likelihood of a targeted and undesirable behavior from happening again
law of effect
responses that produce a satisfying effect after a particular stimulus are likely to occur again
positive reinforcement
desirable stimulus is introduced to encourage certain behavior
negative reinforcement
something that is unwanted is taken away to increase the likelihood of a behavior
positive punishment
giving an undesirable consequence after an unwanted behavior to make it less appealing
negative punishment
removing a pleasant stimulus to decrease a behavior
primary reinforcer
things that motivate behavior because they satiate an individual’s basic survival needs
secondary reinforcer
stimulus that reinforces a behavior after it has been associated with a primary reinforcer
reinforcement discrimination
when an individual learns to respond only to specific cues or signals that indicate when a behavior will be reinforced
reinforcement generalization
when a response that has been reinforced in the presence of one stimulus also occurs in the presence of a similar stimuli
shaping
the process of training a learned behavior that would not normally occur
instinctive drift
tendency of a trained animal to revert back to instinctual behaviors
superstitious behavior
a behavior linked to a particular outcome based on the belief in cause and effect, despite there being no logical or scientific connection between them
learned helplessness
when an individual feels powerless to change their situation due to repeated failures or negative outcomes in the past
continuous reinforcement
when a reinforcer or reward is given every time a desired behavior is exhibited
partial reinforcement
when a reinforcer or reward is given only a portion of the time, rather than every time it occurs
fixed interval schedule
set amount of time between occurrences of a reward or reinforcer
variable interval schedule
where a response is rewarded after an unpredictable amount of time has passed
fixed ratio schedule
schedule of reinforcement that reinforced a response only after a specified number of responses
variable ratio schedule
a schedule of reinforcement where a behavior is reinforced after a random number of responses
graphing of schedules of reinforcement
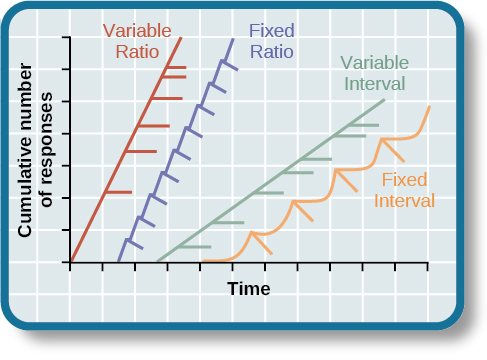
scalloped graph
occurs when responses start slowly but then increase in speed as the time that reinforcement is used nears
social learning
learning that takes place through an observational process of other humans (models)
vicarious conditioning
learning through observing other people’s responses to an environmental stimulus that is most noticeable to the observer
modeling
process of observing and imitating a specific behavior
insight learning
occurs when one suddenly realizes how to solve a problem
cognitive map
mental picture of image or the layout of the physical environment
latent learning
knowledge that only becomes clear when a person has an incentive to display it