Chapter 18: The Digestive System
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Functions (Next 8 Slides)
- Processes food into molecular forms that are transferred into the internal environment, which the circulatory system distributes to cells
Motility
- Movement of food through the gastrointestinal (GI) tract via ingestion, mastication, deglutition, and contraction of smooth muscle (peristalsis & segmentation)
Digestion
Chemical/Mechanical breakdown of food from macromolecules to smaller molecules, for absorption
Secretion
- Release of exocrine and endocrine and endocrine secretions into lumen of GI tract for digestion and regulation of digestion
Absorption
- Movement of digested end products into blood and lymph
Storage and Elimination
Temporary storage followed by elimination of indigestible food molecules (waste)
Immune Barrier
- Physical barrier to pathological organisms and toxins to tight junctions epithelial lining of the intestine
- As GI mucosa (mucous membrane) in in contact with the external environment, almost 80& of immune systems cells are here
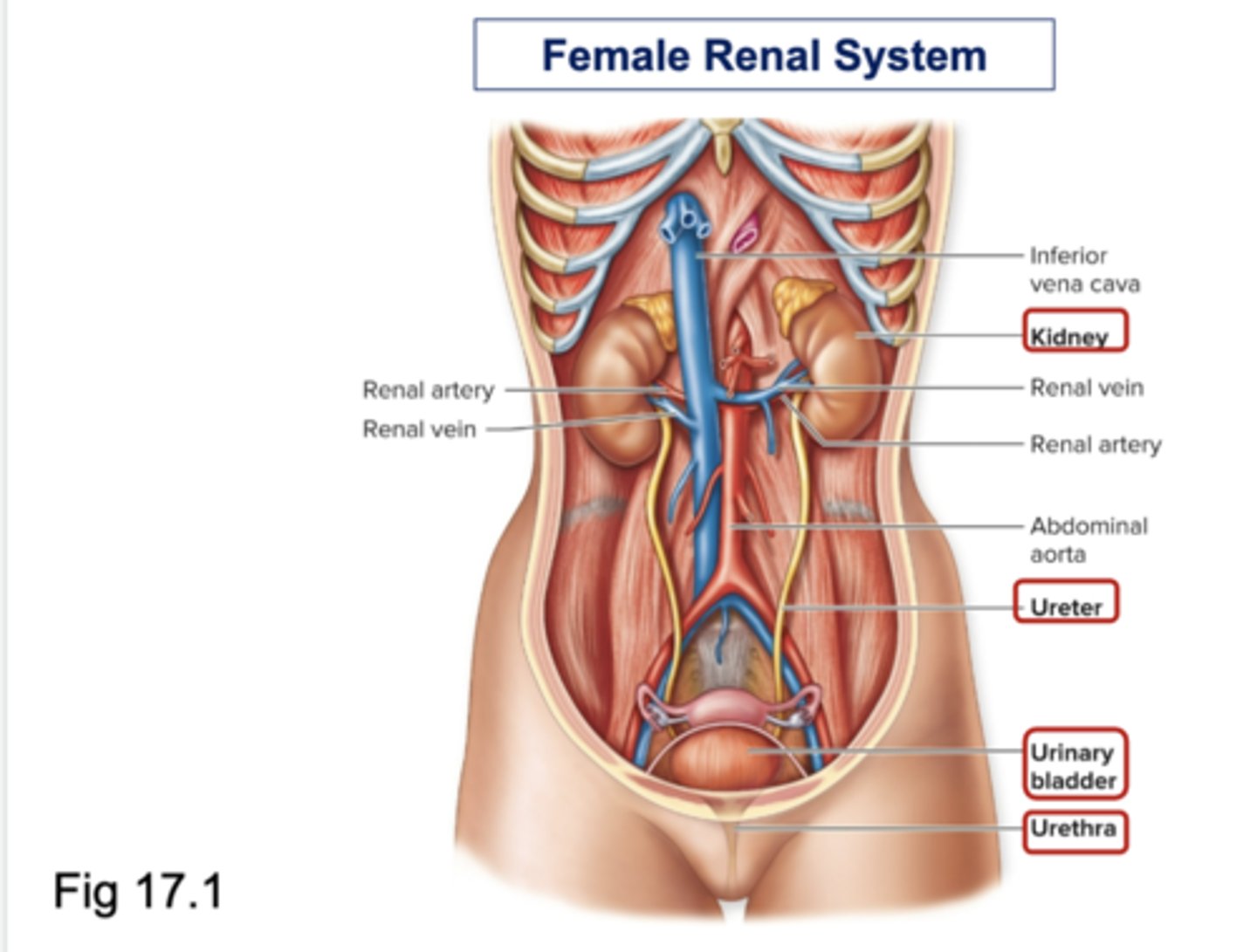
Digestion via Hydrolysis Reactions
☆ Digestion of food molecules occurs by hydrolysis reactions, the chemical breakdown of substance involving a reaction with water
Structures
1. Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract (Alimentary Canal)
2. Accessory Organs and Tissues
Gastrointestinal (GI) Tract (Alimentary Canal)
☆ Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine (SI), large intestine (LI)
- Appx. 30 ft long
Accessory Organs and Tissues
☆ Teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
Four Layers/Tunics of the Gut Wall (Next 4 Slides)
1. Mucosa (Innermost Layer)
2. Submucosa
3. Muscularis
4. Serosa (Outermost Layer)
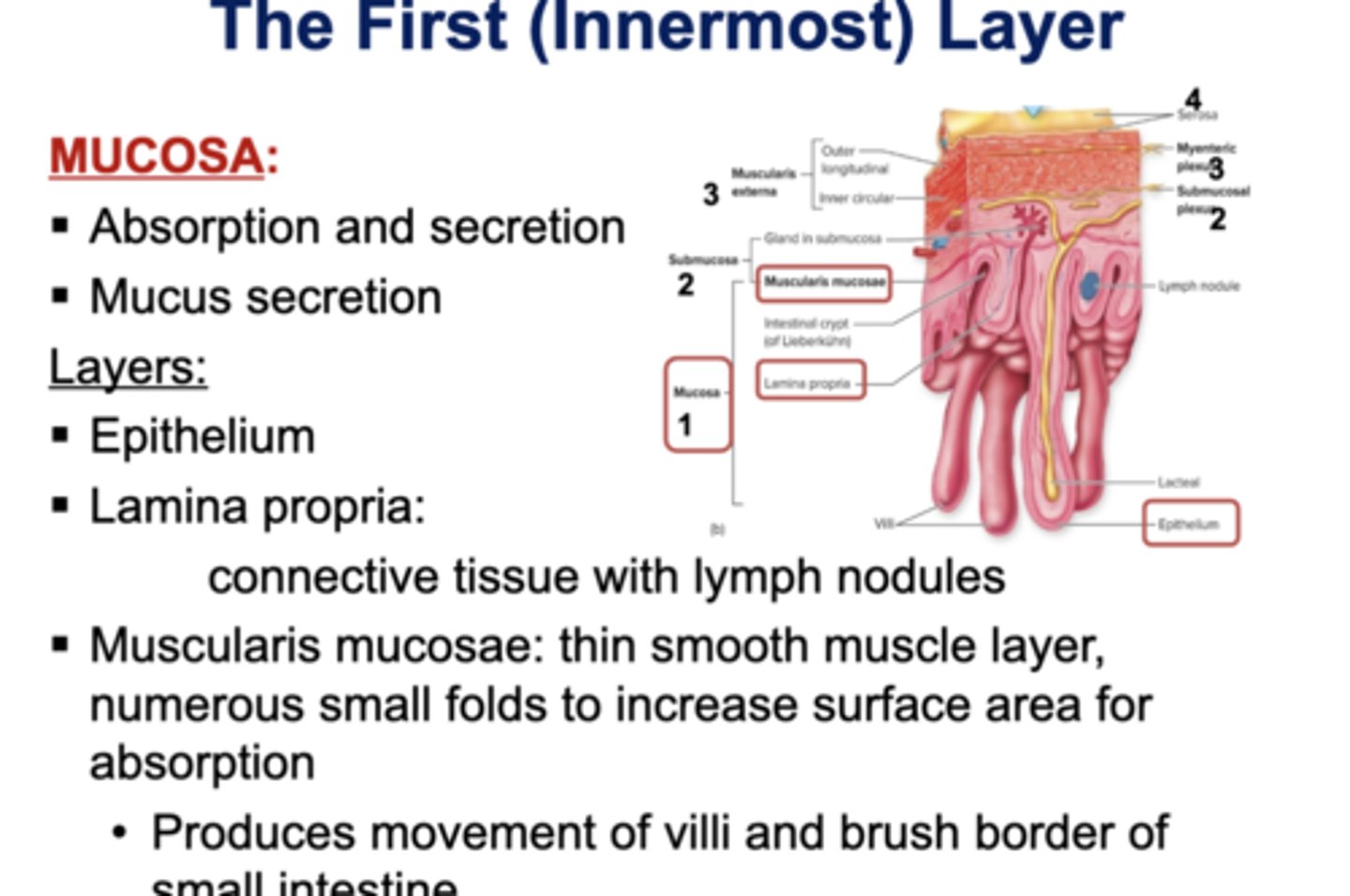
The First (Innermost) Layer
☆ Mucosa:
- Absorption and secretion
- Mucus secretion
☆ Layers:
- Epithelium
- Lamina Propria
~ connective tissue with lymph nodules
- Muscularis mucosae: thin smooth muscle layer, numerous small folds. to increase surface area absorption
~ Produces movement of villi and brush border of small intestine
☆ ELM
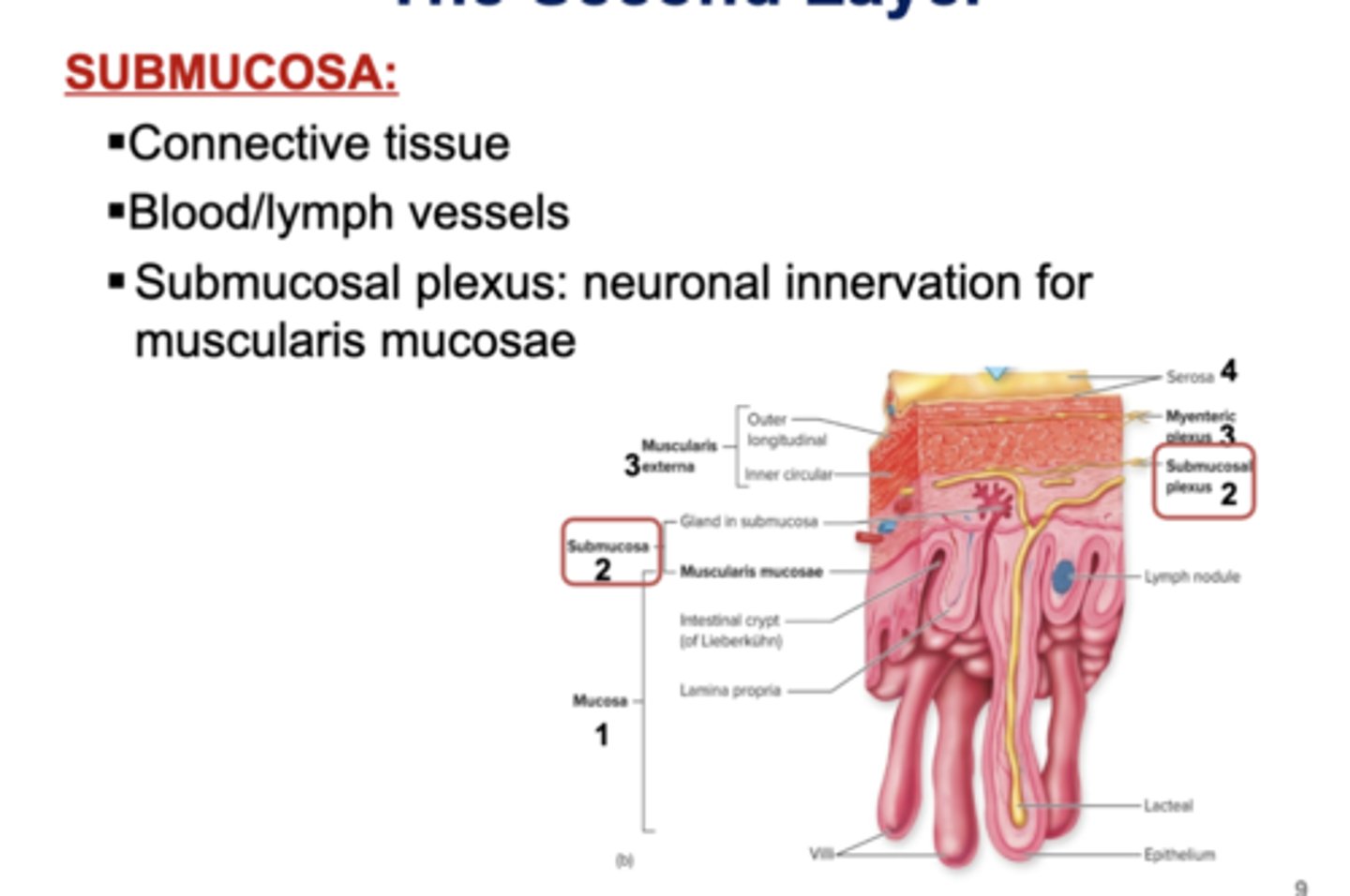
The Second Layer
☆ Submucosa:
- Connective tissue
- Blood/lymph vessels
- Submucosal plexus: neuronal innervation for muscularis mucosae (network of neurons)
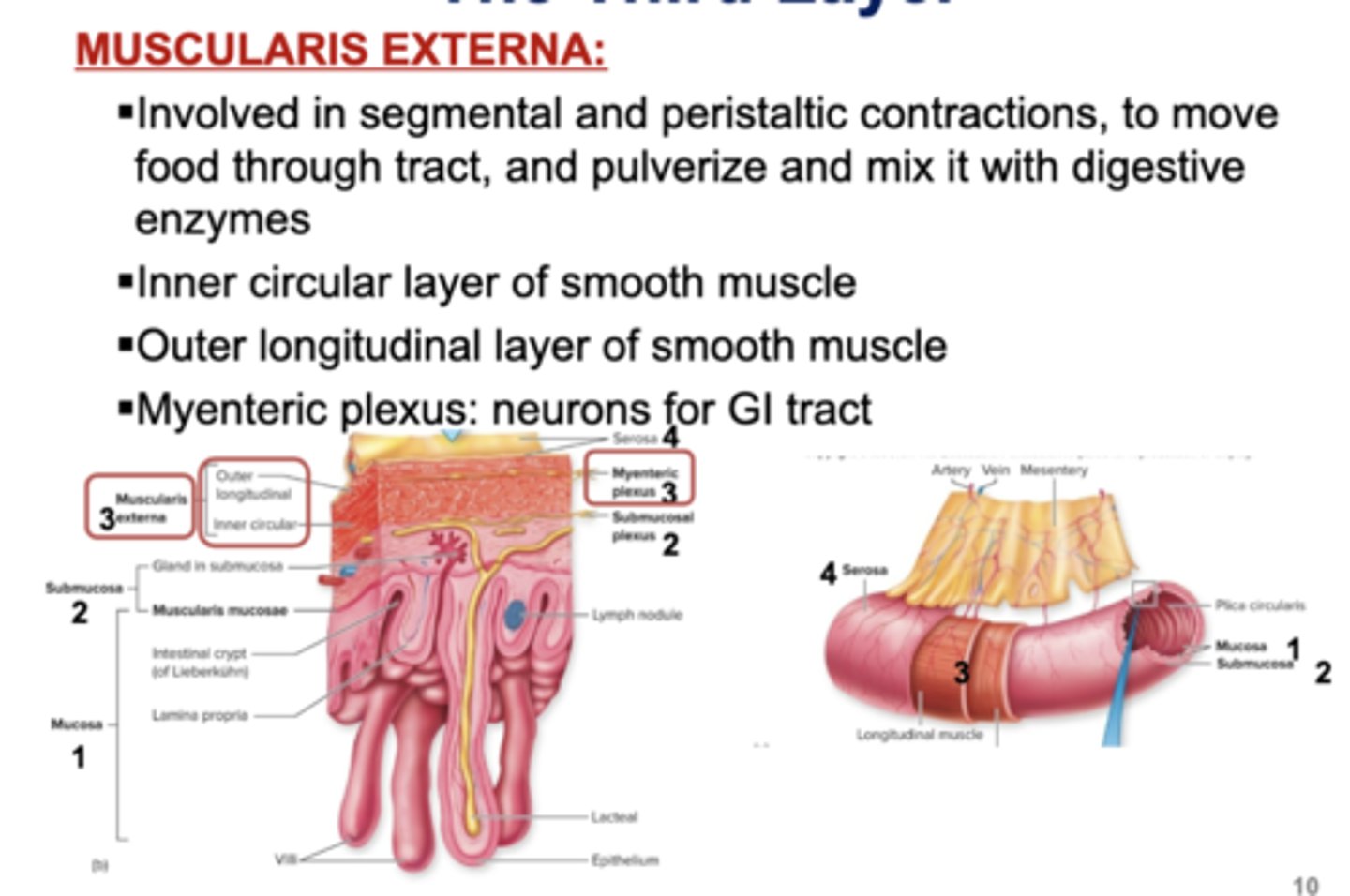
The Third Layer
☆ Muscularis Externa:
- Involved in segmental and peristaltic contraction, to move food through tract, and pulverize and mix it with digestive enzymes
- Inner circular layer of smooth muscle
- Outer longitudinal layer of smooth muscle
- Myenteric plexus: neurons for GI tract
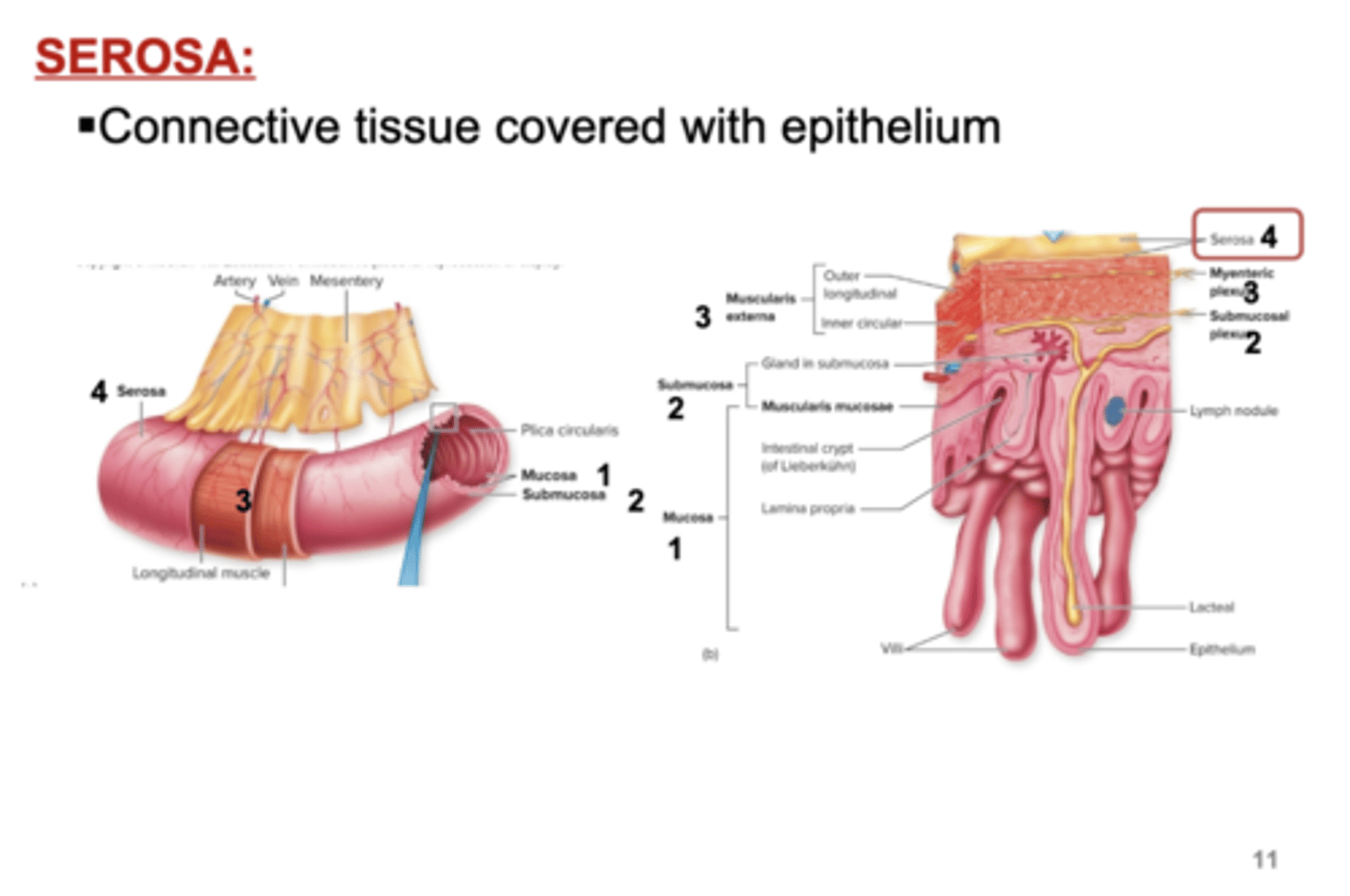
The Fourth (Outermost) Layer
4. Serosa:
- Connective tissue covered with epithelium
From Mouth to Stomach (Next 5)
1. Mastication
2. Deglutition
3.Esophagus
4. Stomach Pt. 1
Mastication
☆ Chewing of food in mouth
- Mixes food with saliva secreted by salivary glands
- Digestion starts with saliva, which contains salivary amylase, an enzyme that catalyzes the partial digestion of starch
Digestion
☆ Deglutition: Swallowing
- Initiated when food or drink stimulates pressure receptors in the pharynx
- The muscles of the mouth and tongue mix the food with saliva to create a bolus
- The tongue pushes the bolus to the back of the pharynx
- The upper esophageal sphincter relaxes
- Food descends into the esophagus
Esophagus
☆ Muscular tube connecting pharynx to stomach, posterior trachea
- Lined with epithelium and skeletal and smooth muscle
- Food passes through lower esophageal sphincter to enter stomach
Peristalsis (Part of Esophagus)
☆ Wavelike muscular contraction that push bolus to the stomach
- Circular smooth muscle contracts above the bolus and relaxes below it
- Then, there is shortening of the tube by longitudinal muscular contraction
Stomach Pt. 1
☆ Stomach:
- Digestion here results in chyme, partially digested food mixed with gastric juice
- Stores food
- Kill bacteria with acidity and gastric juice
- Starts digestion of proteins
- Peristaltic waves mix and propel the chyme
- Moves chyme to small intestine, where most digestion and absorption occur
Stomach Pt. 2
☆ Specialized cells in the stomach synthesize and secrete mucus, enzyme precursors, hydrochloric acid (HCl), and hormones
☆ The inner surface of the stomach contains folds called gastric rugae
☆ The abundant of smooth muscle in the stomach is responsible for gastric motility, the movement of food
Gastric Glands in Stomach (Next 9)
☆ The gastric glands of the mucosa contain various cell types:
1. Mucous neck cells
2. Parietal cells
3. D cells
4. Chief (zymogenic) cells
5. Enterochromaffin-like (ECL) cells
6. G cells
7. Intrinsic facor
8. Ghrelin
9. Gastric juice
Mucous Neck Cells
☆ Secrete mucous
Parietal Cells
☆ Secrete hydrochloric acid (HCl)
D Cells
☆ Secrete somatostatin (hormone that inhibits parietal cells)
Chief (Zymogenic) Cells
☆ Secrete pepsinogen, an inactive form of pepsin (a protein-digesting enzyme)
Enterochromaffin-Like (ECL) Cells
☆ Secrete histamine and serotonin, for regulation of the GI tract
G Cells
☆ Secrete gastrin (hormone that stimulates parietal and ECL cells)
Intrinsic Factor
☆ A polypeptide essential for intestinal absorption of vitamin B12 (need for production of RBCs in bone marrow)
Ghrelin
☆ A hormone that regulates hunger
Gastric Juice
☆ Secretion of gastric cells + Water
Gastric Glands
1. Chief cells synthesize and secrete pepsinogen, the pepsin precursor
2. Parietal cells synthesize and secrete hydrochloric acid (HCL) responsible for acidic pH in the gastric lumen
Activation of Pepsin
☆ The acidity in the gastric lumen (pH < 2) converts pepsinogen (from chief cells) to pepsin
- Pepsin partially digests protein
- Bicarbonate protects the stomach from acid damage
Small Intestine Pt. 1
- Longest part of the GI tract, 3 m long (small diameter)
☆ Digestion of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins
- Brush border enzymes and pancreatic enzymes
☆ Absorption of carbohydrates, lipids, AAs, vitamins, mineral, iron, water, electrolytes, and biles salts, into bloodstream
Small Intestine Pt. 2
☆ Folds in mucosa are called villi
- Microvilli, or brush border, on the villi increase the surface area for absorption
- Brush border enzymes are embedded in microvilli and are exposed to chyme
Brush Border Enzymes
☆ Brush border enzymes are embedded in the plasma membrane of the microvilli
- Their active sites face the chyme in the lumen of the SI
Contraction & Motility in SI
☆ Motility in SI is slow, to ensure proper absorption of nutrients
☆ There is some peristalsis
☆ Main contraction in SI is segmentation
Segmentation
☆ Muscular constrictions of lumen that occur simultaneously in different segments
☆ Mixes & moves chyme
Large Intestine/Colon
☆ Large diameter
☆ No villi
☆ Haustra are pouches on outer surface
☆ No digestion
☆ Absorption of electrolytes, water, vitamins
☆ Excretion of waste products in. feces, through rectum and anal canal
Fluid & Electrolyte Absorption in LI
☆ Around 1.5 L water from food and drink enters Gi tract per day
☆ GI tract also secretes around 8-10 L of fluid into its lumen
- From salivary glands, stomach, intestine, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder
- In LI, there is absorption of most of the fluid, so that < 200 ml of fluid is excreted in feces
- Active transport of sodium into epithelial cells of LI --> osmosis of water into ISF and then into bloodstream
Accessory Organs
1. Liver
2. Gallbladder
3. Pancreas
Liver
☆ Many functions, including synthesis of bile
Gallbladder
☆ Storage of bile from liver and release into SI
Pancreas
☆ Pancreatic juice for digestion in Si
Liver Actions
1. Detoxification of blood
2. Carbohydrate metabolism
3. Lipid metabolism
4. Protein synthesis
5. Secretion of bile
6. Storage of molecules
Section of Liver
1. Groups of lives cells, or hepatocytes are separated by hepatic sinusoids
2. Blood enters a liver lobule (functional unit) through portal triad (hepatic artery, portal vein, bile ductule), passes through hepatic sinusoids, and leaves the. lobule through central vein
3. Central vein is converge to form hepatic veins that take venous blood away from the liver
4. Bile is synthesized by hepatocytes and secreted into bile canaliculi, the canaliculi drain into bile ductules in portal triad
5. The bile is funneled from the ductules into the gallbladder where it is stored, and then delivered into the small intestine
Bile
☆ Main components of bile, a yellow-green fluid:
- Bile pigment (from breakdown of RBCs), bile acid or salts, lecithin (a lipid), bicarbonate, cholesterol, and trace metals
☆ Bile acids are cholesterol-based, and form micelles in aqueous solutions
☆ In the SI, fat enters the micelles, and the amphipathic property of micelles allows emulsification (or breakdown) of fat
Micelles
☆ A group of bile acids in aqueous solutions
Emulsification
☆ Breakdown of large fat globules by bile acids into smaller globules for digestion by lipase
Circulation of Bile
1. Bile enters the small intestine via the common bile duct
2. In the SI, the bile emulsifies fats to break them down before digestion by lipase
Pancreas Pt. 2
☆ Endocrine Functions: insulin and glucagon
☆ Exocrine Functions: pancreatic juice
- Synthesized by acinar cells and delivered to duodenum of SI through pancreatic duct
☆ Pancreatic Juice: is bicarbonate and around 20 enzymes (Next flashcard)
Pancreatic Juice Enzymes
1. Amylase:
- Digests starch
2. Trypsin:
- Digests protein
3. Lipase:
- Digests triglycerides
☆ Many of the enzymes are activated in the SI
☆ Pancreatic enzymes and brush border enzymes accomplish complete digestion of fool molecules in SI
Pancreatic Solutions
☆ The exocrine cells in the pancreas produce digestive enzymes that exit via the pancreatic duct to travel to the small intestine
☆ If digestive enzymes secreted by the pancreas were synthesized in their active form, they would digest the very cells that make them, hence, inactive precursors (zymogens) become activated in the SI
Digestion & Absorption of Carbohydrates
☆ Daily intake is 250-300 g, mostly as starch, a polysaccharide of glucose
☆ Most commonly ingested sugars are sucrose and lactose
☆ Salivary amylase starts digestion in mouth
☆ Pancreatic amylase in SI (most of carb digestion) results in maltose, maltriose, and oligosaccharides
☆ Brush border amylases in SI hydrolyze these sugars into their component monosaccharides, which are then moved across the brush border membrane by active transport, to be absorbed into the bloodstream
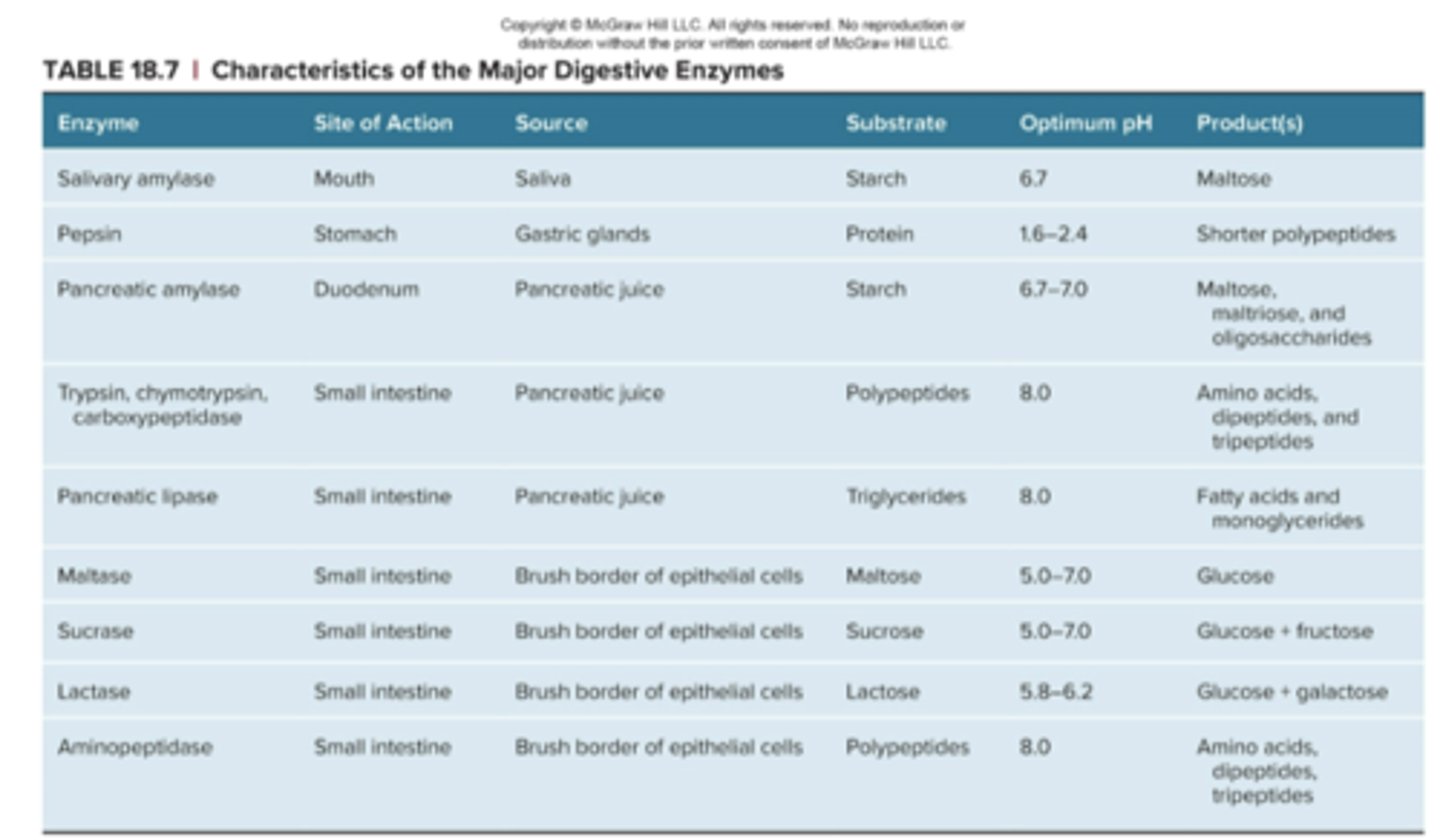
Characteristic of the Major Digestive Enzymes Table
Pancreatic Amylase
☆ Brush border amylases in SI hydrolyze (breaking/reaction down with water) these sugars into their component monosaccharides, which are then moved across the brush border membrane by active transport, to be absorbed into the bloodstream
Digestion & Absorption of Proteins
☆ Daily intake is 60-90 g (needed for AAs)
☆ In stomach, pepsin produces short-chain polypeptides
☆ In SI, pancreatic enzymes trypsin, chymotrypsin, and carboxypeptidase, and brush border enzyme aminopeptidase digest polypeptides into free AAs, dipeptides, and tripeptides
☆ AAs enter epithelial cells in SI by active transport and are secreted into ISF and then absorbed into capillaries
Digestion & Absorption of Lipids
☆ Daily intake is 70-100 g (mostly fat)
1. In SI, bile emulsifies fat
2. Pancreatic lipase liberates free fatty acids and monoglycerides via hydrolysis
3. Free fatty acids and monoglycerides are in mixed micelles
4. Fatty acids and monoglycerides from micelles enter the epithelial cells of the SI
- There, they are resynthesized into tryglycerides
5. Tryglycerides combine with protein to form chylomicrons, which enter lymphatic vessels and eventually enter veins (blood)