acids and bases
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
When a base reacts with an acid, the…
H+ ion from the acid reacts
HCL + NaOH —> NaCl + H2O
Ionic eq
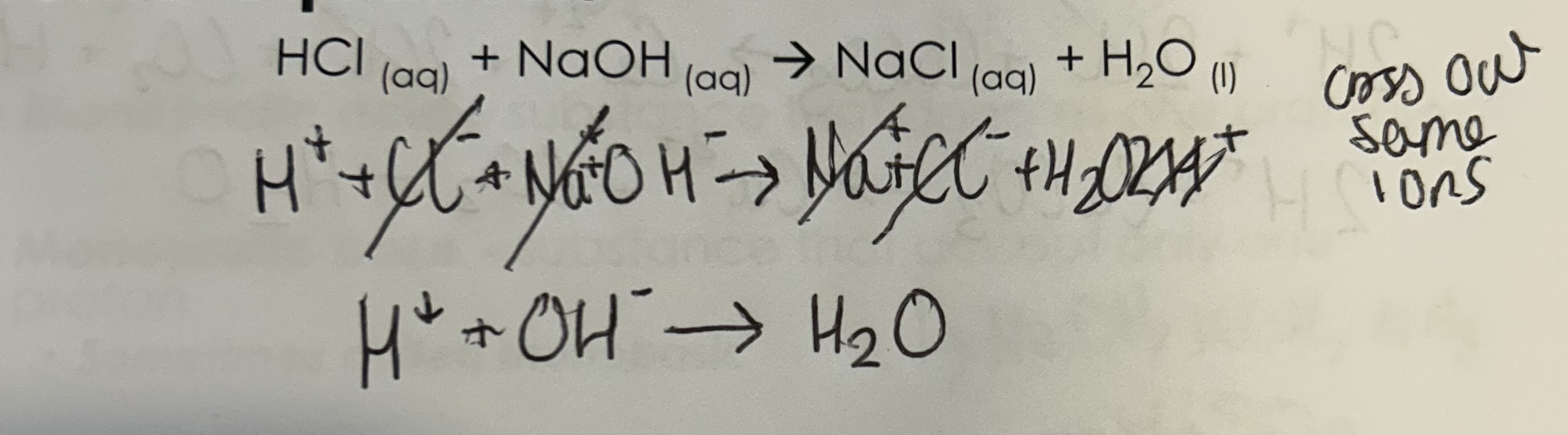
2HCL + CaCO3 —> CaCl2 + CO2 + H2O
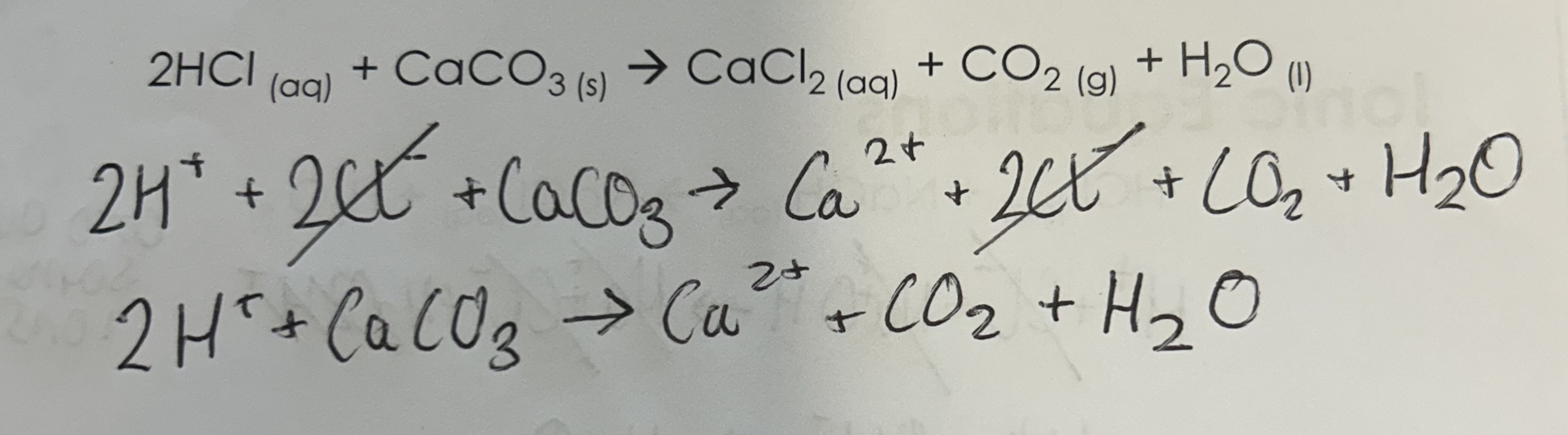
volume equation
conc x old vol/new vol
Bronsted Lowry Acids and bases
Acid is a proton donor
Base is a proton acceptor
Monoprotic acid and base
Acid - substance that donates one proton
Base - substance that accepts only one proton (monobasic)
With Diprotic its 2
Diprotic acid example
H2SO4
rearrange to find conc
[H+] = 10-pH
Acid base pair
Theory that acid has donated a proton air would be able to accept a proton back and then be a base
what is water in terms of acids and bases
amphoteric (water can behave as an acid and a base)
Strong acid
Acids completely ionise in water - all of H+ ions are released
Weak acid
These acids ionise partially in water - only some of the H+ ions are released
Dilute
Less acid molecules in a given volume of solution or more solvent present
Concentrated
Lots of acid molecules for a given volume in a solution
Common bases
Metal oxide and hydroxides And NH3
What is pH
Power of hydrogen
Decreasing pH..
Increases H+ by a factor of 10
pH formula
pH = - log 10 [H+]
pH must be 2 d.p.
H2SO4 thing
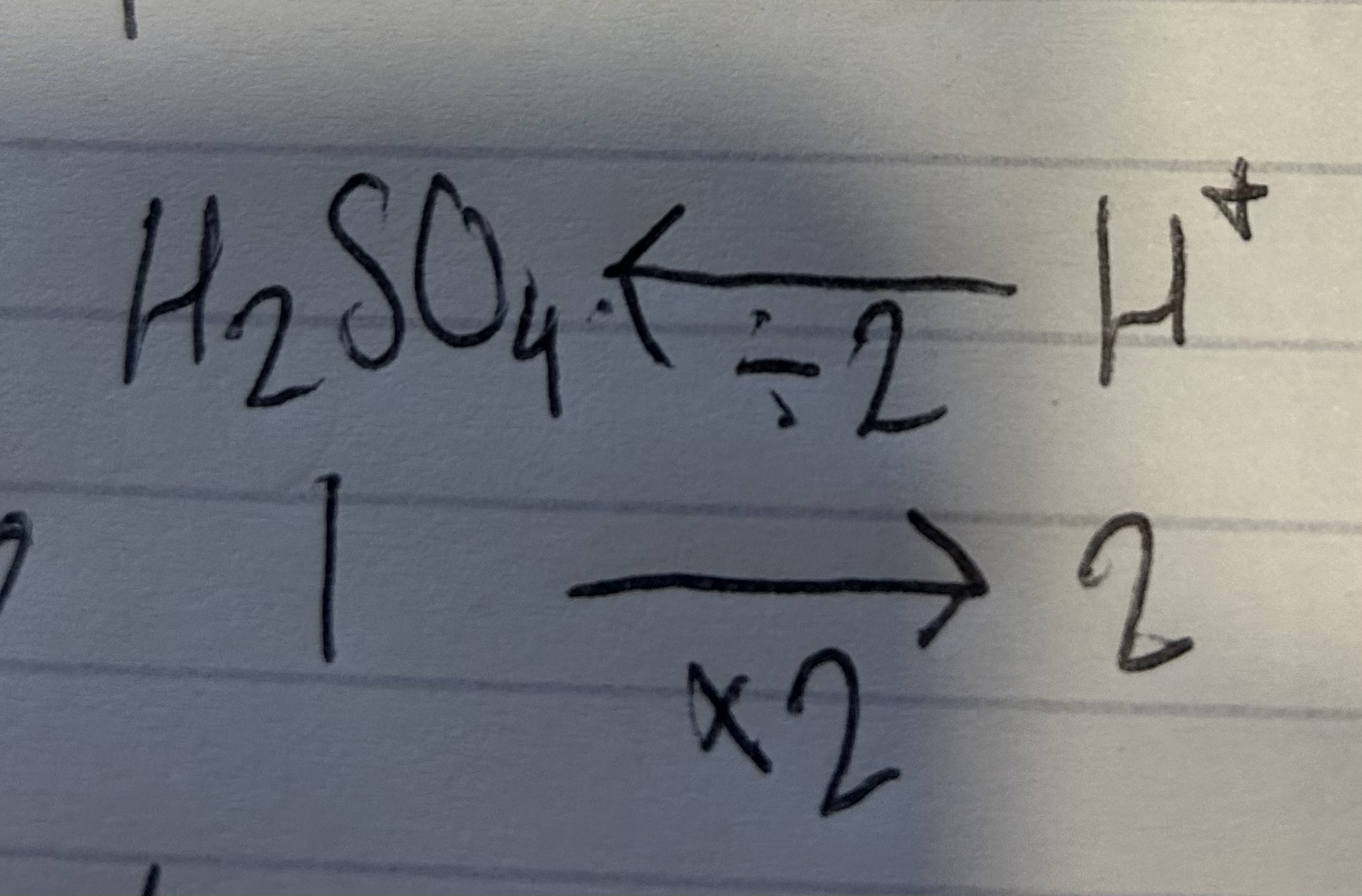
Calculate the pH when 250cm3 of 0.3 mol dm3 H2So4 made up to 1000cm3 solution
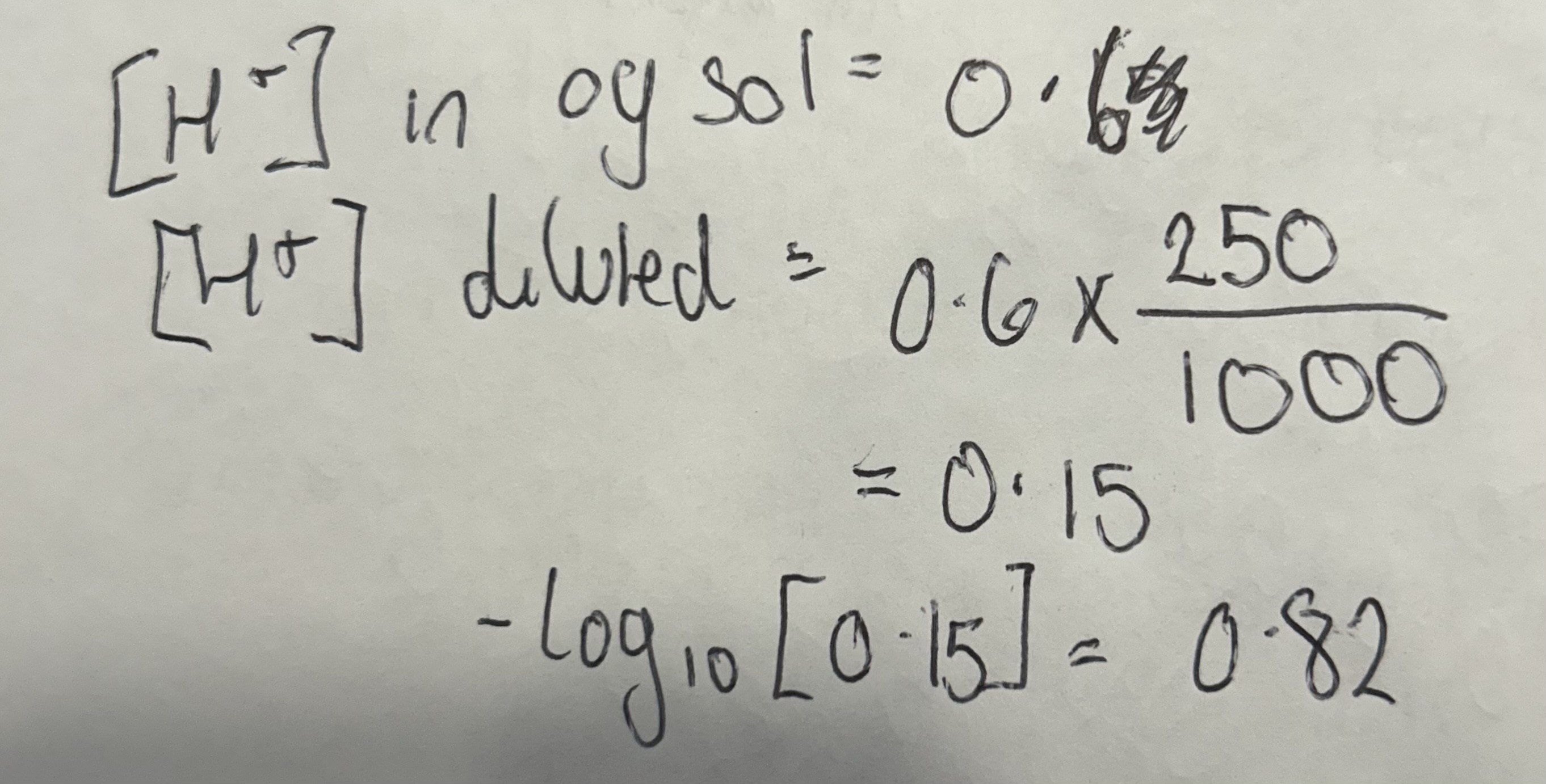
G dm3 to mol dm3
Divide by Mr
calculate pH of 0.2 mol dm3 HCL
0.70
conc of HCL with pH 3.55
2.81 × 10-4
Kw equation
[products]/[reactants]
[H+][OH-] / [H2O]
H2O constant at room temp so simplifies to [H+][OH-] IN PURE WATER
[H+]2
Kw equation rearrangement
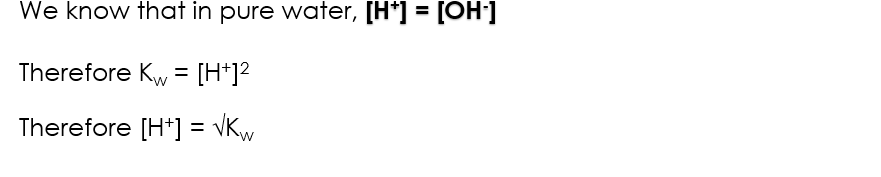
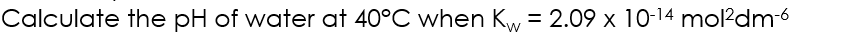
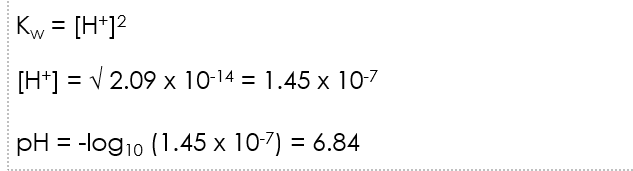


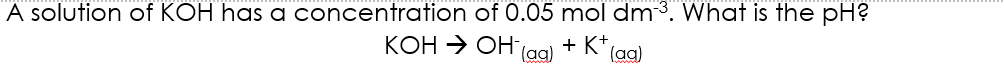
1.0 x 10⁻¹⁴ mol² dm⁻⁶

pK and pKa
pKa = -log10Ka
Ka = 10-pKa