Chapter 13 Offerings
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
CAPITAL FORMATION
What are the 2 options for issuing new securities?
Public offering
Private offering
What are the advantages/disadvantages to a public offering?
Advantage: Provides access to a large # of investors
Disadvantage: Costly and time consuming
What are the advantages/disadvantages to a private offering?
Advantage: Fast, and less costly
Disadvantage: Limits access to certain types of investors
What is the primary market and where do its proceeds go?
What is the secondary market and where do its proceeds go?
When the investor buys directly from the issuer so the proceeds go to the issuer
When one investor buys from another, so proceeds go to the selling party
What is an initial public offering?
What market are these done in?
Issuer offers shares for the 1st time
Primary market
What is a follow on offering?
What market are these done in?
Company issues more shares after already having gone public
Primary market
What is a split offering?
What needs to be disclosed for an offering like this?
When some shares are offered by the issuer while some are offered from existing shareholders looking to sell
Some of the proceeds are going to the selling shareholders
What is a private investment in public equity (PIPE)?
How do these effect the price of trading shares?
When an already public company sells shares to accredited investors through a private offering
The private offering is usually offered at a discount, so it sends the price of the public shares down too
THE ROLE OF AN UNDERWRITER/INVESTMENT BANKER
What is the main purpose of an UW?
What is an UW syndicate?
To help corps/munis issue equity/bonds by bringing buyers and sellers together in the market place
Sometimes a group of BDs will come together to UW a deal together and distribute the risk
What is a firm commitment UW?
What capacity are these done in?
What if it is a split offering?
This is when the syndicate absorbs all the shares of the issue and sells the securities themselves
Principal
The UW will buy all shares from both parties
What is a best efforts UW?
What capacity are these done in?
What is an all or none?
What is a mini/maxi?
The UW makes a bona fide effort in selling shares but can return any unsold shares to the issuer
Agent capacity
If the entire issue is not sold, the offering is cancelled
A minimum threshold needs to be met for the sale to avoid being cancelled
What is a standby agreement offering?
During a follow on offering, preemptive rights are offered to existing shareholders first, if there is not enough demand, the syndicate may agree to take on the additional shares
What is a market-out clause?
The UW may cancel the agreement is something material (like Covid) happens
How is a syndicate formed?
What is a syndicate letter?
Once the managing UW is established, they may invite other firms to form a syndicate
The agreement that is signed by all UWs to participate in the deal
What is the selling group?
What kind of capacity do they act in?
What is the selling group agreement?
In some cases, the syndicate will recruit BDs to assist in selling the issue
Agent, no risk for them
Document that signs a BD in to a selling group
What is the public offering price (POP)?
When is it established?
What price is used for a subsequent offering?
The price the shares are sold at when the issuer begins
Just before the effective date the syndicate will evaluate demand
The market price
What is the UW spread?
It is the difference between the POP and the price the UW buys the shares from the issuer at
essentially the syndicates gross profit
What are the following components of the spread:
Manager’s fee
Memeber’s fee
Concession
Reallowance
Manager’s fee: Portion to the managing UW
Memeber’s fee: Portion to to other syndicate members
Concession: Portion paid to the firm selling the shares
Reallowance: Portion of the concessions paid to the selling group BDs who are not part of the syndicate
SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
What is the main goal of the SA of 1933?
To protect investors against fraud in the sale of a new issue through providing them with enough information
What is the registration statement?
Who is it given to?
Provides full disclosure and info about the issuer and issuer
The SEC to register, BUT NOT APPROVE
What is the prospectus?
Who is it given to?
A summarized version of the registration statement
Potential investors
THE REGISTATION PROCESS
What is the pre-registration period?
When does this period end?
What can’t the UW do during this time?
This is the time when the issuer prepares their registration statement with the UW
The day it is filed with the SEC
The UW cannot discuss the issue with customers yet
What is the shelf regulation?
What is the advantage?
Allows securities to be sold on a delayed or continuous basis
Issuer can wait for a better market environment to issue
What is the cooling off period?
What is the SEC looking for?
The 20 day period where the SEC will review the registration statement that was filed
Anything misleading to investors
What is a deficiency letter?
What needs to be done by the issuer if one is received?
If the SEC finds something misleading they will notify the issuer with this
The issuer will need to amends and resubmit
Can an UW begin talking about the issue?
Can UWs receive any payment for this issue during the period?
What is a red herring and what does it not include?
Yes, they can begin soliciting potential buyers
No
It is a preliminary prospectus that is provided to potential investors but does not have an exact price, only a range
What are state/blue sky laws?
What are they established under?
They are the state registration laws that must be met
The Uniform Security Act
What are the 3 following forms of state notification:
Notification
Coordination
Qualification
Notification: Involves just submitting an application with the state requesting approval for the security
Coordination: Form is completed simultaneously with federal regulations and usually becomes effective the same time
Qualification: Meeting the requirements of the state and is effective if the state administrator approves
Do BDs and their RRs need to be state registered?
Yes, they will need to be registered in whatever states they are doing business in
What is the effective date?
Marks the end of the cooling off period when the security can be sold
Once the BDs get their allocations for the issue to be sold, what should be done?
What happens if an investor now wants to place an order?
They should reach out to investors who received red herrings to see if they are still interested
The RR needs to provide them with the final prospectus and the trade is now binding
What is crowd funding?
Allows certain investors to invest in small business at levels based off their income and net worth
What is a non-listed company?
If doing an IPO, how long does the prospectus need to be provided for?
If doing a follow on, how long does the prospectus need to be provided for?
Company whose stock does not trade on an exchange
90 days
40 days
What is a listed company?
If doing an IPO, how long does the prospectus need to be provided for?
If doing a follow on, how long does the prospectus need to be provided for?
Companies whose stock trade on an exchange
25 days
no delivery requirment
THE NEW ISSUE RULE
What does the new issue rule state?
What does this rule apply to?
FINRA members cannot withhold (buy) shares for itself and restricted persons, they must make a bona fide offering to the public
Equity IPOs sold under a registration statement
So in simpler terms, what does the New Issue Rule prohibit?
What if it is a shared account?
The sale of IPO shares to those associated with member firms
If the FINRA member has more than 10% interest, it cannot be sold to that account
What is a restricted person?
What makes someone considered immediate family?
Those who work for member firms and their immediate family, across the industry
They live in the same household or are dependent on them
What are some other example of restricted persons?
Finders/fiduciaries involved in the offering and their family members
Portfolio managers
Persons who own a BD
What is the general exemption for family in the New Issue Rule?
What are some other exempted parties?
If the immediate family works for the issuer, than they can purchase their own shares
Basically if you’re not a BD, other institutions can purchase (So investment companies, insurance companies, they can purchase)
What is the undersubscribed exemption of the New Issue Rule?
If the issue is under subscribed, then the BD can purchase shares
But the firm cannot sell to other restricted persons or its employees for their own personal account
What is the anti-dilution provision?
What are the requirements?
If there is a restricted person who already owns shares, they can buy the new issue but only to keep their percentage interest
Shares need to have been held for a year prior and the new issue cannot be sold for at least 3 months
EXEMPT SECURITIES
What are some examples of securities that are exempt from need to register under the SA of 1933?
Us Gov and its agencies
Muni securities
Money markets (270 days or less)
Why are they exempt?
What can they still not do?
They are exempt because registering is costly and time consuming
They still cannot fraud investors even though they do no need to register
EXEMPT OFFERINGS
Why are certain offerings exempt?
Under certain regulations and circumstance, certain offerings are exempt from needing to register, simply because it doesn’t make sense
REGULATION A
What is regulation A?
What still needs to be done?
What is the advantage?
If there are $75MM or less being sold over a 12 month period
Offering statement needs to be filed with SEC and offering circular needs to be provided to a prospective investor
Even though things still need to be filed with the SEC, this provides reduced legal costs and a shorter time frame
What is tier 1 in Reg A?
How much can be sold by current shareholders?
What rules is the offering subject to?
Do financials need to be filed?
Who can buy?
A sale of up to $20mm in 12 months
$6mm
SEC and blue sky
No
Anyone
What is tier 2 in Reg A?
How much can be sold by current shareholders?
What rules is the offering subject to?
Do financials need to be filed?
Who can buy?
A sale of up to $75mm in 12 months
$22.5mm
SEC but not blue sky
Yes
Anyone, but non-accredit can only buy up to 10% of their networth
RULE 147 AND 147A
What does Rule 147 allow for?
What needs to be met under the rule?
Provides safe harbor from registering under an intra state offering exemption
Principal place of business in the state and 80% of revenue, assets, and proceeds are in state
What is Rule 147A?
Where does the business need to be organized?
It is an expansion of 174 that says offerings can be made out of state, but sales need to be in state
The business can be organized in any state, but the principal place of business needs to be in state
How has the 80% rule changed from 147 to 147A?
Only 1 of 4 need to be met along with principal place of business in state:
80% revenue in state
80% assets located in state
80% proceeds in state
Majority of the issuer’s employees are in that state
What happens if the issuer changes places of business?
How long does an instate resident have to wait before they sell their securities?
If they move to a new state, they cannot do another offering under 147/A for another 6 months
6 months, there will be a stock legend
REGULATION D
What does Regulation D allow for?
What are these type of transactions called?
It is a safe harbor that allows securities offerings to be sold as private placements without needing to register with the SEC
Exempt transactions
What kind of investors can participate?
What is a private placement memo?
Can a buyer turn around and sell these?
How many non-accredited investors can be sold to?
Sophisticated
The same as a prospectus, just for private placements
No, there is a lock up period
No more than 35
What is an accredited investor?
Institutions
Directors, officers, partners
Individuals who have:
net worth of at least $1mm or
$200K ($300k for married) income for last 2 years
Proper licensing
How long is the lock up period?
Is there an exemption to this rule?
Usually 6 months
Yes, it can be sold to a QIB at anytime
RULE 144
What is Rule 144?
It regulates the sales of restricted and control securities
What is a restricted security?
What is a control security?
Security purchased through private placement (under Reg D)
Acquired by a control person in the secondary market
Who are control persons?
Officers
Directors
Insiders who own more than 10% of the company
Family members
What is a notice of sale?
When would this not be needed?
A notice of sale must be filed with SEC under 144 when selling restricted/control securities
If the sale is less than 5,000 shares of $50,000
What is the volume limitation to sales under 144?
Think 144 rule
1% total shares outstanding or avg weekly trading volume for the prior 4 weeks every 90 days (1/4 year)
RULE 144A
What does Rule 144A state?
Sales of restricted securities are allowed to QIBs without having to meet the standards of 144
What makes a QIB? (3 of them)
Must be an institution
$100MM investor
Purchasing for themself or another QIB
RULE 145
What is Rule 145?
Says that certain security reclassifications are sales so they are subject to requirements of SA of 1933
What kind of transactions are subject?
Substitutions
Mergers/consolidations
Transfers of assets
What kind of transactions are not subject?
Stock splits
Reverse stock splits
Changes in par value
REGULATION S
What is Regulation S?
States that US companies issuing abroad do not need to register with the SEC
Can any sales or advertising be done in the US?
How long does a foreign investor need to wait to sell to someone in the US?
No, nothing can be done in the US
40 days if debt, 1 year if equity
SECONDARY MARKET TRADING OF NEW ISSUES
What is the Green Shoe Clause?
If a new issue is over subscribed, an UW has 30 days to purchase up to 15% additional shares to meet the demand for customers
What is Regulation M?
What kind of transactions do these apply to?
M for manipulation
It restricts issuers and UWs from bidding on the security in the secondary market during an additional offering
Additional/follow on offerings
What is stabilization?
If there is really weak demand, the UW can step into the secondary market and place bids up to the POP but only at the highest bid
Helps to stabilize the price
What is a penalty bid?
If a BDs customers buy the new issue and sells it back to the BD at a stabilizing bid, the BD can lose its concession on the sale as a penalty
THE PRIMARY MARKET FOR MUNICPAL BONDS
Are muni offerings subject to the SA of 1933?
No, but the fraud rules still apply
What is the MSRB?
The main SRO that oversees UWs during muni offerings
What is needed to issue a GO bond?
Is there a maximum amount that can be issued?
Voter approval
Yes, there will be an imposed debt ceiling
What is needed to issue a revenue bond?
A feasibility study must be done
Do munis use UWs for debt issuance?
Yes, same as a company would for equity
What is a negotiated Sale?
What is a competitive sale?
Issuer will choose an UW and negotiate the specifics of the deal after
UWs will submit bids for the UW and the issuer will choose the one with the lowest cost
How is an UW syndicate formed?
What kind of basis are these securities sold on?
So what capacity does the UW syndicate act in?
Similar to an equity issue, there will be an UW manager and other syndicate members to help
firm commitment only
Principal capacity
What is a divided account (Western) sale?
What is an undivided account (Eastern) sale?
Each member is on the hook for only their portion to sell
Each member will pick up their % interest in unsold shares
Think Eastern as in EU, united countries
What are the selling group members?
Are they part of the syndicate?
How are they paid?
They assist in placing securities
No
Concession
What is the spread?
What are the components of spread in a muni UW?
It is the difference between the POP and the price the UW purchases the bonds at from the issuer
Syndicate expenses, managers fee, rest is takedown
How is takedown split up?
IF a selling group is used, they will be paid a concession, and the syndicate member will keep the remaining amount known as the additional takedown
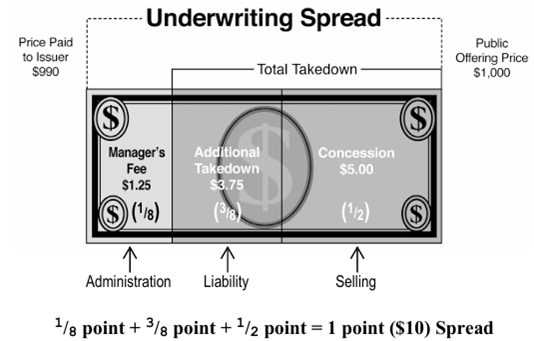
So if a manager sells directly to a customer they get full $10 dollar
If a syndicate member sells to the customer, they get everything but the $1.25 fee
If a BD sells to the customer, they get the $5 concessions, the syndicate member gets the $3.75 additional takedown, and the manager gets the $1.25