ID- Parasitic, Rickettsial and Spirochetal infections
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
Parasitic
___ infections are common in rural parts of Africa, Asia, and Latin America
Helminths and Arthropods (protozoa/bacteria)
What are two classes of parasites?
no
There is typically ___ immune reaction to living worms within a human host
3 multiple choice options
Hookworms
Ancylostoma duodenale and nectar Americanus are both examples of ___
Hookworm disease
Eggs present in soil hatch releasing infected larva that enter the skin via contact and migrate via the blood stream to the alveoli where they are coughed up and swallowed to end up in the GI tract (small intestine)
Hookworms
___ are a major cause of underdevelopment in children as they feed on blood
Duodenum and jejenum
Where do hookworms ultimately attach to the host?
pulmonary stage
Patients develop a dry cough, wheezing, blood tinged sputum and fever during the ___ of a hookworm infection
anorexia, diarrhea, abdominal pain, anemia, protein loss and hypoalbuminemia
Symptoms of severe hookworm infection in the GI stage?
Hookworms
___ consume host's RBCs so symptoms will mimic iron deficiency anemia
- stool = ova/parasites
- microcytic hypochromic anemia
- low serum iron
- hypoalbuminemia
- mild eosinophilia
Lab findings in hookworm infection?
- albendazole 400mg PO x 3 days or Mebendazole 500mg PO x 3 days
- effective BUT teratogenic
- ferrous sulfate if anemic
Tx for hookworm infection?
dog and cat hookworms
Cutaneous larva migrans is associated with ___
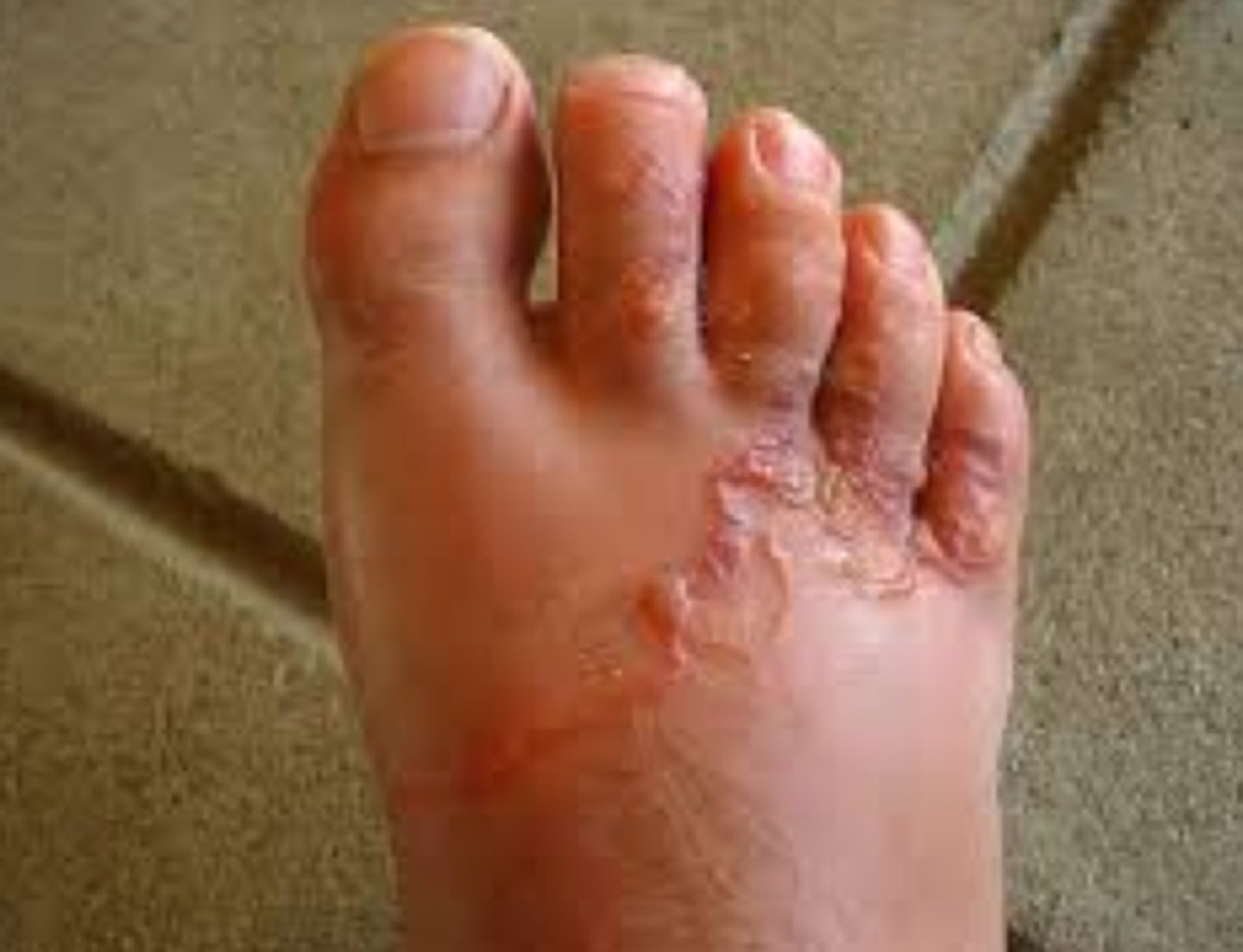
- albendazole 400mg x 3 days
Tx for cutaneous larva migrans?
pinworm infection
Enterobiasis is caused by ___
Enterobiasis vermicularis (pinworm)
M/C nematode infection worldwide
Person to person via ingestion of eggs through food, drink or contact
How is E. vermicularis transmitted?
hatch in duodenum, migrate to cecum where mating occurs, then to perianal skin to deposit eggs at night
Where do eggs hatch and migrate in enterobiasis?
nocturnal perianal pruritis
M/C clinical symptom of enterobiasis infection?
- scotch tape test
- visual identification of worms
- NO eosinophilia = no tissue invasion
Lab findings of enterobiasis infection?
- treat all members of household
- Mebendazole (single 500mg dose, retreat in 2wks) OR albendazole (single 400mg dose)
Tx for enterobiasis infection?
Protozoans
___ are single celled eukaryotic cells
cyst
Exposure to new environments causes a protozoa to shrink into a round armored form called a ___
Cyst
Is the trophozoite or cyst infective?
1 multiple choice option
Trophozoite form
When is a protozoa motile and replicating?
Amoebas, flagellates, ciliates and sporozoa
Four major groups of protozoa?
Amoeba
Naegleriasis is an example of a ___
flagellate
Trichomonas vaginalis is an example of a ___
sporozoas
Malaria and babesiosis are examples of ___
Histolytica
Which entamoeba species is pathogenic?
food or water
Transmission of amebiasis is through ingestion of cysts from fecally contaminated ___
overcrowding, poor sanitation and poor nutrition
Amebiasis is most common in tropical areas under conditions of ___
Intestinal or extraintestinal (portal circulation)
Amebiasis can be classified based on location as ___
Amebiasis
When spread through portal circulation ___ can form hepatic abscesses, lung abscesses and often cause death
intestinal
Mild to moderate colitis with abdominal cramping, flatulence and fatigue without hematochezia or melena can be seen in ___ amebiasis
intestinal amebiasis
In severe ___, symptoms include severe diarrhea, scant hematochezia, necrotic tissue in stools, fever, and tender abdomen w/ hepatomegaly
Amebiasis
When seeing someone from an endemic area always consider ___ for severe diarrhea and hematochezia before IBD
areas of greatest stasis (sigmoid and cecum)
Localized ulcerative colonic lesions of intestinal amebiasis are typically found in ___
Hepatomegaly (+/- abscess)
Most common extraintestinal feature of amebiasis?
Amebiasis
What caused this rash?
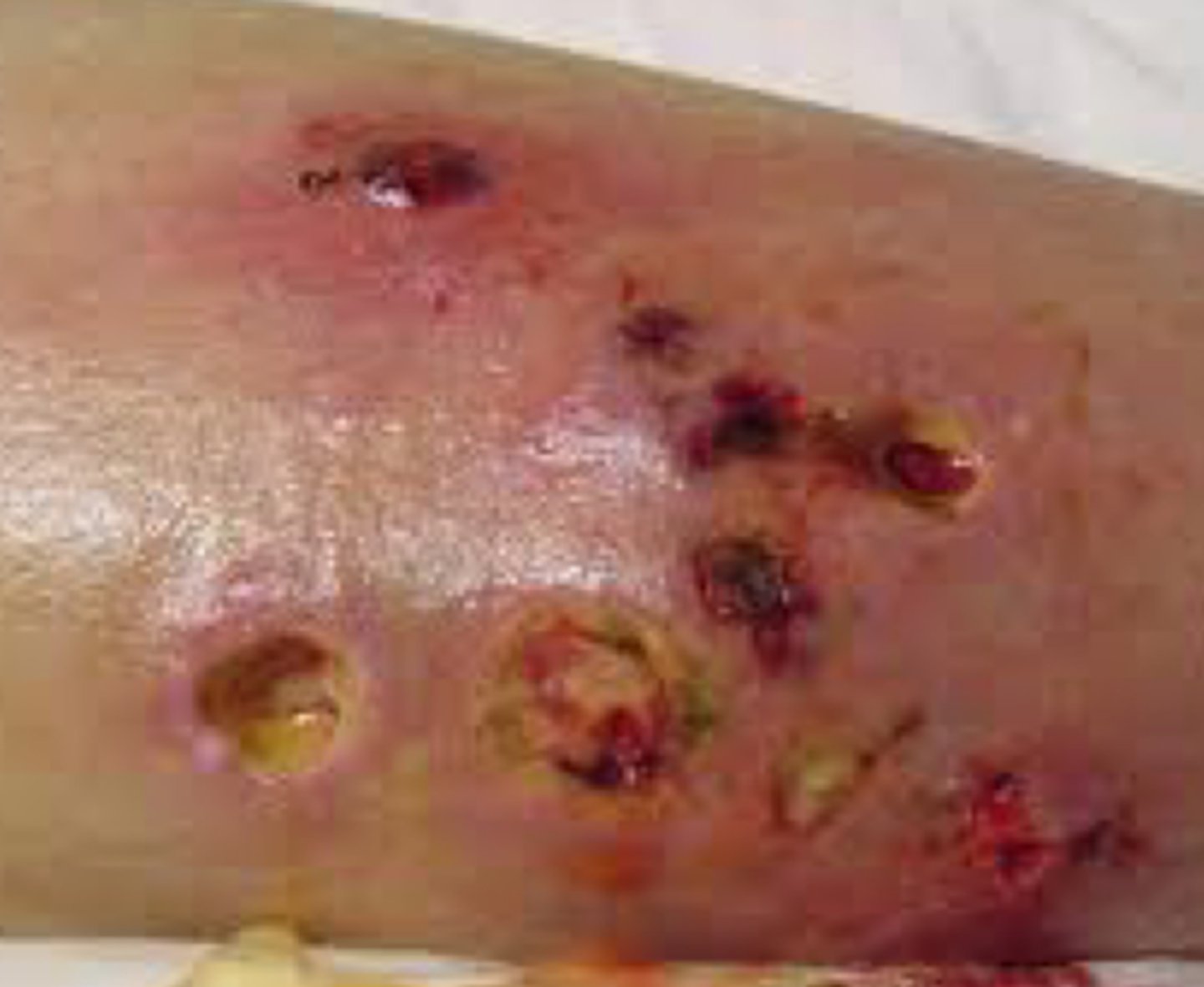
- stool specimen (ova/parasites)
- 3 fresh samples identify antigens/antibodies in severe cases
Lab findings for amebiasis?
- drink bottled water
- avoid ice
- avoid fresh fruits/veggies
- avoid street vendors/properly cook food
Prevention of intestinal amebiasis?
- hydration + pain control
- diagnostics (abdominal CT + colonoscopy)
- 2-4 weeks of metronidazole/tinidazole with paromomycin sulfate/diloxanide furoate
Tx of amebiasis?
Giardiasis
Which type of outbreak occurs when sewage contaminates drinking water?
Giardiasis
___ is harbored by rodents and beavers and can be acquired by 'drinking from a clear stream'
Small intestine wall
Where does a giardiasis trophozoite migrate and adhere?
Giardiasis
Which organism affects the intestinal wall by interfering with fat absorption?
Giardiasis
Greasy, frothy diarrhea with a bad odor is indicative of a ___ infection
- tinidazole 2g PO
- metronidazole 250mg PO TID x 5 days
- Nitazoxanide 500mg PO BID x 3 days
Tx for giardiasis
- Giardia lamblia
- Anaerobic cocci (Bacteroides fragilis, C. diff, Gardenerella vaginalis)
- Trichomonas vaginalis
- Entamoeba histolytica
Metronidazole is useful in treating which infections?
Trichomonas vaginalis
___ is a flagellated protozoan transmitted sexually that resides in the vagina or male urethra
Trichomonas vaginalis
Vaginal pruritis, dysuria, thin, watery, frothy and odorous discharge are signs of ___ infection
- wet mount of discharge
- Urinalysis
Workup for trichomoniasis?
- metronidazole 2g PO single dose
- tinidazole 2g PO single dose
Tx for trichomoniasis?
Toxoplasmosis
___ is found in humans, animals and birds but is most commonly found in cats
Toxoplasmosis
Humans transmit ___ by ingesting raw or undercooked pork, contaminated water, poor handling of cat litter (m/c), or through pregnancy
80
Over ___% of infections with toxoplasmosis are asymptomatic
3 multiple choice options
Toxoplasmosis
Retinochoroiditis is a sign of ___ infection along with fever, malaise, headache, lymphadenopathy, myalgia, arthralgia, neck stiffness, sore throat and hepatosplenomegaly
Toxoplasmosis
___ may resemble mononucleosis in clinical findings
Toxoplasmosis
In pregnancy, ___ is commonly asymptomatic for the mother but leads to neurological or ophthalmic conditions for the fetus
brain and eyes
in AIDS and fetuses, toxoplasmosis is toxic to the ___
- IgG and IgM titers (two samples 3-4 weeks apart)
- can isolate in tissue or fluid specimen
How is toxoplasmosis diagnosed?
- pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine, and leucovorin
Tx for toxoplasmosis?
Chagas
___ is caused by trypanosoma cruzi and is often acquired in childhood in South America/mexico
T. Cruzi
___ survives in rodents, opossums and armadillos
Chagas disease
Reduviid bug (kissing bug) is the vector of ___
Kissing
The feces of ___ bugs tunnel into humans and invade skin, macrophages, lymph nodes and the blood
asymptomatic
70% of people infected with chagas disease are ___
Heart, colon, and esophagus
Which organs are affected with chagas disease?
- chagoma (hardened red area - parasitic site of entry)
- romana sign (unilateral lid edema, conjunctivitis, and lymphadenopathy)
Initial signs of chagas disease?
Acute, latent and chronic phases
Three phases of chagas disease?
asymptomatic
During the latent phase of chagas disease, patients are usually ___ with low levels of parasites and (+) antibodies
Heart (Arrythmias, CHF, embolic disease + dilated cardiomyopathy)
GI (dysphagia, constipation, megacolon, megaesophagus and abdominal pain)
The chronic phase of chagas disease manifests as ___ problems
- acute: blood smear and direct examination
- chronic: serologic assay w/ evidence of T. Cruzi
Diagnostic testing for chagas?
- Nifurtimox and Benznidazole for acute
- no treatment for chronic disease
Tx of Chagas disease?
Malaria
M/C parasitic disease of humans?
equatorial
Malaria is most commonly found in ___ regions
Female mosquito
What is the vector of malaria?
Plasmodium falciparum
Which organism is responsible for most severe cases of malaria?
12-30 days
Incubation period of malaria?
3 multiple choice options
liver
Mosquitoes inject sporozoites which circulate to the ___ and rapidly infect hepatocytes
Merozoites
___ get released from the liver and infect erythrocytes in malaria
Fever
Hallmark symptom of malaria?
Malaria infection
Episodes of shaking chills, fever, diaphoresis over periods of 4-6 hours is indicative of
travelling
Consider malaria in all febrile patients with history of ___
malaria
Giemsa stained thick and thin blood smears are useful for diagnosis of ___
- chloroquine sensitive: chloroquine phosphate
- vivax and oval infections: chloroquine then primaquine /tafenoquine
- chloroquine resistant: coartem/malarone/quinine sulfate + doxy or clindamycin
- severe or complicated infections: artesunate IV or quinidine gluconate
Tx of malaria?
- Chloroquine: areas without resistant P. falciparum
- Malarone/Doxy: areas w/ multidrug resistant P. falciparum
- Mefloquine: areas w/ chloroquine resistant P. falciparum
- Primaquine: P. vivax and P. ovale coverage
- Tafenoquine: alt for P. falciparum
Prophylactic coverage against malaria for travelers?
Babesiosis
Malaria of the northeast?
deer tick (Ixodes scapulars) and blood transfusion
Babesia microti is spread primarily by ___
Babesiosis
Which tick borne illness begins with flu-like illness (headache, myalgias, fever, fatigue)
Babesiosis
___ is typically self limiting but can be severe in the elderly or those w/ prior splenectomy
Babesiosis
Lab findings of ___ include pancytopenia on CBC, intraerythrocytic parasites on Giemsa stain blood smear
- mostly self-limiting
- Atovaquone + azithromycin or Quinine + clindamycin
- consider RBC transfusion in severe cases
Tx of babeosis?
Rickettsial
Typhus, Rickettsiosis, Ehrlichiosis and Q fever are examples of ___ diseases
Rickettsial
___ organisms are small gram (-) rod/cocci bacteria that are obligate intracellular parasites
arthropods
Rickettsial diseases require ___ as a vector
endothelial
Rickettsial diseases have an affinity for ___ cells
Rickettsia prowazekii
Epidemic typhus is spread by ___
Epidemic typhus
___ is spread by lice/flying squirrels and proliferates in conditions of overcrowding and unsanitary conditions