C3: Stoichiometry (copy)
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
2-3: Valency/combining power, the formula of ionic compound 4-5: Equation and state symbols 6: Questions 7-9: Ar and Mr 10-14: Mole 15-16: Limiting reactant 17-19: Percentage yeild 20-24: Percentage purity and percentage mass 25: Questions 26-27 : Empirical and molecular formulae 28-30 : Moles and Concentration 31- : Calculating gas volume
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Key terms (empirical formula, molecular formula, binary compound)
Empirical formula: A formula showing the simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in a compound.
Molecular formula: A formula showing the actual number and type of different atoms of each element present in one molecule of a compound.
Binary compound: a compound contain only two elements.
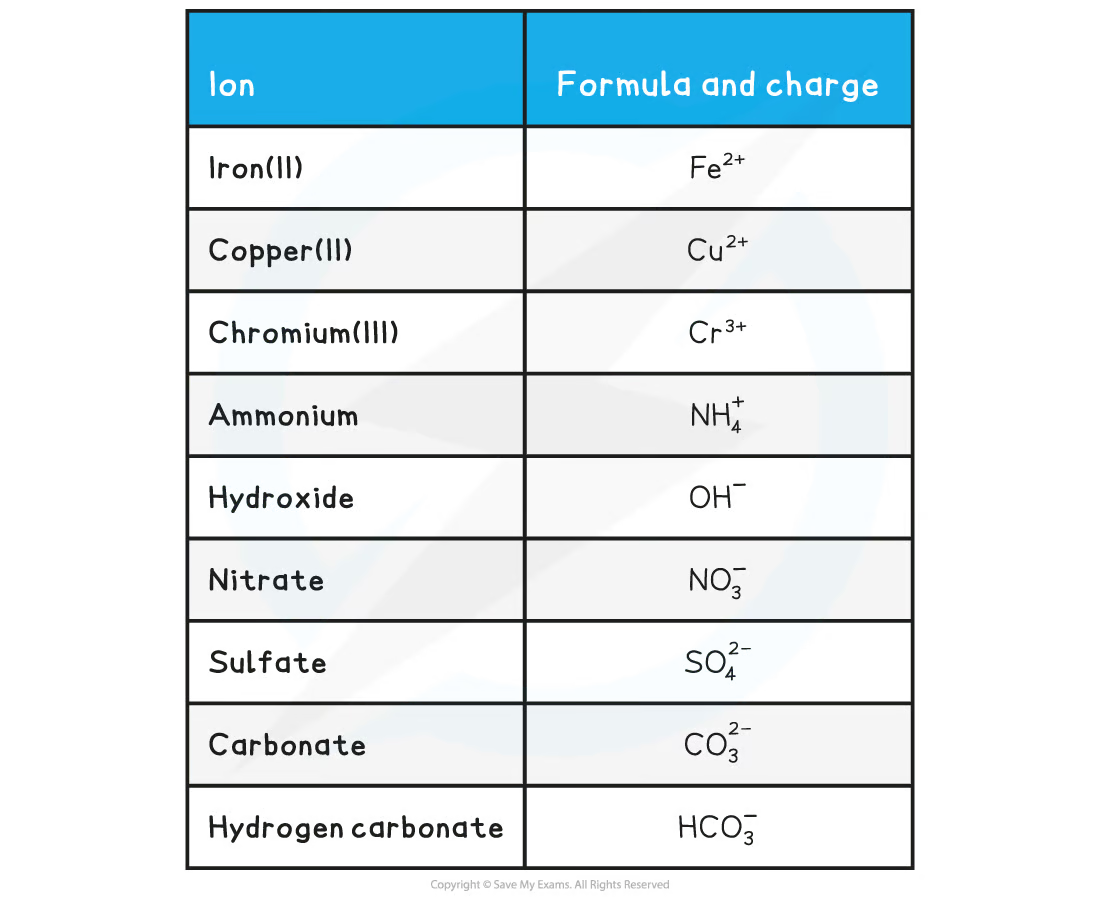
What is combining power/valency?
Metal or non-metal lose/gain electrons?
Combining power or valency is the number of electron that an atom need to lose/gain to have a full outer shell.
Metal tend to lose electrons to form cation, non-metal tend to gain electrons to form anion.
How to work out the formula of an ionic compound?
Write down the chemical symbols of elements.
Find the combining power of each element.
If the combining powers can be canceled down, do so.
Swap the combining power.
Write them as subscript.
If a metal bond with radical, they also have charged
What do the state symbols stand for?
(s): Solid
(l) : liquid
(g) : gas
(aq) : aqueous solution (dissolve in water)

How to write the ionic half equation?
Write out the balanced equation.
Identify the ionic substances and write the ions seperately.
Erase the ions appearing in both side of the equation, and rewrite the equation.


What is relative atomic mass?
The relative atomic mass, Ar, of an element is the average mass of all the isotopes of an element compared to 1/12 of a Carbon-12 atom.
What is relative molecular mass?
The relative molecular mass, Mr, of a compound is the total relative atomic masses (Ar) of all the atom in its formula
How to use Mr to work out masses in a reaction?
The relative molecular masses give the ratios of each element and compound in a reaction.
Use the ratios, we can find the masses of each substance in a reaction.

What is mole?
How many atoms does 1 mole contain?
What is the short way to write mole?
Mole is a unit for the amount of a substance.
1 Mole contain 6.02 × 10^23 atoms.
6.02 × 10^23 is known as Avogadro’s constant.
The unit of mole is mol.
What is one mole of an element or compound equal to?
One mole of an element or compound is equal to its Ar or Mr. This is called the molar mass (g/mol).
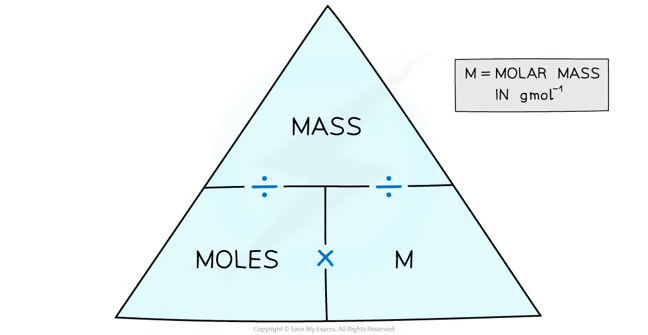
How to calculate the number of moles (formula)?
Number of mole = Mass (g) ÷ Mr
Mass = Number of mole × Mr
Mr = Mass ÷ number of mole
How to calculate the amount of product from a mass of reactant?
Write out the balanced equation.
Work out relative formula masses (Mr) of the reactant and product you’re interested in.
Find out how many moles there are of the substance you know the mass of.
Use the balanced equation to work out how many moles there’ll be of the other substance.
Use the number of mole to calculate mass.

What mass of Magnesium oxide is made when 60g of magnesium is burnt in air?
Ar(Mg): 24
Mr(MgO): 40
Balanced equation: 2Mg + O2 → 2MgO
n = m ÷ M
=> n of Mg is: 60/24 = 2.5 (mol)
2Mg react to produce 2MgO
=> 2 moles of Mg react to produce 2 mole of MgO
or 2.5 moles of Mg react to product 2.5 mole of MgO
=> There’re 2.5 mole of MgO is produced
or 2.5 × 40 = 100 (grams)
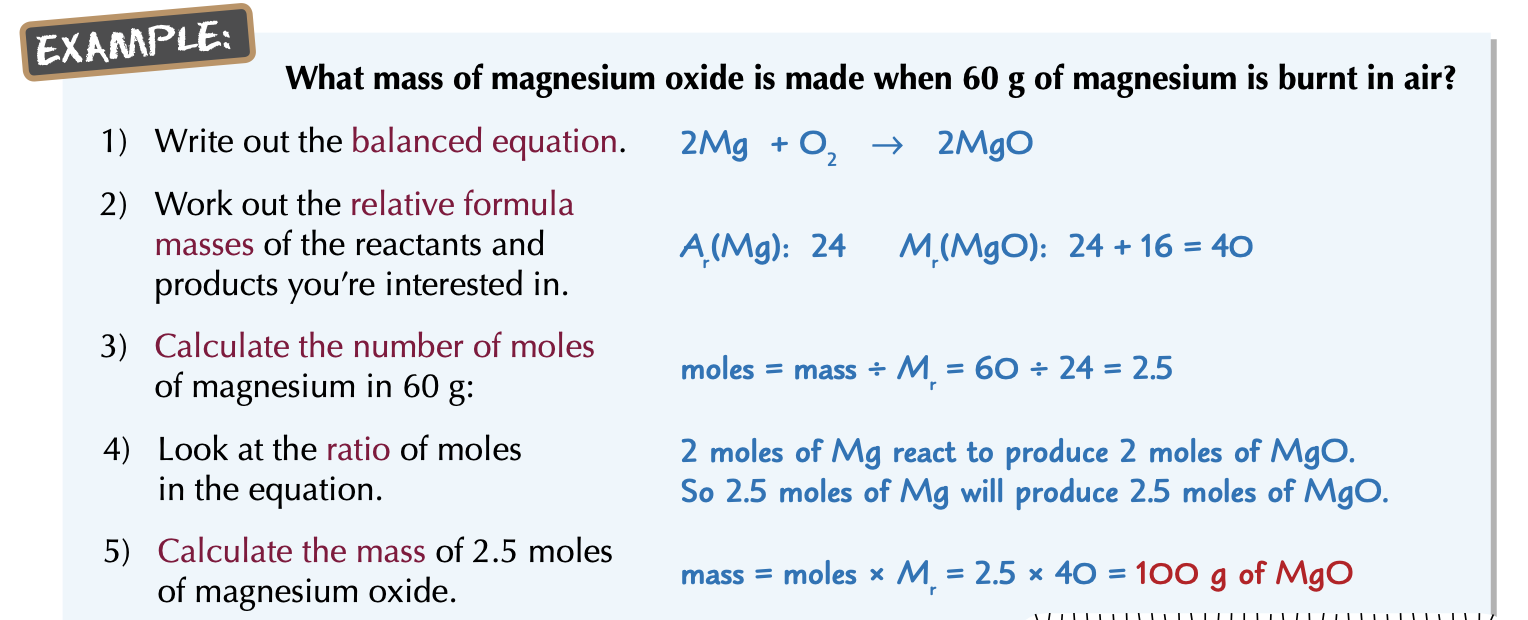
What will the reaction do when one reactant run out?
What is the reactant running out called?
What is the other reactant called?
What is the relationship between the reactant running out and the product?
The reaction will stop when one reactant is used up.
The reactant running out is called limiting reactant.
The other reactant is called excesss.
The amount of product formed is directly proportional to the amount of the limiting reactant used.
How to find the limiting reaction?
Write the balanced equation for the reaction
Calculate the moles of each reactant
Compare the moles & deduce the limiting reactant

What is yield?
What is theoretical yield and actualy yield?
What is percentage yield?
What percentage yield is used for?
The mass of the product formed is called the yield of the reaction.
Theoretical yield is the product calculated from balanced equation.
Actual yield is the real product formed from the reaction.
Percentage yield is the ratio between the actual yeild and the theoretical yield. it’s used to work out the productivity of the reaction.
How to calculate percentage yield?
Percentage yield = Actual yield (g) ÷ Theoretical yield (g) × 100%
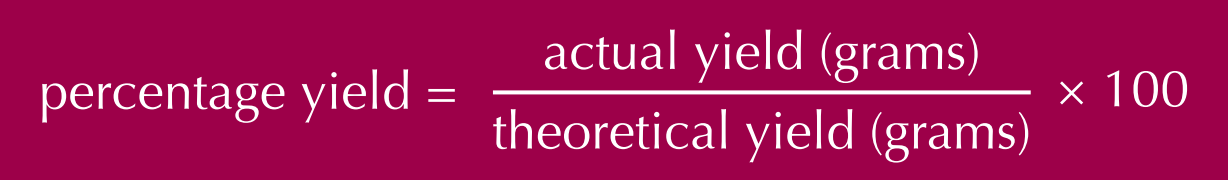
Tips!
Percentage yield is always somewhere between 0% and 100%.
0% mean there’s no product formed.
100% mean the product formed like what we’ve expect (theoretical yield).
If percentage yeild is out of 0%-100%, it’s wrong.
What is percentage purity used for?
Percentage purity is used to find the purity of a sample.
How to calculate the percentage purity?
Percentage purity = Pure yield ÷ Total impure yield × 100%

What is percentage mass?
The percentage of an element in a compound compared to the whole compound.
How to calculate percentage by mass of an element?
Percentage mass = Ar of an element ÷ Total Mr of a compound × 100%

Find the percentage mass of carbon in one molecule of propanol (C3H7OH)
Ar carbon: 12
Ar hydrogen: 1
Ar oxygen 16
We have:
Total Ar of Carbon is: 12×3 = 36
Mr of propanol is: 12×3 + 1×8 + 16 = 60
The percentage of carbon compared to the whole molecule is:
36/60 × 100% = 60%
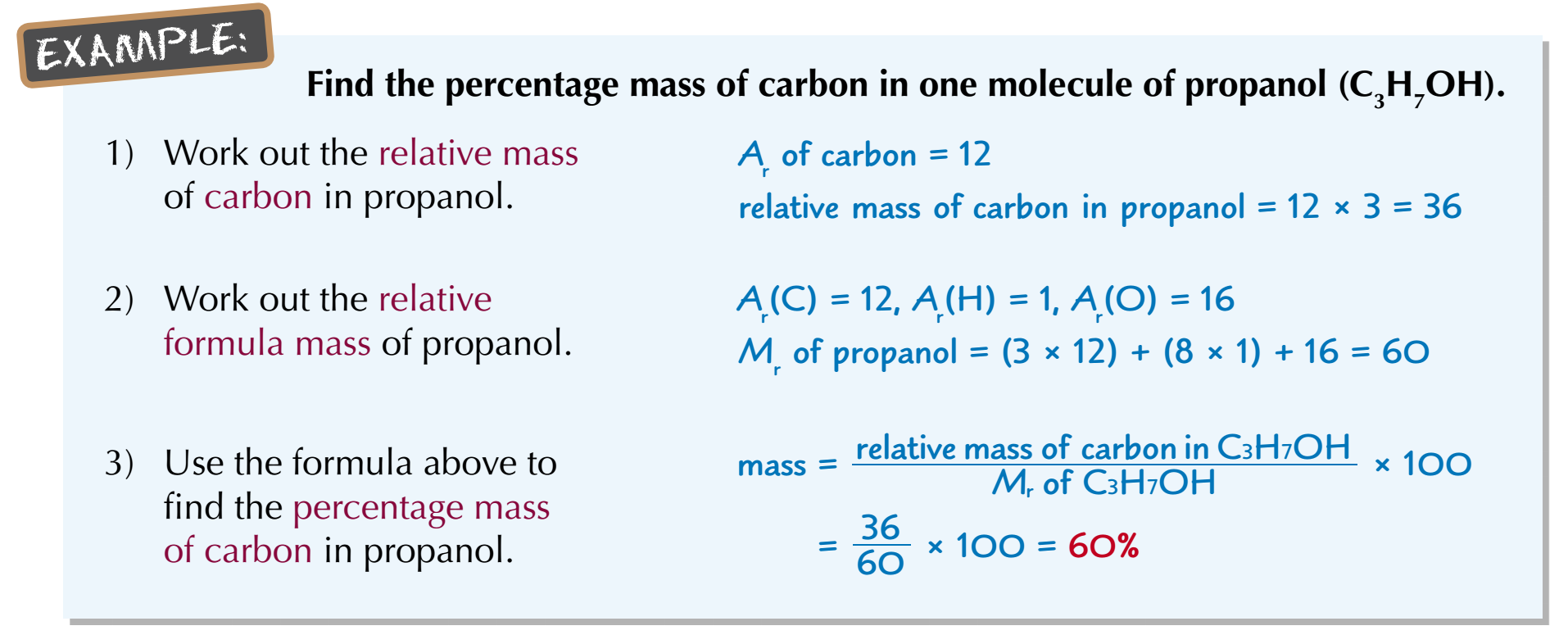

What are empirical and molecular formulae?
Empirical formula is the smallest whole number ratio of a atoms in a compound.
Molecular formula is the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule.
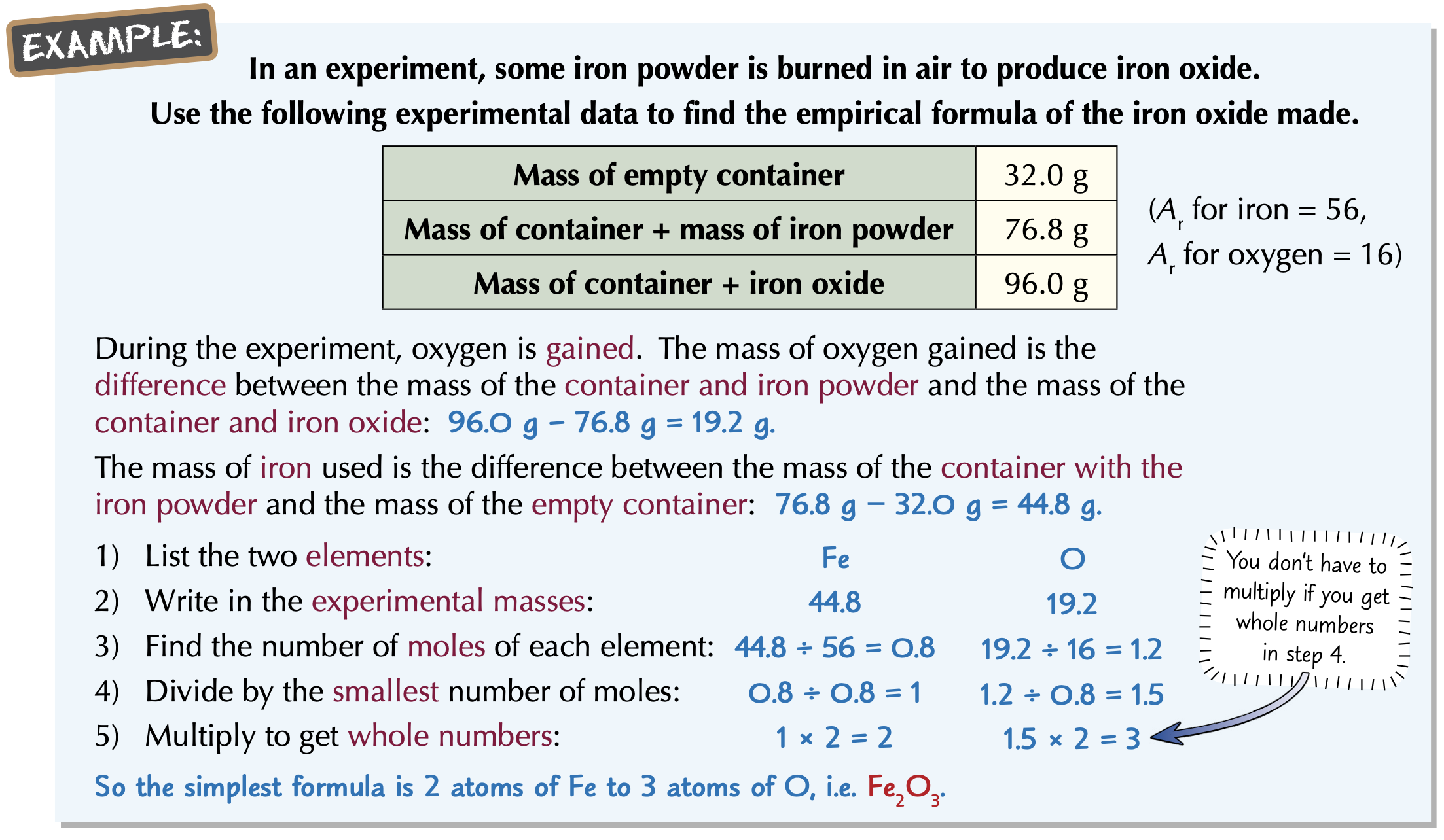
How to find the empirical formula from experimental data?
List the elements in the compound
Below them, write their experimental masses.
Find the number of moles of each element.
Turn those number into simplest whole number form.
What is concentration?
The common unit of concentration?
Concentration is how much of a substance we have in a solution (Concentration is the Amount of Stuff per Unit Volume).
The common unit of cencentration:
Moles per dm³ (mol/dm³)
Grams per dm³ (g/dm³)
How to calculate the concentration?
Unit: Moles/Volume
Concentration = Number of Moles ÷ Volume
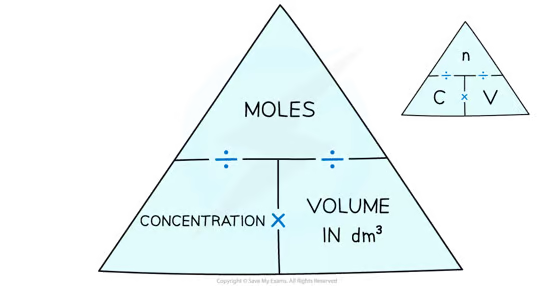
How to calculate the concentration?
Unit: Grams/Volume
Convering Mol/Volume to Grams/Volume.
To convert, we multiply it with the relative molecular mass of the substance.
What is the temperature and pressure of RTP and STP.
RTP - Room temperature and pressure: 20°C and 1 Atmosphere
STP - Standard temperature and pressure: 0°C and 1 Atmosphere
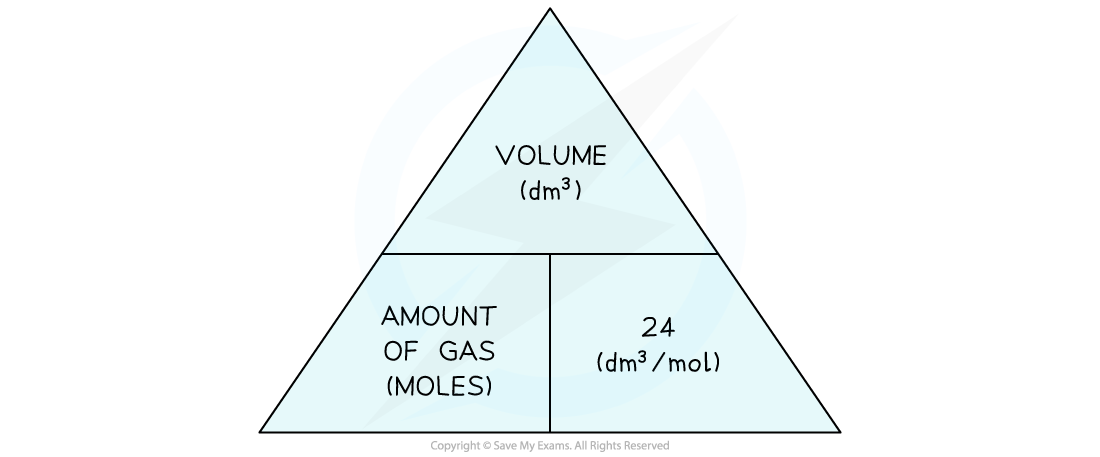
What volume does one mole of gas occcupies?
Avogadro’s law:
One Mole of Any Gas occupies 24 dm³ at RTP.
One Mole of Any Gas occupies 22.4 dm³ at STP.
How to find the volume of any gas (formula) ?
Volume (dm³) = moles of gas × 24