Business Management Toolkit
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
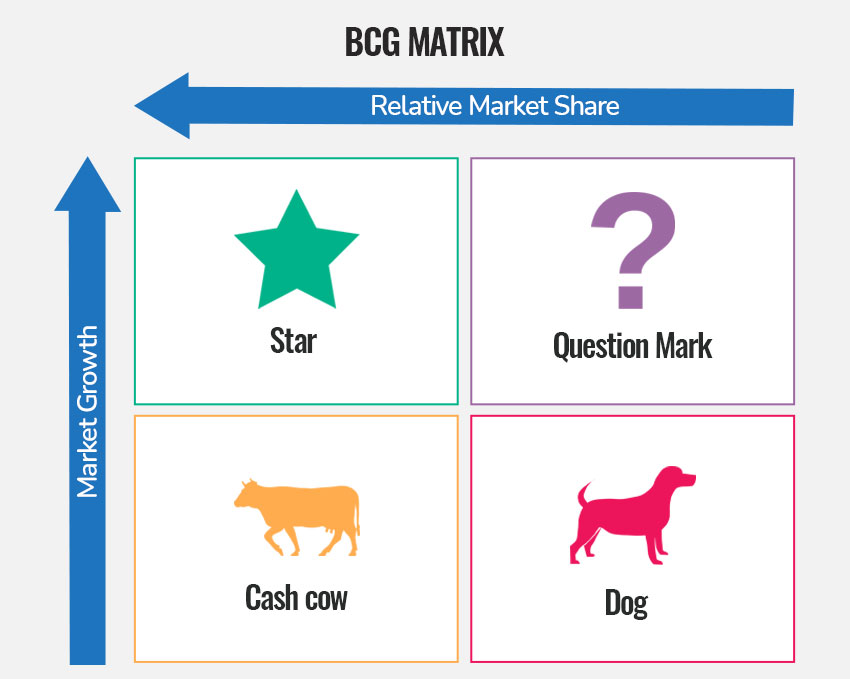
BCG matrix
Descriptive statistics
measures of central tendency - mean, median, mode
measures of spread - quartiles, standard deviation
data visualization - bar charts, pie charts, infographics
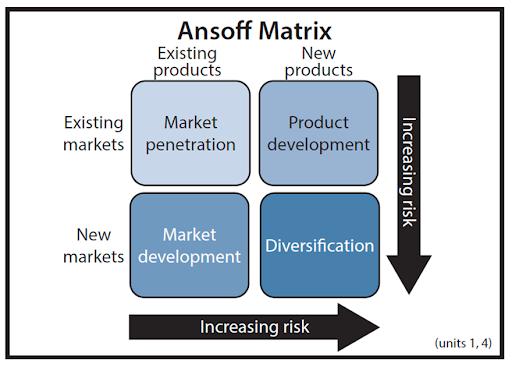
Ansoff matrix
Decision trees
used to help businesses to consider various factors before deciding on a particular venture. They consist of nodes and branches. There are two types of nodes:
Decision nodes - events that a company can control or decide on (represented by squares)
Chance nodes - events that are outside the control of the company (represented by circles)
STEEPLE analysis
Social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, ethical
SWOT analysis
Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats
Business plan
Executive summary – abridged version of the main points of the business plan, written afterwards
Business description – explains the purpose of the business and what it is selling. May address the legal structure, aims, intellectual property information, relations to other organizations, and administrative issues
Human resources plan – description of organizational structure, philosophy and needs, number of employees needed, methods to manage them, and personnel costs
Financial plan – projected figures and information for financial institutions to review before providing funding such as start up cost, ongoing costs, prices for products/services, revenue figures, break even dates, how plan intends to pay back investment/loans
Marketing plan – outlines how the start-up will reach potential customers including market research, analysis of competitors, target market, how to reach target market, projected customer numbers, measurable market targets
Operational plan – relates to the function of operations such as the planned manufacturing process, availability of stock or raw materials, supplier information, how to distribute products
EBHFMO - Elsa bought her friend more oranges
Circular business models
Circular supply models – reduce long term demand for virgin resources and instead use renewable or bio-based resources.
Resource recovery models – recycle waste into secondary raw materials (recycled materials used in the manufacturing process), lowering the need to extract virgin resources
Product extension models – extend the use of existing products, slow the flow of constituent materials through the economy, and reduce need for virgin resources
Sharing models – share underutilized materials to reduce demand for new products and raw materials
Product service system models – market services rather than products, often with incentives to use green and long-lasting products