Study Guide for Simple Machines
Work - Is done when a force causes an object to move in the direction of the force.
Simple Machine - make work easier; NOT LESS WORK
[[==Work = Force (N) x Distance (m)==[[
Example: You push a box with 8N of force and the box moves 6m. How much work is done?
8N x 6N = 48J of Work
Power is the rate at which work is done. The faster you complete work, the more power you are generating.
}}Power (watts) = Work (J) / Time (s)}}
Example: You sand a piece of wood doing 45J of work in 5 seconds. How much power did you generate?
45J / 5 s = 9 watts
Machine - a device that makes work easier by changing the size or direction of the force.
Work Input - the amount of work you put into the machine.
Work Output - the amount of work done by the machine.
{{WORK OUTPUT CAN NEVER BE GREATER THAN WORK INPUT (FRICTION CAUSES THIS).{{
Mechanical Advantage - the number of times the machine multiplies force.
Mechanical Advantage = output force (N) / input force (N)
[[Mechanical Efficiency - work output/work input x 100 (measured as percentage %)[[
TYPES OF MACHINES
1st Class Lever - the fulcrum is between the input force and output force.

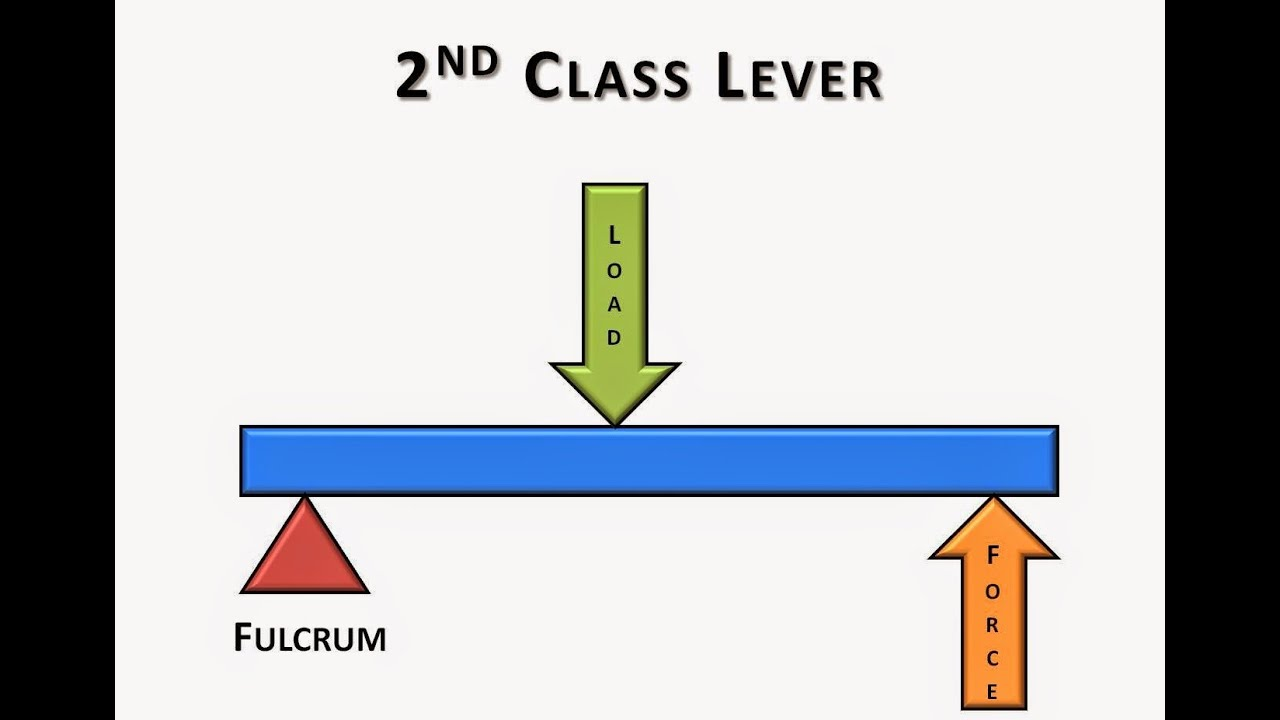
2nd Class Lever - fulcrum at one end with input force at the other end and output force in between.
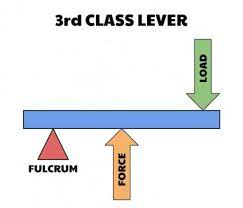
3rd Class Lever - the input force is between the fulcrum and the output force.
Pulleys - a simple machine that has a grooved wheel and a rope or cable.
Wheel and Axle - simple machine consisting of two circular objects of two different sizes.
Incline Plane - a simple machine that is a straight slanted surface (ramp).
Wedges - a pair of inclined planes that move. (knife/axe)
Screws - an inclined plane wrapped around a cylinder.
<<MECHANICAL ADVANTAGE FORMULAS<<
Lever: Distance from Input Force to Fulcrum/Distance from Output Force to Fulcrum.
Incline Plane: Length of ramp/ Height of ramp
Wheel and Axle: Radius of the wheel / Radius of the axle
Pulley: Count # of pulleys
Wedge: Length of the wedge / the thickest part of the wedge.
Compound Machine: two or more machines combined into one.