Hemodynamic Disorders and Shock in Pathology
1/171
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
172 Terms
Hemodynamic Disorders
Conditions affecting blood flow and circulation.
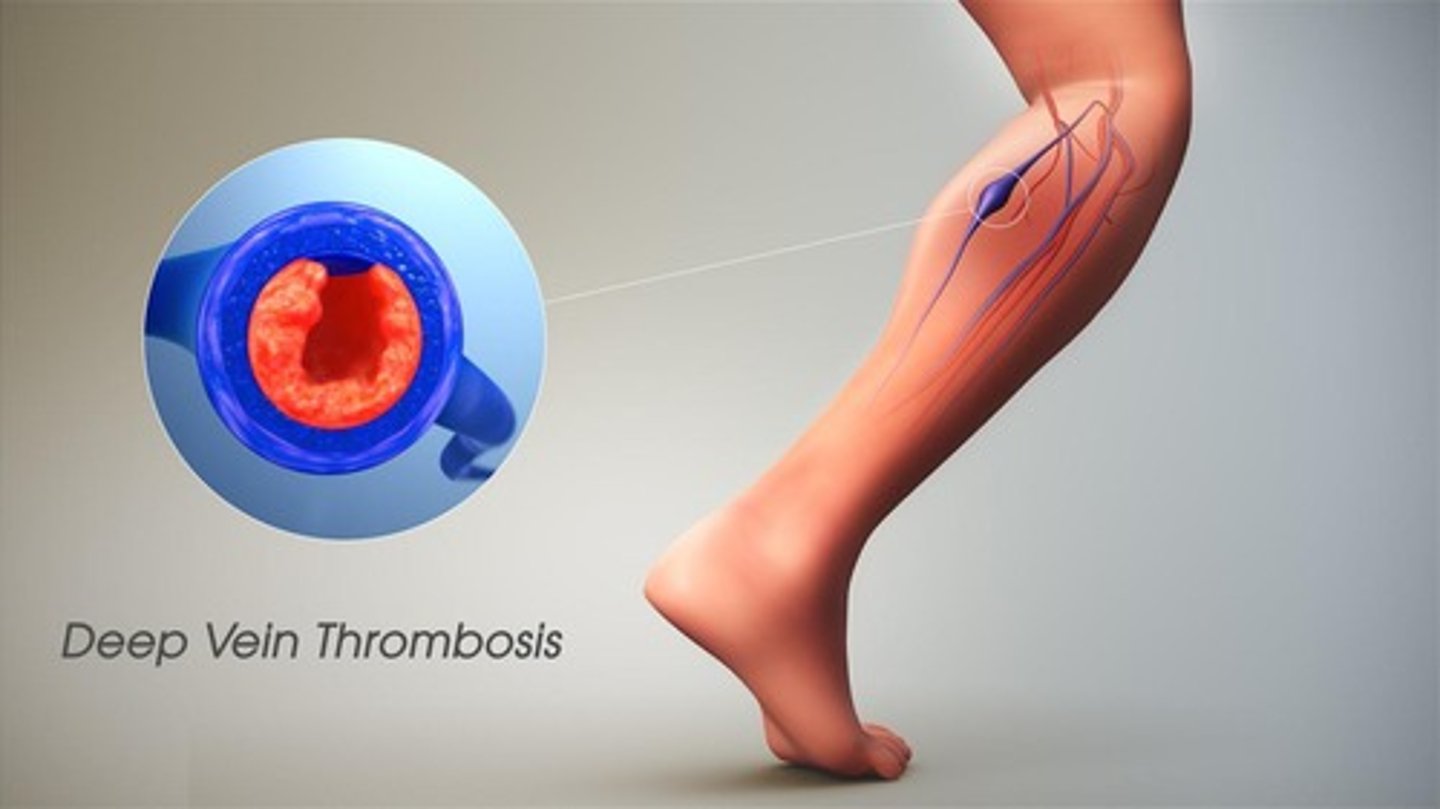
Thromboembolic Disease
Obstruction of blood vessels by clots.
Shock
Critical condition with inadequate blood flow.
Fluid Homeostasis
Balance of fluids in the body.
Vascular Volume
Total blood volume within the circulatory system.
Endothelial Function
Role of endothelial cells in vascular health.
Edema
Excess fluid in interstitial tissue spaces.
Intravascular Pressure
Pressure within blood vessels.
Osmolarity
Concentration of solutes in body fluids.
Thrombosis
Clot formation at inappropriate sites.
Embolism
Migration of clots obstructing blood flow.
Infarction
Tissue death due to lack of blood supply.
Hemorrhage
Excessive bleeding from blood vessels.
Hypotension
Abnormally low blood pressure.
Anasarca
Severe generalized edema with swelling.
Hydrothorax
Fluid accumulation in the pleural cavity.
Hydropericardium
Fluid accumulation in the pericardial cavity.
Hydroperitoneum
Fluid accumulation in the abdominal cavity.
Sodium Retention
Increased sodium levels causing fluid retention.
Water Retention
Increased water levels leading to edema.
Lymphatic Obstruction
Blockage preventing lymph fluid drainage.
Congestive Heart Failure
Heart's inability to pump effectively.
Reduced Cardiac Output
Decreased heart efficiency affecting renal blood flow.
Renal Hypoperfusion
Inadequate blood flow to kidneys causing dysfunction.
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Axis
Hormonal system regulating blood pressure and fluid balance.
Secondary Aldosteronism
Increased aldosterone due to renal hypoperfusion.
Increased Venous Pressure
Elevated pressure in veins due to fluid overload.
Edema
Swelling caused by excess fluid accumulation in tissues.
Reduced Plasma Osmotic Pressure
Lowered pressure due to albumin loss or synthesis reduction.
Nephrotic Syndrome
Kidney disorder causing protein loss and edema.
Cirrhosis
Liver disease leading to fluid retention and edema.
Protein Malnutrition
Insufficient protein intake causing low serum albumin.
Lymphatic Obstruction
Impaired lymphatic drainage leading to localized swelling.
Lymphedema
Swelling due to lymphatic system blockage.
Filariasis
Parasitic infection causing massive lymphatic obstruction.
Elephantiasis
Severe lymphedema of lower limbs from filariasis.
Peau de Orange
Skin appearance resembling orange peel due to edema.
Sodium and Water Retention
Fluid retention contributing to various edema forms.
Increased Hydrostatic Pressure
Elevated pressure in blood vessels causing fluid leakage.
Clinical Correlation
Edema indicates underlying disease, impacting healing.
Pulmonary Edema
Fluid in lungs impairing breathing and can be fatal.
Brain Edema
Swelling in the brain risking herniation and vascular compression.
Hyperemia
Increased blood flow to tissue from arteriolar dilation.
Congestion
Local blood volume increase due to impaired outflow.
Hyperemia
Increased blood flow to tissues, causing redness.
Congestion
Passive blood accumulation due to impaired outflow.
Cyanosis
Blue-red color from deoxygenated hemoglobin accumulation.
Chronic Congestion
Long-standing blood stasis causing chronic hypoxia.
Edema
Swelling due to increased fluid transudation.
Hemorrhage
Extravasation of blood due to vessel rupture.
Hematoma
Localized blood accumulation within tissues.
Petechiae
Minute 1-2 mm hemorrhages in skin or membranes.
Purpura
Slightly larger (>3 mm) hemorrhages in tissues.
Ecchymoses
Larger (>1-2 cm) bruises from trauma.
Bilirubin
Blue-green pigment from hemoglobin breakdown.
Hemosiderin
Gold-brown pigment from degraded hemoglobin.
Hemothorax
Blood accumulation in the pleural cavity.
Hemopericardium
Blood accumulation in the pericardial cavity.
Hemoperitoneum
Blood accumulation in the peritoneal cavity.
Hemarthrosis
Blood accumulation in joint cavities.
Jaundice
Yellowing of skin from bilirubin buildup.
Clinical Correlation
Significance of hemorrhage depends on volume and rate.
Rapid Blood Loss
Loss of up to 20% blood volume is critical.
Capillary Rupture
May cause small foci of hemorrhage.
Macrophages
Cells that degrade and phagocytose red blood cells.
Hemorrhage
Loss of blood leading to potential shock.
Hemorrhagic Shock
Severe blood loss causing inadequate perfusion.
Intracranial Pressure
Pressure within the skull affecting brain function.
Iron-Deficiency Anemia
Anemia due to chronic blood loss, reducing iron.
Normal Hemostasis
Processes maintaining blood in a fluid state.
Hemostatic Plug
Rapid clot formation at injury site.
Thrombosis
Inappropriate clot formation in uninjured vessels.
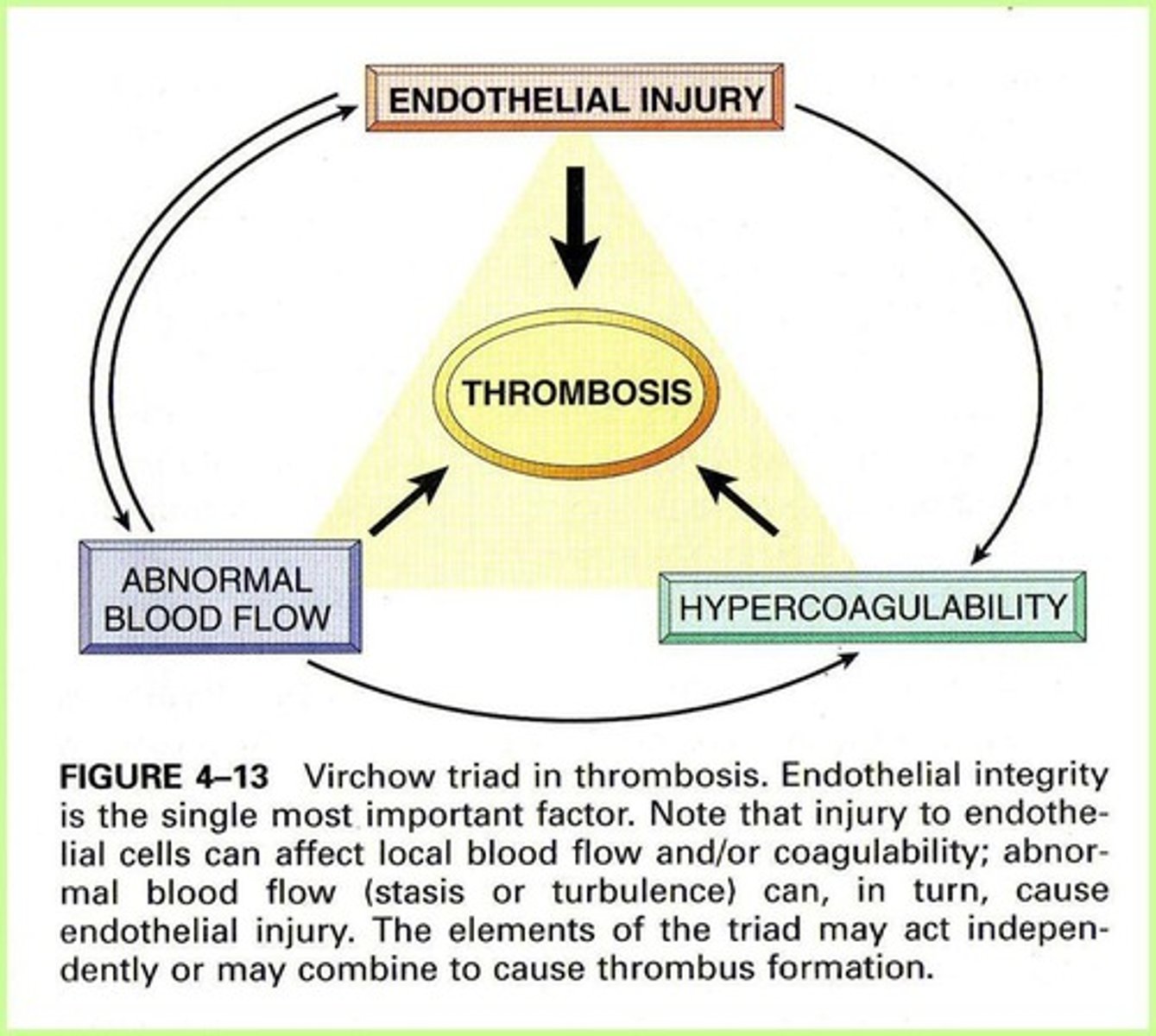
Virchow Triad
Three factors predisposing to thrombus formation.
Endothelial Injury
Damage to blood vessel lining promoting thrombosis.
Blood Stasis
Reduced blood flow increasing thrombus risk.
Blood Hypercoagulability
Increased tendency for blood to clot.
Thrombus Propagation
Thrombus growth due to platelet and fibrin accumulation.
Embolization
Dislodged thrombus traveling to distant sites.
Dissolution
Removal of thrombus by fibrinolytic activity.
Organization
Thrombus-induced inflammation and fibrosis.
Recanalization
Restoration of blood flow through a thrombus.
Venous Thrombosis
Thrombus formation in veins, often legs.
Superficial Venous Thrombi
Thrombi in superficial veins causing local symptoms.
Deep Venous Thrombi
Serious thrombi in deep leg veins.
Varicosities
Enlarged veins predisposing to thrombus formation.
Thrombotic Obstruction
Blockage of vessels due to thrombus presence.
Thrombosis
Formation of a blood clot within a vessel.
Arterial Thrombosis
Clot formation in arteries, often due to atherosclerosis.
Cardiac Thrombosis
Clot formation in the heart, often post-myocardial infarction.
Atherosclerosis
Vascular disease causing abnormal flow and endothelial damage.
Mural Thrombi
Thrombi attached to the heart wall, common in MI.
Rheumatic Heart Disease
Condition leading to atrial thrombi from mitral stenosis.
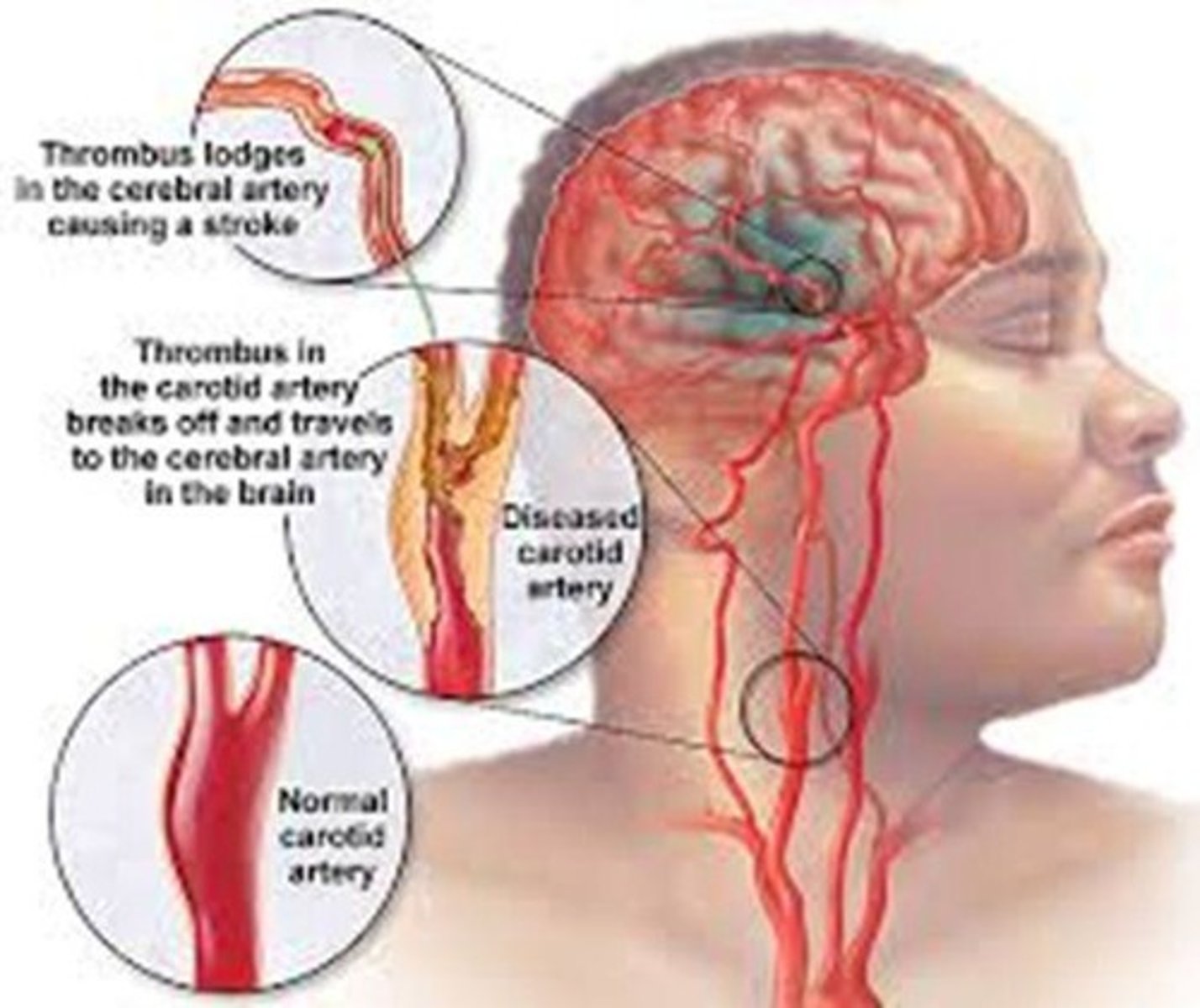
Cerebral Artery Thrombosis
Clot in cerebral arteries leading to cerebral infarction.
Embolism
Detached mass traveling in blood to distant sites.
Thromboembolism
Embolism originating from a dislodged thrombus.
Types of Emboli
Includes fat, air, tumor fragments, and atherosclerotic debris.
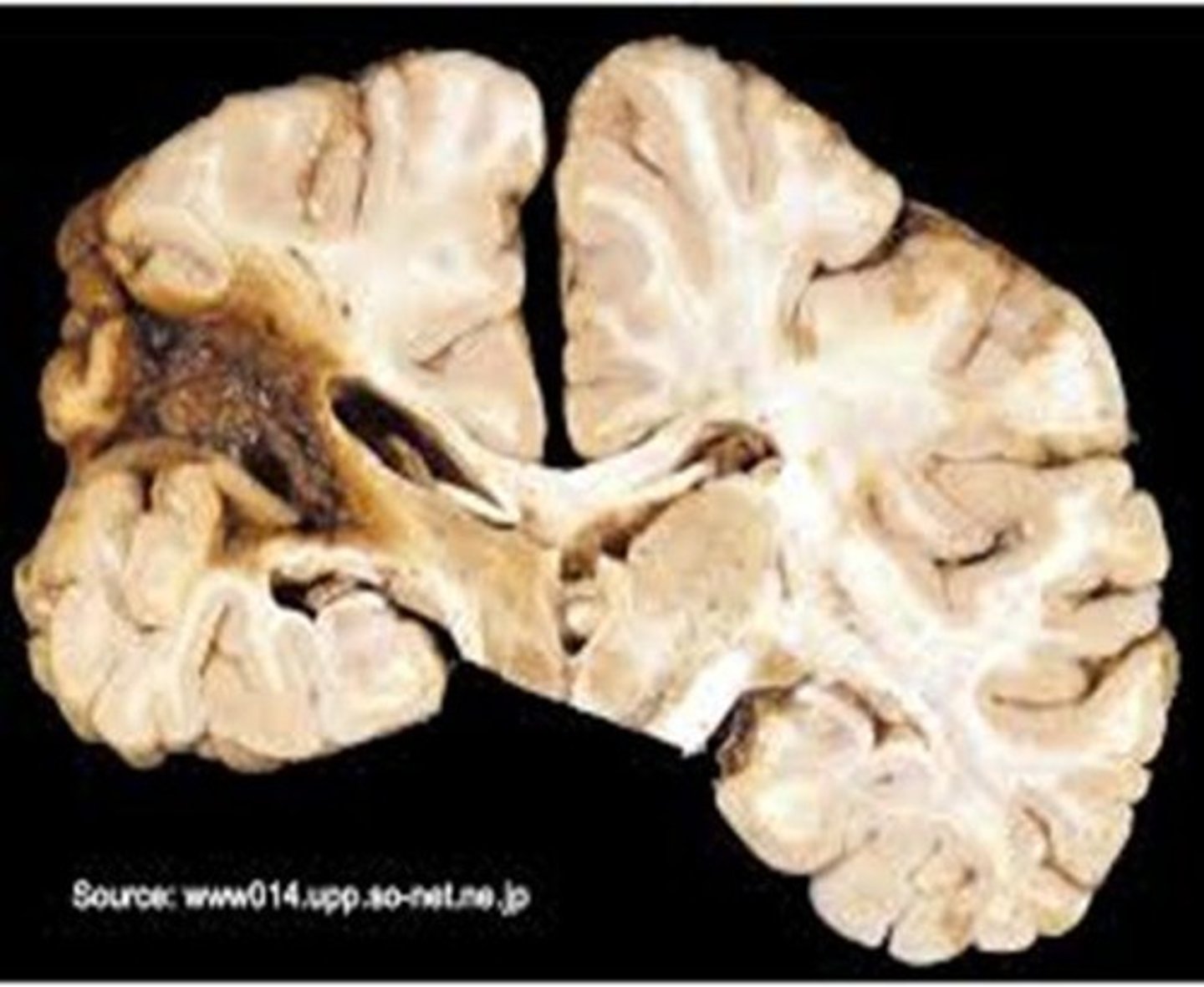
Ischemic Necrosis
Tissue death due to insufficient blood supply, called infarction.
Pulmonary Thromboembolism
Obstruction of pulmonary arteries by emboli.

Saddle Embolus
Embolus occluding the bifurcation of the pulmonary artery.
Clinical Silent Emboli
Small pulmonary emboli often cause no symptoms.