10.3 - Human Immune System
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
_____ are harmful microscopic enemies that can cause disease
pathogens
what are leukocytes?
white blood cells (WBCs)
leukocytes are produced by _____ in red bone marrow
hematopoiesis
(red bone marrow tends to concentrate at the end of long bones (epiphyses))
lymphocytes are special types of leukocytes that originate from ____ but end up concentrate in _____ tissue
bone marrow; lymphatic
lymphocytes can produce _____ & _____
antibodies; cytokines
what are some examples of lymphocytes?
B and T cells
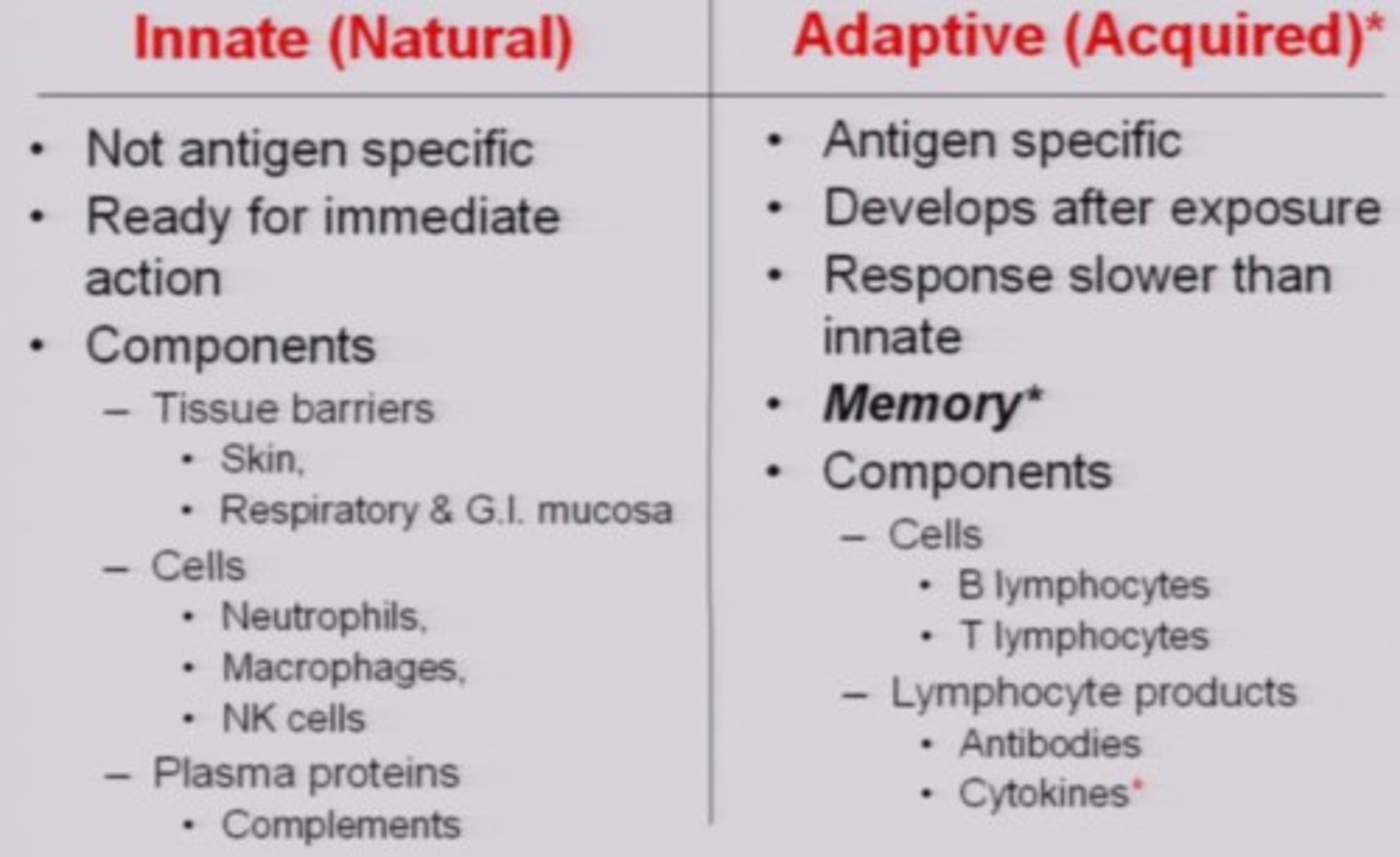
what are the 2 types of immune responses?
innate and adaptive
the _____ immune system is a quick, nonspecific immune response
innate
a human's outer barriers to infection (such as skin) are the first layer of _____ immunity
innate
innate immunity
1. skin
2. cilia
3. stomach acid
4. symbiotic bacteria
what are some of the outer barriers, which are a part of innate immunity? - skin
1. thick epidermis; dermis; hypodermis (subcutaneous)
2. mucus membranes , secrete lysozymes
3.sebaceous glands
pathogens are unable to penetrate which integument layers?
epidermis; dermis; hypodermis (subcutaneous)
mucus membranes in the skin function to secrete _____ and trap pathogens
lysozyme
lysozymes are antimicrobial protein enzymes found in tears, saliva, and mucous, which _____ break down bacterial _____
nonspecifically; cell walls
sebaceous glands of the skin secrete _____, which serves as physical barrier
oil (sebum)
the fatty acids in sebum are _____ & _____
antimicrobial; nonspecific
what are cilia?
hair-like projections that sweep away unwanted invaders
- found in respiratory tract
stomach acid is an _____ barrier of the innate immune system, which _____ kills microbes with low* pH
internal; nonspecifically
_____ bacteria out-compete their more hostile relatives and are an _____ barrier to infection
symbiotic; internal
What occurs when the physical barrier is penetrated?
innate immunity continues with the inflammatory response
mast cells are a type of _____ that sits in tissues
leukocyte
injured tissue and mast cells work together to release _____
histamine
histamine - functions
1. Dilate nearby capillaries —> increase blood flow
2. Make capillary walls more permeable —> fluid and immune cells leak out to the site of
injury.
histamine dilates capillaries (and makes their walls more permeable) near injured vessels, which brings more blood to the injured area - why is this beneficial?
fluid and immune cells leak out to the site of injury
(inflammatory response)
what are the 5 signs associated with inflammation?
Swelling
Loss of function
Increased heat
Pain
Redness
(SLIPR)
heat is an inflammatory sign, which results from _____ and _____
dilation of capillaries; increased blood flow
_____ is an inflammatory sign, which occurs due to the dilation of capillaries
redness
(more blood = red color)
_____ is an inflammatory sign that occurs by permeable capillaries
swelling
(fluid accumulation due to leaky blood vessels)
_____ pain happens right at the time of injury, and it is caused by nerve endings
sharp
_____ pain is felt after the time of injury, and it is due to inflammation
slow, throbbing
- the swollen areas exert pressure on free nerve endings, which causes a continuous pain.
what are the indirect outcomes of inflammation?
loss of function due to swelling and pain
fever
_____ is a systemic response to hinder the growth of (or kill) pathogens
when capillaries dilate during the inflammatory response, leukocytes tend to adhere to the endothelial cells that line the vessels - what is this called?
margination
What is diapedesis?
the process of cells moving from capillaries to tissues
what is chemotaxis?
the process of moving to a location in response to a chemical signal
what are the 5 types of leukocytes in order of abundance?
(Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas)
Neutrophils
Lymphocytes
Monocytes/Macrophages
Eosinophils
Basophils
_____ are the most numerous leukocytes
Neutrophils (Never)
- 40- 70% of WBC
Neutrophils (Never) act as _____ in the _____ immune system
phagocytes; innate
- part of innate response because neutrophils eat all pathogens nonspecifically
which Lymphocytes (Let) are innate and which are adaptive?
natural killer (NK) cells = innate;
- B and T cells = adaptive
- lymphocites all require targets
natural killer (NK) cells
- innate Lymphocytes (Let)
- attack and kill 1 ) virus-infected cells 2) cancerous body cells
natural killer (NK) cells vs. B, T Cells
NK - do not require activation, innate
B, T cells - needs activation, adaptive
NK cells are innate Lymphocytes (Let) that secrete _____ & _____ to fight enemies
perforin; granzymes
(NK cells (innate) and CD8/cytotoxic T cells (adaptive) are both Lymphocytes (Let) that secrete perforin and granzymes)
_____ is a protein that creates a pore to perforate pathogen membranes --> causes cell lysis
perforin
(NK cells (innate) and CD8/cytotoxic T cells (adaptive) are both Lymphocytes (Let) that secrete perforin and granzymes)
granzymes
proteases, which stimulate apoptosis, which is useful for virally infected/cancerous cells
-
(NK cells (innate) and CD8/cytotoxic T cells (adaptive) are both Lymphocytes (Let) that secrete perforin and granzymes)
a _____ is an enzyme that breaks down proteins and peptides
protease
_____is programmed cell death
apoptosis
Monocytes (Monkeys) are a part of the _____ response
innate
(nonspecific)
monocytes vs. macrophages
- Monocytes (Monkeys): immature, in blood vessels
- macrophages: mature once they cross over into an infected tissue via diapedesis
macrophages are mature Monocytes (Monkeys) that act as phagocytes and function as _____ to activate adaptive immunity
antigen-presenting cells
Eosinophils (Eat) are a part of the _____ immune response
innate
(non-specific)
how are monocytes/macrophages similar to neutrophils?
both are phagocytes, nonspecific
Eosinophils (Eat) contain _____ in their cytoplasm, which can be released to kill pathogens (especially effective on ___)
granules;
parasites
Basophils (Bananas) are the _____ numerous leukocyte
least
Basophils (Bananas) contain _____ (like Esoinophils) and have a similar function to _____
granules; mast cells
what are the 2 important components of Basophil (Bananas) granules?
histamine; heparin
heparin
is a component of Basophil (Bananas) granules, which prevents blood from clotting too quickly
mast cells and Basophils (Bananas) are made in _____ and then leave to circulate in the _____
red bone marrow; blood
When released into blood, basophils (Bananas) are _____ in the blood, while mast cells are _____ in the blood
basophils --> mature;
mast cells --> immature
dendritic cells =
- use _____ to observe local environment
= surveillance guards roaming in tissues detecting potential threats.
-
pinocytosis
pinocytosis is a type of endocytosis that is also known as _____
cellular drinking
(endo-/exocytosis are active transport mechanisms)
dendritic cells are part of the _____ immune system, but they travel to lymph nodes to activate _____ immunity
innate; adaptive
(dendritic cells are antigen presenting cells)
dendritic cells and macrophages are both ___
antigen-presenting cells
-then BOTH migrate to lymph nodes along to activate the adaptive immune response
what links innate and adaptive immune systems?
dendritic cells
macrophages
inteferon
interferon is secreted by _____ cells
- purpose:
virus-infected
- to warn non-infected cells in vicinity by binding to non-infected ones
_____ binds to non-infected cells to warn/prepare for viral attack
interferon
interferon activates _____ cells, which further activates adaptive immunity
dendritic
complement system contains a group of _____ that help the immune cells battle pathogens
30 proteins
complement system - innate / adaptive??
innate
how do complement system proteins activate each other
cascade series of activation through release of cytokines
functions of activated complement system
1. opsonization
2. amplify inflammatory response
3. lyse pathogen membrane
opsonization is a feature of the complement system - what does it do?
complement proteins coat the surface of an invader, making them more prone to phagocytosis
- bind complement protein C3b to antigens to improve their "cell eating"
complement system - inflammatory response
certain proteins can bind to mast cells to trigger a stronger histamine release
the complement proteins are activated by _____
IgG and IgM
what are the two mechanisms for complement system activation?
classical and alternative pathways
(don't memorize requirements for each)
describe complement system lyse pathogen membranes
some proteins form a membrane attack complex (MAC) which specifically functions to poke holes in pathogen membranes
- once holes created --> fluid and salts can go into the pathogen --> cell lysis
if innate immunity isn't sufficient to protect against pathogens, what joins?
adaptive immunity
_____ immunity is a specific immune response for specific antigens, and it has _____
adaptive; memory
antigen
is a marker from a foreign molecule that helps distinguish between self/non-self cells
how does the body distinguish between self and non-self cells (in addition to antigens)?
major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
all nucleated cells contain MHC class _____ molecules on their surface
1
antigen presenting cells contain both MHC class _____ & _____ molecules on their surface
1; 2
true or false - genetically unique individuals contain unique MHC 1 molecules
true
exception: identical twins have the same MHC 1
what are the proteins of a MHC class 1 molecule?
alpha 1, 2, 3 and beta-microglobulin protein chains
what are the proteins of a MHC class 2 molecule?
alpha 1 and 2; beta 1 and 2
why do transplanet rejections occur?
different MHC 1 molecules will be labeled as a foreign antigen on the donor organ
transplant patients must take _____ on a life-long basis
immunosuppressants
- to lower/eliminate the immune system's response towards the foreign organ.
- doing so also makes these patients more susceptible to general infections.
in autoimmune diseases, the immune system attacks _____
self-cells
_____ act as a bridge between innate and adaptive immunity
antigen-presenting cells (APCs)
macrophages and dendritic cells are _____
antigen-presenting cells (APCs)
macrophages and dendritic cells contain MHC class _____ and _____ - why?
1; 2
they are antigen presenting cells (APCs)
MHC I vs. II
MHC I : found on all nucleated body cells
- mark for "self"
- foreign MHC I molecules are deemed as antigens (i.e. organ donations)
-
MHC II: found only on APCs
a _____ is the section of an antigen that is recognized by immune cells
epitope
B and T cells are adaptive _____
Lymphocytes (Let)
what are the 3 main types of Lymphocytes (Let)?
NK cells (nnate); B and T cells (adaptive)
B cells stay and mature in the _____, while T cells go and mature in the _____
bone marrow; thymus
_____ are involved with antibody-mediated adaptive immunity (humoral immunity)
B cells
each B cell has 1 type of _____ that is specific for 1 type of antigen epitope
B cell receptor (BCR)
what can B cell receptors (BCRs) bind to?
free-floating antigens or antigens presented by APCs
what happens after a B cell binds to an antigen?
it becomes activated and then divides to make copies of itself
describe the clonal selection model for B cells
B cells have unique BCRs to specific antigens. If those antigens are present, only the B cells with the BCR for antigen binding will amplify (one antigen, one B Cell)