BIO Lab Midterm
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Scientific Method
Observation, Ask a Question, Background Research, Hypothesis, Test through Experiment, Analyze to a Conclusion, Report Results is a systematic process used to investigate phenomena, test ideas, and acquire new knowledge.
Independent Variable (IV)
What gets change, does it impact dependent?
Dependent Variable (DV)
Response variable to IV
Control
What you compare the others too
Replication
ensure results are reliable and consistent by repeating the experiment multiple times.
Corase Adjustment
Big adjustment tool
Fine Adjustment
smaller adjuster
Apeture
where the slides go and focuses light onto the specimen.
Care
Hide microscope base, stored in cubbies, don’t force parts
Objectives
focuses which is 10 * lens for total magnification
Cell Theory
A scientific theory that states all living organisms are composed of cells, which are the basic unit of life, and that all cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Implications of Cell Theory
It implies that all living things share a common cellular structure and that the processes of life arise from cellular activities, emphasizing the importance of cells in biology.
All cells have?
Cell Membrane, Nucleic Acid, Ribsomes, Enzymes
Prokaryotes
Unicellcuar bacteria, archaea, and Cyanobacteria
Eukaryotic
animals, plants, fungi, nimulticellular organisms with membrane-bound organelles. Nucleus
Taxonomic Ranking
A hierarchical system used to classify organisms into categories such as domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species. DEAR KING PHILIP CAME OVER FOR GOOD SOUP

Cellular Respiration
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy (ATP)
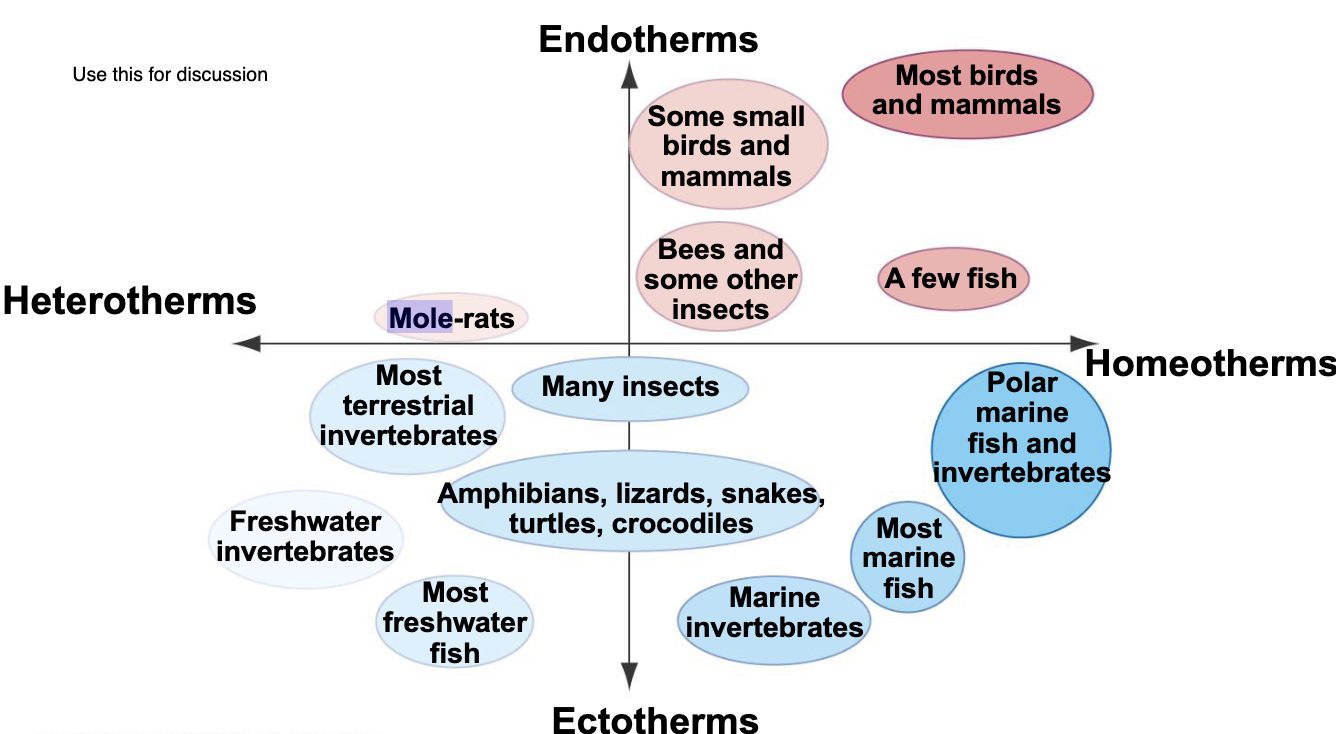
Ectotherms
An animal that gains most of its body heat from external sources as opposed to metabolic processes
Endotherm
An animal that gains most of its body heat from internal metabolic processes (cellular respiration)
Homotherm
An animal that has a constant body temp (most are endotherms) and is able to maintain this temperature regardless of external conditions.
Heterotherm
An animal whose body temperature rises with the environmental temperature (mostly ectotherms)
Heterotherm, Endotherms, Homeotherm. Ecotherms
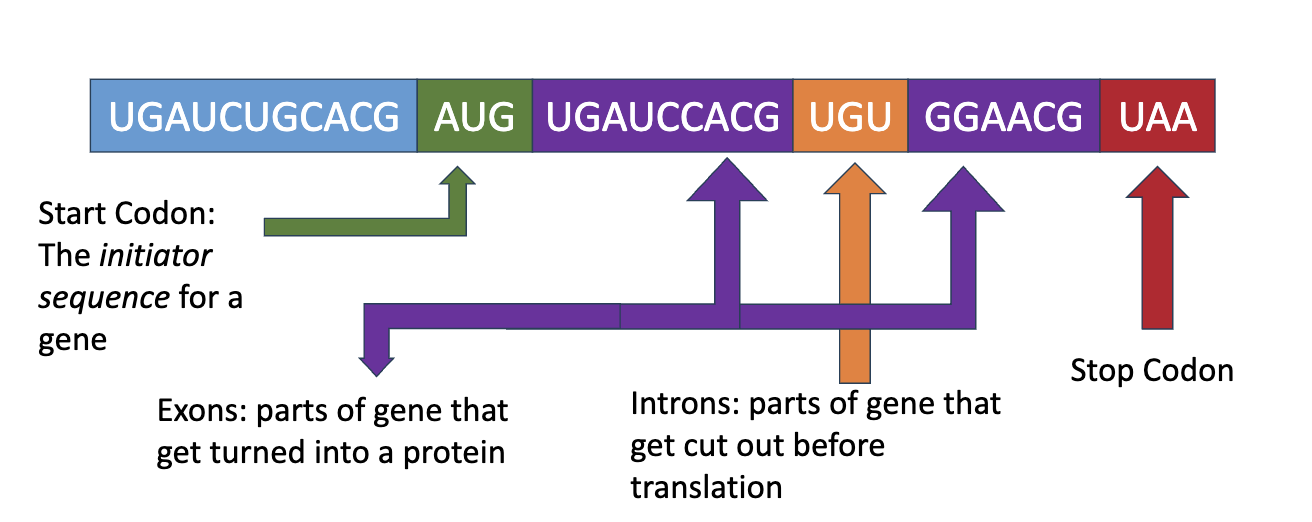
Parts of a gene
Intron: parts of gene that gets cut out before translation
Exons: parts og gene that get turned into a proton
transposon: types of a DNA sequence that can make copies of itself & move itself to different spots of the genome
PCR or Polymerase Chain Reaction
Denaturing: Double-stranded DNA is separated into 2 strands
Annealing: Primers bind to the target DNA sequences
Extension: DNA Polymerase extends the 3’ end of primers along the template strand