Oral Liquids-[Remedies of Technical Problems in Manufacturing]
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Sedimentation
Problem: Settling of solid particles during storage
Reduce particle size (but avoid over-fine particles)
Increase viscosity using suspending agents (e.g., CMC, xanthan gum)
Use flocculating agents to form loose aggregate
Remedies for Sedimentation [3]
Sedimentation
Remedies: Reduce particle size (but avoid over-fine particles)
Sedimentation
Remedies: Increase viscosity using suspending agents (e.g., CMC, xanthan gum)
Sedimentation
Remedies: Use flocculating agents to form loose aggregates
Aggregation/Coagulation
Problem: Can lead to the formation of a non-resuspendable sediment, known as caking.
caking
A non-resuspendable sediment
caking
Aggregation/Coagulation can lead to the formation of a non-resuspendable sediment, known as _____ ?
Changing the salt concentration
Controlling the Particle Size Distribution
Use of a Compatible Surfactant
Remedies for Aggregation/Coagulation [3]
Aggregation/Coagulation
Remedies: Changing the salt concentration
Aggregation/Coagulation
Remedies: Controlling the Particle Size Distribution
Aggregation/Coagulation
Remedies: Use of Compatible Surfactant
Yellow
(red has large size and even particle size)
Which is an example of Aggregation/Coagulation?
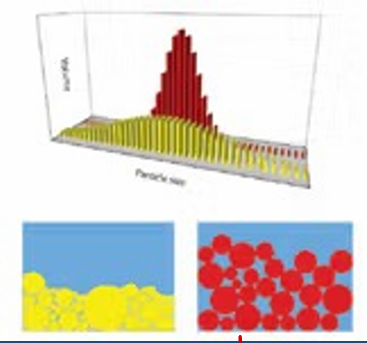
Caking/Claying
Problem: Particles form a distinct cake in the bottom of the vessel. This cake is difficult to re-disperse, and if it forms, the suspension is unlikely to be usable.
Adjust zeta potential.
Controlled Flocculation.
Increase Viscosity of the dispersion medium.
Use of Structured Vehicles (aqueous with surfactant; gel-like structure) to reduce particle movement.
Remedies for Caking/Claying [4]
Caking/Claying
Remedies: Controlled Flocculation (adjust zeta potential)
Caking/Claying
Remedies: (Increase Viscosity of the Dispersion Medium)
Caking/Claying
Remedies: Use of Structured Vehicles (aqueous with surfactant gel like structure)