Enthalpy, Entropy, and Heat Review
All the symbols!
- q - heat needed
- ΔT - Temperature change
- ΔH - Enthalpy change
- ΔH° - in standard conditions
- ΔS - Entropy change
- R - Gas constant (8.314 J/Kmol)
- K - Dissociation rate
- ΔG - Gibbs free energy / available energy
- ΔG° - in standard conditions
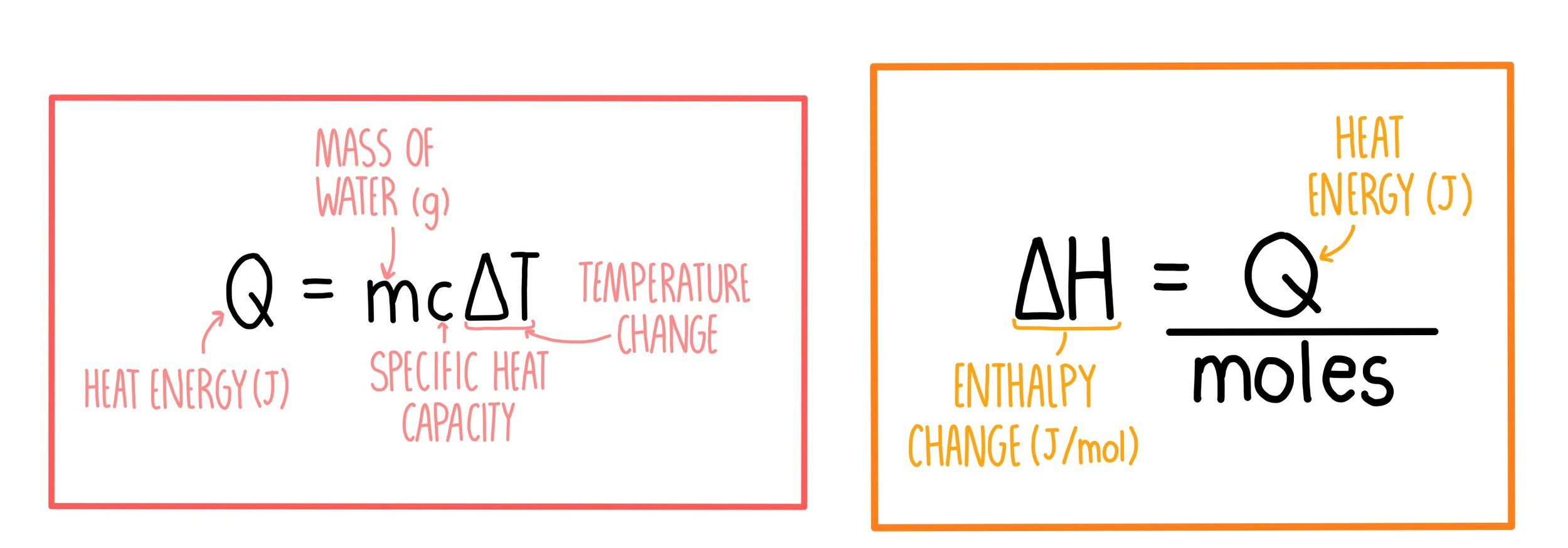
q (Heat)
- q = mcΔT
- q - heat needed (J)
- m - mass of object releasing or absorbing - usually water (4.184 J / gC)
- ΔT - temperature change (C)
Molar Heat
ΔH = q / moles
- q - heat (J)
- ΔH - Enthalpy change (J/mol)
Products - reactants
- Coefficient(enthalpy of formation) - coefficient(enthalpy of formation)
- You are given the equation and enthalpy of formation for each.
Meaning of ΔH
| ΔH > 0 (endothermic / temp of reaction decreases) | ΔH < 0 (exothermic / temp of reaction increases) | |
|---|---|---|
| ΔS > 0 (increase in entropy) | ΔG < 0 at high temperaturesΔG > 0 at low temperaturesSpontaneous at high temperatures. | ΔG < 0Spontaneous |
| ΔS < 0 (decrease in entropy) | ΔG > 0Nonspontaneous | ΔG < 0 at low temperaturesΔG > 0 at high temperaturesSpontaneous at low temperatures. |
ΔG (Gibbs Free Energy)
- ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
- ΔG - change in free energy (kJ)
- ΔH - change in enthalpy (kJ)
- T - absolute temperature (K)
- ΔS - change in entropy (kJ/K)
- Units can change. Make sure ΔH has same units as ΔS. ΔH is given in kJ/mole + ΔS in J/mole
- ΔG° = -RTln(K)
- ΔG° applies to standard-state conditions while ΔG is gibbs free energy given certain condition
- K - [C][D]/[A][B]
- T - temperature (K)
- R - constant (8.314 J / mole K)
- Meaning of ΔG
- Gibb’s free energy.
- ΔG < 0 is thermodynamically favored and exothermic.
- ΔG > 0 is not thermodynamically favored and endothermic.
Hess’s Law
Hard to explain. Please click the title in order to watch a short video on Hess’s Law Problems.
ΔS - Change in Entropy
- Increases as you go from solid to aqueous to liquid to gas
- ΔS = Np(sum of products) - Nr(sum of reactants)
- Np = coefficient of products
- Nr = coefficient of reactants
Coupled Reactions
- Two reactions that share a common intermediate (a product of one reaction is the reactant of another).
- Usually combined with Hess’s law to determine free energy change, ΔG, for the coupled reaction.
Heat of reaction / heat of solution
- The heat of solution is the amount of heat absorbed or released when a solute dissolves in a solvent, while the heat of reaction is the amount of heat absorbed or released during a chemical reaction. The heat of solution is specific to the dissolution process, while the heat of reaction is specific to the chemical reaction taking place.
- Heat of solution
- HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l)
Enthalpy diagram with catalyst
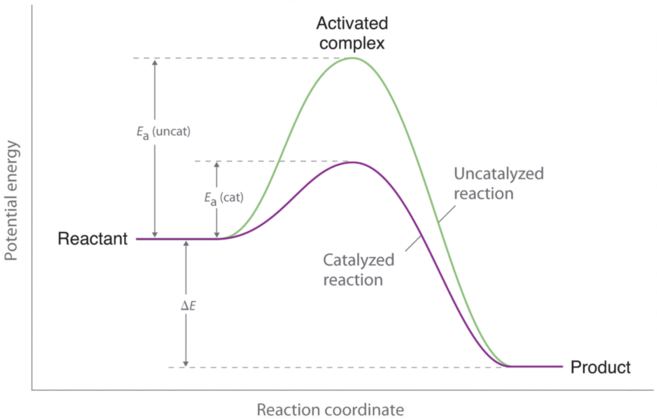
- ΔH is the change between starting and ending energy.
- Energy of activation is the change in starting energy to the peak.
- Starting energy is where the graph starts.
- Endothermic reactions have a higher ending energy than starting energy. Exothermic reactions have a lower ending energy than starting energy.
Maxwell Boltzmann
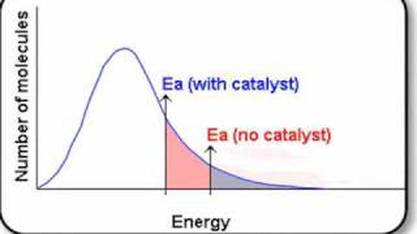
- Higher temperatures move the graph peak right and down.
Lattice Enthalpy
- Bigger charge triumphs size. Smaller size wins if have same charge.
Drivers
| Temperature Change | ΔH | ΔS | Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| ↑ | - | - | Enthalpy (G→L→S) |
| ↓ | + | + | Entropy (S→L→G) |
| - | + | Both |
- A reaction is favored if enthalpy decreases.